7E7F SATs Question Booklet
Diunggah oleh
angeltwinkleDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
7E7F SATs Question Booklet
Diunggah oleh
angeltwinkleHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
Question No. Level Mark Question No. Level Mark
1(05) 3 5 11(95) 5 5
2(01) 3 7 12(05) 5 9
3(01) 4 6 13(01) 5 5
4(01) 4 4 14(01) 6 7
5(03) 4 5 15(97) 6 4
6(03) 4 4 16(99) 6 4
7(97) 4 4 17(05) 7 5
8(95) 5 6 18(95) 7 3
9(99) 5 4 19(97) 7 3
10(97) 5 4
Rainford High Technology College 1
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
1. Table 1 below shows the colour of universal indicator in acidic, neutral and alkaline
solutions.
acidic neutral alkaline
colour of dark
red orange yellow green blue purple
indicator blue
table 1
Ramy tested different liquids with the indicator solution.
His results are shown in table 2 below.
colour of indicator
liquid
solution
Milk green
lemonade orange
water green
fruit juice red
washing-up liquid blue
table 2
(a) Use Ramy’s results to answer the following questions.
(i) Give the name of one acidic liquid in table 2.
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
(ii) Give the name of one neutral liquid in table 2.
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
(b) Ramy dissolved some bicarbonate of soda in distilled water.
This produced an alkaline solution.
(i) Ramy added the indicator to the alkaline solution.
Suggest what colour the indicator became.
Use table 1 to help you.
................................................................
1 mark
Rainford High Technology College 2
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
(ii) Ramy added lemon juice to the solution of bicarbonate of soda.
How could he tell that a gas was produced?
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
(c) Ramy mixed an acid with an alkali and tested the mixture with the indicator
solution.
The indicator solution turned green.
What is the name of the reaction between an acid and an alkali?
Tick the correct box.
condensation
crystallisation
evaporation
neutralisation
1 mark
maximum 5 marks
Rainford High Technology College 3
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
2. The diagrams show two different types of apparatus for measuring volumes of liquid.
Each piece of apparatus contains some dilute hydrochloric acid.
p lu n g e r d il u t e h y d r o c h lo r ic a c id
a p p a ra tu s A 3
cm 6 5 4 3 2 1
3
100 cm
90
80
70
60
a p p a ra tu s B
50
40
30
d ilu te
20
h y d r o c h lo r ic a c id
10
not to scale
(a) What is the name of apparatus B?
……………………………………………………………………………………….
1 mark
(b) What is the volume of dilute hydrochloric acid in:
(i) apparatus A? …………..….. cm3
1 mark
(ii) apparatus B? ..…………….. cm3
1 mark
Rainford High Technology College 4
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
(c) (i) Wayne wants to add exactly 3 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid to some chalk
in a beaker.
How can he remove exactly 3 cm3 of the acid from apparatus A?
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
2 marks
(ii) Wayne adds the acid to the chalk. He sees bubbles.
Which two things does this show? Tick two boxes.
A gas is produced. Chalk is a gas.
Chalk is an acid. The acid reacts with the chalk.
The acid is boiling.
2 marks
Maximum 7 marks
Rainford High Technology College 5
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
3. A Japanese volcano erupted in 1936. Molten sulphur poured out of the volcano.
When it cooled it formed rock sulphur.
o ld e r v o lc a n ic r o c k s s o lid r o c k
s u lp h u r
m o lt e n
s u lp h u r
(a) (i) Which word describes molten rock that is underground?
Choose from lava or magma or oil.
………………………………………
1 mark
(ii) Which type of rock do volcanoes produce?
Choose from igneous or metamorphic or sedimentary.
………………………………………
1 mark
(b) Sulphur is a non-metallic element. It is yellow and melts at 115°C.
Complete the sentences about sulphur.
(i) Sulphur is a poor conductor of
………………………………………
1 mark
(ii) At 115°C sulphur changes from
a …………………………………… into a …………………..……………
2 marks
(c) Sulphur burns in air to form an oxide.
What gas in the air reacts with sulphur when it burns?
………………………………………
1 mark
Maximum 6 marks
Rainford High Technology College 6
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
4. Water from red cabbage can be used to find out if a liquid is acidic, alkaline or neutral.
Type of liquid added to colour of
the cabbage water the cabbage water
acidic red
alkaline blue
neutral purple
John added three different liquids to the cabbage water.
(a) Use the information above to complete the table below.
Liquid added to the colour of Is the liquid
cabbage water the cabbage water acidic, alkaline or
neutral?
water purple
lemon juice acidic
washing up liquid blue
3 marks
(b) What word describes chemicals which change colour in acids or alkalis?
Tick the correct box.
filters indicators
liquids solids
1 mark
Maximum 4 marks
Rainford High Technology College 7
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
5. The table below gives information about three fuels that can be used in cars.
shows a substance is produced when the fuel burns.
X shows a substance is not produced when the fuel burns.
some of the substances produced
energy
fuel physical when the fuel burns
released,
state in kJ/kg carbon sulphur water
monoxide dioxide
petrol liquid 48 000
hydrogen gas 121 000 X X
ethanol liquid 30 000 X
(alcohol)
(a) Which fuel, in the table, releases the least energy per kilogram (kg)?
.....................................................................................................................
1 mark
(b) Some scientists say that if hydrogen is burned as a fuel there will be less
pollution.
From the information in the table, give one reason why there will be less pollution.
.....................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................
1 mark
(c) Which of the three fuels in the table can be compressed into a small container?
...................................................................
1 mark
Rainford High Technology College 8
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
(d) Which gas in the air is needed for fuels to burn?
Tick the correct box.
carbon dioxide
nitrogen
oxygen
water vapour
1 mark
(e) Petrol and ethanol are both fuels. Petrol is made from oil.
Scientists say that oil could run out in 100 years.
In some countries people plant sugar cane and use it to make ethanol.
Sugar cane will not run out. Explain why.
.....................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................
1 mark
Maximum 5 marks
Rainford High Technology College 9
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
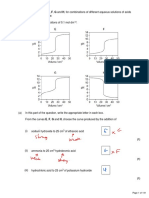
6. The pH scale shown below is used to measure how acidic or alkaline a solution is.
a c id ic n e u tra l a lk a lin e
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
p H s c a le
The graph below shows how the pH of the liquid in Barry's mouth changed as he
ate a meal.
8
p H o f th e B a r r y s ta r te d to e a t
liq u id in
B a r r y 's
m o u th 7
4
t im e
(a) (i) Use the graph to give the pH of the liquid in Barry's mouth before he started
to eat.
pH ..................
1 mark
(ii) What does this pH tell you about the liquid in Barry's mouth before he
started to eat?
Use the pH scale above to help you.
Tick the correct box.
It was acidic. It was alkaline. It was colourless. It was neutral.
1 mark
(b) Look at the graph above.
What happened to the pH of the liquid in Barry's mouth as he ate the meal?
.....................................................................................................................
1 mark
Rainford High Technology College 10
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
(c) Barry chews special chewing gum after each meal. The chewing gum neutralises
the liquid in his mouth.
What type of substance neutralises an acid?
Tick the correct box.
an acid an alkali
an indicator a solid
1 mark
Maximum 4 marks
Rainford High Technology College 11
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
7. Dilute acids react with many things.
Tick the four boxes by the correct descriptions.
Tick no more than four boxes.
Acids always dissolve glass.
Acids can be burned as fuels.
Acids damage teeth.
Acids react with metals such as magnesium.
Acids turn universal indicator solution blue.
Acids may harm your skin.
Acids react with limestone.
Acids are always poisonous.
4 marks
Rainford High Technology College 12
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
8. pH paper is used to show whether a solution is acidic, neutral or alkaline.
One type of pH paper shows the following range of colours.
c o lo u r
of pH re d o ra n g e y e llo w g re e n b lu e p u r p le
paper
pH 0 - 4 5 6 7 8 - 10 11 - 14
v a lu e
Some solutions were tested with pH Paper. The results are shown below.
(a) Complete the following table by placing a tick in the correct column for each
substance.
s u b s ta n c e c o lo u r o f p H a c id ic n e u tra l a lk a lin e
paper
o r a n g e ju ic e re d
e g g w h ite b lu e
o v e n c le a n e r p u r p le
m ilk y e llo w
4 marks
(b) Which substance was the most alkaline?
.....................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................
1 mark
(c) Equal amounts of egg white and milk are mixed. What is the most likely pH
of the mixture?
Tick the correct box.
pH2 pH6 pH7 pH14
1 mark
Maximum 6 marks
Rainford High Technology College 13
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
9. The table shows the pH of five soil samples.
soil sample pH of soil
A 6.0
B 7.5
C 7.0
D 4.5
E 8.0
Use letters from the table to answer questions (a), (b) and (c).
(a) Which soil sample is neutral? ............................
1 mark
(b) (i) Most types of heather grow better in acidic soil.
In which of the soil samples should heather grow well? .........................
1 mark
(ii) Cabbage grows better in alkaline soil. In which
of the soil samples should cabbage grow well? ......................................
1 mark
(c) Lime is an alkaline substance which is sometimes put onto acidic soils.
What type of reaction takes place between the lime and the acid?
.............................................................
1 mark
Maximum 4 marks
Rainford High Technology College 14
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
10. The chart is taken from a bottle of Johnson’s pH5.5 Facial Wash.
10
1 0 .0
7 .3
p H m e a s u re
7 .3 7 .3
5 5 .5 5 .5
0
n o rm a l s o a p w it h n o rm a l J o h n s o n 's h e a lt h y
soap m o is tu r is e r s fa c ia l p H 5 .5 s k in
w ashes fa c ia l w a s h
(a) From the information in the chart give:
(i) a substance which is almost neutral.
..........................................................................................................
1 mark
(ii) the substance which is most alkaline.
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
(b) Tick one box to describe Johnson’s facial wash.
It is very alkaline.
It is slightly alkaline.
It is neutral.
It is slightly acidic.
1 mark
(c) A bee sting is acidic. Which one of the substances given in the chart would be
best to neutralise the sting?
....................................................................................................................
1 mark
Maximum 4 marks
Rainford High Technology College 15
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
Rainford High Technology College 16
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
11. (a) The table shows some of the properties of three different substances, X, Y
and Z. Complete the last column by stating whether each substance is a
metal, a non-metal or a compound.
m e ta l o r
m e ltin g e le c t r ic a l e ffe c t o f n o n – m e ta l
s o lu b ility
s u b s ta n c e p o in t c o n d u c tiv ity h e a tin g or
in w a te r
in a ir com pound
X 11 3 ºC v e ry p o o r in s o lu b le b u rn s to
fo rm o n e
p ro d u c t
w h ic h is a n
a c id ic g a s
Y 9 6 2 ºC v e ry g o o d in s o lu b le lo s e s s h in y
s u r fa c e
Z – 1 8 2 ºC v e ry p o o r a lm o s t b u rn s to
in s o lu b le fo rm tw o
new
s u b s ta n c e s
3 marks
(b) Complete the following using one of the phrases.
Closer together further apart in contact with more particles
Substance Z has a boiling point of –161°C. At room temperature the
particles of Z are ..................................... than the particles of substance X.
1 mark
(c) Substance Z burns in air. What must be present in air for substance Z to burn?
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
Maximum 5 marks
Rainford High Technology College 17
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
12. Molly used a pH sensor to test different liquids. She dipped the probe of the sensor into
each liquid and recorded the pH value in a table.
(a) In the table below, tick one box for each liquid to show whether it is acidic,
neutral or alkaline. One has been done for you.
liquid pH value acidic neutral alkaline
alcohol 7
dilute hydrochloric acid 2
distilled water 7
vinegar 3
sodium hydroxide solution 11
2 marks
(b) Between each test Molly dipped the probe into distilled water.
(i) Why did she do this?
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
(ii) Which other liquid in the table could Molly use between tests to have the
same effect as distilled water?
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
Rainford High Technology College 18
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
3
(c) Molly put a piece of magnesium into a test-tube containing 20 cm of vinegar. She
3
put another piece of magnesium into a test-tube containing 20 cm of dilute
hydrochloric acid.
(i) Molly thought that magnesium would react more vigorously with
hydrochloric acid than with vinegar.
What information in the table made Molly think this?
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
(ii) How would Molly be able to tell if a more vigorous reaction took place with
hydrochloric acid than with vinegar?
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
(d) (i) Complete the word equation for the reaction between magnesium and
hydrochloric acid.
magnesium + hydrochloric .................................. + .................................
acid
2 marks
(ii) After some time this reaction stopped. Why did the reaction stop?
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
maximum 9 marks
Rainford High Technology College 19
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
13. Marie mixed 5 g of carbon with 5 g of lead oxide.
She heated the mixture strongly for 15 minutes in a fume cupboard.
m ix tu r e o f c a r b o n
a n d le a d o x id e
After 15 minutes, Marie found some shiny beads in the mixture.
(a) (i) Marie collected all the shiny beads from this experiment.
How could she test them to show they were metal?
……………..……………………………….…………………..……….……
……………..……………………………….…………………..……….……
1 mark
(ii) Marie’s test showed that the tiny beads were metal.
What metal were the beads likely to be?
……………..……………………………….…………………..……….……
1 mark
(b) Marie also expected carbon dioxide to be formed in this experiment.
(i) In carbon dioxide, what element is combined with carbon?
……………..…………….……
1 mark
(ii) Where, apart from the air, did this element come from in this experiment?
……………..…………….……
1 mark
(c) Give one safety precaution Marie should take during this experiment.
……………..……………………………….…………………..……………………
……………..……………………………….…………………..……………………
1 mark
Maximum 5 marks
Rainford High Technology College 20
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
14. Jessica was investigating the rusting of iron. She set up five experiments as shown
below, and left the test-tubes for three days.
A B C
ir o n n a il in d is t ille d w a t e r ir o n n a il in ta p w a t e r ir o n n a il a n d a c h e m ic a l
w h ic h h a s b e e n b o ile d to to a b s o r b w a te r v a p o u r
r e m o v e d is s o lv e d g a s e s
D E
ir o n n a il in s e a w a t e r ir o n n a il in v in e g a r
Jessica wrote the following results in her book.
Test–tube observation
A nail slightly rusty
B nail still shiny
C nail still shiny
D nail very rusty
E nail slightly rusty, bubbles of gas seen
(a) Explain why the nails had not rusted in test-tubes B and C.
in test-tube B ……………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………..
Rainford High Technology College 21
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
in test-tube C ……………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………..
2 marks
(b) In test-tube E the iron nail reacted with the vinegar.
(i) Is vinegar acidic, alkaline or neutral?
………………………………….
1 mark
(ii) When the iron reacted with the vinegar, bubbles of gas were formed.
What gas was formed?
………………………………….
1 mark
(c) Before putting the iron nail in test-tube D, Jessica weighed the nail.
After three days she dried and weighed the nail and the rust which had formed.
(i) How did the total mass of the nail and rust compare to the mass of the nail
at the beginning?
…………………………………………………………………………………
1 mark
(ii) Give the reason for your answer.
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
1 mark
(d) Jessica concluded that the presence of salt in the water made the nail rust more
quickly.
Explain why she drew that conclusion from her experiments.
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
1 mark
Maximum 7 marks
Rainford High Technology College 22
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
15. The flow chart shows how zinc sulphate can be obtained.
z in c o r e z in c o x id e z in c z in c s u lp h a te
(a) In the reaction zinc oxide zinc an element is removed from zinc oxide
to leave zinc. Give the name of the element.
........................................................
1 mark
(b) (i) Zinc sulphate can be made in a reaction between zinc and an acid.
Give the name of the acid.
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
(ii) In the reaction between zinc and the acid, hydrogen is formed.
Describe the test for hydrogen and the result if hydrogen is present.
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
(iii) How can crystals of zinc sulphate be formed from a dilute solution of
zinc sulphate?
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
Maximum 4 marks
Rainford High Technology College 23
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
16. A teacher designs a flow chart to show how to find the names of three gases.
Complete the flow chart.
A d d f o u r d r o p s o f lim e w a t e r t o
a te s t– t u b e c o n ta in in g t h e g a s
T h e lim e w a te r c h a n g e s .
Its a p p e a r a n c e b e c o m e s T h e lim e w a t e r d o e s
not change.
T h e g a s is P u t a b u r n in g s p lin t
in to a n o th e r te s t– tu b e
c o n ta in in g t h e g a s .
T h e g a s b u r n s w it h T h e b u r n in g s p lin t
a q u ie t p o p . b u r n s m o r e b r ig h tly .
T h e g a s is T h e g a s is
4 marks
Rainford High Technology College 24
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
17. In the eighteenth century, scientists had different ideas about what happens when
metals burn in air.
(a) Imagine you want to investigate the ideas of Priestley and Lavoisier.
Assume you have been given three pieces of different metals.
In a laboratory, metals are heated to high temperatures in crucibles.
You would also have access to all the usual laboratory equipment.
In your plan you must give:
the one factor you would change as you carry out your investigation
(the independent variable);
one factor you would observe or measure to collect your results
(the dependent variable);
one of the factors you would keep the same as you carry out your
investigation;
the evidence that would support Lavoisier’s idea.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
Rainford High Technology College 25
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
...............................................................................................................................
4 marks
(b) In the box below, draw and label a table you could use to record your results.
1 mark
maximum 5 marks
Rainford High Technology College 26
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
18. Magnesium burns in air giving a very bright light.
(a) Complete the word equation below to show this reaction.
magnesium + ............................................. .............................................
1 mark
The diagram shows four gas-jars. Each contains a different gas. Burning
magnesium is put into each jar.
a ir e x h a le d a ir n it r o g e n oxygen
(b) In one of the gas-jars, the magnesium goes out immediately.
Name the gas in this jar.
............................................................
1 mark
Explain your answer.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
Maximum 3 marks
Rainford High Technology College 27
Unit 7E (Acids and alkalis) and Unit 7F (Simple chemical reactions)
19. The exhaust gases of a car with a petrol engine are analysed during its ‘MOT
test’. The results are shown below.
gas % v o lu m e
c a r b o n m o n o x id e 3 .0
c a r b o n d io x id e 1 3 .0
oxygen 0 .4
o th e r g a s e s 8 3 .6
(a) The air going into the engine contains about 20% of oxygen.
Explain why there is only 0.4% of oxygen in the exhaust gases coming out
of the car engine.
....................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................
1 mark
(b) (i) Petrol is a mixture of compounds which contains only carbon and hydrogen.
Complete combustion of petrol produces carbon dioxide and one other
substance. What is this other substance?
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
(ii) When petrol is burned in the car engine, carbon monoxide is produced
as well as carbon dioxide.
Explain why carbon monoxide is dangerous and may kill you.
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
Maximum 3 marks
Rainford High Technology College 28
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- All in One - 10th Class em - Fa-2Dokumen35 halamanAll in One - 10th Class em - Fa-2sai ramxeroxBelum ada peringkat
- G7 - CW - Chapter 5 - Acids, Bases and SaltsDokumen4 halamanG7 - CW - Chapter 5 - Acids, Bases and SaltsPRADEEP SHANJANBelum ada peringkat
- End of Unit Test Higher (H) : © Pearson Education LTD 2019. Copying Permitted ForDokumen5 halamanEnd of Unit Test Higher (H) : © Pearson Education LTD 2019. Copying Permitted ForMina Iskander100% (1)
- 10 Acids and AlkalisDokumen5 halaman10 Acids and Alkalisrashmi_harryBelum ada peringkat
- The Importance of School Climate and Culture - Thomas J. SergiovanniDokumen10 halamanThe Importance of School Climate and Culture - Thomas J. SergiovanniangeltwinkleBelum ada peringkat
- VANESA DEVI A - P DAVEN Moe - WS1 Acid and AlkaliDokumen3 halamanVANESA DEVI A - P DAVEN Moe - WS1 Acid and AlkaliNOKKALAMMAH A/P NARASAYAH MoeBelum ada peringkat
- IMSO 2015 SCIENCE Experiments 1Dokumen6 halamanIMSO 2015 SCIENCE Experiments 1Thanh DinhBelum ada peringkat
- Acid and Alkalis WorksheetDokumen6 halamanAcid and Alkalis WorksheetArslanArsh100% (3)
- Biology IA - Effect of Different Chemicals On The Permeability of Membranes of Beetroot TissueDokumen5 halamanBiology IA - Effect of Different Chemicals On The Permeability of Membranes of Beetroot TissuecarorollsBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise Acid, Alkali, Element, Compound, Mixture, PHDokumen2 halamanExercise Acid, Alkali, Element, Compound, Mixture, PHVita FaridianaBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmaceutical Excipients: Properties, Functionality, and Applications in Research and IndustryDari EverandPharmaceutical Excipients: Properties, Functionality, and Applications in Research and IndustryOtilia M. Y. KooBelum ada peringkat
- The Traveler: Classification and Types of Group TravelersDokumen20 halamanThe Traveler: Classification and Types of Group TravelersChin DhoBelum ada peringkat
- Science Acids and Alkalis Test, Corrected WorkDokumen3 halamanScience Acids and Alkalis Test, Corrected WorktanhaBelum ada peringkat
- STDNT KS3 Year 7 C1 Chapter 4 Acids and AlkalisDokumen8 halamanSTDNT KS3 Year 7 C1 Chapter 4 Acids and Alkalis21tahiradamBelum ada peringkat
- PEQ - Acids & Alkalis - KS3 (PH)Dokumen3 halamanPEQ - Acids & Alkalis - KS3 (PH)yayaBelum ada peringkat
- Acids and Alkalis QsDokumen29 halamanAcids and Alkalis Qsrehanshaikh600Belum ada peringkat
- ACIDS, BASES AND INDICATORSDokumen8 halamanACIDS, BASES AND INDICATORSBaguma MichaelBelum ada peringkat
- Acids, alkalis and pH indicatorsDokumen5 halamanAcids, alkalis and pH indicatorsWere WolfBelum ada peringkat
- Nms Wb2B09 eDokumen28 halamanNms Wb2B09 eShafiquemohammad AsimBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Lab Experiment On SolventsDokumen9 halamanChemistry Lab Experiment On SolventsMarcus GandiaBelum ada peringkat
- WS 10.1-10.4 With AnsDokumen7 halamanWS 10.1-10.4 With Anselephantn63Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 9 Material ChangesDokumen6 halamanChapter 9 Material ChangesFitria Istikomah DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Acids A2ppDokumen141 halamanAcids A2ppDishaBelum ada peringkat
- Geep 105Dokumen6 halamanGeep 105Arnav VashisthBelum ada peringkat
- NCERT Solutions For Class 7 March 31 Science Chapter 5 Acid Bases and SaltsDokumen3 halamanNCERT Solutions For Class 7 March 31 Science Chapter 5 Acid Bases and SaltsvijayalakshmiBelum ada peringkat
- Expt No 7 QUANTIFICATION OF FOOD DYE COLORANTS IN SPORTS DRINKS (ORANGE DYE)Dokumen7 halamanExpt No 7 QUANTIFICATION OF FOOD DYE COLORANTS IN SPORTS DRINKS (ORANGE DYE)Parameswari ArunBelum ada peringkat
- 10.c Acid-Base indicators and BuffersDokumen4 halaman10.c Acid-Base indicators and Buffersmcleodtravis14Belum ada peringkat
- 7 Science Exemplar Chapter 5Dokumen6 halaman7 Science Exemplar Chapter 5Tridasha AithalBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 - Acids and Bases TESTDokumen3 halamanChapter 5 - Acids and Bases TESTsarahisundayBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Questions Unit 2Dokumen13 halamanPractice Questions Unit 2Kaitlyn CarrBelum ada peringkat
- Final - Practical - Med - Chem - III - Exam - 2021 - 1Dokumen6 halamanFinal - Practical - Med - Chem - III - Exam - 2021 - 1JawaherBelum ada peringkat
- Saraswati Vidya Niketan Caribbean Advanced Proficiency Examinations (CAPE) Chemistry-Unit 1 SBA - 4Dokumen3 halamanSaraswati Vidya Niketan Caribbean Advanced Proficiency Examinations (CAPE) Chemistry-Unit 1 SBA - 4Damon HelthBelum ada peringkat
- Week010 LaboratoryExercise003 AcidsandBasesSolubilityEquilibriaDokumen9 halamanWeek010 LaboratoryExercise003 AcidsandBasesSolubilityEquilibriaJosiejj AguilaBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Common Acids and Alkalis PDFDokumen10 halaman10 Common Acids and Alkalis PDFLSWBelum ada peringkat
- Revision Acid and Alkali and Simple ReactionsDokumen10 halamanRevision Acid and Alkali and Simple Reactionsvictorwu.uk100% (1)
- Periodical Test Grade 5 q1Dokumen5 halamanPeriodical Test Grade 5 q1toffy luckBelum ada peringkat
- 46. Eton_KS_ScienceDataPaper_2010Dokumen6 halaman46. Eton_KS_ScienceDataPaper_2010kabirBelum ada peringkat
- 7f End of Unit Test HigherDokumen5 halaman7f End of Unit Test Highermuhammed.azaan.alli100% (1)
- Answers To Further Questions: For The StudentDokumen5 halamanAnswers To Further Questions: For The StudentRumana KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Test1 Acids Bases and SaltsDokumen1 halamanTest1 Acids Bases and SaltsAnand KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Scicent PPT 9 2 R eDokumen99 halamanScicent PPT 9 2 R eApple LouBelum ada peringkat
- Week010 LaboratoryExercise003 AcidsandBasesSolubilityEquilibriaDokumen9 halamanWeek010 LaboratoryExercise003 AcidsandBasesSolubilityEquilibriaMae Borja MisadorBelum ada peringkat
- Acidsandbases AllDokumen95 halamanAcidsandbases AllarindamBelum ada peringkat
- O Level Paperr 42Dokumen9 halamanO Level Paperr 42Dhanishta BooneadyBelum ada peringkat
- Acids and Bases: 5 SC - Strive For ExcellentDokumen12 halamanAcids and Bases: 5 SC - Strive For ExcellentCikgu AnitaBelum ada peringkat
- A1 Carbonyl WS1Dokumen23 halamanA1 Carbonyl WS1chantellelimBelum ada peringkat
- SCGS 2022 Prelim Chemistry P3 QPDokumen8 halamanSCGS 2022 Prelim Chemistry P3 QPVictor LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Ldpe LC-MSDokumen31 halamanLdpe LC-MSWei LuoBelum ada peringkat
- NPTEL'AC'23'Assignment 4Dokumen5 halamanNPTEL'AC'23'Assignment 4SathishBelum ada peringkat
- year_7_acids_and_alkalis_and_simple_chemical_reactions-2Dokumen10 halamanyear_7_acids_and_alkalis_and_simple_chemical_reactions-2Baanu ThushyanthanBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/33Dokumen12 halamanCambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/33akmalabdimuminov03Belum ada peringkat
- Access Answers To NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 5Dokumen7 halamanAccess Answers To NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 5Harsh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Nitric AcidDokumen7 halamanNitric AcidJakub WyrwińskiBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Booklet Separate Only TitrationDokumen7 halamanPractical Booklet Separate Only TitrationEliasBelum ada peringkat
- Fall18 Chem213 Quiz7 Synthetics PRACTICE!Dokumen8 halamanFall18 Chem213 Quiz7 Synthetics PRACTICE!cr7rules4everBelum ada peringkat
- Acid Base and Salts - Index-Notes FinalDokumen5 halamanAcid Base and Salts - Index-Notes FinalYatish BalamuruganBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory Exercise: Objective/sDokumen9 halamanLaboratory Exercise: Objective/sMarvin TorreBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 9 Assignment BookDokumen28 halamanUnit 9 Assignment BookXenability0% (1)
- Acids Bases IndicatorsDokumen8 halamanAcids Bases Indicatorsjoshua.yuBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Qualitative Analysis LabDokumen5 halamanIntroduction to Qualitative Analysis LabskilzaceBelum ada peringkat
- It Is Amammalia It Bears A DiaphragmDokumen9 halamanIt Is Amammalia It Bears A DiaphragmmalingaisrealBelum ada peringkat
- Lipids Chemical TestDokumen9 halamanLipids Chemical TestMiles Acosta100% (2)
- Research Flow Chart 2016-2018Dokumen1 halamanResearch Flow Chart 2016-2018angeltwinkleBelum ada peringkat
- World Travel Trend Report 2015Dokumen17 halamanWorld Travel Trend Report 2015Zia UllahBelum ada peringkat
- Vengesayi PDFDokumen11 halamanVengesayi PDFangeltwinkleBelum ada peringkat
- Northouseintro2e Study Resources Questionnaires 89527 05qDokumen2 halamanNorthouseintro2e Study Resources Questionnaires 89527 05qangeltwinkle100% (1)
- Northouseintro2e Study Resources Questionnaires 89527 05qDokumen2 halamanNorthouseintro2e Study Resources Questionnaires 89527 05qangeltwinkle100% (1)
- Yr 10&11 - Number - WorksheetDokumen3 halamanYr 10&11 - Number - WorksheetangeltwinkleBelum ada peringkat
- Chocolate Zucchini BreadDokumen4 halamanChocolate Zucchini BreadangeltwinkleBelum ada peringkat
- Food Chains & Food Webs: 7C Environment and Feeding Relationships - Year 7Dokumen5 halamanFood Chains & Food Webs: 7C Environment and Feeding Relationships - Year 7angeltwinkleBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Science - MathsDokumen20 halaman4 Science - MathsangeltwinkleBelum ada peringkat
- 7E Acids and Alkalis ExerciseDokumen3 halaman7E Acids and Alkalis ExerciseangeltwinkleBelum ada peringkat
- Planets of The Solar SystemDokumen1 halamanPlanets of The Solar SystemangeltwinkleBelum ada peringkat
- F2 - Chapt 7 ExerciseDokumen1 halamanF2 - Chapt 7 ExerciseangeltwinkleBelum ada peringkat
- Personality Assessment For Teens - RemovedDokumen7 halamanPersonality Assessment For Teens - RemovedBetoBelum ada peringkat
- Brihan Mumbai Ganit Adhyapak Mandal, Mumbai: ST NDDokumen5 halamanBrihan Mumbai Ganit Adhyapak Mandal, Mumbai: ST NDDivyansha Potphode100% (1)
- HIP4081Dokumen18 halamanHIP4081armin rahmatiBelum ada peringkat
- MATH 1300 Limit Worksheet 1/23/15Dokumen3 halamanMATH 1300 Limit Worksheet 1/23/15Kiesha AltheaBelum ada peringkat
- ....Dokumen18 halaman....stream socialBelum ada peringkat
- Grammar and Composition Sentences vs FragmentsDokumen11 halamanGrammar and Composition Sentences vs FragmentsIoannes Amare Et ServireBelum ada peringkat
- Installation and User Manual KJR 120G1 G2 14LDokumen35 halamanInstallation and User Manual KJR 120G1 G2 14LDavid MinerBelum ada peringkat
- 2022 PS Prod Chart Novogen Brown Classic GBFRESDokumen6 halaman2022 PS Prod Chart Novogen Brown Classic GBFRESAmapolley Titus MensahBelum ada peringkat
- Allameh 2014Dokumen18 halamanAllameh 2014Minkhatul FikriyahBelum ada peringkat
- M4M13 SING - PHYS182.finalreportDokumen4 halamanM4M13 SING - PHYS182.finalreportNicholas Bonn SingBelum ada peringkat
- Moral Dan Etika KerjaDokumen83 halamanMoral Dan Etika KerjaChong Hou YiBelum ada peringkat
- Purposeful Birdwatching - Contents and Sample ChapterDokumen22 halamanPurposeful Birdwatching - Contents and Sample ChapterPelagic PublishingBelum ada peringkat
- Training Regulations: Visual Graphic Design NC IiiDokumen118 halamanTraining Regulations: Visual Graphic Design NC IiiApril AbengozaBelum ada peringkat
- The Tempic Field: Verbatim Extracts From The Smith ArchiveDokumen3 halamanThe Tempic Field: Verbatim Extracts From The Smith ArchiveAnton DremlyugaBelum ada peringkat
- Aktivitas Antioksidan Dan Sitotoksik Ekstrak Etanol Daun Hantap (Sterculia Coccinea Jack.)Dokumen12 halamanAktivitas Antioksidan Dan Sitotoksik Ekstrak Etanol Daun Hantap (Sterculia Coccinea Jack.)Danang RaharjoBelum ada peringkat
- Sheetcam manual español tutorialDokumen2 halamanSheetcam manual español tutorialnellacazorla50% (2)
- 027 - B.Tech CSE Result (Affiliated Institutes) - 2nd Semester - May 2019 PDFDokumen347 halaman027 - B.Tech CSE Result (Affiliated Institutes) - 2nd Semester - May 2019 PDFDivyansh AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Oxygen SensorsDokumen39 halamanManual Oxygen SensorsIoanBelum ada peringkat
- cnst0819 Ezine PDFDokumen128 halamancnst0819 Ezine PDFsamontoyaBelum ada peringkat
- The Application of Cellulose Acetate Replication Sheets in Enamel Wear InvestigationsDokumen10 halamanThe Application of Cellulose Acetate Replication Sheets in Enamel Wear InvestigationsKara WhiteBelum ada peringkat
- State Bank of India: (Advertisement No. CRPD/CR/2021-22/09) (Main Examination Held On 1st and 17th October 2021)Dokumen1 halamanState Bank of India: (Advertisement No. CRPD/CR/2021-22/09) (Main Examination Held On 1st and 17th October 2021)Akshay kaleBelum ada peringkat
- Nawa Pharma Sdn. BHD: Bank Muamalat Malaysia BerhadDokumen14 halamanNawa Pharma Sdn. BHD: Bank Muamalat Malaysia Berhadabdul muhaiminBelum ada peringkat
- Study of Free Vibration Characteristics of Cantilever Beams Through Modal Testing and Analysis 2017-18Dokumen70 halamanStudy of Free Vibration Characteristics of Cantilever Beams Through Modal Testing and Analysis 2017-18ranjithkrajBelum ada peringkat
- Resistance of Zippers To Salt Spray (Fog) : Standard Test Method ForDokumen3 halamanResistance of Zippers To Salt Spray (Fog) : Standard Test Method ForShaker QaidiBelum ada peringkat
- Calculation of UOP Characterization Factor and Estimation of Molecular Weight of Petroleum OilsDokumen14 halamanCalculation of UOP Characterization Factor and Estimation of Molecular Weight of Petroleum OilsLuis Ernesto Marin JaimesBelum ada peringkat
- Combined Differential and Common-Mode Scattering Parameters - Theory and Simulation PDFDokumen10 halamanCombined Differential and Common-Mode Scattering Parameters - Theory and Simulation PDFJustin WalkerBelum ada peringkat
- ITC Construction Management Plan - Building D1Dokumen38 halamanITC Construction Management Plan - Building D1richu rasheedBelum ada peringkat
- Bsoa Loja Et Al Prelim DoneDokumen10 halamanBsoa Loja Et Al Prelim DoneZainahl Danica DangcatanBelum ada peringkat
- Trends in Tourists from Countries and Continents to Australia and Germany 1960-2010Dokumen2 halamanTrends in Tourists from Countries and Continents to Australia and Germany 1960-2010Thiện MinhhBelum ada peringkat