April
Diunggah oleh
Maria Oreo0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
13 tayangan2 halamanHak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
13 tayangan2 halamanApril
Diunggah oleh
Maria OreoHak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
April. 30.
2011
Biochemistry:
Energy is released when a bond is formed.
o Energy must be supplied or absorbed to break a bond.
Ionic bond-electrons are transferred.
o Anion is negative.
o Cation is positive.
Covalent bond-electrons are shared.
o Creates molecules.
o Nonpolar bond: electrons shared equally, alike atoms (H-H, H2)
o Polar bond: electrons shared unequally, unalike atoms (H-O-H, H2O)
Polar-Polar attraction: negative end of polar molecule attracts positive end of another
polar molecule.
Hydrogen bonding: …
Nonpolar molecules: only Van der Waals (weakest attractions) exists.
Hydrophobic: hates water.
Hydrophilic: loves water.
o Polar substances dissolve in water, nonpolar do not.
o Like dissolves like.
Water: asymmetrical and polar.
o High specific heat.
o High heat of vaporization.
o High adhesion properties.
o Universal solvent.
o Strong cohesion tension.
o Ice is less dense then water.
pH:
o Buffers resist change in pH.
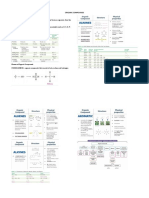
Organic Compounds: contain carbon.
o Carbohydrates: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Supply quick energy.
One gram releases four calories when burned.
Three classes: monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides.
1) Monosaccharides: have chemical formula C6H12O6.
a. Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula, but with different
structures (glucose, fructose, galactose).
b.
2) Disaccharides: have chemical formula C12H22O11.
a. Two monosaccharides joined by process known as dehydration synthesis.
b. Hydrolysis is the breakdown of a compound.
i. Digestion.
ii. Reverse of dehydration synthesis.
3) Re
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Biological Molecules Chapter on Water and CarbohydratesDokumen30 halamanBiological Molecules Chapter on Water and CarbohydratesAlicia LamBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Exam 4 Study GuideDokumen12 halamanBiology Exam 4 Study GuideKhusbu PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1 Lesson 2 Water AbstractionDokumen3 halamanModule 1 Lesson 2 Water AbstractionMarialBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen: Syllabus: Unitix: Hydrogen 04 PeriodsDokumen70 halamanHydrogen: Syllabus: Unitix: Hydrogen 04 Periodsanikesh JainBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Molecular BiologyDokumen25 halaman2 Molecular BiologyMarisa KruppaBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Class OverviewDokumen85 halamanBiology Class OverviewAchilleBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Bio ChemistryDokumen7 halaman3 Bio ChemistryartichokeyBelum ada peringkat
- Biochem NotesDokumen28 halamanBiochem NotesillyBelum ada peringkat
- BIOENERGETICSDokumen341 halamanBIOENERGETICSAvinashBelum ada peringkat
- Ap - Chemistry of LifeDokumen58 halamanAp - Chemistry of Lifeapi-251015600Belum ada peringkat
- Basic Biology I: Cells: How Organisms WorkDokumen57 halamanBasic Biology I: Cells: How Organisms WorkGorby ResuelloBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 Notes BiologyDokumen117 halamanUnit 1 Notes BiologyTwaiba AdmaniBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Quiz 12 - Water Carbon Chemistry Carbohydrates LipidsDokumen11 halamanBiology Quiz 12 - Water Carbon Chemistry Carbohydrates LipidsMafalda SeabraBelum ada peringkat
- BioChemistry UNIT TESTDokumen8 halamanBioChemistry UNIT TESTKezia BijuBelum ada peringkat
- BioChemistry UNIT TEST-2Dokumen16 halamanBioChemistry UNIT TEST-2Kezia BijuBelum ada peringkat
- Walang MakakaseethisDokumen3 halamanWalang MakakaseethisAlissa YangBelum ada peringkat
- BiologyStudySheetBasicChemistryandWater PDFDokumen4 halamanBiologyStudySheetBasicChemistryandWater PDFSam MonellaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 2Dokumen9 halamanLecture 2hfzyahmd613Belum ada peringkat
- London Dispersion ForcesDokumen4 halamanLondon Dispersion Forceskimdaniel2006Belum ada peringkat
- Review - Expt. 1 - Ionic - Molecular CompoundsDokumen1 halamanReview - Expt. 1 - Ionic - Molecular CompoundsKaren Joy MagbanuaBelum ada peringkat
- Life, The Universe, and EverythingDokumen12 halamanLife, The Universe, and EverythingBatisane Kantsu MathumoBelum ada peringkat
- Honors Biology Study Guide Chapters 1-8Dokumen13 halamanHonors Biology Study Guide Chapters 1-8Jessica LeeBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd LectureDokumen72 halaman3rd Lecturebliss polleyBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry of Life Elements, Compounds and BondingDokumen9 halamanChemistry of Life Elements, Compounds and Bondingraghad mohammedBelum ada peringkat
- The Chemistry of LifeDokumen8 halamanThe Chemistry of LifeAda Gay Olandia Serencio0% (1)
- Water ChemistryDokumen4 halamanWater Chemistryapi-296793567Belum ada peringkat
- 2.1-2.6 Biology Review 1Dokumen21 halaman2.1-2.6 Biology Review 1Victoria FinolBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - Basic ChemistryDokumen22 halamanChapter 2 - Basic ChemistryHannah Lee LumosbogBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 2 - Lifes - Chemical - BasisDokumen25 halamanLecture 2 - Lifes - Chemical - BasisPooja ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Biological ChemistryDokumen62 halamanBiological ChemistryCapital AceBelum ada peringkat
- BIO Unit One BabyDokumen77 halamanBIO Unit One Babybisma nadeemBelum ada peringkat
- Ap Bio Review Unit 1 Biochemistry: Elements, Compounds, Atoms, Molecules, Ions and BondsDokumen6 halamanAp Bio Review Unit 1 Biochemistry: Elements, Compounds, Atoms, Molecules, Ions and BondsddBelum ada peringkat
- LSM2106 SI Forces, PH, Buffers (2023 2024 SemI)Dokumen46 halamanLSM2106 SI Forces, PH, Buffers (2023 2024 SemI)Jojo LomoBelum ada peringkat
- Water Chemistry PropertiesDokumen19 halamanWater Chemistry Propertiesyuvimessi100% (2)
- Hydrogen: The Simplest Yet Complex ElementDokumen8 halamanHydrogen: The Simplest Yet Complex ElementVivan TBelum ada peringkat
- Compounds: From Elements To CompoundsDokumen3 halamanCompounds: From Elements To CompoundsUnikeBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 - BiochemistryDokumen9 halamanUnit 1 - Biochemistrych.town321Belum ada peringkat
- Properties of Water: Hydrogen Bonds, Liquidity, ReactionsDokumen2 halamanProperties of Water: Hydrogen Bonds, Liquidity, ReactionsasadBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Water LectureDokumen37 halaman5 Water Lecturevanessa biliyaBelum ada peringkat
- 4.7 Intermolecular ForcesDokumen5 halaman4.7 Intermolecular ForcesrachpBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen 1Dokumen39 halamanHydrogen 1prasathBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen BondsDokumen2 halamanHydrogen BondsJohnBelum ada peringkat
- Biochem Midterms ReviewerDokumen45 halamanBiochem Midterms ReviewerGGonzales KarlaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - The Molecules of Cells - DoneDokumen6 halamanChapter 2 - The Molecules of Cells - DoneApostolos KoutsaftisBelum ada peringkat
- HydrogenDokumen6 halamanHydrogenShaikhamirfaheemBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Revision - C4, C5, C6Dokumen11 halamanChemistry Revision - C4, C5, C6Yasmin AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Chemistry Lecture on Chemical Bonding and Pollutants(209Dokumen20 halamanEnvironmental Chemistry Lecture on Chemical Bonding and Pollutants(209Maaz WaseemBelum ada peringkat
- Chapters 1-4 Chapter 1 - Cell Theory: The Kool-Aid Is Cloudy. Why Is The Kool-Aid Cloudy?Dokumen5 halamanChapters 1-4 Chapter 1 - Cell Theory: The Kool-Aid Is Cloudy. Why Is The Kool-Aid Cloudy?jackardiBelum ada peringkat
- Anaphysio C2Dokumen7 halamanAnaphysio C2KIABelum ada peringkat
- POLARITY OF A MOLECULE TO ITS PROPERTIESDokumen25 halamanPOLARITY OF A MOLECULE TO ITS PROPERTIESCherry-Ann BernardezBelum ada peringkat
- Gen Chem 1 - Handout - Q2 - Weeks 5 7Dokumen15 halamanGen Chem 1 - Handout - Q2 - Weeks 5 7Keyaru HealerBelum ada peringkat
- DOC-20231116-WA0000.Dokumen68 halamanDOC-20231116-WA0000.Praveen MutyalaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Two: Chemical Basis of Life Lecture Outline Module OneDokumen48 halamanChapter Two: Chemical Basis of Life Lecture Outline Module OneKaitlynn StubbsBelum ada peringkat
- Water Why Is Water PolarDokumen3 halamanWater Why Is Water PolarDaneilla BanksBelum ada peringkat
- 2016 2.2 WaterDokumen9 halaman2016 2.2 WaterSaiam ShahBelum ada peringkat
- AP Bio Chemistry of LifeDokumen3 halamanAP Bio Chemistry of LifeAniket BinwadeBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Estructura Moléculas y Compuestos.5.4.21Dokumen34 halaman2 Estructura Moléculas y Compuestos.5.4.21Gaby YepezBelum ada peringkat
- Electrochemistry For Materials Science - BELTOWSKA - 2 PDFDokumen50 halamanElectrochemistry For Materials Science - BELTOWSKA - 2 PDFSumit ShankarBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Chemical BasisDokumen5 halamanChapter 2 Chemical BasisJade Karen Lingo-lingoBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2Dari EverandChemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2Belum ada peringkat