Alcohols and Phenols
Diunggah oleh
Jam ConstantinoDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Alcohols and Phenols
Diunggah oleh
Jam ConstantinoHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chem31.
1: Alcohols and Phenols
An alcohol is any organic compound in which a hydroxyl functional group (-OH) is bound to a carbon atom, usually connected to other carbon or hydrogen atoms. An important class is the simple acyclic alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH. Of those, ethanol (C2H5OH) is the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, and in common speech the word alcohol refers specifically to ethanol.
Phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol (C6H5OH). Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids.
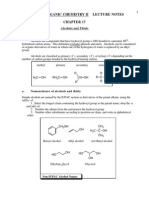
TEST Na+ Test
REAGENTS Na Metal
(+) RESULTS Evolution of H2 gas
Lucas Test
ZnCl2 in HCl
Formation of an insoluble layer (RX)
Oxidation
K2Cr2O7 or KMnO4 in H2SO4 3% FeCl3 Br2 in H2O Hg(NO3)2 in H2O
Change in color of solution due to change in oxidation state of metal Formation of colored ferric-phenol complexes Formation of precipitates; mono, di, tribromophenols Formation of colored Hg-nitrophenol complexes
FeCl3 Bromine Water Test Millons Test
(+) FOR Alcohols 1o Fastest; 2o Fast; 3o Slowest Alcohols 1o NO RXN; 2o Relatively Fast; 3o Fastest Alcohols 1o RCOOH; 2o Ketones; 3o NO RXN Phenols Phenols Phenolic Groups Tyrosine in Proteins
Chem31.1
Page 1
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hydroxy CompoundsDokumen9 halamanHydroxy Compoundschong56Belum ada peringkat
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDokumen4 halamanAlcohols, Phenols and EthersAnonymous GO6JVW9Wud100% (6)
- Alcohols & Phenols:: GeneralizationsDokumen27 halamanAlcohols & Phenols:: GeneralizationsdoudoudoudouBelum ada peringkat
- Organic Derivatives of WaterDokumen9 halamanOrganic Derivatives of Waterpagaduanjoshuaj8227100% (2)
- Identification of Alcohols and PhenolsDokumen15 halamanIdentification of Alcohols and PhenolsSALIFU91% (22)
- Cape Chemistry Unit Ii Module I Alcohols and Phenol and Alkenes Worksheet and Revision GuideDokumen10 halamanCape Chemistry Unit Ii Module I Alcohols and Phenol and Alkenes Worksheet and Revision GuideAshli GrantBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohols-Phenols and EthersDokumen16 halamanAlcohols-Phenols and EthersTr Mazhar PunjabiBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 9 Formal Report On Classification Test of Hydroxyl-Containing and Carbonyl-Containing Organic CompoundsDokumen16 halamanExperiment 9 Formal Report On Classification Test of Hydroxyl-Containing and Carbonyl-Containing Organic CompoundsLuisGabito100% (1)
- Exp 7 ATQDokumen3 halamanExp 7 ATQDean Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersDari EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsDari EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersDari EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (2)
- Review - Expt. 3 - Alcohols - PhenolsDokumen2 halamanReview - Expt. 3 - Alcohols - PhenolsKaren Joy MagbanuaBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohol, Phenol and EtherDokumen21 halamanAlcohol, Phenol and EtherAditya NandaBelum ada peringkat
- CH102 Lab 4 Idasfadent Alcohol and PhenolDokumen9 halamanCH102 Lab 4 Idasfadent Alcohol and PhenolDex JHBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohols Phenols and Ethers: Unit 11Dokumen24 halamanAlcohols Phenols and Ethers: Unit 11Meenal JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDokumen25 halamanChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethershamdy solimanBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohols Phenols and Ethers Anil HssliveDokumen16 halamanAlcohols Phenols and Ethers Anil HsslivemartyBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 10 Determination of and Unknown AlcoholDokumen6 halamanLab 10 Determination of and Unknown AlcoholgioBelum ada peringkat
- Classification and Properties of Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDokumen18 halamanClassification and Properties of Alcohols, Phenols and EthersPrakharBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 9 EditionDokumen99 halamanChapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 9 Edition張湧浩Belum ada peringkat
- Alcohol Phenols and EthersDokumen13 halamanAlcohol Phenols and EthersShivaanee SKBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohols, Phenols & EthersDokumen27 halamanAlcohols, Phenols & Ethershgp9ms5gjcBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohols: CH CHDokumen4 halamanAlcohols: CH CHGeraldyn CorpuzBelum ada peringkat
- Hsslive Xii CH 7 Alcohols AnilDokumen13 halamanHsslive Xii CH 7 Alcohols AnilFathima NithinshaBelum ada peringkat
- Classification and Nomenclature of Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDokumen16 halamanClassification and Nomenclature of Alcohols, Phenols and EthersTr Mazhar PunjabiBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohol Phenol and Ether FinalDokumen33 halamanAlcohol Phenol and Ether FinalC.S. KrithikBelum ada peringkat
- 14.hydroxyl Compounds Lecture NotesDokumen22 halaman14.hydroxyl Compounds Lecture Notesgeoboom12100% (4)
- Chapter 8Dokumen41 halamanChapter 8민규강Belum ada peringkat
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - WatermarkDokumen44 halamanAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers - Watermarkasp212009Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture. 13,14,15 PDFDokumen45 halamanLecture. 13,14,15 PDFsarah100% (1)
- Hydroxyl Compounds: Alcohol & PhenolDokumen59 halamanHydroxyl Compounds: Alcohol & PhenolUMMU MARDHIAH ABDUL HALIMBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan IGF AlimDokumen11 halamanLaporan IGF Alimppg.risdaniar99130Belum ada peringkat
- Organic Derivatives of WaterDokumen6 halamanOrganic Derivatives of WaterCelyn Ann RamosBelum ada peringkat
- McMurry's Organic Chemistry Chapter 17: Alcohols and PhenolsDokumen36 halamanMcMurry's Organic Chemistry Chapter 17: Alcohols and PhenolsArk Olfato ParojinogBelum ada peringkat
- AlcoholsDokumen16 halamanAlcoholsNirvaniBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohol: Jully Tan School of EngineeringDokumen46 halamanAlcohol: Jully Tan School of EngineeringSàtz ÑÖÑïtBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohols - Structure and Synthesis - Chapter 10Dokumen23 halamanAlcohols - Structure and Synthesis - Chapter 10lotannaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers-NotesDokumen16 halamanChapter-11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers-NotesAdithya kumar JhaBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohols 1 PDFDokumen23 halamanAlcohols 1 PDFSamah Pharm.D.Belum ada peringkat
- Alcohol Phenol and EtherDokumen25 halamanAlcohol Phenol and EtherSmit Domadiya100% (1)
- CHAPTER 7 Alcohols RESTOREDDokumen51 halamanCHAPTER 7 Alcohols RESTOREDsukaina fatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohol Notes 2014Dokumen4 halamanAlcohol Notes 2014chenjudeBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 - Alcohols, Phenols and ThiolsDokumen102 halamanChapter 7 - Alcohols, Phenols and ThiolsCute ni LeynesBelum ada peringkat
- Module 9. Alcohols: Nomenclature, Preparation and ReactionsDokumen3 halamanModule 9. Alcohols: Nomenclature, Preparation and ReactionsPeña, RodolfoBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohols and PhenolsDokumen47 halamanAlcohols and PhenolsniyazrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Phenol 203Dokumen47 halamanPhenol 203ajibolaakorede20Belum ada peringkat
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers: ClassificationDokumen13 halamanAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers: ClassificationDUHA GORASHIBelum ada peringkat
- CHM 121 Lecture NoteDokumen13 halamanCHM 121 Lecture NoteOyedotun TundeBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohol molecul-WPS OfficeDokumen14 halamanAlcohol molecul-WPS OfficeUSCLOUD MINERBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDokumen16 halamanAlcohols, Phenols and Etherskanit8713Belum ada peringkat
- Ch-11 Part-2 Alcohols, Phenols ðersDokumen57 halamanCh-11 Part-2 Alcohols, Phenols ðersBhavishya VermaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Formula Chapter11 Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDokumen26 halamanChemistry Formula Chapter11 Alcohols, Phenols and EthersPramod NairBelum ada peringkat
- Class 12 Alcohols Phenols Ethers NotesDokumen23 halamanClass 12 Alcohols Phenols Ethers NotesIpsita SethiBelum ada peringkat
- AlcoholDokumen8 halamanAlcoholSri DharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Ch103 Alcohols and Phenols: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 7 EditionDokumen40 halamanCh103 Alcohols and Phenols: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 7 EditionEvelyn MushangweBelum ada peringkat
- CH 17Dokumen18 halamanCH 17MirjanaBelum ada peringkat
- Revision Notes For Class 12 CBSE Chemistry, Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - TopperlearningDokumen10 halamanRevision Notes For Class 12 CBSE Chemistry, Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - TopperlearningRishabh Bhandari67% (3)
- 51719Dokumen38 halaman51719nandhakishore412Belum ada peringkat
- Classification of Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers and their ReactionsDokumen11 halamanClassification of Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers and their ReactionsSandeepBelum ada peringkat
- AnnexA MedicalCaseRatesDokumen127 halamanAnnexA MedicalCaseRatesJimmySyBelum ada peringkat
- Pedia TicklerDokumen60 halamanPedia TicklerCharlotte Anne Villero TiuBelum ada peringkat
- 6 ClinicalDokumen47 halaman6 ClinicalJnana YumnaBelum ada peringkat
- Rmeg PDFDokumen750 halamanRmeg PDFJam ConstantinoBelum ada peringkat
- B20M6L8 - Local AnesthesiaDokumen9 halamanB20M6L8 - Local AnesthesiaJam ConstantinoBelum ada peringkat
- GOLD 2020 POCKET GUIDE Ver1.0 - FINAL WMVDokumen53 halamanGOLD 2020 POCKET GUIDE Ver1.0 - FINAL WMVRupesh MohandasBelum ada peringkat
- 6 ClinicalDokumen47 halaman6 ClinicalJnana YumnaBelum ada peringkat
- 2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice GuidelinesDokumen24 halaman2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice GuidelinesLinda KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- GOLD 2020 POCKET GUIDE Ver1.0 - FINAL WMVDokumen53 halamanGOLD 2020 POCKET GUIDE Ver1.0 - FINAL WMVRupesh MohandasBelum ada peringkat
- COVID GuidelinesDokumen54 halamanCOVID GuidelinesHBBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomical LandmarksDokumen5 halamanAnatomical LandmarksJam ConstantinoBelum ada peringkat
- Covid Guidelines JulyDokumen55 halamanCovid Guidelines JulyJam ConstantinoBelum ada peringkat
- Acidity and Alkyl HalidesDokumen1 halamanAcidity and Alkyl HalidesJam ConstantinoBelum ada peringkat
- 10 02 06Dokumen23 halaman10 02 06Jam ConstantinoBelum ada peringkat
- Stoich Prac XtraDokumen4 halamanStoich Prac XtraJam ConstantinoBelum ada peringkat