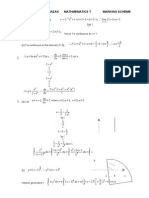
CET - 2011 Functions, Limits & Differentiation Solutions
Diunggah oleh
Sharath Aefdsffdf FdJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CET - 2011 Functions, Limits & Differentiation Solutions
Diunggah oleh
Sharath Aefdsffdf FdHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CET - 2011 CET - 2011
FUNCTIONS, LIMITS & CONTINUITY DIFFERENTIATION FUNCTIONS, LIMITS & CONTINUITY DIFFERENTIATION
1.
n
lim
n n n
n 1 n 1 n 1
2 3 4
2 3 4
+ + +
+ +
+ +
=
1) 0 2)
1
9
3)
1
2
4)
1
4
2. Domain of the function sin
1
(e
x
) is
1) ( 0] 2) [ 1 1] 3) ( 1 0] 4)
1
e
e
`
,
3.
x 0
lim
cos 7x cos9x
cos3x cos 7x
=
1)
1
2
2)
1
2
3)
4
5
4)
8
5
4.
x
3
lim
( )
2sin x
3
1 2cos x
=
1)
1
2
2)
2
3
3)
2
3
4)
1
3
5. In the interval (0 2 ) the function [sin x] is discontinuous at k points . Then k =
1) 1 2) 2 3) 3 4) 0
6.
x
lim
sin x
x
=
1) 0 2) 1 3) 4) 1 or 1
7.
x 0
lim
x
log(x 1)
4 1
+
=
1) log
e
4 2)
1
2
log
e
4 3) log
4
e 4) 0
8.
x 0
lim
2
2 cos x 1
x
=
1)
1
2
2)
1
2
3)
1
2 2
4) 1
9.
x 0
lim
x x
6 3
sin3x
=
1)
1
3
log 2 2)
1
3
log 3 3) 3 log 2 4) 3 log 3
10. In order that f (x) = (x + 1)
cosec x
is continuous at x = 0, f (0) must be defined as
1) 0 2) e 3)
1
2
4) 1
11. If f(x) = log
x
(log x) . log x, then f (e
1
) is
1)
e
1
2)
e
1
3) e 4) e
12. If f(x) = sin
1
,
`
.
|
+
x 3
x 3
+ sec
1
,
`
.
|
+
x 3
x 3
, then f (1) =
1) not defined 2) 0 3)
6
4) 1
13. If f and g are inverse functions of each other then which of the following is true ?
M 04
1) f (g (x)) = 1 2) f (g(x)) =
) x ( g
1
3) f(g (x)) =
) x ( g
1
4) f(g (x)) = f (g(x))
14. If sin xy + e
xy
= x
2
y
2
, then xy =
1) x 2) y 3) cos xy + e
xy
4)
x
y
15. If u = sin
1
2
x 1
x 2
+
and v = tan
1
2
x 1
x 2
, then
dv
du
=
1) x 2) 1 3) 1 4) x
2
16. If f
,
`
.
|
x
1
x
= x
2
2
x
1
, then f (1) =
1)
5
6
2)
5
3
3) 5 4) 0
17. If f(x) = 1 + sin x +
! 2
x sin
2
+
! 3
x sin
3
+ . then f (x) =
1) f(x) 2) f(x) cos x 3) f(x) cosec x 4) f(x) sin x
18. y = (sin
1
x)
2
+ (cos
1
x)
2
, then (1 x)
2
2
2
dx
y d
x
dx
dy
=
1) 2 2) 4 3) 0 4) 1
19. If x = a cos
3
, y = a sin
3
, then the value of
2
dx
dy
1
,
`
.
|
+ at x = is
1) 0 2) 1 3) 1 4)
20. If y = 1 + x + x
2
+ x
3
+ . then (1 x)
2
(y + y ) =
1) 1 x 2) 1 + x 3) x 2 4) 2 x
21. If x = ...... y y y
2 2 2
+ + + then
dx
dy
=
1)
y 2
1 x 2
2)
x 2
1 y 2
3)
2
1
4)
x 2
1 y 2 +
22. If y = (1 + x) (1 + x
2
) (1 + x
4
) (1 + x
8
) .. (1 + x
1024
) then y =
1)
x 1
x 1024 y
1023
2)
x 1
x 2048 y
2047
3) 2048 x
2047
+ y 4) (1 x) (1 x
2
) (1 x
3
) (1 x
1024
)
23. If x
5
y
6
= (x + y)
11
, then
2
2
dx
y d
at (a, b)
1) is 0 2) depends on a and b 3) depends on a but not b 4) depends on b but not on a
24. If x = t
2
+ 1, y = 2at then y at t = a is
1)
a
1
2)
2
a 2
1
3)
2
a 2
1
4) 0
25. If 3
y
x
+ 4
x
y
= 7 (cosec
1
y
x
+ cos
1
x
y
), then
2
2
dx
y d
at (1, 1) is
1) 1 2)
3
1
3) 0 4) 2
CET - 2011 CET - 2011
FUNCTIONS, LIMITS & CONTINUITY FUNCTIONS, LIMITS & CONTINUITY DIFFERENTIATION DIFFERENTIATION
SOLUTIONS SOLUTIONS
M 04
1. (4)
L =
n
lim
n n
n n
1 3
1
2 4
1 3
2 3. 4
2 4
| ` | `
+ +
. , . ,
| ` | `
+ +
. , . ,
=
1
0 0
4
0 0 4
+ +
+ +
=
1
4
2. (1)
By data, 1 e
x
1 but e
x
0 0 e
x
1 ; e
x
= 0 x , e
x
= 1 x = 0
3. (3)
L =
1
(81 49)
2
1
(49 9)
2
=
32
40
=
4
5
4. (2)
L =
x
3
lim
2cos x
3
2sin x
| `
. , =
1
3
2
=
2
3
5. (2)
[sin x] =
0 , 0 x
2
1 , x
2
0 , x
2
1 , x 2
< <
'
< <
<
f(x) is not continuous at
2
and
6. (1)
sin x is a finitely oscillating quantity and hence L = 0
7. (3)
L =
x 0
lim
x
1
x 1
4 log 4
+
=
1
log 4
=
4
log e
8. (1)
L H Rule,
sin x
2 cos x
1
2x
1
2 1
.
1
2
=
1
2
9. (1)
L =
0 x
lim
x x
6 log6 3 log3
3cos3x
=
log6 log3
3
=
1
3
log 2
10. (2)
f (0) =
0 x
lim
(1 + x)
1 x
.
x sin x
= e
1
= e
11. (4)
f(x) =
x log
) x (log log
. log x = log (log x)
f (x) =
x
1
.
x log
1
f
,
`
.
|
e
1
=
) 1 (
1
.
e
1
1
= e
12. (2)
f(x) = sin
1
u + cos
1
u =
2
f (x) = 0
13. (2)
f(g(x)) = 1 ; differentiating wrt x : f (g(x)) . g (x) = 1
f (g(x)) =
) x ( g
1
14. (2)
xy is common in all the terms Every term will have
dx
d
(xy) i.e., [xy + y] as common
xy + y = 0 xy = y
15. (2)
Put x = tan , u = 2 ; v = 2 u = v
dv
du
= 1
16. (1)
x
2
2
x
1
=
,
`
.
|
x
1
x
,
`
.
|
+
x
1
x
=
,
`
.
|
x
1
x
4
x
1
x
2
+
,
`
.
|
(a + b)
2
= (a b)
2
+ 4ab
Put t = x
x
1
. Then f(t) = t 4 t
2
+
f (t) =
4 t
2
+
+
4 t
t
2
2
+
f (1) = 5 +
5
1
=
5
6
17. (2)
f(x) is in exponential form; f(x) = e
sin x
f (x) = e
sin x
cos x = f(x) . cos x
18. (2)
y =
2
1
x 1
x sin 2
2
1
x 1
x cos 2
2
x 1
y = 2 (sin
1
x cos
1
x) ; differentiate w.r.t x
2
x 1
. y + y . 2
x 1 2
1
. ( 2x) = 2
,
`
.
|
2 2
x 1
1
x 1
1
(1 x
2
) y xy = 4
19. (2)
dx
dy
=
) sin ( cos 3 . a
cos sin 3 . a
2
2
= tan
2
dx
dy
1
,
`
.
|
+ =
+
2
tan 1
= | sec | = 1 at =
20. (4)
y = S
of a G.P =
x 1
1
y =
( )
2
x 1
1
(1) =
( )
2
x 1
1
(1 x)
2
y = 1 ; (1 x)
2
y = (1 x) . Required sum = (1) + (1 x) = 2 x
21. (1)
x
2
= y
2
+ x 2x = 2y . y + 1 , y =
y 2
1 x 2
22. (2)
(1 x) y = 1 x
2048
(1 x) y y = 2048 x
2047
y =
x 1
x 2048 y
2047
23. (1)
dx
dy
=
x
y
(from memory) ;
2
2
dx
y d
=
2
x
) 1 ( y
x
y
. x
,
`
.
|
=
2
x
0
= 0
24. (2)
y =
dt
dy
dt
dx
=
t 2
a 2
=
t
a
y =
2
t
a
2t =
3
t 2
a
; At t = a, y =
2
a 2
1
25. (3)
3x
2
+ 4y
2
7 .
2
xy = 0, is a homogeneous second degree equation in x and y y = 0, x.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Inverse Trig Functions DerivativesDokumen5 halamanInverse Trig Functions DerivativesAparjan PatrikaBelum ada peringkat
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADokumen10 halamanAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremBelum ada peringkat
- 2014 2 Sar Tun Abdul RazakDokumen4 halaman2014 2 Sar Tun Abdul RazakMasytah YazidBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering MathsDokumen8 halamanEngineering MathsSanthosh SanBelum ada peringkat
- Continuity and Differentiation: Points To RememberDokumen8 halamanContinuity and Differentiation: Points To RememberAakash ChanBelum ada peringkat
- 2007 Ajc h2 Prelims Paper 1 SolutionsDokumen9 halaman2007 Ajc h2 Prelims Paper 1 Solutionsvincesee85Belum ada peringkat
- Inequation & Equation Solutions FinalDokumen67 halamanInequation & Equation Solutions FinalAkshay PatelBelum ada peringkat
- C D I 2 L E - D: X X X F X X X X FDokumen0 halamanC D I 2 L E - D: X X X F X X X X Fglobaltech164768Belum ada peringkat
- MatematicasDokumen9 halamanMatematicasYoel Lopez MejiasBelum ada peringkat
- Limit ContinuiTY Differential ASSIGNMENT FOR IIT-JEEDokumen17 halamanLimit ContinuiTY Differential ASSIGNMENT FOR IIT-JEEApex Institute100% (2)
- AJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Dokumen12 halamanAJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongBelum ada peringkat
- Lista 11 - Cálculo Diferencial e Integral - 1Dokumen1 halamanLista 11 - Cálculo Diferencial e Integral - 1Matheus BorelliBelum ada peringkat
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADokumen6 halamanAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremBelum ada peringkat
- 2014 2 JOHOR SMKTinggiKluang Maths QADokumen8 halaman2014 2 JOHOR SMKTinggiKluang Maths QASK100% (2)
- Derivadas PDFDokumen12 halamanDerivadas PDFRocio LEON AYABelum ada peringkat
- Derivadas PDFDokumen12 halamanDerivadas PDFRocio LEON AYABelum ada peringkat
- DERIVATIVES_CALCULATIONSDokumen12 halamanDERIVATIVES_CALCULATIONSRocio LEON AYABelum ada peringkat
- Derivadas PDFDokumen12 halamanDerivadas PDFRocio LEON AYABelum ada peringkat
- Differential and Integral Calculus Success GuideDokumen66 halamanDifferential and Integral Calculus Success GuideAnkit RaiBelum ada peringkat
- © Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C4 Paper IDokumen3 halaman© Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C4 Paper IPa GesBelum ada peringkat
- Limits: (EAMCET 2009)Dokumen6 halamanLimits: (EAMCET 2009)vipulBelum ada peringkat
- Useful Identities ListDokumen1 halamanUseful Identities ListKimberly WaltersBelum ada peringkat
- 2010 DHS Paper 1solDokumen10 halaman2010 DHS Paper 1solnothingtodo1992Belum ada peringkat
- Avaliações 2009-1 - GabaritoDokumen13 halamanAvaliações 2009-1 - GabaritoEduardobelloBelum ada peringkat
- Solucion 3Dokumen1 halamanSolucion 3Clases particulares en la LagunaBelum ada peringkat
- Tarea 7 MAT-211 - DeRIVADASdocxDokumen9 halamanTarea 7 MAT-211 - DeRIVADASdocxDoloris Hernandez D LeonBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10 Differential EquationsDokumen22 halamanChapter 10 Differential EquationsAloysius Raj50% (2)
- Trabajo de Maematicas IIDokumen4 halamanTrabajo de Maematicas IIRAFAEL SANABRIA CANOBelum ada peringkat
- MA1521 Solution3Dokumen5 halamanMA1521 Solution3Ray TanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 FWSDokumen32 halamanChapter 8 FWSChan KarlokBelum ada peringkat
- Taller de Derivadas.Dokumen7 halamanTaller de Derivadas.Alejandra VeraBelum ada peringkat
- HCI 2008 Promo W SolutionDokumen12 halamanHCI 2008 Promo W SolutionMichael CheeBelum ada peringkat
- RjesenjaDokumen2 halamanRjesenjaAdnanKapetanovicDadoBelum ada peringkat
- MATHS Method of differentiationDokumen14 halamanMATHS Method of differentiationHussain AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- 2xy-4 6 2x 6x +4 Dy DX Solución Explicita yDokumen4 halaman2xy-4 6 2x 6x +4 Dy DX Solución Explicita yJonathan A. Carreño LaguadoBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 Chapter 13 AnswersDokumen8 halamanUnit 2 Chapter 13 AnswersashtigosineBelum ada peringkat
- Guiao 2teste Matematica Geral 2022 AMDokumen2 halamanGuiao 2teste Matematica Geral 2022 AMTonny AntonyBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Bab-I & Bab IiDokumen28 halamanTugas Bab-I & Bab IiblackzmillianBelum ada peringkat
- IntegralDokumen8 halamanIntegralthinkiitBelum ada peringkat
- Guia 1 Inf 11Dokumen4 halamanGuia 1 Inf 11Ingrid GuerraBelum ada peringkat
- Section G: Integer Answer Type: X FX F XDokumen10 halamanSection G: Integer Answer Type: X FX F XsatwiksmBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise 3Dokumen3 halamanExercise 3LolBelum ada peringkat
- Derivadas: Hallar, SiDokumen6 halamanDerivadas: Hallar, SiYack Brenan Palma PilcoBelum ada peringkat
- Pure Mathematics: For CAPEDokumen11 halamanPure Mathematics: For CAPERonaldoBelum ada peringkat
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADokumen7 halamanAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremBelum ada peringkat
- Derivadas de funções trigonométricas inversasDokumen5 halamanDerivadas de funções trigonométricas inversasDamasio AgostinhoBelum ada peringkat
- Functions Ex.2 (B)Dokumen20 halamanFunctions Ex.2 (B)Gokul NathBelum ada peringkat
- MIDTERM MTH3112 Sem1!16!17 Solution Nov16Dokumen7 halamanMIDTERM MTH3112 Sem1!16!17 Solution Nov16Nik Muhd AriffBelum ada peringkat
- Jee Main 10 April 2023 Shift 1 Reliable Mathematics Question Paper With SolutionsDokumen12 halamanJee Main 10 April 2023 Shift 1 Reliable Mathematics Question Paper With SolutionsPankaj BabareBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Test 2Dokumen2 halamanPractice Test 2WilburBelum ada peringkat
- © Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C4 Paper ADokumen3 halaman© Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C4 Paper AKonstantinos KonstantinouBelum ada peringkat
- © Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C4 Paper ADokumen3 halaman© Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C4 Paper APa GesBelum ada peringkat
- Practica #1 Diagnostico: F (X) 2 X X X F (X) X X F X) 8 XDokumen3 halamanPractica #1 Diagnostico: F (X) 2 X X X F (X) X X F X) 8 XJorgeBelum ada peringkat
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesDari EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesBelum ada peringkat
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageDari EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsDari EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDari EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsDari EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsBelum ada peringkat
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesDari EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesPenilaian: 1.5 dari 5 bintang1.5/5 (2)
- Finite Element Analysis of 1D Structural Systems Using Higher Order ElementsDokumen77 halamanFinite Element Analysis of 1D Structural Systems Using Higher Order ElementsfefahimBelum ada peringkat
- Matlab Code For Implementation of Routhharwitz Table TableDokumen5 halamanMatlab Code For Implementation of Routhharwitz Table TableEngr. Naveed Mazhar50% (2)
- A Novel Approach To The Fast Computation of Zernike Moments: Sun-Kyoo Hwang, Whoi-Yul KimDokumen12 halamanA Novel Approach To The Fast Computation of Zernike Moments: Sun-Kyoo Hwang, Whoi-Yul KimSaasiBelum ada peringkat
- Gauss History FFTDokumen13 halamanGauss History FFTMaría MarchianoBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 2 Applications of System of Linear Equations-1Dokumen6 halamanActivity 2 Applications of System of Linear Equations-1LoraineCundangan-medinaBelum ada peringkat
- Amano and Sunden - Computational Fluid Dynamics and Heat TransferDokumen506 halamanAmano and Sunden - Computational Fluid Dynamics and Heat Transferseriouslion100% (2)
- CVEN2002 Week5Dokumen43 halamanCVEN2002 Week5Kai LiuBelum ada peringkat
- Video Lectures - Differential Equations - Mathematics - MIT OpenCourseWareDokumen4 halamanVideo Lectures - Differential Equations - Mathematics - MIT OpenCourseWareyashwant1299523Belum ada peringkat
- Relations and FunctionsDokumen11 halamanRelations and FunctionsTushar GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Connor Structural AnalisysDokumen630 halamanConnor Structural AnalisysKaren Esther Acuña VelasquezBelum ada peringkat
- Equation For Line in SpaceDokumen6 halamanEquation For Line in Spaceعبد العزيز وليد عبد العزيزBelum ada peringkat
- CNN Overview: Convolutional Neural Networks ExplainedDokumen23 halamanCNN Overview: Convolutional Neural Networks ExplainedAnand AmsuriBelum ada peringkat
- Grades 9 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level 9 Teacher Learning Area MATHEMATICS Teaching Dates and Time Quarter FIRSTDokumen10 halamanGrades 9 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level 9 Teacher Learning Area MATHEMATICS Teaching Dates and Time Quarter FIRSTAnnie Glen LovesParamore CanilaoBelum ada peringkat
- Three Basic Questions on Boolean FunctionsDokumen19 halamanThree Basic Questions on Boolean FunctionsRashid AliBelum ada peringkat
- List of Important MathematiciansDokumen8 halamanList of Important MathematiciansEris SodaliteBelum ada peringkat
- Wittrick - WilliamsDokumen4 halamanWittrick - WilliamsBrendon MenezesBelum ada peringkat
- Artoza - Fourier Analysis NotesDokumen15 halamanArtoza - Fourier Analysis NotesJelo ArtozaBelum ada peringkat
- Solutions To Exercises - Week 42 Exercise 7.47: Complete Sufficient Statistics and Best Unbiased EstimatorsDokumen4 halamanSolutions To Exercises - Week 42 Exercise 7.47: Complete Sufficient Statistics and Best Unbiased Estimatorswindowme98naver.comBelum ada peringkat
- School Grade Level Teacher Learning AreaDokumen7 halamanSchool Grade Level Teacher Learning AreaJerson YhuwelBelum ada peringkat
- GeniDokumen7 halamanGeniAnonymusBelum ada peringkat
- (Y - SQRT X) 2+x - Google PenelusuranDokumen1 halaman(Y - SQRT X) 2+x - Google PenelusuranRereBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes 19: Lorentz Transformation of Electromagnetic Fields (Slight Return)Dokumen18 halamanLecture Notes 19: Lorentz Transformation of Electromagnetic Fields (Slight Return)Najrul IslamBelum ada peringkat
- Hint & SolutionDokumen5 halamanHint & SolutionJohn CienBelum ada peringkat
- Math4 ExamsDokumen66 halamanMath4 ExamsGamal AbdelwahidBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding and Using Newton's MethodDokumen7 halamanUnderstanding and Using Newton's MethodAlejandro AguirreBelum ada peringkat
- AIR Basic Calculus Q3 W3 - Module 7 CorrectedDokumen13 halamanAIR Basic Calculus Q3 W3 - Module 7 CorrectedLove EpiphanyBelum ada peringkat
- Thomas Early Transcendals Thirteen Edition Preface and ContentDokumen14 halamanThomas Early Transcendals Thirteen Edition Preface and ContentSVR12Belum ada peringkat
- Rudolph E. Langer-A First Course in Ordinary Differential Equations-John Wiley & Sons (1954) PDFDokumen265 halamanRudolph E. Langer-A First Course in Ordinary Differential Equations-John Wiley & Sons (1954) PDFjam reb50% (2)
- 2022 Amc 12b Problems and AnswersDokumen12 halaman2022 Amc 12b Problems and AnswersSuragaBelum ada peringkat