Unit 1 (ULTIMATE LIMITS STATE DESIGN CONCEPT) - REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
Diunggah oleh
Zara NabilahJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Unit 1 (ULTIMATE LIMITS STATE DESIGN CONCEPT) - REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
Diunggah oleh
Zara NabilahHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/
UNIT 1
ULTIMATE LIMITS STATE DESIGN CONCEPT
OBJECTIVES
GENERAL OBJECTIVE:
GENERAL OBJECTIVE To understand the philosophy and structural design concepts of reinforced structural design in Ultimate Limit States.
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES At the end of this unit, you should be able to: state the aim of the structural design. explain the design philosophy explain the statistical relationships between the strength of materials and characteristic load. calculate the characteristic strength of materials and characteristic load. identify and use partial safety factors
INPUT 1
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/
1.1 Definition What is structural design? Design involves the selection of materials and determination of structural element sizes. The aim of design is to build structures which are safe and that can be used as intended, with minimum cost, during constructions and maintenance.
Reinforced concrete is made by reinforcing concrete with steel reinforcements. Concrete is a composite material of cement, aggregate, sand and water. The compressive strength of concrete is higher than its tensile strength but it is very weak in resisting compressive force and lateral stability. Reinforced concrete is a very strong durable and versatile structural material. It is a combination of concrete and steel.
1.2 Design Process Normally a project starts when the client (individual, government, or company) wants to build a structure for his/ her intended purpose. The client will consult an architect or an engineer who will then transform the project into drawings after taking careful considerations into accounts and possibility in choosing the materials, and the method of construction.
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/
Based on the architects drawings, the engineer will determine the structural layout such as the structural frame, structural elements, sizes and dimensions e.g. beams, columns, foundation etc.
The engineer will carry out the structural analysis. This involves the calculation and determination of the force on each structural element. After that, the sizes of the elements, their positions and their numbers will be calculated as shown in the detailed drawings. The design process and how the project is accomplished is shown in Figure 1.1
Architects Drawings
Layout Plan
Load calculations / Structural Analysis
Detailed Drawings
Structural Design
Figure 1.1 Design Process
1.3 Reinforced concrete structures
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/
Generally, reinforced concrete structures consist of various elements e.g. beam, slab, column, wall, staircase and foundation. Each of them will be specifically located at a particular place as designed by the engineer and architect.
1.4 Code of Practice
During the design stage, the engineer will continuously refer to a particular code of practice. Code of practice is a document with contains the standard practices i.e. best practices experienced by enquiries and research which have been compiled and documented. The British Standard is generally referred to when the designing reinforced concrete structures.
As far as reinforced concrete design is concerned, the codes of practice that are normally referred to are as follow:-
1.
BS 8110: 1985 : Structural Use of Concrete Part 1: Code of Practice for Design and Constructions. Part 2: Code of Practice for Special Circumstances Part 3: Design charts for singly beams, doubly beams and rectangular columns.
2.
BS 6399 : 1984 : Design Loading for building
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/
Part 1: Code of Practice for Dead and Imposed Loads. 3. CP3 : 1972 : Chapter V : Loading Part 2: Wind Loads
1.5 Design Method
Design which is in accordance with BS 8110 is based on Limit States Method. This method ensure that the structures are safe and fit for use i.e. they will not achieve their limit states during their service life.
The limit states mentioned earlier are as follows: a) Ultimate Limit State (ULS) ULS in concerned with the maximum load carrying capacity of the structure within the limits of strength of the materials used.
b)
Serviceability Limit State (SLS) SLS is concerned with the appearance of the structure, the effects of deflection or deformation on other elements and the durability of the structure.
c)
Additional Limit State
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/
The overall stability of the building is, of course, of paramount importance. It is of no use when an individual satisfies all the design criteria if the connections between the structure elements are incapable of withstanding at least some effect from misuse or accidents. In this context it is difficult to consider structural elements in isolation, as they form an integral part of the structure.
Generally speaking, reinforced concrete structures are designed to fulfill the ultimate limit state and are checked against the serviceability limit state. This process is of paramount importance because the main purpose of structural elements of a building is to withstand any load without jeopardizing the safety of the occupants.
For water retaining structures, cracks are the most important criteria. They have to be watertight. Therefore the structure should be designed for Ultimate Limit State (ULS) and checked against the Ultimate Limit State.
In addition to that, the durability of reinforced concrete structures should not be ignored. They should be given some attention during the selection of materials and when designing details.
ACTIVITY 1a
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/
TEST YOUR UNDERSTANDING BEFORE YOU CONTINUE TO THE NEXT INPUT! Fill in the blanks with the correct answers:
1.1 The purpose of design may, perhaps be started as the provision of a structure complying with the __________ and the ________requirements.
1.2
The _________________ is preferred to collapse.
1.3
The purpose of design is to ensure that it will not reach a _____________.
1.4 Reinforced concrete is a composite material consisting of _____________ and _________________.
1.5 Deflection is categorized and checked in accordance to the ________ limit state.
1.6 The essential basis of the design method is to consider each ___________ and to provide a suitable margin of _______________________________.
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/
1.7 The purpose of design consists of finding and dealing with the most economical structures associated with ________________ and
______________________ requirements.
1.8 BS 8110 defines the limit state as ______________________ and __________________________.
1.9 BS 6399 is the code of practice for ___________________ and ______________ load.
1.10
Beams, slabs, columns and foundation are reinforced concrete structural ___________________ that have to be designed by the engineer.
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/
FEEDBACK 1a
The answers are given below:
1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10
clients , users Ultimate Limit State limit state concrete , steel reinforcement serviceability limit state , safety safety , serviceability Ultimate Limit State (ULS) , Serviceability Limit State ( SLS ) Dead , Imposed elements
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 10
INPUT 2
1.6 Load Generally, load on any structural members cannot be determined accurately. For most structures, it is uneconomical to design using anticipated maximum load. Therefore, in normal design practice, the load to be used is based on the characteristic load. Characteristic load is defined as the minimum load that statistically will not exceed during the design life of the structure. There are 3 types of load: 1) Characteristic dead load ( gk ) Characteristic dead loads are fixed loads that will not be much different from the estimated load. Some examples of dead load are the weight of the elements, finishes, ceiling and fixed equipment, such as water pipes. BS 6399 Part 1 gives some of characteristic dead load to be used in designs. 2) Characteristic imposed load ( qk ) This load is not fixed but may vary such as the weight of occupants, equipment, furniture, etc. Characteristic imposed load, gk may also be obtained from BS 6399: Part 1 Code of Practice for Loads. Dead and Imposed
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 11
3) Wind load ( wk ) Wind load depends on the location, form, and dimension of the building and the wind velocity of that particular area. CP3 Chapter 5 Part 2 gives some guidelines on how to estimate wind load.
The load is calculated as follows;
Design Load = characteristic load partial safety factor = ( gk , qk , wk ) f
Design load and partial safety factor for various load combination and limit states are given in 2.1, BS 8110 Part 1.
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 12
ACTIVITY 1b
TEST YOUR UNDERSTANDING BEFORE YOU CONTINUE TO THE NEXT INPUT! Answer the following questions
1.11
What is characteristic load?
1.12
State the 3 types of load.
a) . b) ........................................................... .....................................................................................................................
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 13
c) .... 1.13 State the code of practice that gives estimates of dead and imposed loads?
1.14
The code of practice that gives guideline for calculating wind load?
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 14
FEEDBACK 1b
Please check your answers below:
Answers:
1.11
Minimum load that will not exceed during design life.
1.12
a) Dead load b) Imposed load c) Wind load
1.13
BS 6399 : Part 1
1.14
CP3 Chapter 5 : Part 2
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 15
INPUT 3
1.7 Strength of Materials
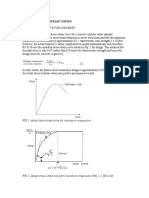
Characteristic strength is used to represent the strength of material. Mean strength is not suitable to be used because normally 50% of test results will fail. Characteristic strength is represented by the area under the normal distribution curve with a value of 0.05. This is shown in Figure 1.2 below:
Probability distribution
Characteristic strength
Mean strength
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 16
Area = 0.05 Strength
Figure 1.2: Characteristic Strength
From figure 1.2, characteristic strength is calculated as follows:
Characteristic strength = Mean strength 1.64 Standard deviation ()
It can be shown that 5 % of the test rests will be less than the characteristic strength. For example, to produce a concrete with a characteristic strength of 30 N/ mm2, and a standard deviation of 5 N/mm2, you need to have a mean strength of 38.2 N/mm2. The calculation is as follows:
i.e.:
Characteristic strength = Mean strength 1.64 Mean strength = Characteristic strength + 1.64 = 30 + 1.64 (5) = 30 + 8.2 = 38.2 N/mm2
Characteristic strength of concrete ( fcu ) is the strength of concrete at the age of 28 days . Concrete of grade 25, 30, 35, 40 and 50 N/mm2 is normally used.
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 17
Characteristic strength of steel reinforcement ( f y) is the yield stress of steel. Three (3) types of steel reinforcement are high yield steel (T) with a strength of 460 N/mm2, mild steel (250 N/mm2 ) and fabric reinforcement (BRC) with a strength of 485 N/mm2.
Design strength is defined as; Design strength =
characteri stic strength partial safety factor
( f cu , f y )
1.8 Partial Safety Factor
Partial Safety Factor is used in design to take into account any variation that could happen to load and strength during design and construction. BS 8110 has established its values in Table 2.2, Part 1. Various factors which contribute to these values are;
1.15
Since ultimate limit state is more severe, so the safety factors are much bigger than those for serviceability limit state.
1.16
Safety factor for steel reinforcement is less than for concrete because steel produced is of a stringent quality and it is controlled.
1.17
Safety factor for imposed load is more than for dead load because dead load could be estimated more accurately that imposed load
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 18
ACTIVITY 1c
TEST YOUR UNDERSTANDING BEFORE YOU CONTINUE TO THE NEXT INPUT!
1.15
How do you define characteristic strength?
1.16
If a concrete of grade 40 is to be produced, what mean strength is needed if = 4N/mm2?
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 19
1.17
State three (3) types of reinforcement used in reinforced concrete structures.
a)
b)
c)
1.18
Given fy = 250 N/mm2, m = 1.15. What is the steel design strength?
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 20
1.19
What is the partial safety factor for concrete in flexure?
FEEDBACK 1c
Lets check the answers together! Answers: 1.15 1.16 Characteristic strength = Mean strength - 1.64 Standard deviation Mean strength = 40 1.64 (4) = 33.44N/mm2 1.17 a) high yield steel b) mild steel
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 21
c) BRC 1.18 1.19 Steel design strength =
250 = 217 .39 N / mm 2 1.15
m = 1.50 (From Table 2.2, BS 8110)
Congratulations! You have successfully completed UNIT 1. Please check to the answers that you have fulfilled to all the objectives of this unit. If you havent done this, do not hesitate to go through this unit again. Now you should do the self-assessment section. But before doing so, please read the summary of UNIT 1.
SUMMARY
1.
The aim of structural design is to build structures, which are safe and that which can be used for intended purposes during it service life.
2.
Reinforced concrete is an important construction material, as it is a very strong, durable, fire resistant and versatile.
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 22
3.
The design process starts immediately after the client proposes his or her intention to the architect or engineer.
4.
The design process includes the preparation of the layout plan, structural analysis, load calculations, structural design and the preparation of working drawings.
5.
BS 8110 is the code of practice that should be referred to when designing reinforced concrete structural elements.
6.
BS 8110 uses the Ultimate Limit State method of design.
7. 8.
Loads are categorized as dead load, imposed load, and wind load. Design load is equal to characteristic load multiplied by partial safety factor.
9.
Characteristic strength is used to represent the strength of materials.
10.
Partial Safety Factors is used to take into account any inaccuracies during the design and construction of reinforced concrete structures.
Are you ready to do the self assessment? This test is in the form of multiple-choice questions. You have to answer all the questions given in 30 minutes. Award 1 mark for every correct answer. You may refer to BS 8110 if you want to.
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 23
SELF-ASSESSMENT
1. Which of the following is not included in the aims of structural design? A. Safety B. Cost C. Maintenance D. Aesthetic
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 24
2. Structural concrete should have the following EXCEPT. A. B. C. D. durable commercial value resistance to misuse fire resistant
3.
In the appropriate overall structural scheme, the engineer is guided by the following codes of practice EXCEPT A. B. C. D. ISO 9000 BS 8110 BS 6399 CP 3
4.
Which of the following failures occur when Ultimate Limit State in exceeded?
A. B. C. D.
Deflection Vibration Collapse Cracking
5.
The design method used in BS 8110 is one of the following. Select the answers.
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 25
A. B. C. D.
Plastic State Design Conservative Design Limit State Design Simple Design
6. Given that fm = 35 N/mm2 = 3.5 N/mm2 What is the characteristic strength of concrete?
A. B. C. D.
0.29 N/mm2 2.9 N/mm2 29.0 N/mm2 290.0 N/mm2
7. Given that f = 1.6 and characteristics load = 58 kN
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 26
What is the design load?
A. B. C. D.
928 kN 0.928 kN 9.28 kN 92.8 kN
8.
Partial safety factor, m for concrete in shear without shear reinforcement is equal to... A. B. C. D. 1.50 1.25 1.40 1.30
9. Given that m = 1.15, fy = 460 N/mm2. What is the design strength?
A. B. C. D.
400 N/mm2 450 N/mm2 500 N/mm2 550 N/mm2
10. Given that Gk = 50 kN, Qk = 100 kN. What is the design load?
A.
23 kN
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 27
B. C. D.
230 kN 2300 kN 23, 000 kN
FEEDBACK ON SELF-ASSESSMENT
Award one mark for every correct answer. The total is 100% for 10 marks. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. D B A C C C
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURAL DESIGN
C4301/UNIT1/ 28
7. 8. 9. 10.
D B A B
Now calculate the marks you have got. You should get at least 80% to pass this unit. If you have got more than 80%, congratulations! You are a good student. But if you have got less than 80%, you should go through this unit again.
END OF UNIT 1
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Celebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985Dari EverandCelebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985Belum ada peringkat
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignDari EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Unit 2 (CHARACTERISTICS OF MATERIALS)Dokumen33 halamanUnit 2 (CHARACTERISTICS OF MATERIALS)Zara Nabilah100% (5)
- Unit 12 (REINFORCED CONCRETE COLUMNS)Dokumen30 halamanUnit 12 (REINFORCED CONCRETE COLUMNS)Zara Nabilah100% (4)
- Unit 3 (DESIGN THEORY: LIMIT STATES AND BENDING)Dokumen23 halamanUnit 3 (DESIGN THEORY: LIMIT STATES AND BENDING)Zara Nabilah100% (7)
- Unit 8 (SERVICEABILITY LIMIT STATE (SLS) )Dokumen26 halamanUnit 8 (SERVICEABILITY LIMIT STATE (SLS) )Zara Nabilah100% (2)
- Unit 10 (TORSION)Dokumen22 halamanUnit 10 (TORSION)Zara Nabilah100% (3)
- Unit 11 (DESIGN OF REINFORCED CONCRETE SLABS (RCS) )Dokumen48 halamanUnit 11 (DESIGN OF REINFORCED CONCRETE SLABS (RCS) )Zara NabilahBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 5 DESIGN OF FLANGED BEAM T BEAMDokumen41 halamanUnit 5 DESIGN OF FLANGED BEAM T BEAMIan JamillaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2: Characteristics of MaterialsDokumen33 halamanUnit 2: Characteristics of MaterialsAnnur KamarudinBelum ada peringkat
- LECTURE NOTE 01 - RCC DesignDokumen14 halamanLECTURE NOTE 01 - RCC DesignMohamed AbdBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 14 (DESIGN OF SLENDER COLUMNS)Dokumen33 halamanUnit 14 (DESIGN OF SLENDER COLUMNS)Zara Nabilah96% (24)
- Unit 6 (DESIGN OF REINFORCED CONCRETE CONTINUOUS BEAMS)Dokumen26 halamanUnit 6 (DESIGN OF REINFORCED CONCRETE CONTINUOUS BEAMS)Zara Nabilah90% (30)
- Reinforced Concrete Lecture Notes University of HongKongDokumen32 halamanReinforced Concrete Lecture Notes University of HongKongApril Ingram100% (4)
- Chapter 07-Unit 04 - Design of Continous Beam For FlexureDokumen14 halamanChapter 07-Unit 04 - Design of Continous Beam For FlexureabdullahBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 9 (DESIGN OF SHEAR REINFORCEMENT)Dokumen29 halamanUnit 9 (DESIGN OF SHEAR REINFORCEMENT)Zara Nabilah76% (25)
- Unit 13 (DESIGN OF SHORT BRACED COLUMNS)Dokumen21 halamanUnit 13 (DESIGN OF SHORT BRACED COLUMNS)Zara Nabilah80% (15)
- Lecture Notes RC DesignDokumen53 halamanLecture Notes RC DesignchandrasekarBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 5 (DESIGN OF FLANGED BEAM: T-BEAM)Dokumen41 halamanUnit 5 (DESIGN OF FLANGED BEAM: T-BEAM)Zara Nabilah84% (31)
- Unit 4 (DESIGN OF RECTANGULAR BEAM SECTIONS)Dokumen37 halamanUnit 4 (DESIGN OF RECTANGULAR BEAM SECTIONS)Zara Nabilah100% (14)
- Example 3.1 Selection of Minimum Strength Class and Nominal Concrete Cover To Reinforcement (BS 8110)Dokumen53 halamanExample 3.1 Selection of Minimum Strength Class and Nominal Concrete Cover To Reinforcement (BS 8110)Mohamed AbdBelum ada peringkat
- Reinforced Concrete Design ReportDokumen11 halamanReinforced Concrete Design ReportAchala Fernando67% (3)
- Solved Example On Design of Slender Columns According To EC2Dokumen7 halamanSolved Example On Design of Slender Columns According To EC2Mouhamad Wehbe100% (1)
- Design Continuous Beam ReinforcementDokumen15 halamanDesign Continuous Beam ReinforcementMuhammad Farhan Gul100% (2)
- Unit 7 (DESIGN DETAILS OF BEAMS)Dokumen35 halamanUnit 7 (DESIGN DETAILS OF BEAMS)Zara Nabilah94% (16)
- Week 4 N 5 - Design of Rectangular Beam SectionDokumen77 halamanWeek 4 N 5 - Design of Rectangular Beam SectionTeaMeeBelum ada peringkat
- Retaining Wall-BS 8110-SacademicusDokumen13 halamanRetaining Wall-BS 8110-SacademicusSacademicusBelum ada peringkat
- Slab DesignDokumen88 halamanSlab DesignNOORFARAH HUSNA BINTI INTAZALI100% (1)
- Design Reinforced Concrete SlabDokumen14 halamanDesign Reinforced Concrete SlabLi ChianBelum ada peringkat
- Staircase AssignmentDokumen10 halamanStaircase AssignmentNabila Faiqah Zayn100% (1)
- Beam Design PDFDokumen20 halamanBeam Design PDFkabwe ngomaBelum ada peringkat
- Continuous BeamDokumen32 halamanContinuous Beamdixn__100% (1)
- Beam Design & Detailing (Simply Supported)Dokumen58 halamanBeam Design & Detailing (Simply Supported)dixn__100% (8)
- Reinforced Concrete Design IIDokumen52 halamanReinforced Concrete Design II'Izzad Afif100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To RCDokumen34 halamanChapter 1 - Introduction To RCBeanBelum ada peringkat
- Example 3.8 - Design of Short Column Subjected To Biaxial BendingDokumen3 halamanExample 3.8 - Design of Short Column Subjected To Biaxial BendingMuhammad Farhan Gul0% (2)
- Introduction to Steel and Timber StructuresDokumen47 halamanIntroduction to Steel and Timber StructuresMubarek AbduljebarBelum ada peringkat
- Example 6.1 - Slab-Simply Supported (One-Way) PDFDokumen5 halamanExample 6.1 - Slab-Simply Supported (One-Way) PDFnur100% (1)
- Reinforced Concrete Design 1 Design of Column (Examples and Tutorials)Dokumen19 halamanReinforced Concrete Design 1 Design of Column (Examples and Tutorials)maizansofiaBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Reinfonced Concrete Slab by Eng:Kusundwa 0757-537605Dokumen53 halamanDesign of Reinfonced Concrete Slab by Eng:Kusundwa 0757-537605GoodluckBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 07-Unit 05 - Design For Shear PDFDokumen19 halamanChapter 07-Unit 05 - Design For Shear PDFMohamed AbdBelum ada peringkat
- Braced CutDokumen14 halamanBraced CutAnikBelum ada peringkat
- UiTM Structural Concrete Design AppendixDokumen37 halamanUiTM Structural Concrete Design AppendixMuhammad Farhan Gul67% (6)
- Corbel DesignDokumen12 halamanCorbel DesignURVESHKUMAR PATELBelum ada peringkat
- Reinforced Concrete - I DMU Lecture NotesDokumen206 halamanReinforced Concrete - I DMU Lecture NotesAntenehBelum ada peringkat
- Foundation by SamuelDokumen78 halamanFoundation by SamuelTefera Temesgen100% (1)
- Design of Raft Foundations for Low Bearing SoilDokumen1 halamanDesign of Raft Foundations for Low Bearing SoilAhmed Al-AmriBelum ada peringkat
- Foundation Engineering Questions and AnswersDokumen25 halamanFoundation Engineering Questions and AnswersGetachew AdmasuBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Quiz 6 LevelsDokumen59 halamanTechnical Quiz 6 LevelsGoutham RathoreBelum ada peringkat
- CH 3 - AE Analysis and Design of Two-Way SlabsDokumen111 halamanCH 3 - AE Analysis and Design of Two-Way Slabsephrem100% (3)
- Slab Design NoteDokumen112 halamanSlab Design NoteBeza GetachewBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 2 - Analysis of Flanged Section (Ec2)Dokumen20 halamanTopic 2 - Analysis of Flanged Section (Ec2)RCdesign201267% (3)
- Chapter 5 Column DesignDokumen25 halamanChapter 5 Column DesigneltaibzhBelum ada peringkat
- Reinforced Concrete Columns: J. P. ForthDokumen25 halamanReinforced Concrete Columns: J. P. ForthJeff Sun100% (1)
- Unit 1: Ultimate Limits State Design ConceptDokumen28 halamanUnit 1: Ultimate Limits State Design ConceptAnnur Kamarudin100% (1)
- Unit No 1: Reinforced Concrete IntroductionDokumen29 halamanUnit No 1: Reinforced Concrete IntroductionOladimeji Ibukun IjaodolaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit No 1: Reinforced Concrete IntroductionDokumen29 halamanUnit No 1: Reinforced Concrete IntroductionAbdur Rasheed RasheedBelum ada peringkat
- RC design topic 1 and 2Dokumen16 halamanRC design topic 1 and 2thuo19601Belum ada peringkat
- Reinforced Concrete StructuresDokumen5 halamanReinforced Concrete StructuresopulitheBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Structural ElementsDokumen22 halamanDesign of Structural Elementsengsam777Belum ada peringkat
- Buoyancy and StabilityDokumen8 halamanBuoyancy and StabilityZara NabilahBelum ada peringkat
- Momentum EquationsDokumen11 halamanMomentum EquationsZara NabilahBelum ada peringkat
- Estimating Earthwork - Kontrak Prosedur 2Dokumen27 halamanEstimating Earthwork - Kontrak Prosedur 2Zara Nabilah100% (6)
- Analysis of Statically 2D Frame StructureDokumen14 halamanAnalysis of Statically 2D Frame StructureZara Nabilah100% (2)
- Unit 4 (STATISTICAL ESTIMATION AND SMALL SAMPLING THEORIES )Dokumen26 halamanUnit 4 (STATISTICAL ESTIMATION AND SMALL SAMPLING THEORIES )Zara NabilahBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 14 (DESIGN OF SLENDER COLUMNS)Dokumen33 halamanUnit 14 (DESIGN OF SLENDER COLUMNS)Zara Nabilah96% (24)
- Unit 2 (PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS)Dokumen50 halamanUnit 2 (PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS)Zara NabilahBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3 (SAMPLE AND SAMPLE DISTRIBUTIONS)Dokumen32 halamanUnit 3 (SAMPLE AND SAMPLE DISTRIBUTIONS)Zara Nabilah100% (2)
- Unit 13 (DESIGN OF SHORT BRACED COLUMNS)Dokumen21 halamanUnit 13 (DESIGN OF SHORT BRACED COLUMNS)Zara Nabilah80% (15)
- Unit 5 (CORRELATION AND REGRESSION)Dokumen23 halamanUnit 5 (CORRELATION AND REGRESSION)Zara NabilahBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 15 (DESIGN OF FOUNDATIONS)Dokumen48 halamanUnit 15 (DESIGN OF FOUNDATIONS)Zara Nabilah100% (31)
- Unit 1 ( PROBABILITY THEORY ) - StatistikDokumen48 halamanUnit 1 ( PROBABILITY THEORY ) - StatistikZara Nabilah100% (1)
- Unit 9 (DESIGN OF SHEAR REINFORCEMENT)Dokumen29 halamanUnit 9 (DESIGN OF SHEAR REINFORCEMENT)Zara Nabilah76% (25)
- Unit 5 (LAND DEALINGS)Dokumen16 halamanUnit 5 (LAND DEALINGS)Zara Nabilah93% (14)
- Unit 11 (DESIGN OF REINFORCED CONCRETE SLABS (RCS) )Dokumen48 halamanUnit 11 (DESIGN OF REINFORCED CONCRETE SLABS (RCS) )Zara NabilahBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4 (DESIGN OF RECTANGULAR BEAM SECTIONS)Dokumen37 halamanUnit 4 (DESIGN OF RECTANGULAR BEAM SECTIONS)Zara Nabilah100% (14)
- Unit 6 (DESIGN OF REINFORCED CONCRETE CONTINUOUS BEAMS)Dokumen26 halamanUnit 6 (DESIGN OF REINFORCED CONCRETE CONTINUOUS BEAMS)Zara Nabilah90% (30)
- Unit 7 (DESIGN DETAILS OF BEAMS)Dokumen35 halamanUnit 7 (DESIGN DETAILS OF BEAMS)Zara Nabilah94% (16)
- Unit 6 (MALAY RESERVATIONS - THE MALAY RESERVE ENACTMENT F.M.S. Cap 142)Dokumen14 halamanUnit 6 (MALAY RESERVATIONS - THE MALAY RESERVE ENACTMENT F.M.S. Cap 142)Zara Nabilah79% (14)
- Unit 4 (CONVERSION, SUB-DIVISION, PARTITION AND AMALGAMATION OF LAND)Dokumen17 halamanUnit 4 (CONVERSION, SUB-DIVISION, PARTITION AND AMALGAMATION OF LAND)Zara Nabilah90% (21)
- Unit 5 (DESIGN OF FLANGED BEAM: T-BEAM)Dokumen41 halamanUnit 5 (DESIGN OF FLANGED BEAM: T-BEAM)Zara Nabilah84% (31)
- Unit 7 (LAND ACQUISITION - THE LAND ACQUISITION ACT 1960, ACT 486)Dokumen20 halamanUnit 7 (LAND ACQUISITION - THE LAND ACQUISITION ACT 1960, ACT 486)Zara Nabilah86% (7)
- Unit 3 (DISPOSAL OF LAND BY OTHER THAN ALIENATION)Dokumen20 halamanUnit 3 (DISPOSAL OF LAND BY OTHER THAN ALIENATION)Zara Nabilah100% (5)
- Unit 2 (DISPOSAL OF LAND BY ALIENATION)Dokumen23 halamanUnit 2 (DISPOSAL OF LAND BY ALIENATION)Zara Nabilah89% (19)