AL 1992 Physics Marking Scheme
Diunggah oleh
api-373884186%(7)86% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (7 suara)
9K tayangan22 halamanHak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PDF atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF atau baca online dari Scribd
86%(7)86% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (7 suara)
9K tayangan22 halamanAL 1992 Physics Marking Scheme
Diunggah oleh
api-3738841Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 22
-
f
cA
Cow's me a
RESTRICTED Pusiactt
‘WeAL-PHY A
Marking Scheme i
1 @) tnd Laws The momentum of a body }
+ i propatioual. :
to the dasulant fog acting on the body and this occurs }
in the digection of this force. }
. (i) + 3rd Law - If'a body,A exerts a force ona body.B. } *
then body exerts an eysul but ggpasite force on body A.)
® ision cd ana m2
Before collision m,, u, and sm, uy :
1 time of impact is t and vy > v, =
Body Avvall exert a force F on body B for a time t and by Newton's i
3rd Law body B will exert « force 6 on bouy A (opposite direction). § X=
By Newt's tad Law, force = cal of change of momentum (ons }
of proportionality = 1)
Hence F = B=
Since forces on
#0 mat aah, = uy, ns,
afd linear moment
No -K.E. muy not be conserve
however conwerved}
ow
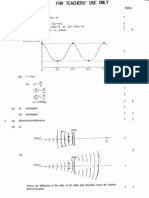
‘The voltage +¥ is varied between the cathode and anode
vacuum tube containing Hg vapor.
A sinall retarding potential exists between an intermedi
i pret elotron esctinganeder Sn
From O ~ B electrons accelerate snd current increases,
ALB,C,D inelastic coli
take place with Hg atoms rising their internal energy tony
‘quantised valve,
‘Current { Yrons due.to 4 loss of KE, of electrons. }
RESTRIC TEM hissy
Pa
‘ RESTRICTED Puabocte
P2
‘Machine Scheme
L G w “
: : a
near Emee mo
: ot ees
aD
large range of K.E."s, Since all electrons
rent fot sane internat process 3 Py
+ tulad energy should be constant } ”
Hence postulation of auother ‘maig-less* particle - the neuteing’
: to curry rest of encrgy. toe 3 ” as
\
‘Explain the mveanings of Newion's second and third Laws of Motion. (@ uarks)
(©) Apply these laws wo the rapid impact between two boule, which were inililly moving with unequal
velocities along the same direction, and show that linear momentum it conserved, , Explain whether
the (otal kinetic energy ie neceesaity conserved, or nol. (7 mathe)
"(@) -, Belely discuss the couscevation of energy in reppeio “| t .
() ~ the results of the Franck-Hertz experiment and te
(i) the energy spectrum of the Popaticles ented uatucally by some nucle!
"(ho experimental circuit‘delails or theoretical details are expected.) vi * on
PECTHRICTOEN rears -
REST KICT ED UabSctE - :
Pa
‘Marking Scheme . i
A 2. (8) Kinetic theory assumptions are :
(1) ivermotecular forces are negligible, }
* except in collisions.
.@ Volume occupied by molecules is negligible, }
* compared with volume of gas, }
G) All eolsionbetven molecule
and with the wall of container
are elastic (no energy lost). }
"Time of contact during collisions 3 4
fr is negligible compared with tine between collsi “4
! © ©
5 . .
“
ie i
-
a :
y Molecule A travels to A" rapidly with high average speed. ° t %
. However 10 travel from A to B i bas to suffer many collisions 4
and changes of direction 4
= resulting in a slow diffusion rate, z
(i) MEP is the average distance moved by & molecule between nh
2 successive collisions with other molecules, ”
rc 14 ‘Molecules have lite probability of colliding with their )-
; igbbouring molecule Scr } *
since they are all movi in direct 4
= 8 Hence the M.F.P. > > average separation of molecules. } ho}
rat _
my
aie? RESTRICTED. putpsci?
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- 1994 AL Chemistry Paper I Marking SchemeDokumen10 halaman1994 AL Chemistry Paper I Marking Schemeapi-3738841100% (1)
- 2002 AL Chemistry Paper 1+2 Marking SchemeDokumen36 halaman2002 AL Chemistry Paper 1+2 Marking Schemeapi-373884138% (8)
- 1990 AL Chemistry Paper I Marking SchemeDokumen11 halaman1990 AL Chemistry Paper I Marking Schemeapi-373884160% (5)
- 1993 AL Chemistry Paper I Marking SchemeDokumen7 halaman1993 AL Chemistry Paper I Marking Schemeapi-373884150% (2)
- 1998 AL Chemistry Paper 1+2 Marking SchemeDokumen36 halaman1998 AL Chemistry Paper 1+2 Marking Schemeapi-3738841100% (1)
- 2000 AL Chemistry Paper I Marking SchemeDokumen20 halaman2000 AL Chemistry Paper I Marking Schemeapi-3738841Belum ada peringkat
- 1997 AL Chemistry Paper I Marking SchemeDokumen22 halaman1997 AL Chemistry Paper I Marking Schemeapi-3738841Belum ada peringkat
- 1995 AL Chemistry Paper 1 Marking SchemeDokumen21 halaman1995 AL Chemistry Paper 1 Marking Schemeapi-3738841100% (1)
- 1996 AL Chemistry Marking SchemeDokumen34 halaman1996 AL Chemistry Marking Schemeapi-373884175% (4)
- 2000 AL Chemistry Paper II Marking SchemeDokumen15 halaman2000 AL Chemistry Paper II Marking Schemeapi-3738841Belum ada peringkat
- 1998 AL Chemistry Paper 1+2 Marking SchemeDokumen36 halaman1998 AL Chemistry Paper 1+2 Marking Schemeapi-3738841100% (1)
- 1997 AL Chemistry Paper 2 Marking SchemeDokumen12 halaman1997 AL Chemistry Paper 2 Marking Schemeapi-37388410% (2)
- 1997 AL Chemistry Paper 2 Marking SchemeDokumen12 halaman1997 AL Chemistry Paper 2 Marking Schemeapi-37388410% (2)
- 1999 AL Chemistry Marking SchemeDokumen34 halaman1999 AL Chemistry Marking Schemeapi-373884125% (4)
- 2001 AL Chemistry Paper II Marking SchemeDokumen16 halaman2001 AL Chemistry Paper II Marking Schemeapi-373884163% (8)
- 2003 AL Chemistry Paper 1 Marking SchemeDokumen16 halaman2003 AL Chemistry Paper 1 Marking Schemeapi-3738841100% (1)
- AL 1993 Physics Marking SchemeDokumen16 halamanAL 1993 Physics Marking Schemeapi-3738841100% (3)
- AL 1990 Physics Marking Scheme IIADokumen13 halamanAL 1990 Physics Marking Scheme IIAapi-373884167% (3)
- AL 1991 Physics Marking SchemeDokumen22 halamanAL 1991 Physics Marking Schemeapi-373884150% (2)
- AL 1994 Physics Marking Scheme IADokumen14 halamanAL 1994 Physics Marking Scheme IAapi-3738841100% (2)
- 1999 AL Chemistry Marking SchemeDokumen34 halaman1999 AL Chemistry Marking Schemeapi-373884125% (4)
- AL 1991 Physics Marking Scheme IIADokumen12 halamanAL 1991 Physics Marking Scheme IIAapi-37388410% (3)
- AL 1994 Physics Marking Scheme IIBDokumen14 halamanAL 1994 Physics Marking Scheme IIBapi-3738841Belum ada peringkat
- AL 1995 Physics Marking Scheme IIBDokumen7 halamanAL 1995 Physics Marking Scheme IIBapi-3738841100% (1)
- AL 1996 Physics Marking SchemeDokumen14 halamanAL 1996 Physics Marking Schemeapi-3738841100% (4)
- AL 1997 Physics Marking SchemeDokumen15 halamanAL 1997 Physics Marking Schemeapi-373884167% (3)
- AL 1998 Physics Marking SchemeDokumen15 halamanAL 1998 Physics Marking Schemeapi-373884175% (8)
- AL 2000 Physics Marking SchemeDokumen40 halamanAL 2000 Physics Marking Schemeapi-373884180% (10)
- AL 1999 Physics Marking SchemeDokumen15 halamanAL 1999 Physics Marking Schemeapi-373884150% (2)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- ShteDokumen57 halamanShteKaiash M YBelum ada peringkat
- LEP 2.2.01 Interference of Light: Related Topics Set-Up and ProcedureDokumen3 halamanLEP 2.2.01 Interference of Light: Related Topics Set-Up and ProcedureMuhammad AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- B.Tech CSE (DS) - R23Dokumen53 halamanB.Tech CSE (DS) - R23MUKESH KUMARBelum ada peringkat
- 351 - 27435 - EE419 - 2020 - 1 - 2 - 1 - 0 5 EE419 Lec9 Solution of State EquationsDokumen15 halaman351 - 27435 - EE419 - 2020 - 1 - 2 - 1 - 0 5 EE419 Lec9 Solution of State Equationsyoussef hossamBelum ada peringkat
- Yasir Mudakir Khan: Familiarization With The Oscilloscope and Proteus SoftwareDokumen4 halamanYasir Mudakir Khan: Familiarization With The Oscilloscope and Proteus SoftwareSaad AliKhanBelum ada peringkat
- Ship Stability Notes & Examples Kemp & Young 2001, PDFDokumen184 halamanShip Stability Notes & Examples Kemp & Young 2001, PDFSumit Kumar100% (2)
- Science Dec 01 06Dokumen168 halamanScience Dec 01 06ABCBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-2 satellite AOCS subsystemsDokumen33 halamanUnit-2 satellite AOCS subsystemsMahaBaliBelum ada peringkat
- Eye StructureDokumen15 halamanEye StructurekathyBelum ada peringkat
- 7KM21120BA003AA0Dokumen8 halaman7KM21120BA003AA0jaydeeppanchalBelum ada peringkat
- Transistors by Le CroissetteDokumen296 halamanTransistors by Le CroissetteDeepam kulshreshthaBelum ada peringkat
- Mapua University: Experiment No. 4.A Liquid Limit of SoilDokumen7 halamanMapua University: Experiment No. 4.A Liquid Limit of SoilMike SyBelum ada peringkat
- Final .Mat Energy Collector Using Piezoelectric Sensor For Public ChargingDokumen68 halamanFinal .Mat Energy Collector Using Piezoelectric Sensor For Public ChargingArneitou Queroyla CagungunBelum ada peringkat
- Cat. 6 PVC cords technical data sheetDokumen2 halamanCat. 6 PVC cords technical data sheetRicardo PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Bedside Monitor: Service ManualDokumen152 halamanBedside Monitor: Service Manualkatabalwa eric100% (1)
- Ultra Sonic Sensor Security SensorDokumen13 halamanUltra Sonic Sensor Security SensorAbhiram Grandhi100% (1)
- Modelling and motion control of a double-pendulum driven cartDokumen13 halamanModelling and motion control of a double-pendulum driven cartDawit AssfawBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry Lecture 3Dokumen18 halamanGeneral Chemistry Lecture 3Niloy GhoshBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus - S6Dokumen85 halamanSyllabus - S6B 15 Aravinth VKBelum ada peringkat
- Sbi Clerk Quantitative Aptitude PDF 26Dokumen8 halamanSbi Clerk Quantitative Aptitude PDF 26HMT liveBelum ada peringkat
- L12121en BDokumen16 halamanL12121en Bemisario destinoBelum ada peringkat
- Dekton Technical Manual ENDokumen24 halamanDekton Technical Manual ENIzrada FotografijaBelum ada peringkat
- Go-Kart Designing ReportDokumen56 halamanGo-Kart Designing ReportPraveen Sah84% (25)
- Fault Code 435 Oil Pressure Switch Sensor Circuit - Data Erratic, Intermittent or IncorrectDokumen11 halamanFault Code 435 Oil Pressure Switch Sensor Circuit - Data Erratic, Intermittent or IncorrectAhmedmah100% (1)
- Determination of Blood Glucose LevelsDokumen49 halamanDetermination of Blood Glucose LevelsGayatri DewiBelum ada peringkat
- VX - UFOs and Aliens Are Man Made.Dokumen422 halamanVX - UFOs and Aliens Are Man Made.niksaniksa780Belum ada peringkat
- Solu of Assignment 7Dokumen4 halamanSolu of Assignment 7dontstopmeBelum ada peringkat
- Crack Initiation & Propagation: Beach Marks, StriationsDokumen4 halamanCrack Initiation & Propagation: Beach Marks, StriationsJay-m DG. FaminiBelum ada peringkat
- Calculation of Natural Gas Isentropic ExponentDokumen8 halamanCalculation of Natural Gas Isentropic ExponentsekharsamyBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 2Dokumen3 halamanTutorial 2danielruthers2Belum ada peringkat