Ascariasis
Diunggah oleh
belleboy0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
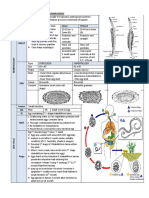
19 tayangan2 halamanAscariasis is a parasitic roundworm infection acquired by ingesting fertilized eggs from contaminated soil or food. The eggs hatch in the small intestine and larvae migrate through the lungs before reaching maturity in the jejunum approximately 65 days later. Adults feed in the intestines and do not multiply, but infection can persist if re-exposure to eggs occurs before the worms' 2-year lifespan ends.
Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniAscariasis is a parasitic roundworm infection acquired by ingesting fertilized eggs from contaminated soil or food. The eggs hatch in the small intestine and larvae migrate through the lungs before reaching maturity in the jejunum approximately 65 days later. Adults feed in the intestines and do not multiply, but infection can persist if re-exposure to eggs occurs before the worms' 2-year lifespan ends.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
19 tayangan2 halamanAscariasis
Diunggah oleh
belleboyAscariasis is a parasitic roundworm infection acquired by ingesting fertilized eggs from contaminated soil or food. The eggs hatch in the small intestine and larvae migrate through the lungs before reaching maturity in the jejunum approximately 65 days later. Adults feed in the intestines and do not multiply, but infection can persist if re-exposure to eggs occurs before the worms' 2-year lifespan ends.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
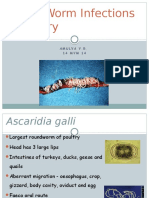
Ascariasis
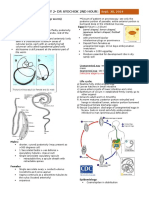
Fertilized eggs released into favorable soil
Larva develops within the egg in the soil
Fertilized eggs may become infectious within 5-10 days. Eggs may remain viable in soil for up to 17 months.
Infection occurs through soil contamination of hands or food, ingestion, and the subsequent hatching of eggs in the small intestine
Second-stage larvae pass through the intestinal wall and migrate through the portal system to the liver and then the lungs
A significant exposure may produce subsequent pneumonia and eosinophilia
Signs/Symptoms: Wheezing Dyspnea nonproductive cough hemoptysis fever
Larvae are expectorated and swallowed.
Larvae eventually reaching the jejunum, where they mature into adults in approximately 65 days
Adult worms feed on digestion products of the host.
Signs/Symptoms: protein, caloric, or vitamin A deficiency retarded growth increased susceptibility to infectious diseases Large and tangled worms may cause intestinal (usually ileal), common duct, pancreatic, or appendiceal obstruction
Worms do not multiply in the host. For infection to persist beyond the 2-year maximum lifespan of the worms, re-exposure must occur
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!Dari Everand911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- AscarisDokumen3 halamanAscarisColette BarrometroBelum ada peringkat
- Roundworm Infections, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandRoundworm Infections, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Round Worm Infections of PoultryDokumen24 halamanRound Worm Infections of PoultryAmulyaVemulapadBelum ada peringkat
- Ascaris Lumbricoides: MorphologyDokumen7 halamanAscaris Lumbricoides: MorphologyIntan HaddadBelum ada peringkat
- Handouts Avian Salmonellosis Fall 2020Dokumen8 halamanHandouts Avian Salmonellosis Fall 2020NabeelBelum ada peringkat
- Ascari As IsDokumen16 halamanAscari As IsCici Novelia ManurungBelum ada peringkat
- Swine Production PPT-2Dokumen98 halamanSwine Production PPT-2The Municipal AgriculturistBelum ada peringkat
- Ascari As IsDokumen20 halamanAscari As IsDeladem EmmanuelBelum ada peringkat
- Module 33 Ascariasis EditedDokumen10 halamanModule 33 Ascariasis EditedPrincess Mae Sierra PacificoBelum ada peringkat
- Nematode Infections 2019 Student PDFDokumen272 halamanNematode Infections 2019 Student PDFCharlene SuliganBelum ada peringkat
- Case Presentation: Ascariasis: Mrs. Lailanie Evangelista DotimasDokumen10 halamanCase Presentation: Ascariasis: Mrs. Lailanie Evangelista DotimasRodelen MarañoBelum ada peringkat
- CoccidiosisDokumen6 halamanCoccidiosisAnaBelum ada peringkat
- Life CycleDokumen2 halamanLife CycleChristine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- Zoology AscriseDokumen12 halamanZoology AscrisepappunaagraajBelum ada peringkat
- Ascaris LumbricoidesDokumen33 halamanAscaris LumbricoidesBio SciencesBelum ada peringkat
- AscariasisDokumen50 halamanAscariasisAnaleah MalayaoBelum ada peringkat
- Ascaris LumbricoidesDokumen33 halamanAscaris LumbricoidesRosi Gustina100% (5)
- Avian Digestive ProblemsDokumen83 halamanAvian Digestive Problemsابراهيم القويعىBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3.2 CoccidiosisDokumen113 halamanLesson 3.2 CoccidiosisnickswipoBelum ada peringkat
- Aljas&Bama (Microbm9evaluate)Dokumen8 halamanAljas&Bama (Microbm9evaluate)Mary Clare Fuentes BamaBelum ada peringkat
- Enteritis Viral JubbDokumen17 halamanEnteritis Viral JubbSandraBelum ada peringkat
- CoccidiosisDokumen45 halamanCoccidiosissherinshahs2010Belum ada peringkat
- Ascaris Lumbricoides: I. MorphologyDokumen6 halamanAscaris Lumbricoides: I. MorphologyJoseline SorianoBelum ada peringkat
- Liver FluksDokumen28 halamanLiver Flukszaid nabeelBelum ada peringkat
- Nematodes 10-11Dokumen128 halamanNematodes 10-11microperadeniya100% (4)
- Diarrhea in Neonatal RuminantsDokumen8 halamanDiarrhea in Neonatal Ruminantsbarbybackup2Belum ada peringkat
- Helminthic Worms Are Highly Prevalent andDokumen4 halamanHelminthic Worms Are Highly Prevalent andPeter MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Parasite 3Dokumen4 halamanParasite 3Neric Ico MagleoBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Activity - FecalysisDokumen2 halamanLab Activity - FecalysisARRWEN DOMINIQUE YZABELLE TUAZONBelum ada peringkat
- Bolus AskarisDokumen10 halamanBolus AskarisDina Fitri FauziahBelum ada peringkat
- Intestinal Nematodes: Dr. Devika DdawelaDokumen127 halamanIntestinal Nematodes: Dr. Devika DdawelaPraveenKumarBelum ada peringkat
- Ascaris LumbricoidesDokumen15 halamanAscaris LumbricoidesJyoti DasBelum ada peringkat
- Brief Introduction To Protozoan Diseases of PoultryDokumen5 halamanBrief Introduction To Protozoan Diseases of Poultrykarki Keadr Dr100% (4)
- Poultry Diseases and Their TreatmentDokumen159 halamanPoultry Diseases and Their TreatmentAbubakar Tahir Ramay67% (12)
- Anisakis SPP 2Dokumen246 halamanAnisakis SPP 2erickpaul.cajano.mnlBelum ada peringkat
- Clostridial infections-LR3Dokumen8 halamanClostridial infections-LR3yomifBelum ada peringkat
- Presented by Amir Sadaula BVSC & Ah, 8 Sem Rampur Campus Roll No: 01Dokumen19 halamanPresented by Amir Sadaula BVSC & Ah, 8 Sem Rampur Campus Roll No: 01naturalamirBelum ada peringkat
- Ministry of Higher Education and Science Research Sulaimani Polytechnic University Kalar Technical Institute ..Department SubjectDokumen20 halamanMinistry of Higher Education and Science Research Sulaimani Polytechnic University Kalar Technical Institute ..Department Subjectsoran najebBelum ada peringkat
- Bahsakam KotaeyDokumen19 halamanBahsakam Kotaeysoran najebBelum ada peringkat
- STH's Unholy TrinityDokumen9 halamanSTH's Unholy TrinityEunice AndradeBelum ada peringkat
- CORONADokumen44 halamanCORONAtejasbhukal567Belum ada peringkat
- Enterobius VermicularisDokumen10 halamanEnterobius VermicularisSree GouriBelum ada peringkat
- Aspergillosis by Gaurav KambojDokumen4 halamanAspergillosis by Gaurav KambojmehakBelum ada peringkat
- Ascaris: LumbricoidesDokumen5 halamanAscaris: LumbricoidessibinBelum ada peringkat
- Ascaris LumbricoidesDokumen14 halamanAscaris LumbricoidesLuis MercadoBelum ada peringkat
- Liver Fluke An Overview For PractitionersDokumen14 halamanLiver Fluke An Overview For PractitionersAli KareemBelum ada peringkat
- Zoonotic DiseasesDokumen96 halamanZoonotic DiseasesWakjira GemedaBelum ada peringkat
- Revision: Types of Life Cycle in Trematoda and CestodaDokumen71 halamanRevision: Types of Life Cycle in Trematoda and CestodaMicroscopeGeekBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD)Dokumen19 halamanUnderstanding Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD)nurulBelum ada peringkat
- Other AphasmidsDokumen4 halamanOther AphasmidsJayricDepalobosBelum ada peringkat
- Intestinal and Tracheal Parasites of PoultryDokumen4 halamanIntestinal and Tracheal Parasites of Poultrywalden c. aseralBelum ada peringkat
- Soil Transmitted Helminths: Dr. Madhusudan Swarnkar Professor, Community Medicine, JMC, JhalawarDokumen34 halamanSoil Transmitted Helminths: Dr. Madhusudan Swarnkar Professor, Community Medicine, JMC, Jhalawarmadhusudan swarnkarBelum ada peringkat
- Ascaris Lumbricoides: Ascariasis. Infections Most Often Seen in Young Children byDokumen7 halamanAscaris Lumbricoides: Ascariasis. Infections Most Often Seen in Young Children byThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Cdnursing PPT 2021Dokumen37 halamanCdnursing PPT 2021yuuki konnoBelum ada peringkat
- FInal Laboratory Activity Microbiology LABESORESDokumen10 halamanFInal Laboratory Activity Microbiology LABESORESJAN ELMER L. LABESORESBelum ada peringkat
- Feline PanleukopeniaDokumen15 halamanFeline PanleukopeniaVetlife DvpBelum ada peringkat
- Intestinal Nematodes: Ascaris Lumbricoides GEO Dist: HabitatDokumen3 halamanIntestinal Nematodes: Ascaris Lumbricoides GEO Dist: HabitatMegat Muhammad Syarif HamdaniBelum ada peringkat
- Hymenolepsis Nana LabDokumen3 halamanHymenolepsis Nana LabMary Jane TiangsonBelum ada peringkat