PHYS CH 8 Homework
Diunggah oleh
Kali SmithJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
PHYS CH 8 Homework
Diunggah oleh
Kali SmithHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Physics Homework Problems and Solutions
Chapter 8: Work, Energy, and Power
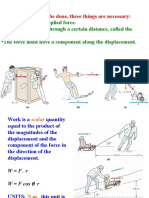
Work
8-1. What is the work done by a force of 20 N acting through a parallel distance of 8 m? What force will do the same work
through a distance of 4 m?
Work = (20 N)(8 m) = 160 J ; F (4 m) = 160 J; F = 40.0 N
8-2. A worker lifts a 40 lb weight through a height of 10 ft. How many meters can a 10-kg block be lifted by the same
amount of work?
Work = (20 lb)(10 ft) = 200 ft lb;
1.356 J
200 ft lb 271 J
1 ft lb
Work
| |
= =
|
\ .
Work = Fs = mgs;
2
271 J
(10 kg)(9.8 m/s )
Work
s
mg
= = ; s = 2.77 m
8-3. A tugboat exerts a constant force of 4000 N on a ship, moving it a distance of 15 m. What work is done?
Work = (4000 N)(15 m); Work = 60,000 J
8-7. A horizontal force pushes a 10-kg sled along a driveway for a distance of 40 m. If the coefficient of sliding friction is
0.2, what work is done by the friction force?
Work = (F cos u)s = (F) (cos 180
0
)s = - F s; but F =
k
N =
k
mg
Work =
k
mg s = (0.2)(10 kg)(9.8 m/s
2
)(40 m); Work = 784 J
*8-11. A 10-kg block is dragged 20 m by a parallel force of 26 N. If
k
= 0.2, what is the resultant work and what
acceleration results.
F =
k
N =
k
mg F = 0.2(10 kg)(9.8 m/s
2
) = 19.6 N
Work
= F
R
s = (P F)s; Work = (26 N 19.6 N)(20 m) Work = 128 J
F
R
= (26 N 19.6 N) = 6.40 N;
6.4 N
10 kg
F
a
m
= = ; a = 0.640 m/s
2
Work and Kinetic Energy
8-18. What is the kinetic energy of a 6-g bullet at the instant its speed is 190 m/s? What is the kinetic energy of a 1200-kg
car traveling at 80 km/h? (80 km/h = 22.2 m/s)
E
k
= mv
2
= (0.006 kg)(190 m/s)
2
; E
k
= 217 J
E
k
= mv
2
= (1200 kg)(22.2 m/s)
2
; E
k
= 296 kJ
*8-22. A 2400-lb car increases its speed from 30 mi/h to 60 mi/h? What resultant work was required? What is the equivalent
work in joules?
v
o
= 30 mi/h = 44 ft/s; v
f
= 60 mi/h = 88 ft/s;
2
2400 lb
75.0 slugs
32 ft/s
m = =
Work = mv
f
2
- mv
o
2
= (75 slugs)(88 ft/s)
2
- (75 slugs)(44 ft/s)
2
;
Work = 217,800 ft lb ; Work =
1 J
217,800 ft lb
0.7378 ft lb
| |
|
\ .
= 295 kJ
*8-23. A 0.6-kg hammer head is moving at 30 m/s just before striking the head of a spike. Find the initial kinetic energy.
What work can be done by the hammer head?
E
k
= mv
2
= (0.6 kg)(30 m/s)
2
; E
k
= 270 J
Work = AE
k
= 0 200 J; Work = - 270 J
F
20 m
26 N
Potential Energy
8-31. At a particular instant a mortar shell has a velocity of 60 m/s. If its potential energy at that point is one-half of its
kinetic energy, what is its height above the earth?
E
k
= mv
2
and E
p
= mgh; At the instant in question, E
p
= E
k
2 2
1 1
or 4
2 2
mgh mv gh v
| |
= =
|
\ .
and
2
4
v
h
g
=
2
2
(60 m/s)
4(9.8 m/s )
h = h = 91.8 m
8-34. A 64-lb weight is lifted to a height of 10 ft and then released to fall freely. What is the potential energy, the kinetic
energy and the total energy at (a) the highest point, (b) 3 ft above the ground, and (c) at the ground?
(W = 64 lb, g = 32 ft/s
2
)
(a) E
P
= Wh = (64 lb)(10 ft) = 640 ft lb; E
P
= 640 ft lb
E
k
= mv
2
= 0 ( v
o
= 0); E
T
= E
P
+ E
k
= 640 ft lb + 0
At 10 ft: E
P
= 640 ft lb; E
k
= 0; and E
T
= 640 ft lb
(b) E
P
= Wh = (64 lb)(3 ft) = 192 ft lb; E
P
= 192 ft lb
E
k
= E
T
E
P
; E
k
= 640 ft lb 192 ft lb; E
k
= 448 ft lb
At 3 ft: E
P
= 192 ft lb; E
k
= 448 ft lb; and E
T
= 640 ft lb
(c) At 0 ft h = 0 and E
T
is same: E
P
= 0 ft lb; E
k
= 640 ft lb; and E
T
= 640 ft lb
*8-43. An 80-lb girl sits in a swing of negligible weight. If she is given an initial velocity of 20 ft/s, to what height will she
rise?
Energy conservation: 0 + mgh = mv
2
+ 0;
2
2
(20 ft/s)
2 2(32 ft/s )
v
h
g
= = h = 6.25 ft
Energy and Friction Forces
*8-45. A 500-g block is released from the top of a 30
0
inline and slides 160 cm to the bottom. A constant friction force of
0.9 N acts the entire distance. What is the total energy at the top? What work is done by friction? What is the
velocity at the bottom?
W = mg = (0.5 kg)(9.8 m/s
2
) = 4.90 N;
h = (1.60 m) sin 30
0
= 0.800 m; E
T
= E
P
+ E
k
E
T
= Wh + 0; E
T
= (4.90 N)(0.80 m); E
T
= 3.92 J
(Work)
F
= F s = (-0.900 N)(1.60 m); (Work)
F
= -1.44 J (negative work)
Total energy at top = total energy at bottom + work done against friction
3.92 J = mv
2
+| F s | ; 3.92 J = (0.5 kg) v
2
+ 1.44 J
Solving for v, we obtain: v = 3.15 m/s
Note that the work done BY friction is negative, but when applying
conservation of energy we use the work AGAINST friction (+1.44 J) to account for the LOSS
Power
8-54. A 300-kg elevator is lifted vertical distance of 100 m in 2 min. What is the output power?
2
(300 kg)(9.8 m/s )(100 m)
;
120 s
Fs mgs
P P
t t
= = = ; P = 2.45 kW
h = 10 ft
h = 3 ft
h
W
F
N
30
0
30
0
h
s = 160 m
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Find the Resultant Vector Using Graphical and Trigonometric MethodsDokumen24 halamanFind the Resultant Vector Using Graphical and Trigonometric MethodsErna Margarette Trambulo0% (1)
- Work, Energy & Power: AP Physics 1Dokumen25 halamanWork, Energy & Power: AP Physics 1Teacher MaryBelum ada peringkat
- Physics ReviewDokumen8 halamanPhysics ReviewThomas HendersonBelum ada peringkat
- Uniform Relativistic Acceleration PDFDokumen15 halamanUniform Relativistic Acceleration PDFJedwin VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- Work - Power - and EnergyDokumen13 halamanWork - Power - and Energyraj78678Belum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 7 Force and Motion Form 2Dokumen17 halamanCHAPTER 7 Force and Motion Form 2Akmar Matali100% (2)
- Oxfordaqa International As and A Level Maths SpecificationDokumen36 halamanOxfordaqa International As and A Level Maths SpecificationkarinaBelum ada peringkat
- Forms of Energy (Tutorial Part 2)Dokumen3 halamanForms of Energy (Tutorial Part 2)asapamore100% (1)
- Work and EnergyDokumen28 halamanWork and EnergyMir'atun Nissa QuinalendraBelum ada peringkat
- Work, Energy and Power-1Dokumen32 halamanWork, Energy and Power-1Ian HaroldBelum ada peringkat
- Work Power and EnergyDokumen33 halamanWork Power and EnergyYfel UndagBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Chapter 2 PDFDokumen77 halamanPhysics Chapter 2 PDFMaisarah NuraliaBelum ada peringkat
- Trabajo, Energía y PotenciaDokumen23 halamanTrabajo, Energía y PotenciaRamiro Paredes AzabaBelum ada peringkat
- PHYSICSDokumen7 halamanPHYSICSCherryl FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Work - Power - EnergyDokumen83 halamanWork - Power - EnergyKy VergaraBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8. Work, Energy, and PowerDokumen24 halamanChapter 8. Work, Energy, and PowerEdgar Linares0% (1)
- Understanding Physics Concepts of Charge and CurrentDokumen14 halamanUnderstanding Physics Concepts of Charge and CurrentMarie Joy EngayBelum ada peringkat
- Phy11 Reviewer FinalsDokumen32 halamanPhy11 Reviewer FinalsasaadadadsaddBelum ada peringkat
- Work, Energy, and Power ChapterDokumen22 halamanWork, Energy, and Power Chapteraku 223Belum ada peringkat
- p6 Merged PDFDokumen251 halamanp6 Merged PDFVal Andrea TuazonBelum ada peringkat
- Energy & PowerDokumen25 halamanEnergy & PowerProf. Vijay PingaleBelum ada peringkat
- Work, Energy and PowerDokumen32 halamanWork, Energy and PowerHahahahahahahahahaBelum ada peringkat
- Newton's Second Law ExplainedDokumen15 halamanNewton's Second Law ExplainedAlan Martinez100% (2)
- Work-Energy & PowerDokumen26 halamanWork-Energy & PowerProf. Vijay PingaleBelum ada peringkat
- Class 9 Work Energy Power Solved Numerical Questions - 7Dokumen4 halamanClass 9 Work Energy Power Solved Numerical Questions - 7tamishraza26Belum ada peringkat
- Physics 5Dokumen12 halamanPhysics 5ジョンBelum ada peringkat
- Work, Energy and PowerDokumen4 halamanWork, Energy and PowerGianne Karl AlmarinesBelum ada peringkat
- Ngel of God, My Guardian Dear, To Whom God's Love Commits Me Here, Ever This Day, Be at My Side To Light and Guard, To Rule and GuideDokumen10 halamanNgel of God, My Guardian Dear, To Whom God's Love Commits Me Here, Ever This Day, Be at My Side To Light and Guard, To Rule and GuideClaire Valdeavilla - DudasBelum ada peringkat
- Work and Energy FormulasDokumen45 halamanWork and Energy FormulasAnghel jhed ViescaBelum ada peringkat
- AP Chapter 6Dokumen39 halamanAP Chapter 6Wei WeiBelum ada peringkat
- Work done, power, energy and impulse calculationsDokumen6 halamanWork done, power, energy and impulse calculationsWemn JuniofBelum ada peringkat
- Physics ProblemDokumen6 halamanPhysics ProblemWemn JuniofBelum ada peringkat
- Calculate kinetic energy of satellite in orbitDokumen129 halamanCalculate kinetic energy of satellite in orbitJesus Feijoo100% (2)
- Test 2 Study Guide PhysicsDokumen11 halamanTest 2 Study Guide PhysicsKerry Roberts Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- NumericalsDokumen6 halamanNumericalsaditya dhapodkarBelum ada peringkat
- In The Image On The Left, The Total Mechanical Energy IsDokumen17 halamanIn The Image On The Left, The Total Mechanical Energy IsSebastian PaezBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 6 Work and Energy ProblemsDokumen8 halamanProblem Set 6 Work and Energy ProblemsClaireBelum ada peringkat
- Physics ProblemDokumen18 halamanPhysics ProblemReinier CabreraBelum ada peringkat
- Physics: Aemeryn A. Montoya 9-MakilingDokumen7 halamanPhysics: Aemeryn A. Montoya 9-MakilingAemeryn MontoyaBelum ada peringkat
- WorkDokumen6 halamanWorkRowin Mark SabornidoBelum ada peringkat
- Work, Energy PowerDokumen37 halamanWork, Energy Powertchr keiBelum ada peringkat
- ExamDokumen136 halamanExamMichael Vincent MirafuentesBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 3_WORK, ENERGY, POWER_MABBORANG, MARY KRISTELLE U.docxDokumen4 halamanCHAPTER 3_WORK, ENERGY, POWER_MABBORANG, MARY KRISTELLE U.docxyram LetsirkBelum ada peringkat
- Kerja Dan Tenaga: Hajah Amani Abdullah MubarakDokumen28 halamanKerja Dan Tenaga: Hajah Amani Abdullah MubarakCQChoongBelum ada peringkat
- CH 8 - Energy & WorkDokumen23 halamanCH 8 - Energy & WorkJonni Maruli Tua SitorusBelum ada peringkat
- Additional Sample ProblemsDokumen5 halamanAdditional Sample ProblemsMarifer CavintaBelum ada peringkat
- 221HCh04 PDFDokumen25 halaman221HCh04 PDFisele1977Belum ada peringkat
- Unit Term 2 Energy Review QuestionsDokumen57 halamanUnit Term 2 Energy Review QuestionsLissa Hannah100% (1)
- Wpe WorksheetDokumen2 halamanWpe WorksheetLin Xian Xing0% (1)
- Problem - 7A PDFDokumen9 halamanProblem - 7A PDFMonicaBelum ada peringkat
- Is The Amount of Force Applied To An Object Over A DistanceDokumen44 halamanIs The Amount of Force Applied To An Object Over A Distancemarife gupaalBelum ada peringkat
- Ap Chapter 6Dokumen39 halamanAp Chapter 6amberBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation Physics EnglishDokumen12 halamanPresentation Physics EnglishhutterincBelum ada peringkat
- 6P Le KnabDokumen10 halaman6P Le KnabAbigail AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Maximum Range of ProjectileDokumen31 halamanMaximum Range of ProjectileOmprakash Dhaka100% (2)
- Work and Energy ConceptsDokumen4 halamanWork and Energy ConceptsSharonBelum ada peringkat
- AP Physics 1 - CH 5 Work and EnergyDokumen25 halamanAP Physics 1 - CH 5 Work and EnergyNeil SolasBelum ada peringkat
- Work and Energy Problem Sets Week 9Dokumen10 halamanWork and Energy Problem Sets Week 9nics100% (1)
- Physics-Work and EnergyDokumen7 halamanPhysics-Work and EnergyKenneth SilvaBelum ada peringkat
- RecitationDokumen4 halamanRecitationSavaliya HardikBelum ada peringkat
- Experimentno.6 Uniformly Accelerated Motion - Free Fall I. ObjectivesDokumen6 halamanExperimentno.6 Uniformly Accelerated Motion - Free Fall I. ObjectivesStephanie AzucenaBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Lesson PlanDokumen5 halamanDetailed Lesson PlanNikki Angelie TerrenalBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1-4 Sci204 MechanicsDokumen44 halamanChapter 1-4 Sci204 MechanicsNoreen Fae T. AguinaldoBelum ada peringkat
- YTU Mechanical Engineering Department Exam ReviewDokumen6 halamanYTU Mechanical Engineering Department Exam ReviewAsniah HADJISALAMBelum ada peringkat
- Ap Phys1 - Dynamics 2d Ap Style Free Response Questions - 2019 08 19Dokumen27 halamanAp Phys1 - Dynamics 2d Ap Style Free Response Questions - 2019 08 19Abdullah MalikBelum ada peringkat
- A Framework For Analysis of Aircraft ManeuverabilityDokumen13 halamanA Framework For Analysis of Aircraft ManeuverabilityJeff BeckBelum ada peringkat
- Phy 111 DDokumen22 halamanPhy 111 DCharisse StevensBelum ada peringkat
- 1.Dr - Mohamed Ail - Mechanics 1Dokumen20 halaman1.Dr - Mohamed Ail - Mechanics 1Khaled AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Web Wise Speed-Time GraphsDokumen7 halamanWeb Wise Speed-Time Graphsapi-271141909Belum ada peringkat
- Nelson Thornes Answer To Practice ProblemsDokumen36 halamanNelson Thornes Answer To Practice ProblemsMitul KaziBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamic Column AnalysisDokumen40 halamanDynamic Column AnalysisDhanaji ChavanBelum ada peringkat
- Centripetal ForceDokumen4 halamanCentripetal ForceSiddharth Soni0% (1)
- Module 2.1 Rectilinear KinematicsDokumen4 halamanModule 2.1 Rectilinear KinematicsMLNDG boysBelum ada peringkat
- Note Differentiation FormulasDokumen2 halamanNote Differentiation FormulasSiti Khadijah Mohd ZainBelum ada peringkat
- Ansys Act App 7t Trajectory: Draws 3D Path (Trajectory) of Points (Vertices or Nodes)Dokumen24 halamanAnsys Act App 7t Trajectory: Draws 3D Path (Trajectory) of Points (Vertices or Nodes)benssjBelum ada peringkat
- PHYF111 MIDSem QuestPaperDokumen3 halamanPHYF111 MIDSem QuestPaperf20231045Belum ada peringkat
- May June 2018 M1Dokumen16 halamanMay June 2018 M1jerom ranaweerageBelum ada peringkat
- Motion in Two DimetionDokumen10 halamanMotion in Two DimetionMohamed JameelBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 1 SolutionsDokumen5 halamanProblem Set 1 SolutionssagarnitishpirtheeBelum ada peringkat
- DADF3 D 01Dokumen255 halamanDADF3 D 01Raja BalaBelum ada peringkat
- Sheet Kinematics Student Copy With AnsDokumen44 halamanSheet Kinematics Student Copy With AnsSwatiBelum ada peringkat
- Conservation of angular momentum examplesDokumen4 halamanConservation of angular momentum examplesidraumrBelum ada peringkat
- Newtonian Revolution: Mechanics Is The Branch of Physics That Focuses On The MotionDokumen12 halamanNewtonian Revolution: Mechanics Is The Branch of Physics That Focuses On The MotionVillamor BaculiBelum ada peringkat
- Force And Laws Of Motion Class 9 CBSE Notes Revision NotesDokumen19 halamanForce And Laws Of Motion Class 9 CBSE Notes Revision Notesagain Kumar bisoiBelum ada peringkat