Ece
Diunggah oleh
Christine Joy Guinhawa DalisayDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ece
Diunggah oleh
Christine Joy Guinhawa DalisayHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
IDENTIFICATION AND FUNCTION BATTERIES Batteries are also pretty easy to identify, and are well marked with
their specs. A battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery (or "voltaic pile") in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power source for many household and industrial applications.
SYMBOL
IMAGE
SWITCH A switch is an electronic and electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another. Switches do have the on or off buttons.
CRYSTALS AND OSCILLATORS Crystals and Oscillators are also fairly easy to identify by sight. Most are clearly marked with their operating frequency printed on them. They are typically marked with an X or a Y on a circuit board. A crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses the mechanical resonance of a vibrating crystal of piezoelectric material to create an electrical signal with a very precise frequency.
IDENTIFICATION AND FUNCTION POTENTIOMETERS A potentiometer is a manually adjustable electrical resistor that uses three terminals. In many electrical devices, potentiometers are what establish the levels of output. Potentiometers are variable resistors. They normally have their value marked on them, normally marked with the maximum value in Ohms. Smaller trimpots may use a 3-digit code where the first 2 digits are significant, and the 3rd is the multiplier (basically the number of 0s after the first 2 digits).
SYMBOL
IMAGE
RELAYS A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal (with complete electrical isolation between control and controlled circuits), or where several circuits must be controlled by one signal. Relays are typically enclosed in plastic, and many have their specs printed on them. They are typically marked with a K on a circuit board. The relay takes advantage of the fact that when electricity flows through a coil, it becomes an electromagnet.
IDENTIFICATION AND FUNCTION FUSES A fuse is a type of low resistance resistor that acts as a sacrificial device to provide over current protection, of either the load or source circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows, which interrupts the circuit in which it is connected. Short circuit, overloading, mismatched loads or device failure are the prime reasons for excessive current. Fuses can be easy to identify, and typically have their voltage and amperage rating marked on them.
SYMBOL
IMAGE
TRANSISTORS A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current flowing through another pair of terminals. Many different kinds of transistors are used in analog circuits, for different reasons. This is not the case for digital circuits. In a digital circuit, only two values matter; on or off
IDENTIFICATION AND FUNCTION TRANSFORMERS A transformer is a device used to change the voltage of an alternating current in one circuit to a different voltage in a second circuit, or to partially isolate two circuits from each other. Transformers consist of two or more coils of conducting material, such as wire, wrapped around a core (often made of iron). The magnetic field produced by an alternating current in one coil induces a similar current in the other coils. Transformers are normally pretty easy to identify by sight, and many have their specs printed on them. They are typically marked with a T on a circuit board. THERMISTOR A thermistor is a temperature-sensing element composed of sintered semiconductor material which exhibits a large change in resistance proportional to a small change in temperature. Thermistors usually have negative temperature coefficients which means the resistance of the thermistor decreases as the temperature increases. Thermistors are temperature sensitive resistors. All resistors vary with temperature, but thermistors are constructed of semiconductor material with a resistivity that is especially sensitive to temperature. However, unlike most other resistive devices, the resistance of a thermistor decreases with increasing temperature.
SYMBOL
IMAGE
IDENTIFICATION AND FUNCTION Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits visible light when an electric current passes through it. The light is not particularly bright, but in most LEDs it is monochromatic, occurring at a single wavelength. The output from an LED can range from red (at a wavelength of approximately 700 nanometers) to blue-violet (about 400 nanometers). LEDs are available in red, orange, amber, yellow, green, blue and white. Blue and white LEDs are much more expensive than the other colours.
SYMBOL
IMAGE
LAMPS A lamp is a replaceable component such as an incandescent light bulb, which is designed to produce light from electricity. These components usually have a base of ceramic, metal, glass or plastic, which makes an electrical connection in the socket of a light fixture. This connection may be made with a screw-thread base, two metal pins, two metal caps or a bayonet cap. Relamping is the replacement of only the removable lamp in a light fixture. Lamps emit light when an electric current passes through them. All of the lamps shown on this page have a thin wire filament which becomes very hot and glows brightly when a current passes through it. The filament is made from a metal with a high melting point such as tungsten and it is usually wound into a small coil. Filament lamps have a shorter lifetime than most electronic components because eventually the filament 'blows' (melts) at a weak point.
ELECTRONICS CIRCUIT SYMBOLS:
Wires and connections Component Wire Circuit Symbol Function of Component To pass current very easily from one part of a circuit to another. A 'blob' should be drawn where wires are connected (joined), but it is sometimes omitted. Wires connected at 'crossroads' should be staggered slightly to form two T-junctions, as shown on the right.
Wires joined
Wires not joined
In complex diagrams it is often necessary to draw wires crossing even though they are not connected. I prefer the 'bridge' symbol shown on the right because the simple crossing on the left may be misread as a join where you have forgotten to add a 'blob'!
Power Supplies Component Circuit Symbol Function of Component Supplies electrical energy. The larger terminal (on the left) is positive (+). A single cell is often called a battery, but strictly a battery is two or more cells joined together. Supplies electrical energy. A battery is more than one cell. The larger terminal (on the left) is positive (+).
Cell
Battery
DC supply
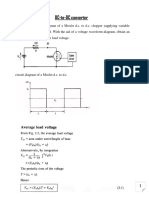
Supplies electrical energy. DC = Direct Current, always flowing in one direction. Supplies electrical energy. AC = Alternating Current, continually changing direction. A safety device which will 'blow' (melt) if the current flowing through it exceeds a specified value. Two coils of wire linked by an iron core. Transformers are used to step up (increase) and step down (decrease) AC voltages. Energy is transferred between the coils by the magnetic field in the core. There is no electrical connection between the coils. A connection to earth. For many electronic circuits this is the 0V (zero volts) of the power supply, but for mains electricity and some radio circuits it really means the earth. It is also known as ground.
AC supply
Fuse
Transformer
Earth (Ground)
Output Devices: Lamps, Heater, Motor, etc. Component Circuit Symbol Function of Component A transducer which converts electrical energy to light. This symbol is used for a lamp providing illumination, for example a car headlamp or torch bulb.
Lamp (lighting)
Lamp (indicator)
A transducer which converts electrical energy to light. This symbol is used for a lamp which is an indicator, for example a warning light on a car dashboard.
Heater
A transducer which converts electrical energy to heat.
Motor
A transducer which converts electrical energy to kinetic energy (motion).
Bell
A transducer which converts electrical energy to sound.
Buzzer
A transducer which converts electrical energy to sound.
Inductor (Coil, Solenoid)
A coil of wire which creates a magnetic field when current passes through it. It may have an iron core inside the coil. It can be used as a transducer converting electrical energy to mechanical energy by pulling on something.
Switches Component Push Switch (push-to-make) Push-to-Break Switch Circuit Symbol Function of Component A push switch allows current to flow only when the button is pressed. This is the switch used to operate a doorbell. This type of push switch is normally closed (on), it is open (off) only when the button is pressed.
On-Off Switch (SPST)
SPST = Single Pole, Single Throw. An on-off switch allows current to flow only when it is in the closed (on) position. SPDT = Single Pole, Double Throw. A 2-way changeover switch directs the flow of current to one of two routes according to its position. Some SPDT switches have a central off position and are described as 'on-offon'. DPST = Double Pole, Single Throw. A dual on-off switch which is often used to switch mains electricity because it can isolate both the live and neutral connections.
2-way Switch (SPDT)
Dual On-Off Switch (DPST)
Reversing Switch (DPDT)
DPDT = Double Pole, Double Throw. This switch can be wired up as a reversing switch for a motor. Some DPDT switches have a central off position.
Relay
An electrically operated switch, for example a 9V battery circuit connected to the coil can switch a 230V AC mains circuit. NO = Normally Open, COM = Common, NC = Normally Closed.
Capacitors Component Circuit Symbol Function of Component
Capacitor
A capacitor stores electric charge. A capacitor is used with a resistor in a timing circuit. It can also be used as a filter, to block DC signals but pass AC signals. A capacitor stores electric charge. This type must be connected the correct way round. A capacitor is used with a resistor in a timing circuit. It can also be used as a filter, to block DC signals but pass AC signals.
Capacitor, polarised
Variable Capacitor
A variable capacitor is used in a radio tuner.
Trimmer Capacitor
This type of variable capacitor (a trimmer) is operated with a small screwdriver or similar tool. It is designed to be set when the circuit is made and then left without further adjustment.
Audio and Radio Devices Component Circuit Symbol Function of Component
Microphone
A transducer which converts sound to electrical energy.
Earphone
A transducer which converts electrical energy to sound.
Loudspeaker
A transducer which converts electrical energy to sound.
Piezo Transducer
A transducer which converts electrical energy to sound.
Amplifier (general symbol)
An amplifier circuit with one input. Really it is a block diagram symbol because it represents a circuit rather than just one component.
Aerial (Antenna)
A device which is designed to receive or transmit radio signals. It is also known as an antenna.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Crime PreventionDokumen11 halamanCrime PreventionChristine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- PowerDokumen4 halamanPowerChristine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- Business Practices and EtiquetteDokumen28 halamanBusiness Practices and EtiquetteChristine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- Jocuri EnergizerDokumen24 halamanJocuri Energizerbogdan_2007100% (1)
- Political Science & International Studies Public Administration Social Welfare Sociology Cultural AnthropologyDokumen2 halamanPolitical Science & International Studies Public Administration Social Welfare Sociology Cultural AnthropologyChristine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
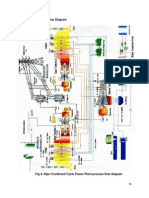
- Ilijan CombinedDokumen1 halamanIlijan CombinedChristine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- B. Power Plant Flow DiagramDokumen1 halamanB. Power Plant Flow DiagramChristine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- Blood BankDokumen15 halamanBlood BankAnsari ShariqBelum ada peringkat
- CJ Training PlanDokumen2 halamanCJ Training PlanChristine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- Common Engineering TermsDokumen23 halamanCommon Engineering TermsAitazaz Ahsan0% (1)
- Annals 2012 2 20Dokumen6 halamanAnnals 2012 2 20Christine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- Common Engineering TermsDokumen23 halamanCommon Engineering TermsAitazaz Ahsan0% (1)
- Life CycleDokumen2 halamanLife CycleChristine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- Engr ManagemntDokumen2 halamanEngr ManagemntChristine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- TVM NPVDokumen86 halamanTVM NPVChristine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- CALORIMETERDokumen12 halamanCALORIMETERChristine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Fuel and Their CharacteristicsDokumen13 halamanTypes of Fuel and Their CharacteristicsjacopanyBelum ada peringkat
- Design TermsDokumen6 halamanDesign TermsChristine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- ThyroidDokumen4 halamanThyroidChristine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Pump CycleDokumen25 halamanHeat Pump CycleDario Rajmanovich100% (1)
- HeatDokumen5 halamanHeatChristine Joy Guinhawa DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Eeng 432 Microwave Theory and Design Lab: Marks Obtained Total MarksDokumen5 halamanEeng 432 Microwave Theory and Design Lab: Marks Obtained Total MarksSohail KhiljiBelum ada peringkat
- Rotary Cam SwitchesDokumen5 halamanRotary Cam Switchesasalasv65Belum ada peringkat
- بور الكترونيكDokumen20 halamanبور الكترونيكawabBelum ada peringkat
- .FinFET TechnologyDokumen7 halaman.FinFET TechnologyRAZBelum ada peringkat
- ME300 Installation Introduction - EN - 20190916 - BKDokumen2 halamanME300 Installation Introduction - EN - 20190916 - BKCharlez ManaloBelum ada peringkat
- QuestionDokumen11 halamanQuestionJevan CalaqueBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 33 ExerciseDokumen1 halamanChapter 33 ExerciseChoa Pei Shuang100% (1)
- L&T MX Contactor Catalogue PDFDokumen9 halamanL&T MX Contactor Catalogue PDFAnonymous lFFnnXmjUuBelum ada peringkat
- Lok - TRAFO BCT Size R0Dokumen9 halamanLok - TRAFO BCT Size R0Nageswar MakalaBelum ada peringkat
- VSKT106 16S90P VishayDokumen9 halamanVSKT106 16S90P VishayjoseBelum ada peringkat
- Weld Cheat SheetDokumen1 halamanWeld Cheat SheetBruce BrownBelum ada peringkat
- 5SDD 71B0210Dokumen4 halaman5SDD 71B0210Merter TolunBelum ada peringkat
- ManualDokumen1 halamanManualJuan Francisco BallestasBelum ada peringkat
- Control Switch ManualDokumen16 halamanControl Switch Manualajitnav4381Belum ada peringkat
- DPH42 InstallationDokumen14 halamanDPH42 InstallationRoxana BirtumBelum ada peringkat
- Driver L297 + L6203Dokumen2 halamanDriver L297 + L6203TatiiieleeeBelum ada peringkat
- 3mn0304 00 MN Pa 15900 Premier New by Acr Rev 4Dokumen2 halaman3mn0304 00 MN Pa 15900 Premier New by Acr Rev 4Muhammad Nur SalimBelum ada peringkat
- A6. Design Features of Low Speed Permanent Magnet GeneratorDokumen4 halamanA6. Design Features of Low Speed Permanent Magnet Generatorwalidghoneim1970Belum ada peringkat
- Junction/Inverter Unit: BankDokumen29 halamanJunction/Inverter Unit: BankPhong DoanBelum ada peringkat
- LSI Muirfield Series Luminaire & Parts Sheet 1981Dokumen2 halamanLSI Muirfield Series Luminaire & Parts Sheet 1981Alan MastersBelum ada peringkat
- Esquema Eletrônico PDFDokumen5 halamanEsquema Eletrônico PDFFabio MoriBelum ada peringkat
- Multifunctional With 1 C/o (SPDT) Contact: Electronic Timer CT-MFD.12Dokumen11 halamanMultifunctional With 1 C/o (SPDT) Contact: Electronic Timer CT-MFD.12Felipe JaimesBelum ada peringkat
- UkerDokumen6 halamanUkerJkp BukuljaBelum ada peringkat
- Examples Zener DiodeDokumen17 halamanExamples Zener DiodeHussin TalibBelum ada peringkat
- Warning:: VLT 2880-2882 Spare PartsDokumen4 halamanWarning:: VLT 2880-2882 Spare PartsIván CascudoBelum ada peringkat
- MLE Complete Product Range 2015Dokumen86 halamanMLE Complete Product Range 2015Suresh KotaBelum ada peringkat
- Guam+ - 20 Exploded View - Moto G9 Play - XT2083Dokumen1 halamanGuam+ - 20 Exploded View - Moto G9 Play - XT2083Ysrael Agurto SejuroBelum ada peringkat
- TEBS G2 схемыDokumen30 halamanTEBS G2 схемыDimaBelum ada peringkat
- OM-2075 90C24 Con PlanosDokumen236 halamanOM-2075 90C24 Con PlanosLider TallerBelum ada peringkat
- Operation and Maintenance of MotorsDokumen6 halamanOperation and Maintenance of MotorsNaseer HydenBelum ada peringkat