Exfoliation Glaucome
Diunggah oleh
Asyiyatur RaudhahDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Exfoliation Glaucome
Diunggah oleh
Asyiyatur RaudhahHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Exfoliation (Pseudoexfoliation) Syndr
Robert Ritch, M.D.
Exfoliation syndrome (XFS) is characterized by the production and progressive ac material in many ocular tissues. When averaged across the globe, it is the most co worldwide, and in some countries accounts for the majority of glaucoma. It leads t angle-closure glaucoma, and has been causatively associated with cataract, lens occlusion. Eyes with XFS have a greater frequency of complications at the time of dialysis, capsular rupture, and vitreous loss. Based on the identification of accumu specimens, and visceral organs, XFS appears to be a generalized disorder of the ramifications of this disorder appear to be far more important than ever before rea appeared in the past year.47, 62 Epidemiology
Click above to change contrast or text size.
XFS occurs worldwide, although reported prevalence rates vary extensively. This differences due to racial, ethnic, or other as-yet-unknown reasons; the age and se population group examined; the clinical criteria used to diagnose XFS; the ability o the thoroughness of the examination; and the awareness of the observer. 1 Recen Spain and Hungary, suggest literally an order of magnitude higher prevalence of X patients than reported 30-40 years ago. This obviously represents improvement in material clinically.
In Scandinavia, where XFS was first described, the highest rates in studies of pers from Iceland (about 25%), 8, 59 and Finland (over 20%) 8, 25, 26 Rates in Norway and while those in Denmark have been reported to be much less. Russian Jewish imm a very high prevalence of XFS. 30 XFS is also very common in Ireland, the Middle
New York Glaucoma Research Institute 310 East 14th St. New York, NY 9753 (212) 477-7540
The prevalence of XFS may also vary within countries in similar environments and among ethnically homogeneous persons or between ethnic groups living in close p investigations. In four prefectures in Crete, Kozobolis et al 24 found XFS in person 27%. In France, the overall prevalence over age 70 (in a report by several observe in Brest, to 3.6% in Toulon. 4, 5 Ringvold et al 44 found rates of 10.2%, 19.6%, and municipalities in central Norway. In New Mexico, Spanish-American men are near than are non-Spanish-Americans. 17
XFS increases in prevalence with age. Men and women are probably equally affec affected much more often than African-Americans. Genetic factors predisposing to explored, and no clear hereditary pattern has been identified. One study found a n
degree relatives over age 40 compared to the general population, 2 suggesting au preponderance of maternal transmission of XFS in families reported has raised the inheritance.6
Glaucoma occurs more commonly in eyes with XFS than in those without it. Eleva damage occurs in approximately 25% of persons with XFS, or about 6 to 10 times Exfoliative glaucoma has a more serious clinical course and worse prognosis than is a significantly higher frequency and severity of optic nerve damage at the time o poorer response to medications, more severe clinical course, and more frequent n Persons with elevated IOP and XFS are much more likely to develop glaucomatou are those without XFS.
XFS is the only common glaucoma which usually affects only one eye or affects o a rule of thumb, anyone over age 50 with unilateral glaucoma should be suspecte and "monocular" are misleading. When only one eye is clinically involved, the fello humor dynamics or glaucomatous damage. Since early pigment-related signs of X unaffected fellow eyes, and since exfoliation fibers may be detected on conjunctiv fellow eyes, these cases are actually asymmetric. 12, 41 Clinical Findings
Lens: Deposits of white material on the anterior lens surface are the most consiste XFS. The classic pattern consists of three zones: a central disc corresponding rou granular, often layered, peripheral zone, and a clear area separating the two (Figu homogeneous, white sheet and is often absent, while the peripheral zone is alway created by rubbing of the iris over the surface of the lens during pupillary moveme lens because of damage to the zonules which hold the lens in place, is common a predisposing to an increase in complications at the time of cataract surgery. Spon of the lens can occur (Figure 3).
Iris: Iris changes are an early and well recognized clinical feature in XFS. Next to t prominent at the pupillary border (Figure 4). Pigment loss from the iris sphincter re chamber structures is a hallmark of XFS. Loss of iris pigment and its deposition th reflected in iris sphincter region transillumination defects (Figure 5), loss of the pup dispersion in the anterior chamber after pupillary dilation (Figure 7), pigment depo trabecular meshwork pigmentation (Figure 8), and pigment deposition on the iris s
The blood vessels of the iris are often narrowed and may become obliterated. In a wall degenerate completely. Fluorescein angiographic studies have shown partial associated with hypoperfusion, a reduced number of vessels, formation of tiny new fluorescein dye leakage.
Cornea: Flakes of exfoliation material may be present on the endothelium. There m pigmentation of the central endothelium, occasionally having the pattern of a Kruk characteristically deposited on Schwalbe's line and sometimes as a wavy line or li (Sampaolesi line, Figure 8). The number of corneal endothelial cells is reduced an greater in eyes with XFS, perhaps reflecting early corneal dysfunction. 43 These ch decompensation at only moderate rises of IOP or after cataract surgery. 35
Other findings: Eyes with XFS often dilate poorly. Exfoliation material may be dete and zonules, which are often frayed and broken. Abnormal zonular attachment to the development of lens subluxation or dislocation. Deposits of exfoliation materia
processes in the pars plicata.
Increased trabecular pigmentation is a prominent sign of XFS and is apparent in v evident disease. The distribution of the pigment tends to be uneven or splotchy an almost always denser in the involved eye. There appears to be a highly significant the degree of pigmentation of the meshwork. 33 In virtually all studies of patients w trabecular pigment is almost always denser in the involved eye. 27, 46 Eyes with exf pigmentation than eyes with XFS but without glaucoma. 42, 50 and eyes with exfolia pigmentation than eyes with COAG. 9, 19 Marked IOP rises can occur in eyes with examination. Post-dilation IOPs should be checked routinely and the anterior cham all patients receiving dilating drops.
Ocular Associations: Increasing evidence suggests an causal association between pigment epithelium and the lens surface, both coated with exfoliation material, ten particularly when pupillary movement is inhibited by miotic therapy (Figure 9). Vigo the entire iris pigment epithelium onto the lens surface.
Patients with XFS are much more prone to have complications at the time of catar less well and have greater incidences of capsular rupture, zonular dehiscence, an zonular fragility have been suggested as the most important risk factors for capsul fragility increases the risk of lens dislocation, zonular dialysis, or vitreous loss up t complications of posterior capsular opacification, capsule contraction syndrome, in inflammation are also greater in eyes with XFS.
A possible association of XFS with retinal vein occlusion has also been suggested XFS, ipsilateral pulsatile ocular blood flow 56 and carotid blood flow 53 have been more prone to developing dry eye syndrome, especially if treated with beta-adrene
Extraocular findings: Aggregates of exfoliation fibers have been identified in skin a lung, liver, kidney, gall bladder, and cerebral meninges in two patients with ocular present in the interstitial fibrovascular connective tissue septa of these organs, fre elastic microfibrils, collagen fibers, fibroblasts, and to the walls of small blood vess
In the Blue Mountains Eye Study (Australia), XFS correlated positively with a histo infarction or stroke, suggestive of vascular effects of the disease. 32 In another stu cardiovascular disease, three times the rate of the unaffected subjects. 7 In anothe associated with aneurysms of the abdominal aorta, but not with carotid artery occl mortality in patients with XFS has been reported. 45, 55 Mechanisms of Glaucoma
Open-angle glaucoma: Potential causes of elevated IOP in eyes with XFS include the meshwork by exogenous and endogenous exfoliation material, blockage of the trabecular cell dysfunction, and coexisting primary open-angle glaucoma. Obstruc by pigment or exfoliation material or both is generally considered the most likely ca develop later in life in patients who have had bilateral pigment dispersion syndrom patient with signs of bilateral pigment dispersion and unilateral glaucoma warrants development of XFS.28, 48, 61
Angle-closure glaucoma: Although two important series noted a high incidence of with XFS, 29, 63 angle-closure glaucoma was until recently considered rare in patien be coincidental. Ritch 46 found either clinically apparent XFS or exfoliation materia (28.3%) consecutive patients with uncomplicated primary ACG or occludable angl
patients had occludable angles. 7 Characteristics of eyes with XFS which predispo the predisposition to posterior synechia formation, zonular weakness and associat stiffness and rigidity, and a smaller pupil. Patients with ACG or occludable angles to have deeper anterior chambers than those without XFS. Management
Glaucoma associated with XFS tends to respond less well to medical therapy than to timolol in eyes with XFS and elevated IOP. 22 Dorzolamide is almost as effective it.13, 21 Cholinergic agents are effective and probably have a greater additive effect POAG. Not only do miotics lower IOP, but should enable the meshwork to clear m outflow and should slow the progression of the disease by limiting pupillary movem suggestive evidence that treatment with aqueous suppressants leads to worsening
Argon laser trabeculoplasty (ALT) is particularly effective, at least early on, in eyes higher than in eyes with POAG undergoing ALT and the initial drop in IOP is great develop sudden, late rises of IOP within the first two years after treatment. 37, 49 Co overwhelm the restored functional capacity of the trabecular meshwork, and maint papillary movement after ALT might counteract this. The increased effectiveness m trabecular meshwork pigmentation found in XFS. Long-term success drops to app
The results of trabeculectomy are comparable to those in POAG, but complication trabeculectomy has been reported to be lower in eyes with exfoliative glaucoma th 54 Trabeculotomy has been reported to have success rates of 79% at 3 years and 6 medication. 60Jacobi and Krieglstein 14 have presented a procedure termed trabec outflow facility. Trabecular aspiration combined with phacoemulsification was sign surgery alone in reducing postoperative IOP and the necessity for antiglaucoma m effective than phacoemulsification combined with trabeculectomy. 16 References
1.
Aasved H: The geographical distribution of fibrillopathia epitheliocapsularis Acta Ophthalmo
2.
Aasved H: Study of relatives of persons with fibrillopathia epitheliocapsularis (pseudoexfolia 53:879-886, 1975.
3.
Becker B: Does hyposecretion of aqueous humor damage the trabecular meshwork? (edito
4.
Colin J, Bonissent JF, Resnikoff S. Epidemiology of the exfoliation syndrome. 17th Congr E 231.
5.
Colin J, Le Gall G, Le Jeune B, et al: The prevalence of exfoliation syndrome in different ar 184):86-89, 1988.
6.
Damji KF: Is pseudoexfoliation syndrome inherited? A review of genetic and nongenetic fac Genetics 19:175-185, 1998.
7.
Damji KF, Bains HS, Amjadi K, et al: Familial occurrence of pseudoexfoliation in Canada C
8.
Forsius H: Prevalence of pseudoexfoliation of the lens in Finns, Lapps, Icelanders, Eskimos 99:296-298, 1979.
9.
Futa R, Shimizu T, Furuyoshi N: Clinical features of capsular glaucoma in comparison with Ophthalmol 70:214-219, 1992.
10. Georgopoulos GT, Chalkiadakis J, Livir-Rallatos G, et al: Combined clear cornea phacoem treatment of pseudoexfoliative glaucoma associated with cataract Graefes Arch Clin Exp O
11. Goder GJ: Our experiences in planned extracapsular cataract extraction in the exfoliation s 128, 1988.
12. Hammer T, Schltzer-Schrehardt U, Naumann GOH: Unilateral or asymmetric pseudoexfol Ophthalmol in press, 2001.
13. Heijl A, Strahlman E, Sverrisson T, et al: A comparison of dorzolamide and timolol in patien ocular hypertension Ophthalmology 104:137-142, 1997.
14. Jacobi PC, Dietlein TS, Krieglstein GK: Bimanual trabecular aspiration in pseudoexfoliation glaucoma surgery Ophthalmology 105:886-894, 1998.
15. Jacobi PC, Dietlein TS, Krieglstein GK: Comparative study of trabecular aspiration versus t treat pseudoexfoliation glaucoma Arch Ophthalmol 117:1311-1318, 1999.
16. Jacobi PC, Dietlein TS, Krieglstein GK: The risk profile of trabecular aspiration versus trabe Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 238:545-551, 2000.
17. Jones W, White RE, Magnus DE: Increased occurrence of exfoliation in the male, Spanish
Optom Assoc 63:643-648, 1992.
18. Karjalainen K, Tarkkanen A, Merenmies L: Exfoliation syndrome in enucleated haemorrhag 65:320-322, 1987.
19. Konstas AGP, Dutton GN: Gonioscopic findings in Greek patients with exfoliation glaucoma
20. Konstas AGP, Jay JL, Marshall GE, et al: Prevalence, diagnostic features, and response to Ophthalmology 100:619-627, 1993.
21. Konstas AGP, Maltezos A, Bufidis T, et al: Twenty-four hour control of intraocular pressure exfoliaiton and primary open-angle glaucoma Eye 14:73-77, 2000.
22. Konstas AGP, Maltezos A, Mantziris DA, et al: The comparative ocular hypotensive effects exfoliation versus primary open-angle glaucoma patients Eye 13:314-318, 1999.
23. Kozobolis VP, Detorakis ET, Tsopakis GM, et al: Evaluation of tear secretion and tear film s Ophthalmol Scand 77:406-409, 1999.
24. Kozobolis VP, Papatzanaki M, Vlachonikolis IG, et al: Epidemiology of pseudoexfoliation in 75:726-729, 1997.
25. Krause U: Frequency of capsular glaucoma in central Finland Acta Ophthalmol 51:235-240
26. Krause U, Alanko HI, Krm J, et al: Prevalence of exfoliation syndrome in Finland Acta Op
27. Kunishi Y, Kunishi M, Yoshino H, et al: Gonioscopic features of pseudoexfoliation Jpn J Cli
28. Layden WE, Ritch R, King DG, et al: Combined exfoliation and pigment dispersion syndrom
29. Layden WE, Shaffer RN: Exfoliation syndrome Am J Ophthalmol 78:835-841, 1974.
30. Levey SB, Wahl SM, Abrams DA, et al: Pseudoexfoliation syndrome in the Russian immigr 1995.
31. Meyer E, et al: Pseudoexfoliation: Epidemiology, clinical and scanning electron microscopic
32. Mitchell P, Wang JJ, Smith W: Association of pseudoexfoliation with increased vascular risk
33. Moreno-Montas J, Quintero Alonso A, Alvarez Serna A, et al: Pseudoexfoliation syndrom Fr Ophtalmol 13:183-188, 1990.
34. Naumann GOH, Kchle M, Schonherr U: Pseudoexfoliation as a risk factor for vitreous loss Ophthalmol 86:543-545, 1989.
35. Naumann GOH, Schltzer-Schrehardt U: Keratopathy in pseudoexfoliation syndrome as a clinicopathologic study Ophthalmology 107:1111-1124, 2000.
36. Naumann GOH, the "Erlanger Augenbltter-Group": Exfoliation syndrome as a risk factor fo Acta Ophthalmol 66 (Suppl 184):129-131, 1988.
37. Pohjanpelto P: Late results of laser trabeculoplasty for increased intraocular pressure Acta
38. Pohjanpelto P: Long-term prognosis of visual field in glaucoma simplex and glaucoma caps
39. Popovic V, Sjostrand J: Course of exfoliation and simplex glaucoma after primary trabecule
40. Prince AM, Ritch R: Clinical signs of the pseudoexfoliation syndrome Ophthalmology 93:80
41. Prince AM, Streeten BW, Ritch R, et al: Preclinical diagnosis of pseudoexfoliation syndrom
42. Puska P: The amount of lens exfoliation and chamber-angle pigmentation in exfoliation syn
Ophthalmol 73:226-232, 1995.
43. Puska P, Vasara K, Harju M, et al: Corneal thickness and corneal endothelium in normoten syndrome Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 238:659-663, 2000.
44. Ringvold A, Blika S, Elss T, et al: The prevalence of pseudoexfoliation in three separate m 65(Suppl 182):17-20, 1988.
45. Ringvold A, Blika S, Sandvik L: Pseudo-exfoliation and mortality Acta Ophthalmol 75:255-2
46. Ritch R: Exfoliation syndrome: `s and occurrence in patients with occludable angles Trans A
47. Ritch R: Exfoliation syndrome Curr Opin Ophthalmol 12:124-130, 2001.
48. Ritch R, Mudumbai R, Liebmann JM: Combined exfoliation and pigment dispersion: An ove 2000.
49. Ritch R, Podos SM: Laser trabeculoplasty in exfoliation syndrome Bull NY Acad Med 59:33
50. Rouhiainen H, Tersvirta M: Pigmentation of the anterior chamber angle in normal and pse 702, 1990.
51. Schltzer-Schrehardt U, Koca MR, Naumann GOH, et al: Pseudoexfoliation syndrome. Ocu Ophthalmol 110:1752-1756, 1992.
52. Schumacher S, Schlotzer-Schrehardt U, Martus P, et al: Pseudoexfoliaiton syndrome and 357:359-360, 2001.
53. Scullica L, Buceti R, Castagna I, et al: Functional aspects of pseudoexfoliation: Physiopath 168, 1993.
54. Serguhn S, Spiegel D: Efficacy of trabeculectomy for pseudoexfoliation glaucoma and prim
Augenheilkd 215:281-286, 1999.
55. Shrm KR, Hattenhauer MG, Hodge D: Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular mortality asso Ophthalmol 129:83-86, 2000.
56. Sibour G, Finazzo C, Boles Carenini A: Monolateral pseudoexfoliatio capsulae: A study of c 75(Suppl 224):13-14, 1997.
57. Skuta GL, Parrish RK, II, Hodapp E, et al: Zonular dialysis during extracapsular cataract ex Ophthalmol 105:632-634, 1987.
58. Streeten BW, Li ZY, Wallace RN, et al: Pseudoexfoliative fibrillopathy in visceral organs of Ophthalmol 110:1757-1762, 1992.
59. Sveinsson D: The frequency of senile exfoliation in Iceland Acta Ophthalmol 52:596-602, 1
60. Tanihara H, Negi A, Akimoto M, et al: Surgical effect of trabeculotomy ab externo on adult e pseudoexfoliation syndrome Arch Ophthalmol 111:1653-1661, 1993.
61. Tarkkanen A, Kivela T: Unilateral capsular glaucoma after long-standing bilateral pigmenta
62. Vesti E, Kivel T: Exfoliation syndrome and exfoliation glaucoma Prog Retinal Eye Res 19:
63. Wishart PK, Spaeth GL, Poryzees EM: Anterior chamber angle in the exfoliation syndrome
NY Glaucoma Research Institute Website by Castle Builder Design
http://www.glaucoma.net/nygri/glaucoma/topics/exfoliation.asp
Pengelupasan syndrome (XFS) ditandai oleh akumulasi produksi dan progresif dari bahan ekstraselular dgn urat saraf pada jaringan okular banyak. Ketika rata-rata di seluruh dunia, itu adalah penyebab yang dapat diidentifikasi yang paling umum dari glaukoma di seluruh dunia, dan dalam beberapa rekening negara untuk sebagian besar glaukoma. Ini menyebabkan kedua glaukoma sudut terbuka dan sudut tertutup glaukoma, dan telah causatively terkait dengan katarak, dislokasi lensa, dan oklusi vena sentral retina. Mata dengan XFS memiliki frekuensi lebih besar dari komplikasi pada saat ekstraksi katarak, seperti dialisis zonular, pecah kapsuler, dan kehilangan vitreous. Berdasarkan identifikasi akumulasi dalam jaringan orbital, spesimen kulit, dan organ visceral, XFS tampaknya menjadi gangguan umum dari matriks ekstraseluler. Konsekuensi potensi gangguan ini tampaknya jauh lebih penting daripada sebelumnya direalisasikan. Dua review dari XFS telah muncul di year.47 terakhir, 62 Epidemiologi XFS terjadi di seluruh dunia, meskipun prevalensi yang dilaporkan bervariasi secara luas. Hal ini mencerminkan kombinasi dari perbedaan benar karena alasan yang belumdiketahui ras, etnis, atau lainnya, usia dan distribusi jenis kelamin pasien atau kelompok penduduk diperiksa; kriteria klinis digunakan untuk mendiagnosa XFS, kemampuan pemeriksa untuk mendeteksitahap awal; ketelitian pemeriksaan; dan kesadaran pengamat. 1 Penelitian terbaru di beberapa negara, seperti Spanyol dan Hungaria, menunjukkan harfiah urutan besarnya lebih tinggi dari prevalensi XFS dalam populasi dan pada pasien glaukoma dibandingkan yang dilaporkan 30-40 tahun lalu. Hal ini jelas merupakan peningkatan kemampuan untuk mencari dan mengidentifikasi bahan klinis. Di Skandinavia, dimana XFS pertama kali dijelaskan, tingkat tertinggi dalam studi tentang orang di atas usia 60 telah dilaporkan dari Islandia (sekitar 25%), 8, 59 dan Finlandia (lebih dari 20%) 8, 25, 26 Lihat di Norwegia dan Swedia rata sekitar setengah ini, sementara mereka di Denmark telah dilaporkan jauh lebih sedikit.Imigran Yahudi Rusia ke Amerika Serikat juga memiliki prevalensi yang sangat tinggi XFS. 30 XFS juga sangat umum di Irlandia, Timur Tengah, India, dan Jepang. Prevalensi XFS juga dapat bervariasi dalam negara dalam lingkungan yang sama dan jarak pendek. Perbedaan antara orang-orang etnis homogen atau antara kelompok etnis yang tinggal di dekat dapat mengakibatkan investigasi berguna. Dalam empat prefektur di Kreta, Kozobolis dkk 24 menemukan XFS pada orang di atas usia 40 sampai berkisar dari 11,5% menjadi 27%. Di Perancis, prevalensi keseluruhan atas usia 70 (dalam laporan oleh beberapa pengamat) adalah sekitar 5,5%, mulai dari 20,6% di Brest, menjadi 3,6% di Toulon. 4, 5 Ringvold dkk 44 menemukan angka sebesar 10,2%, 19,6%, dan 21,0% di tiga kota dekat terletak di pusat Norwegia. Di New Meksiko, Spanyol-Amerika laki-laki hampir enam kali lebih mungkin untuk mengembangkan XFS dari non-Spanyol-Amerika. 17 XFS meningkatkan prevalensi dengan usia. Pria dan wanita mungkin sama-sama mempengaruhi. Di Amerika Serikat, putih yang terpengaruh jauh lebih sering daripada Afrika-Amerika. Faktor genetik predisposisi terhadap kerentanan hampir tidak mulai dieksplorasi, dan tidak ada pola herediter yang jelas telah diidentifikasi. Satu studi menemukan peningkatan prevalensi sembilan kali lipat pada kerabat tingkat pertama di atas usia 40 dibandingkan dengan populasi umum, 2 menunjukkan pewarisan dominan autosomal. Sebuah dominan transmisi ibu XFS dalam keluarga dilaporkan telah meningkatkan kemungkinan mitokondria inheritance.6 Glaukoma terjadi lebih sering pada mata dengan XFS dibandingkan pada mereka tanpa
itu. TIO meningkat dengan atau tanpa kerusakan glaukoma terjadi pada sekitar 25% dari orang dengan XFS, atau sekitar 6 sampai 10 kali tingkat di mata tanpa XFS. Eksfoliatif glaukoma memiliki perjalanan klinis yang lebih serius dan prognosis lebih buruk dari primer sudut terbuka glaukoma. Ada frekuensi jauh lebih tinggi dan tingkat keparahan kerusakan saraf optik pada saat diagnosis, kerusakan lapangan buruk visual, tanggapan yang lebih buruk terhadap obat, kursus klinis yang lebih berat, dan kebutuhan lebih sering untuk intervensi bedah. Orang dengan TIO tinggi dan XFS jauh lebih mungkin untuk mengembangkan glaukoma kerusakan jangka panjang tindak lanjut daripada mereka yang tidak XFS. XFS adalah glaukoma hanya umum yang biasanya hanya mempengaruhi satu mata atau mempengaruhi satu mata lama di muka yang lain. Sebagai aturan praktis, orang di atas usia 50 dengan glaukoma sepihak harus dicurigai memiliki XFS. Istilah "sepihak" dan "bermata" adalah menyesatkan. Bila hanya satu mata secara klinis terlibat, mata sesama sering memiliki dinamika humor yang abnormal berair atau kerusakan glaukoma. Sejak awal pigmen yang berhubungan dengan tanda-tanda XFS ditemukan di sebagian besar mata sesama terpengaruh, dan karena serat pengelupasan kulit dapat dideteksi pada konjungtiva biopsi di hampir semua mata sesama terpengaruh, kasus ini sebenarnya asimetris. 12, 41 Temuan Klinis Lensa: Simpanan bahan putih pada permukaan lensa anterior adalah fitur diagnostik yang paling konsisten dan penting dari XFS.Pola klasik terdiri dari tiga zona: disc pusat sesuai kasar dengan diameter pupil, sebuah, butiran sering berlapis, zona perifer, dan area jelas memisahkan dua (Gambar 1). Zona pusat adalah lembaran, homogen putih dan sering tidak ada, sedangkan zona perifer adalah selalu hadir (Gambar 2). Zona jelas dibuat dengan menggosok dari iris di atas permukaan lensa selama gerakan pupil. Phacodonesis, atau kelonggaran dari lensa karena kerusakan pada zonules yang memegang lensa di tempat, adalah umum dan merupakan salah satu faktor predisposisi utama peningkatan komplikasi pada saat operasi katarak. Spontan dislokasi parsial atau lengkap lensa dapat terjadi (Gambar 3). Iris: Iris perubahan adalah fitur klinis awal dan dikenal dengan baik di XFS. Di sebelah lensa, bahan pengelupasan kulit paling menonjol di perbatasan pupil (Gambar 4). Pigmen kerugian dari daerah sfingter iris dan deposisi pada struktur ruang anterior merupakan ciri dari XFS. Hilangnya pigmen iris dan deposisi di seluruh segmen anterior tercermin di wilayah cacat transiluminasi iris sfingter (Gambar 5), hilangnya ruff pupil (Gambar 6), pigmen dispersi dalam bilik mata depan setelah pelebaran pupil (Gambar 7), deposisi pigmen pada permukaan iris, peningkatan pigmentasi trabecular meshwork (Gambar 8), dan deposisi pigmen pada permukaan iris. 40 Pembuluh darah dari iris sering menyempit dan dapat menjadi dihapuskan. Pada tahap lanjut, sel-sel dinding pembuluh merosot sepenuhnya. Studi fluorescein angiografik telah menunjukkan oklusi parsial radial iris kapiler terkait dengan hipoperfusi, berkurangnya jumlah kapal, pembentukan kecil pembuluh darah baru, dan menyebar kebocoran, tambal sulam fluorescein pewarna. Kornea: Serpihan bahan pengelupasan kulit dapat hadir pada endothelium. Mungkin ada pigmentasi, diffuse nonspesifik endotelium pusat, kadang-kadang memiliki pola spindle Krukenberg. Pigmen ini bersifat diendapkan pada garis Schwalbe dan kadang-kadang sebagai garis bergelombang atau garis anterior garis Schwalbe itu (Sampaolesi baris, Gambar 8). Jumlah sel endotel kornea berkurang dan ketebalan kornea sentral juga lebih besar di mata dengan XFS, mungkin mencerminkan disfungsi kornea awal. 43 Perubahan ini menyebabkan rentan terhadap dekompensasi kornea awal pada hanya naik moderat TIO
atau setelah operasi katarak. 35 Temuan lain: Mata dengan XFS sering membesar buruk. Bahan Pengelupasan dapat dideteksi paling awal pada proses ciliary dan zonules, yang sering terbakar dan rusak. Lampiran zonular abnormal lensa atau badan ciliary dapat menjelaskan perkembangan lensa subluksasi atau dislokasi. Deposit bahan pengelupasan kulit menutupi puncak-puncak dari proses ciliary di pars plicata. Peningkatan pigmentasi trabecular adalah tanda menonjol dari XFS dan terlihat di hampir semua pasien dengan penyakit klinis jelas. Distribusi pigmen cenderung tidak rata atau kotor dan, dalam kasus klinis sepihak, hampir selalu padat di mata terlibat.Tampaknya ada korelasi yang sangat signifikan antara TIO meningkat dan derajat pigmentasi meshwork tersebut. 33 Dalam hampir semua studi pasien dengan keterlibatan sepihak, pigmen trabecular hampir selalu padat di mata terlibat. 27, 46 Mata dengan glaukoma exfoliative cenderung memiliki pigmentasi lebih besar dari mata dengan XFS tetapi tanpa glaukoma. 42, 50 dan mata dengan glaukoma exfoliative memiliki pigmentasi lebih besar dari mata dengan COAG. 9, 19 Ditandai TIO naik dapat terjadi pada mata dengan XFS setelah pelebaran untuk pemeriksaan retina.Pasca pelebaran IOPS harus diperiksa secara rutin dan ruang anterior diperiksa untuk pembebasan pigmen pada semua pasien yang menerima tetes dilatasi. Asosiasi okular: Meningkatkan bukti menunjukkan hubungan sebab akibat antara XFS dan pembentukan katarak. Pigmen epitel iris dan permukaan lensa, baik dilapisi dengan bahan pengelupasan kulit, cenderung untuk mematuhi (sinekia posterior), khususnya ketika gerakan pupil dihambat oleh terapi miotic (Gambar 9).Pelebaran kuat dapat mengakibatkan adhesi epitel pigmen iris seluruh ke permukaan lensa. Pasien dengan XFS jauh lebih rentan untuk mengalami komplikasi pada saat ekstraksi katarak. Mata dengan XFS melebarkan kurang baik dan memiliki insiden yang lebih besar pecah kapsuler, dehiscence zonular, dan kehilangan vitreous. Diameter pupil dan kerapuhan zonular telah diusulkan sebagai faktor risiko terpenting untuk pecah kapsuler dan kehilangan vitreous. Kerapuhan Zonular meningkatkan risiko dislokasi lensa, dialisis zonular, atau kehilangan vitreous hingga sepuluh kali. 11, 34, 36, 57 komplikasi pascaoperasi dari kekeruhan kapsul posterior, sindrom kapsul kontraksi, decentration lensa intraokular, dan peradangan juga lebih besar di mata dengan XFS. Sebuah hubungan yang mungkin dari XFS dengan oklusi vena retina ini juga telah diusulkan. 18, 31, 38 Dalam kasus klinis sepihak XFS, mata ipsilateral aliran darah berdenyut 56 dan aliran darah karotis 53 telah dilaporkan menjadi berkurang. Mata mungkin lebih rentan terhadap sindrom mata kering berkembang, terutama jika diobati dengan betaadrenergik blocking agen. 23 Temuan luar mata: Agregat dari serat pengelupasan kulit telah diidentifikasi dalam kulit dan dalam spesimen autopsi jantung, paru hati, ginjal kandung kemih, empedu, dan meninges palsy pada dua pasien dengan XFS okular. 51, 58 Deposito adalah focally hadir dalam jaringan ikat interstisial fibrovascular septa organ-organ ini, sering berdekatan dengan serat elastis, elastis mikrofibril, serat kolagen, fibroblas, dan dinding pembuluh darah kecil. Dalam Studi Eye Blue Mountains (Australia), XFS berkorelasi positif dengan riwayat hipertensi, angina, infark miokard atau stroke, sugestif efek vaskular penyakit. 32 Dalam studi lain, 50% dari orang dengan XFS memiliki penyakit kardiovaskular, tiga kali tingkat dari subyek terpengaruh. 7 Dalam studi lain, XFS secara bermakna dikaitkan dengan aneurisma dari aorta perut, tetapi tidak dengan oklusi arteri karotis. 52 Namun demikian, tidak ada peningkatan angka kematian pada pasien dengan XFS telah dilaporkan. 45, 55 Mekanisme Glaukoma
Glaukoma sudut terbuka: penyebab Potensi TIO meningkat pada mata dengan XFS termasuk disfungsi sel trabekula, penyumbatan meshwork dengan bahan pengelupasan kulit eksogen dan endogen, penyumbatan meshwork dengan pigmen iris dibebaskan, disfungsi sel trabekula, dan hidup bersama primer sudut terbuka glaukoma . Obstruksi trabecular meshwork baik oleh pigmen atau bahan pengelupasan kulit atau keduanya umumnya dianggap sebagai penyebab paling mungkin. Sindrom Pengelupasan dapat berkembang di kemudian hari pada pasien yang memiliki pigmen sindrom dispersi bilateral, dan presentasi pasien yang lebih tua dengan tanda-tanda dispersi pigmen bilateral dan unilateral glaukoma menjamin sebuah pemeriksaan yang cermat untuk pengembangan XFS.28, 48, 61 Glaukoma sudut tertutup: Meskipun dua seri penting mencatat tingginya insiden sudut sempit atau occludable di mata dengan XFS, 29, 63 sudut tertutup glaukoma adalah sampai saat ini dianggap langka pada pasien dengan XFS dan biasanya dianggap kebetulan. Ritch 46 ditemukan baik XFS klinis jelas atau bahan pengelupasan kulit pada konjungtiva biopsi di 17 dari 60 (28,3%) pasien berturut-turut dengan ACG primer tidak rumit atau sudut occludable. Dalam studi lain, 5 dari 18 pasien yang terkena memiliki sudut occludable. 7 Karakteristik mata dengan XFS yang menyebabkan rentan terhadap glaukoma sudut tertutup termasuk kecenderungan untuk posterior synechia formasi, kelemahan zonular dan gerakan lensa yang terkait ke depan, kekakuan iris dan kekakuan, dan seorang murid yang lebih kecil. Pasien dengan ACG atau sudut occludable dan XFS cenderung lebih rabun dan memiliki lebih dalam bilik anterior daripada mereka yang tidak XFS. Pengelolaan Glaukoma yang terkait dengan XFS cenderung kurang menanggapi terhadap terapi medis daripada POAG. Apraclonidine adalah aditif untuk timolol mata dengan XFS dan TIO meningkat. 22 dorzolamide hampir seefektif timolol dan juga aditif dengan it.13, 21 agen Kolinergik efektif dan mungkin memiliki efek aditif lebih besar dengan beta-blocker dalam XFS daripada di POAG. Tidak hanya miotics rendah TIO, tetapi harus memungkinkan meshwork untuk membersihkan lebih cepat dengan meningkatkan arus keluar berair dan harus memperlambat perkembangan penyakit dengan membatasi gerakan pupil. Becker 3 telah mengajukan bukti sugestif bahwa pengobatan dengan penekan berair menyebabkan memburuknya fungsi trabecular. Argon Laser trabeculoplasty (ALT) sangat efektif, setidaknya sejak awal, di mata dengan XFS. TIO awal biasanya lebih tinggi daripada di mata dengan POAG menjalani ALT dan drop awal dalam TIO lebih besar. Sekitar 20% pasien mengembangkan tiba-tiba, naik akhir TIO dalam dua tahun pertama setelah pengobatan. 37, 49 pembebasan pigmen Lanjutan mungkin membanjiri kapasitas fungsional yang dipulihkan trabecular meshwork, dan pemeliharaan terapi miotic untuk meminimalkan gerakan papiler setelah ALT mungkin melawan ini. Efektivitas meningkat mungkin terkait dengan peningkatan pigmentasi meshwork trabecular ditemukan di XFS.Sukses jangka panjang turun menjadi sekitar 3555% pada 3-6 tahun. Hasil trabeculectomy sebanding dengan yang di POAG, tetapi komplikasi lebih sering. TIO setelah trabeculectomy telah dilaporkan lebih rendah di mata glaukoma dengan eksfoliatif daripada di mata dengan POAG. 20, 39, 54Trabeculotomy telah dilaporkan memiliki tingkat keberhasilan 79% pada 3 tahun dan 64% pada 5 tahun, dengan pengobatan. 60Jacobi dan Krieglstein 14 telah menyajikan suatu prosedur disebut aspirasi trabecular, yang dirancang untuk meningkatkan fasilitas outflow. Aspirasi trabecular dikombinasikan dengan phacoemulsification secara signifikan lebih efektif daripada operasi katarak sendiri dalam mengurangi TIO pasca operasi dan perlunya obat antiglaucoma.10, 15 Namun, itu kurang efektif daripada phacoemulsification dikombinasikan dengan trabeculectomy. 16
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Pediatric Shock AWSDokumen77 halamanPediatric Shock AWSAsyiyatur RaudhahBelum ada peringkat
- Identifikasi RisikoDokumen0 halamanIdentifikasi RisikoShezye FaBelum ada peringkat
- Pancreatitis PD AnkDokumen13 halamanPancreatitis PD AnkAsyiyatur RaudhahBelum ada peringkat
- ProcitisDokumen7 halamanProcitisAsyiyatur RaudhahBelum ada peringkat
- ProcitisDokumen7 halamanProcitisAsyiyatur RaudhahBelum ada peringkat
- MDN Femoral Interlocking Recon Nail Intramedullary Fixation Metal Guide Surgical TechniqueDokumen28 halamanMDN Femoral Interlocking Recon Nail Intramedullary Fixation Metal Guide Surgical TechniqueAsyiyatur RaudhahBelum ada peringkat
- Osteomielitis PDFDokumen14 halamanOsteomielitis PDFAsyiyatur RaudhahBelum ada peringkat
- Human Body Muscles With Internal Organs Catalog Number: GD/A10001Dokumen3 halamanHuman Body Muscles With Internal Organs Catalog Number: GD/A10001Asyiyatur RaudhahBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- MCQsDokumen25 halamanMCQsdrstraoBelum ada peringkat
- Patellofemoral Pain After Total Knee Arthroplasty PDFDokumen8 halamanPatellofemoral Pain After Total Knee Arthroplasty PDFSergiu PlescaBelum ada peringkat
- Access Medicine - TableDokumen2 halamanAccess Medicine - Tablecode-24Belum ada peringkat
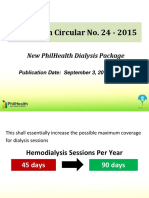
- 09 Dialysis DataDokumen11 halaman09 Dialysis DataThinkingPinoyBelum ada peringkat
- Colonic InertiaDokumen20 halamanColonic InertiaAndina Destiyani PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Resp TestDokumen7 halamanResp TestKong KongBelum ada peringkat
- Homeopathic Remedy Price List 2009-10Dokumen1 halamanHomeopathic Remedy Price List 2009-10yvranprasad100% (1)
- Constraints PDFDokumen4 halamanConstraints PDFArun Gopal100% (1)
- Management of Patients With Gastric and Duodenal DisordersDokumen47 halamanManagement of Patients With Gastric and Duodenal DisordersJor GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Test Bank QuestionDokumen97 halamanNursing Test Bank QuestionADEDIRAN ABIONABelum ada peringkat
- Personal Trainer Magazine PDFDokumen54 halamanPersonal Trainer Magazine PDFdixieakerszBelum ada peringkat
- Upadacitinib Efficacy For The Treatment of Concomitant Psoriasis and Alopecia AreataDokumen4 halamanUpadacitinib Efficacy For The Treatment of Concomitant Psoriasis and Alopecia AreataAthenaeum Scientific PublishersBelum ada peringkat
- The Soulmate DietDokumen24 halamanThe Soulmate DietShana MarieBelum ada peringkat
- HAAD Exam For Nurses Questions 2018Dokumen46 halamanHAAD Exam For Nurses Questions 2018Asif Newaz100% (6)
- Body Condition Scoring As A Tool For Dairy Herd Management PDFDokumen5 halamanBody Condition Scoring As A Tool For Dairy Herd Management PDFfrankyBelum ada peringkat
- Pooja - 1Dokumen61 halamanPooja - 1Shobhit GoswamiBelum ada peringkat
- Psychometric Asssessment: A Psychometric Test Must BeDokumen8 halamanPsychometric Asssessment: A Psychometric Test Must BePoojaBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroglossal CystsDokumen4 halamanThyroglossal CystsCondurache Ilie-AndreiBelum ada peringkat
- ADHD in ChildrenDokumen16 halamanADHD in ChildrenCoco Hithere100% (1)
- Surgery MnemonicsDokumen6 halamanSurgery MnemonicsMarkoMilivojevic50% (2)
- Category-Wise Opening & Closing Rank-Ayur - BHU Int.Dokumen5 halamanCategory-Wise Opening & Closing Rank-Ayur - BHU Int.srikanth PosaBelum ada peringkat
- Yakima Co (WA) Protocols 2010Dokumen117 halamanYakima Co (WA) Protocols 2010Anthony James-Hartwell100% (1)
- Cervicogenic HeadacheDokumen32 halamanCervicogenic HeadacheasasakopBelum ada peringkat
- For Older People, Medications Are Common AGS Beers Criteria Aims To Make Them Appropriate, TooDokumen3 halamanFor Older People, Medications Are Common AGS Beers Criteria Aims To Make Them Appropriate, TooindriBelum ada peringkat
- Rehabilitation of Glossectomy Cases With Tongue Prosthesis: A Literature ReviewDokumen4 halamanRehabilitation of Glossectomy Cases With Tongue Prosthesis: A Literature ReviewmujtabaBelum ada peringkat
- Diarrhea CPDokumen8 halamanDiarrhea CPAsma SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Case Group 1Dokumen10 halamanCase Group 1JASMEEN RAVALBelum ada peringkat
- Health Related Millennium Development Goals Part IDokumen24 halamanHealth Related Millennium Development Goals Part IGudegna GemechuBelum ada peringkat
- Temporomandibular Joint DisorderDokumen9 halamanTemporomandibular Joint DisorderTannels100% (1)
- Betamethasone (Drug Study)Dokumen4 halamanBetamethasone (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)