Kisi
Diunggah oleh
NuzululRachmaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Kisi
Diunggah oleh
NuzululRachmaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
82
Lampiran 12 KISI-KISI SOAL Subject : Chemistry Grade/semester : XI/2 Time allocation : 4 x 45 minutes Standard competence : Understanding the acid-base properties, measuring method and the application Basic Competence : Calculating amount of reactant and product in electrolyte solution from the result of acid-base titration. No Indicator Question Answer Domain 1 Calculating mole of a In order to determine 0,1 M solution Volume = 500 ml C3 substances, volume, and of Ca(OH)2, how much Ca(OH)2 Molarity = 0,1 M also concentration of required to be dissolved in a 500 Mw = 74 g/mol solution. ml volumetric flask? Mass= .?
Explaining the way to make certain molarity solution.
For an experiment, a student needs 300 ml of HNO3 solution 0,25 M. In the laboratory available 2.0 M solution of HNO3. Explain how does he get the solution he wants, if in laboratory available volumetric flask in volume 250 ml, 500 ml, and 1000 ml?.
0,1M x 74 g/mol x 500 ml = mass x 1000 3700 gram = mass x 1000 3,7 gram = mass So, we need 3,7 grams of Ca(OH)2 Initial molarity = 2,0 M Final molarity = 0,25 M in 300 ml Used the volumetric flask in volume 500 ml to get 300 ml of 0, 25 M HNO3 with once diluting process. M1. V1 = M2 . V2 2 M . V1 = 0,25 M . 500 ml 2 M. V1 = 125 M. ml
C4
83
No
Answer V1 = 125 M. ml/ 2 M V1 = 62,5 ml. So, we can put 62,5ml of 2,0 M solution to make 500 ml of 0,25 M HNO3. And we can put 300 ml of this solution by using volumetric pipette and beaker glass or graduated cylinder. Calculating mole of a Determine the [H+] of 1,8 ml of Initial Volume of H2SO4 = 1,8 ml substance, volume and concentrated H2SO4 98% with Final Volume of H2SO4 = 200 ml also concentration of density 1,8 Kg/L dissolved in 200 % mass = 98% solution ml of water! = 1,8 kg/L Mr = 98 [H2SO4initial] = [H2SO4initial] = 18 M M1. V1 = M2 . V2 18 M. 1,8 ml = M2. 200 ml M2 = 0,162 M [H+] = 2x [H2SO] = 2 x 0,162M = 0,324 M Initial Volume of CH3COOH = 10 ml [CH3COOH] initial = 0,1 M Final Volume of CH3COOH = 1 liter = 1000 ml. pH of CH3COOH before diluted: [H+] = = = = 10-3
Indicator
Question
Domain
C3
Calculating mole of a substance, volume and also concentration of solution
A student has 10 ml of vinegar solution 0,1 M. It will be dissolved to be 1 liter solution. Determine the pH of this vinegar solution before and after diluting process! (Ka= 1x10-5)
C3
84
No
Indicator
Question
Calculating mole of a There is 100 ml of NH4OH solution substance, volume and with pH 10. How many mole of that also concentration of solution?(Kb = 10-5) solution
Calculating the number of reactant required or product obtained from
Determine the amount of Calcium metal required to displace sodium in its 20 ml of 0,15 M sodium sulphate
Answer pH = - log [H+] = - log [10-3] = 3. pH of CH3COOH after diluted: M1. V1 = M2 . V2 0,1M. 10 ml = M2. 1000 ml M2 = 0,001 M [H+] = = = = 10-4 pH = - log [H+] = - log [10-4] = 4 Volume of NH4OH = 100 ml = 0,1 L pH = 10 pOH = 14-10 = 4 [OH-] = 10-4 [OH-] = 10-4 = Mb = 10-8/ 10-5 = 10-3M Mb = mole / volume 10-3M = mole / 0,1 L Mole = 10-2 Mole It is metal displacement reaction Mmol Na2SO4 = 20 ml.0,15 M = 3 mmol Ca + Na2SO4 CaSO4 + 2Na
Domain
C3
C3
85
No
Indicator electrolyte solution reaction.
Identifying the kinds of chemical reaction in electrolyte solution.
Calculating the number of reactant required or product obtained from electrolyte solution reaction.
Answer mol Ca = mmol Na2SO4 = 3 mmol = 0,003 mol Mass of Ca = mole Ca x Mr.Ca = 0,003 mol x 40 gr/mol = 0,12 grams Look at this picture: a. It is a is metal displacement reaction b. The reaction can be occurred because the displacing metal or Mg is in the left side of Hydrogen in HCl in volta series. c. Mol Mg = mass/ Mw Mg = 4 gr/24 gr mol-1 4,0 gr of = 0,16 mol Mg metal Mol HCl = 10 ml x 0,4 M 10 ml of m = 4 mmol = 0,004 mol 0,4M HCl Mg + 2 HCl MgCl2 + H2 a. What kinds of this reaction? 0,16mol 0,004 mol b. Why the reaction can be 0,002mol 0,004 mol 0,002 mol occurred? 0,158mol 0,002 mol c. Calculate the concentration of the [MgCl2] = 0,002 mol/0,01L = 0,2 M product! There is a reaction of acid oxide and pH = 13 base pOH = 14-13 = 1 SO3(g) + Ba(OH)2 BaSO4(aq) + [OH-] = 10-1M H2O(aq) [Ba(OH)2] = x 0,1 M = 0,05 M Determine the mass of salt are Mol Ba(OH)2 = 1 L x 0,05 M = 0,05 mol formed from 1L Ba(OH)2 pH 13 Mol SO3 = 4,48/22,4 = 0,2 mol and 4,48 liter SO3 gas (STP)! SO3(g) + Ba(OH)2 BaSO4(aq) + H2O(aq) solution!
Question
Domain
C4
C3
86
No
Indicator
Question
Identifying the kinds of Preparation of Silver bromide for chemical reaction in the manufacture of black and white electrolyte solution film in industry is a metathesis reaction between silver nitrate and calcium bromide. a. Write the reaction equation! b. Determine the volume of volume of silver nitrate 0,2M that will completely react with 70 ml of 0,2M calcium bromide! c. How many particles of silver bromide are formed?
10
Calculating the number of reactant required or product obtained from
50 ml of 0,1 NaOH mixed with 60 ml of 0,1M of HCl. Determine the pH of this solution. If it isnt neutral
Answer 0,2 mol 0,05 mol 0,05 mol 0,05 mol 0,05 mol 0,15 mol 0,05 mol Mass of BaSO4 = mole x Mr BaSO4 = 0,05 mole x 223 = 11,65 grams a. The reaction equation : 2AgNO3(aq) + CaBr2(aq) 2AgBr(s) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) b. [CaBr2] = 0,2 M Volume CaBr2 = 70 ml Mmol CaBr2 = M. V = 0,2 M. 70 ml = 14 mmol Mmol AgNO3= 2 x mmol CaBr2 = 2 x 14 mmol = 28 mmol Volume AgNO3 = mmol/ M = 28 mmol/ 0,2M = 140 ml c. Mmol AgBr = mmol AgNO3 = 28 mmol = 0,028 mol Number of particles = mol x 6,02. 1023 = 0,028 x 6,02. 1023 = 16,9 x 1021 molecules Mmol NaOH = 50 ml . 0,1M = 5 mmol Mmol HCl = 60 ml . 0,1M
Domain
C3
C4
87
No
Indicator electrolyte solution reaction.
Question Answer solution, how do you neutralize this = 6 mmol solution if in the laboratory The reaction: available H2SO4 0,05M and NaOH + HCl NaCl + Ca(OH)2 0,1 M? i: 5 mmol 6 mmol r: 5 mmol 5 mmol 5 mmol r: 1 mmol 5 mmol [H+] = mmol/v total = 1mmol/ 110 ml = 0,009M pH = - log 9 x 10-3 = 3 log 9 (acid properties) It can be neutralized with Ca(OH)2
Domain H2 O
11
Calculating the number of reactant required or product obtained from electrolyte solution reaction.
8,5 grams of mixture magnesium metal and iron metal react with copper(III) sulphate. Mg(s) + CuSO4(aq) MgSO4(aq) + Cu(s) 2Fe(s) + 3CuSO4(aq) Fe2(SO4)3(aq) + 3Cu(s)
2HCl + Ca(OH)2 CaCl2 + 2H2O Mmol HCl must equal with mmol Ca(OH)2 Mmol Ca(OH)2 = mmol HCl = . 1 mmol = 0,5 mmol V Ca(OH)2 = mmol / M = 0,5 mmol/ 0,1M = 5 ml. Mass Mg + Fe = 8,5 grams Mass of Mg = x Mole Mg = x/24 Mass of Fe = 8,5 x Mole Fe = (8,5 -x)/56 Mg + CuSO4 MgSO4 + Cu Mole Cu = mole Mg
C3
88
No
Indicator
12
Calculating the number of reactant required or product obtained from electrolyte solution reaction.
Question Answer From the reaction we get 15, 875 = x/24 grams of copper precipitate. 2Fe + 3CuSO4 Fe2(SO4)3 + 3Cu Determine the mass of each metal Mole Cu = 3/2 mole Fe as reactant! = 3/2 ((8,5 -x)/56) = (25,5 3x)/ 112 Mole Cu = x/24 + (25,5 3x)/ 112 15,875/63,5 = x/24 + (25,5 3x)/ 112 0,25 x 24x112= 112x + 612 72x 672 = 612 + 40x 60 = 40 x x = 1,5 gr. (mass of Mg) mass of Fe = 8,5 1,5 = 7 grams 0,56 grams of M metal react with Mass of M = 0,56 grams 50 ml HCl produce 0,05 mole of H2 Volume HCl = 50 ml gas and MCl2 solution. M + 2HCl MCl2 + H2 a. Determine the atomic mass of M a. Mole of H2 = 0,05 mole metal and the concentration of Mole of H2 = mole M = mole of HCl HCl solution! Mole M = 0,005 mole b. If in certain Pressure and Ar M = mass/ mole = 56/0,05 = 112 temperature 2 liter of CO has Mole HCl = 2 x mole H2 mass 0,28 grams. Determine the = 2 x 0,05 = 0,1 mole volume of H2! [HCl] = mole/v = 0,1 mole/0,05L = 2 M b. V CO = 2 liters n CO = 0,28 gram/28 = 0,01 mole n H2 = 0,05 mole v Co/ v H2 = nCo/n H2
Domain
C3
89
No
Indicator
Question
13
Calculating the number of reactant required or product obtained from electrolyte solution reaction.
mixture contains of 40% calcium carbonate and 60% calcium hydroxide. Determine the volume of 2 M hydrogen chloride to dissolve 25 grams of mixture
14
Doing the acid-base titration.
Explain why volumetric pipette and burette are rinsed with a little of the solution before being used to measure out volume the solution?
Answer 2/ v H2 = 0,01/0,05 2 x 0,05 = 0,01 x v H2 0,1 / 0,01 = v H2 10 Liters = v H2 CaCO3 + CaOH2 = 25 gram Mass CaCO3 = 40% x 25 = 10 grams Mole CaCO3 = 10/100 = 0,1 mole Mass Ca(OH)2 = 60% x 25 = 15 grams Mole Ca(OH)2 = 15/58 = 0,26 mole CaCO3 + 2HCl CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O Mole HCl = mole CaCO3 = 0,1mole = 0,05 mole Ca(OH)2 + 2HCl CaCl2 + 2H2O Mole HCl = mole Ca(OH)2 = 0,26 = 0,13 mole Volume HCl = 0,05/2M + 0,13/2 = 0,025 + 0,065 = 0,09 L = 90 ml. It in order to the volume of the solution measured exactly.
Domain
C2
15
Calculating the concentration acidbase solution from the
Consider titration of 100 ml of 0,1 V HNO3 = 100 ml M HNO3 with 0,1 M of KOH [HNO3] = 0,1M a. How many milliliters of KOH are [KOH] = 0,1 M
C3
90
No
Indicator result of acid-base titration.
Question required to reach the equivalence point? b. What is the pH at reach the equivalence point? c. Sketch the general shape of titration curve!
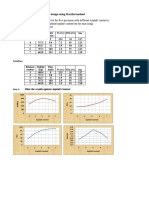
Answer a. To reach the equivalence point the acid and base must be reacted completely. HNO3 + KOH KNO3 + H2O Because the reaction coefficient of HNO3 and KOH are same. So the mole of KOH = mole HNO3 [KOH]. Vol KOH = [HNO3]. Vol HNO3 0,1 M. vol KOH = 0,1 M. 100 ml Vol KOH = 10mmol/0,1M = 100ml b. It is a titration between strong acid and strong base. [H+] = [OH-] = [H+] = = 10-7 pH = - log [H+] = 7 c. The curve:
Domain
16
Calculating the concentration acidbase solution from the result of acid-base titration.
Consider 80 ml of sulphuric acid can be neutralized by 50 ml of potassium hydroxide 0,2 M. Determine the mass of sulphuric acid that occurred in every liter of solution! (Mr H2SO4 = 98)
Volume H2SO4 = 80 ml Volume KOH = 50 ml [KOH] = 0,2 M Mass of H2SO4? The pH = neutral, so the reactant react completely H2SO4 + 2KOH K2SO4 + 2H2O
91
No
Indicator
17
Calculating the concentration acidbase solution from the result of acid-base titration.
Answer Mmol H2SO4 = mmol KOH 80 ml. [H2SO4] = 50 ml. 0,2M [H2SO4] = 5 mmol/ 80 ml = 0,0625M Mol H2SO4 = M. V = 0,00625M. 80 ml = 5 mmol = 0,005 mol Mass = mol x Mr = 0,005 x 98 = 0,49 grams There are titration results of 20 ml V H2SO4 = 20 ml of H2SO4 solution with 0,1 M of [NaOH] = 0,1 M NaOH bellow: a. H2SO4 + 2NaOH Na2SO4 + 2H2O b. The molarity of H2SO4 in first titration Volume of Titration NaOH added 1 10,1 ml 2 10,0 ml 40 ml x Ma = 1,01 mmol 3 9,9 ml Ma = 0,0252 The molarity of H2SO4 in second titration a. Write the reaction equation! b. Calculate the molarity of acid that reacted! c. What is indicator that used in titration! 40 ml x Ma = 1,0 mmol Ma = 0,0250 The molarity of H2SO4 in third titration
Question
Domain
C4
92
No
Indicator
Question
Answer
Domain
18
Calculating the concentration acidbase solution from the result of acid-base titration.
100 ml of acetic acid (Ka= 10-5) 0,1 M is titrated by 100 ml NaOH . if in the reaction the base is remained and the pH of mixture is 12. Determine the mass of NaOH that added!
40 ml x Ma = 0,99 mmol Ma = 0,0248 M H2SO4 = (M1 + M2 + M3)/3 = (0,0252+ 0,0250 + 0,0248)/3 = 0,025 M c. Indicator that used is phenolphthalein because it is a titration between strong acid and strong base with pH range between 8,2 10,0 V CH3COOH = 100 ml [CH3COOH] = 0,1 M V NaOH = 100 ml pH mixture = 12 POH = 2 [OH-] = 10-2 M = M NaOH CH3COOH + NaOH CH3COONa + H2O NaOH is remained Mmol NaOH remain = V total x M NaOH = 200 x 10-2 = 2 mmol Mass NaOH = 2 mmol x Mr = 2 mmol x 40 = 80 g
C3
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Logic and Set Theory PropositionDokumen3 halamanLogic and Set Theory PropositionVince OjedaBelum ada peringkat
- Entity Level ControlsDokumen45 halamanEntity Level ControlsNiraj AlltimeBelum ada peringkat
- Game Rules PDFDokumen12 halamanGame Rules PDFEric WaddellBelum ada peringkat
- KPMG Inpection ReportDokumen11 halamanKPMG Inpection ReportMacharia NgunjiriBelum ada peringkat
- Guiding Childrens Social Development and Learning 8th Edition Kostelnik Test BankDokumen16 halamanGuiding Childrens Social Development and Learning 8th Edition Kostelnik Test Bankoglepogy5kobgk100% (27)
- ESA Knowlage Sharing - Update (Autosaved)Dokumen20 halamanESA Knowlage Sharing - Update (Autosaved)yared BerhanuBelum ada peringkat
- Impact of IT On LIS & Changing Role of LibrarianDokumen15 halamanImpact of IT On LIS & Changing Role of LibrarianshantashriBelum ada peringkat
- The Berkeley Review: MCAT Chemistry Atomic Theory PracticeDokumen37 halamanThe Berkeley Review: MCAT Chemistry Atomic Theory Practicerenjade1516Belum ada peringkat
- Data Sheet: Experiment 5: Factors Affecting Reaction RateDokumen4 halamanData Sheet: Experiment 5: Factors Affecting Reaction Ratesmuyet lêBelum ada peringkat
- SEO-Optimized Title for Python Code Output QuestionsDokumen2 halamanSEO-Optimized Title for Python Code Output QuestionsTaru GoelBelum ada peringkat
- AsiaSat 7 at 105Dokumen14 halamanAsiaSat 7 at 105rahman200387Belum ada peringkat
- Petty Cash Vouchers:: Accountability Accounted ForDokumen3 halamanPetty Cash Vouchers:: Accountability Accounted ForCrizhae OconBelum ada peringkat
- Controle de Abastecimento e ManutençãoDokumen409 halamanControle de Abastecimento e ManutençãoHAROLDO LAGE VIEIRABelum ada peringkat
- DNA Gel Electrophoresis Lab Solves MysteryDokumen8 halamanDNA Gel Electrophoresis Lab Solves MysteryAmit KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Federal Complaint of Molotov Cocktail Construction at Austin ProtestDokumen8 halamanFederal Complaint of Molotov Cocktail Construction at Austin ProtestAnonymous Pb39klJBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Mapping GuideDokumen28 halamanBiology Mapping GuideGazar100% (1)
- ERP Complete Cycle of ERP From Order To DispatchDokumen316 halamanERP Complete Cycle of ERP From Order To DispatchgynxBelum ada peringkat
- 3ccc PDFDokumen20 halaman3ccc PDFKaka KunBelum ada peringkat
- Postgraduate Notes in OrthodonticsDokumen257 halamanPostgraduate Notes in OrthodonticsSabrina Nitulescu100% (4)
- Yellowstone Food WebDokumen4 halamanYellowstone Food WebAmsyidi AsmidaBelum ada peringkat
- House Rules For Jforce: Penalties (First Offence/Minor Offense) Penalties (First Offence/Major Offence)Dokumen4 halamanHouse Rules For Jforce: Penalties (First Offence/Minor Offense) Penalties (First Offence/Major Offence)Raphael Eyitayor TyBelum ada peringkat
- STAT455 Assignment 1 - Part ADokumen2 halamanSTAT455 Assignment 1 - Part AAndyBelum ada peringkat
- GMWIN SoftwareDokumen1 halamanGMWIN SoftwareĐào Đình NamBelum ada peringkat
- "Behind The Times: A Look at America's Favorite Crossword," by Helene HovanecDokumen5 halaman"Behind The Times: A Look at America's Favorite Crossword," by Helene HovanecpspuzzlesBelum ada peringkat
- Marshal HMA Mixture Design ExampleDokumen2 halamanMarshal HMA Mixture Design ExampleTewodros TadesseBelum ada peringkat
- Antenna VisualizationDokumen4 halamanAntenna Visualizationashok_patil_1Belum ada peringkat
- Brick TiesDokumen15 halamanBrick TiesengrfarhanAAABelum ada peringkat
- Family Service and Progress Record: Daughter SeptemberDokumen29 halamanFamily Service and Progress Record: Daughter SeptemberKathleen Kae Carmona TanBelum ada peringkat
- Pita Cyrel R. Activity 7Dokumen5 halamanPita Cyrel R. Activity 7Lucky Lynn AbreraBelum ada peringkat
- Theory of Linear Programming: Standard Form and HistoryDokumen42 halamanTheory of Linear Programming: Standard Form and HistoryJayakumarBelum ada peringkat