Mathcad - Extra7
Diunggah oleh
Desejo SozinandoDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Mathcad - Extra7
Diunggah oleh
Desejo SozinandoHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Computer Programming Skills MathCad Solution by DF Sozinando
Student at the Vaal University of
Technology
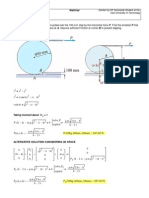
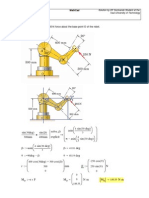
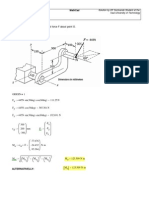
*Force F is in equilibrium with the weight of semi cylinder and a friction characterized by a
coefficient prevents it from slipping on the horizontal plane. AC is horizontal and F is
perpendicular to AB.
1- Consider a Cartesian reference plane with origin at O (point of contact between the
simi-cylinder and the horizontal floor) and write in a matrix (vector) form coordinates of A, B,
D and G (the center of gravity of semi-cylinder) in a 3-D space respectively.
2- Derive an expression of distance OA.
3- Develop the equation equilibrium between the applied force F and the appropriate frictional
force.
4- Write the equation equilibrium of moments about O.
5- Derive the coefficient of friction as function of angle under the established conditions of
equilibrium and plot the graph to investigate the coefficient of friction when change the angle
0 s 90 s .
TIP:
1. Redraw the figure and O is the point of coordinates (0,0). It is essential to draw the OX ,
OY Cartesians axes and negligible OZ axes. D is the center of the full circle D will thus be
vertically aligned with O. D is a point of coordinates (0,r). G is the center of gravity of half
circle, with coordinates.
2. Split the applied force F into vertical and horizontal components and normal force used for
the frictional force is mg-F
y
; multiplying density and volume results into the mass.
Solution:
Computer Programming Skills MathCad Solution by DF Sozinando
Student at the Vaal University of
Technology
1. Force direction of the respective points:
a
4 r
3
= from semi-circle Center of Gravity
A
r - cos ( )
r r sin ( ) +
0
|
\
|
|
|
.
= B
r cos ( )
r r sin ( ) -
0
|
\
|
|
|
.
= D
0
r
0
|
\
|
|
|
.
= G
4 - r
3
sin ( )
r
4 r
3
cos ( ) -
0
|
\
|
|
|
|
|
|
.
=
2. Derivation of an expression for distance OA:
a
2
b
2
c
2
+ 2 b c cos A ( ) - = from cosine rule
OA ( )
2
r cos ( ) ( )
2
r r sin ( ) + ( )
2
+ 2 r cos ( ) ( ) r r sin ( ) + ( ) cos 90 ( ) - =
OA r cos ( )
2
2 cos 90 ( ) cos ( ) sin ( ) - 2 cos 90 ( ) cos ( ) - sin ( )
2
+ 2 sin ( ) + 1 + =
3. Developing Equation of horizontal equilibrium (Deriving an expression for F):
Horizontal Forces: F sin ( ) F
- 0 = F
m g F cos ( ) - ( ) = m
2
r
2
t =
F sin ( )
2
r
2
t g F cos ( ) -
|
\
|
|
.
- 0 = solve for F it's will be:
F
g r
2
t
2 sin ( ) cos ( ) + ( )
=
Computer Programming Skills MathCad Solution by DF Sozinando
Student at the Vaal University of
Technology
4. Equation Equilibrium of moments about O (Deriving an expression for F):
symbolic evaluating this
equation its will be:
r - cos ( )
r r sin ( ) +
0
|
\
|
|
|
.
F sin ( )
F cos ( )
0
|
\
|
|
|
.
4 - r
3
sin ( )
r
4 r
3
cos ( ) -
0
|
\
|
|
|
|
|
|
.
0
2
- r
2
t g
0
|
\
|
|
|
|
|
.
+
2 g r
3
t sin ( )
3
F sin ( ) r r sin ( ) + ( ) - F r cos ( )
2
- 0 = solve for F its will be:
F
2 g r
2
t sin ( )
3 cos ( )
2
3 sin ( )
2
+ 3 sin ( ) +
=
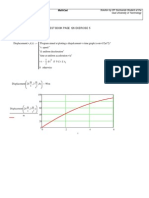
5. Deriving an expression for coefficient of friction as a function of
angle:
F
static
F
kinematic
=
2 g r
2
t sin ( )
3 cos ( )
2
3 sin ( )
2
+ 3 sin ( ) +
g r
2
t
2 sin ( ) cos ( ) + ( )
= solve for it's will be:
( )
4 sin ( )
2
3 cos ( )
2
4 cos ( ) sin ( ) - 3 sin ( )
2
+ 3 sin ( ) +
:=
0 20 40 60 80
0
0.1
0.2
( )
deg
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Mathcad - Beam ProgrammingDokumen1 halamanMathcad - Beam ProgrammingDesejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra39Dokumen1 halamanMathcad - Extra39Desejo Sozinando100% (1)
- Gyrops 22 08 2016Dokumen7 halamanGyrops 22 08 2016Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Hydraulic Machines IIIDokumen73 halamanHydraulic Machines IIIDesejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra38Dokumen2 halamanMathcad - Extra38Desejo Sozinando0% (1)
- Mathcad - Extra44Dokumen1 halamanMathcad - Extra44Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Test 1Dokumen3 halamanMathcad - Test 1Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Test 2Dokumen2 halamanMathcad - Test 2Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra30Dokumen2 halamanMathcad - Extra30Desejo Sozinando50% (2)
- Mathcad - Extra43Dokumen1 halamanMathcad - Extra43Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Proramming Spot2Dokumen2 halamanMathcad - Proramming Spot2Desejo Sozinando100% (1)
- Mathcad - Extra37Dokumen2 halamanMathcad - Extra37Desejo Sozinando0% (1)
- Mathcad - Spot Questions1Dokumen5 halamanMathcad - Spot Questions1Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - ProgrammDokumen1 halamanMathcad - ProgrammDesejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra42Dokumen2 halamanMathcad - Extra42Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra41Dokumen2 halamanMathcad - Extra41Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra33Dokumen1 halamanMathcad - Extra33Desejo Sozinando50% (2)
- Mathcad - Extra40Dokumen1 halamanMathcad - Extra40Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra31Dokumen1 halamanMathcad - Extra31Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra32Dokumen2 halamanMathcad - Extra32Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra35Dokumen2 halamanMathcad - Extra35Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra36Dokumen2 halamanMathcad - Extra36Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra34Dokumen1 halamanMathcad - Extra34Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra29Dokumen1 halamanMathcad - Extra29Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra27Dokumen2 halamanMathcad - Extra27Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra28Dokumen3 halamanMathcad - Extra28Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra26Dokumen1 halamanMathcad - Extra26Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra24Dokumen2 halamanMathcad - Extra24Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra25Dokumen1 halamanMathcad - Extra25Desejo Sozinando0% (1)
- Mathcad - Extra23Dokumen2 halamanMathcad - Extra23Desejo SozinandoBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Exp-1. Evacuative Tube ConcentratorDokumen8 halamanExp-1. Evacuative Tube ConcentratorWaseem Nawaz MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Siart, Et. Al (2018) Digital GeoarchaeologyDokumen272 halamanSiart, Et. Al (2018) Digital GeoarchaeologyPepe100% (2)
- DC CheatsheetDokumen2 halamanDC CheatsheetRashi SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Test Unit 7 m.2Dokumen6 halamanTest Unit 7 m.2Petchara SridakunBelum ada peringkat
- Information HandoutsDokumen6 halamanInformation HandoutsPooja Marwadkar TupcheBelum ada peringkat
- UN Habitat UPCL Myanmar TranslationDokumen254 halamanUN Habitat UPCL Myanmar TranslationzayyarBelum ada peringkat
- Tomas Del Rosario College: Department: EDUCATIONDokumen12 halamanTomas Del Rosario College: Department: EDUCATIONveehneeBelum ada peringkat
- Operation 490BDokumen60 halamanOperation 490BYe Min Htike100% (1)
- (Math 6 WK 5 L9) - Problems Involving Addition and or Subtraction of DecimalsDokumen43 halaman(Math 6 WK 5 L9) - Problems Involving Addition and or Subtraction of DecimalsRhea OciteBelum ada peringkat
- The Truth of Extinction: 7.1 Nietzsche's FableDokumen2 halamanThe Truth of Extinction: 7.1 Nietzsche's FableGraciela Barón GuiñazúBelum ada peringkat
- Conductivity NickelDokumen2 halamanConductivity Nickelkishormujumdar998Belum ada peringkat
- Lolita An Intelligent and Charming Holstein Cow Consumes Only TwoDokumen1 halamanLolita An Intelligent and Charming Holstein Cow Consumes Only Twotrilocksp SinghBelum ada peringkat
- 3.1-Pile Design Calculation For Boundary (p1 To p50)Dokumen24 halaman3.1-Pile Design Calculation For Boundary (p1 To p50)layaljamal2Belum ada peringkat
- Republic of The Philippines Iba, Zambales: President Ramon Magsaysay State UniversityDokumen3 halamanRepublic of The Philippines Iba, Zambales: President Ramon Magsaysay State UniversityErika Joy EscobarBelum ada peringkat
- ASIA INTERNATIONAL FURNITURE MATERIALS CONTRACTDokumen2 halamanASIA INTERNATIONAL FURNITURE MATERIALS CONTRACTSALOME URUCHI AGUILARBelum ada peringkat
- 1993 - Kelvin-Helmholtz Stability Criteria For Stratfied Flow - Viscous Versus Non-Viscous (Inviscid) Approaches PDFDokumen11 halaman1993 - Kelvin-Helmholtz Stability Criteria For Stratfied Flow - Viscous Versus Non-Viscous (Inviscid) Approaches PDFBonnie JamesBelum ada peringkat
- ResumeDokumen5 halamanResumeSaeed SiriBelum ada peringkat
- Individual Moving Range (I-MR) Charts ExplainedDokumen18 halamanIndividual Moving Range (I-MR) Charts ExplainedRam Ramanathan0% (1)
- COP Oil: For Epiroc Components We Combine Technology and Environmental SustainabilityDokumen4 halamanCOP Oil: For Epiroc Components We Combine Technology and Environmental SustainabilityDavid CarrilloBelum ada peringkat
- CFLM1 Chapter 1Dokumen24 halamanCFLM1 Chapter 1Jonathan TawagBelum ada peringkat
- Influence of Oxygen in Copper - 2010Dokumen1 halamanInfluence of Oxygen in Copper - 2010brunoBelum ada peringkat
- DANA 6800-1 Parts ManualDokumen4 halamanDANA 6800-1 Parts ManualDude manBelum ada peringkat
- Ethanol: Safety Data SheetDokumen19 halamanEthanol: Safety Data SheetNitika SinhaBelum ada peringkat
- India An Archaeological History Palaeolithic Beginnings To Early Historic Foundations (Dilip K. Chakrabarti) (Z-Library)Dokumen437 halamanIndia An Archaeological History Palaeolithic Beginnings To Early Historic Foundations (Dilip K. Chakrabarti) (Z-Library)soumadri.2023.1301Belum ada peringkat
- Tithi PRAVESHADokumen38 halamanTithi PRAVESHAdbbircs100% (1)
- Quiz 1Dokumen3 halamanQuiz 1JULIANNE BAYHONBelum ada peringkat
- ST326 - Irdap2021Dokumen5 halamanST326 - Irdap2021NgaNovaBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic Braking SystemDokumen14 halamanElectromagnetic Braking SystemTanvi50% (2)
- NACE CIP Part II - (6) Coatings For Industry - (Qs - As)Dokumen23 halamanNACE CIP Part II - (6) Coatings For Industry - (Qs - As)Almagesto QuenayaBelum ada peringkat