VIII. Nursing Care Plan
Diunggah oleh
Nefre Dayap DarrocaDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
VIII. Nursing Care Plan
Diunggah oleh
Nefre Dayap DarrocaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CHAPTER VIII Nursing Care Plan
This chapter presents the summary of the tree highest priority problems. Assessments are given to prove the diagnosis. Goals, interventions and evaluations are stated. This would indicate how well the patient responds to the prescribed therapeutic regimen.
A. Problem List
Problem Acute Pain related to inflammatory process as manifested by facial grimace
Date Identified
Time
Date Resolved
01/16/2012
8:00A.M.
1/16/2012
Diarrhea related to presence of toxins as manifested by watery stools and abdominal pain
01/16/2012
10:00A.M.
1/17/2012
Risk for Deficient fluid volume related to excess fluid volume loss as manifested by vomiting and watery stools
01/16/2012
10:30A.M.
1/17/2012
90
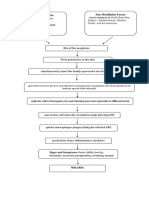
DIAGNOSIS Subjective Cues: Sakit akong tiyan, as verbalized by the patient. Objective Cues: - Received sitting on bed; with IVF of D5IMB x 100 hooked at left arm at 50 gtts/min at 380 cc level - afebrile ; T: 36.50C - not in respiratory distress -PR:124 bpm ; RR: 23 breaths/min. (-) tenderness (+) vomiting (+) watery stools - with pain scale of 8 where 10 is the highest possible rating - with good skin turgor - weakness noted - guarding behaviour on the abdomen -facial grimace
Nursing Care Plans DESIRED NURSING NEED OUTCOME INTERVENTION General: Independent: P Within 70 of 1. Monitor and H nursing record vital Y interventions signs. S the patient I will be able to O report pain is L relieved from O pain. 2. Review factor G that I Specific: aggravate or C 1. report alleviate pain. pain is N relieved E from a E pain scale 3. Educate D of 8/10 to significant S 0/10. others on 2. follow pain prescribed reduction pharmacol techniques to ogical apply it to the regimen. patient. 3. demonstra te non4. Provide pharmacol adequate ogic 91
RATIONALE Independent: 1. To provide baseline data and note deviations from normal. 2. Helpful in establishi ng diagnosis and treatment needs. 3. To reduce pain and promote relief/comf ort.
EVALUATION Goal Met After 40 patient was able to report that pain is relieved from a pain scale of 8/10 to 0/10. She was able to follow prescribed pharmacologic al regimen. Demonstrated nonpharmacologic methods that provide relief and the use of relaxation skills and diversional activities, as indicated, for individual situation.
MODIFICATION
4. To promote healing.
Nursing Diagnosis: Acute Pain related to inflammatory process as manifested by facial grimace Background Knowledge: Gastroenteritis is the inflammation of the stomach and intestinal tract that primarily affects the small bowel. One of the manifestations of gastroenteritis is abdominal pain. During the course of inflammation, the bodys immune response, causing the release of cytokine and prostaglandin causing an increase in vascular permeability and causes pain, which felt by the patient in the abdomen. (Joyce M. Black, 2008)
methods rest. that 5. Provide provide diversional relief. activities like 4. demonstra playing. te use of 6. Instruct client relaxation to perform skills and deep diversiona breathing l activities, exercises as (DBE). indicated, for individual situation. 7. Monitor effectiveness of pain medications.
5. For clients comfort and relief from pain. 6. Deep breathing exercises may reduce pain sensation/ used in pain managem ent. 7. To promote timely interventio n/ revision of plan of care. Dependent: 1. To decrease abdominal pain.
Dependent: 1. Administer Zantac (ranitidine) to maintain acceptable 92
level of pain if not contraindicat ed.
93
DIAGNOSIS Subjective Cues: Sige lang na siya ug libang ug basa labi na gahapon, as verbalized by the mother of the patient. Objective Cues: - Received sitting on bed; with IVF of D5IMB x 100 hooked at left arm at 50 gtts/min at 380 cc level - afebrile ; T: 36.50C - not in respiratory distress -PR:124 bpm ; RR: 23 breaths/min. (-) tenderness (+) vomiting (+) watery stools - weakness noted - increased peristalsis - abdominal pain noted Nursing Diagnosis: Diarrhea related to presence of toxins as manifested by watery
NEED P H Y S I O L O G I C N E E D S
DESIRED OUTCOME General: Within 70 of nursing interventions the patient will be able to reestablish and maintain normal pattern of bowel functioning.
NURSING INTERVENTION Independent: 1. Assess general condition and vital signs.
RATIONALE Independent: 1. To provide baseline data and note deviations from normal. 2. For presence, location, and characteri stics of bowel sounds. 3. For patient education.
EVALUATION Goal Partially Met Significant others was able to verbalized understanding of causative factors and rationale for treatment regimen and reported reduction on frequency in defecating with the characteristic of watery stool. Patient was able to demonstrate appropriate behaviour to assist with resolution of causative
MODIFICATION Continue nursing interventions due to its effectiveness but provide more health teachings regarding foods that would help towards passing out normal stool consistency.
2. Auscultate abdomen.
Specific: 1. significant others will be able to verbalize understan ding of causative factors and rationale for treatment regimen.
3. Discuss the different causative factors and rationale for treatment regimen to significant others. 4. Monitor I & O. 4. To monitor if the intake 94
stools and abdominal pain Background Knowledge: Diarrheal illness occurs when microbial virulence overwhelms normal host defenses. In addition to the ingestion of pathogenic organisms or toxins, other intrinsic factors can lead to infection. An alteration of normal bowel flora can create a biologic void that is filled by pathogens. The exact mechanism of vomiting in acute diarrheal illness is not known, although serotonin release has been postulated as a cause, stimulating visceral afferent input to the chemoreceptor trigger zone in the lower brainstem. Preformed neurotoxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus
2. demonstra te appropriat e behaviour to assist with resolution of causative factors. 3. significant others will be able to report reduction on frequency in defecating 4. significant others will be able to report normal and firm consistenc y of stool.
and factors. output of fluid is balanced. 5. Promote use 5. To of relaxation decrease technique. stress and anxiety 6. Encourage to 6. For fluid increase oral replaceme fluid intake nt. 7. Educate the 7. To patient about prevent the spread of importance of infectious handwashing. diseases.
Dependent: 1. Administer antidiarrheals as prescribed by the physician.
Dependent: 1. Decrease s GI motility or peristalsis and diminishes digestive secretions to relieve cramping and diarrhea.
95
cereus, when ingested, can cause severe vomiting. http://emedicine.medscap e.com/article/775277overview#a0104
Collaborative: 1. Provide for changes in dietary intake
Collaborative: 1. To allow foods/sub stances that precipitate diarrhea
96
DIAGNOSIS Subjective Cues: Sige lang na siya ug libang ug basa labi na gahapon, as verbalized by the mother of the patient. Objective Cues: - Received sitting on bed; with IVF of D5IMB x 100 hooked at left arm at 50 gtts/min at 380 cc level - afebrile ; T: 36.50C - not in respiratory distress -PR:124 bpm ; RR: 23 breaths/min. (-) tenderness (+) vomiting (+) watery stools - weakness noted - increased peristalsis - abdominal pain noted - dehydration - nausea Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for Deficient fluid
NEED P H Y S I O L O G I C N E E D S
DESIRED NURSING OUTCOME INTERVENTION RATIONALE General: Independent: Independent: Within 70 of 1. Monitor and 1. To provide nursing record vital baseline interventions signs. data and the patient note will be able to deviations maintain fluid from volume as normal. evidenced by 2. Monitor I & O. 2. Fluid adequate replaceme urinary nt needs output, stable are based vital signs, on moist mucous correction membranes, of current good skin deficits turgor and and capillary refill. ongoing losses. 3. Evaluate 3. Impaired Specific: clients ability gag and 1. significant to manage swallow others will own refand be able to hydration. change in verbalize level of understan conscious ding of ness are causative among 97
EVALUATION Goal Met After 70 patient was able to maintain fluid volume as evidenced by urinary output, stable vital signs, moist mucous membranes, good skin turgor and capillary refill. Significant others was able to verbalize understanding of causative factors and purpose of individual therapeutic interventions and medications.
MODIFICATION
volume related to excess fluid volume loss as manifested by vomiting and watery stools Background Knowledge: Infectious agents usually cause acute gastroenteritis. These agents cause diarrhea by adherence, mucosal invasion, enterotoxin production, and/or cytotoxin production. These mechanisms result in increased fluid secretion and/or decreased absorption. This produces an increased luminal fluid content that cannot be adequately reabsorbed, leading to dehydration and the loss of electrolytes and nutrients. http://emedicine.medscap e.com/article/775277overview#a0104
factors and purpose of individual therapeuti c interventio 4. Provide skin ns and and mouth medicatio care. ns. 2. demonstra te behaviour s to monitor and correct deficit, as indicated, when condition 5. Determine is chronic. effects of 3. stabilize age. vital signs. 4. maintain the intake and output of fluid is balanced. 98
the factors that affect clients ability to replace fluids orally. 4. Skin and mucous membran es are dry with decreased elasticity because of vasoconst riction and reduced intracellul ar water. 5. Very young and extremely elderly individuals are quickly affected by fluid volume
Patient was able to demonstrate behaviours to monitor and correct deficit, as indicated, when condition is chronic and maintained the intake and output of fluid is balanced.
deficit 6. Turn frequently, gently massage skin, and protect bony prominences. 6. Tissues are susceptibl e to breakdow n because of vasoconst riction and increased fragility. Dependent: 1. Decrease s GI motility or peristalsis and diminishes digestive secretions to relieve cramping and diarrhea. 2. To deliver fluids accurately and at
Dependent: 1. Administer antidiarrheals as prescribed by the physician.
2. Administer Intravenous fluids as prescribed 99
desired rates. Collaborative: Collaborative: 1. Assist with 1. Refer to identification listing of and treatment predisposi of underlying ng or cause. contributin g factors to determine treatment needs. 2. Monitor 2. Depending laboratory on the studies. avenue of fluid loss, differing electrolyte and metabolic imbalance s may be present and require correction. 3. Ascertain 3. Relieves clients thirst and beverage discomfort preferences, 100
and set up a 7-hour schedule for fluid intake.
of dry mucous membran es and augments parenteral replaceme nt.
101
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- NCPsDokumen13 halamanNCPsRocel DevillesBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen23 halamanNursing Care PlanLorielle HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- NCP EndoDokumen8 halamanNCP EndoJan Rainier Carlos BalariaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlansDokumen5 halamanNursing Care PlansMargaret SibugBelum ada peringkat
- Case Pres Paralytic IleusDokumen9 halamanCase Pres Paralytic IleusEric Benedict Shea HidalgoBelum ada peringkat
- Complications in PregnancyDokumen36 halamanComplications in PregnancyJADE PATEGABelum ada peringkat
- German MeaslesDokumen8 halamanGerman MeaslesYdynn Parejas GavinaBelum ada peringkat
- CASE STUDY PheumoniaDokumen5 halamanCASE STUDY PheumoniaEdelweiss Marie CayetanoBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen8 halamanNCPJose Benit DelacruzBelum ada peringkat
- NCP LeprosyDokumen3 halamanNCP LeprosyJane MinBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen7 halamanNCPmftaganasBelum ada peringkat
- Patho DiagramDokumen4 halamanPatho DiagramNielArmstrongBelum ada peringkat
- Case StudyDokumen1 halamanCase StudyChristian Mark Alberca100% (2)
- Case Studies - Tetralogy of FallotDokumen16 halamanCase Studies - Tetralogy of FallotKunwar Sidharth SaurabhBelum ada peringkat
- Case StudyDokumen27 halamanCase StudyMikko Anthony Pingol AlarconBelum ada peringkat
- Impaired Tissue Integrity FinalDokumen1 halamanImpaired Tissue Integrity Finaljanine marie oraizBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Albano, Bautista, Cimatu, Purificacion, SieteralesDokumen84 halamanDiabetic Ketoacidosis: Albano, Bautista, Cimatu, Purificacion, SieteralesSyd BautistaBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Nsg. Diagnosis Sci. Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen6 halamanAssessment Nsg. Diagnosis Sci. Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRoMarie AbainzaBelum ada peringkat
- Neonatal JaundiceDokumen12 halamanNeonatal JaundiceJustine NyangaresiBelum ada peringkat
- Knowledge DeficitDokumen5 halamanKnowledge DeficitteamstrocaBelum ada peringkat
- ScriptDokumen2 halamanScriptKeith AquinoBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesBelum ada peringkat
- University of Eastern Philippines: Scientific RationaleDokumen3 halamanUniversity of Eastern Philippines: Scientific RationaleJane MinBelum ada peringkat
- NCP CSDokumen7 halamanNCP CSTwobee Kriz LeghidBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Pyelonephritis Nursing Care PlansDokumen2 halamanAcute Pyelonephritis Nursing Care PlansJoannah Marie Juloya Kiat-ong100% (1)
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Dokumen10 halamanSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- NCP For ChildrenDokumen17 halamanNCP For ChildrenRachel Niu IIBelum ada peringkat
- Health Teaching Plan School Age: Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Normal Road, Zamboanga CityDokumen12 halamanHealth Teaching Plan School Age: Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Normal Road, Zamboanga CityJinaan MahmudBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Case Scenario BronchitisDokumen5 halaman2nd Case Scenario BronchitisKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs StudyDokumen15 halamanDrugs StudyNelle Agni0% (1)
- Rabi PurDokumen3 halamanRabi PurDiana Laura LeiBelum ada peringkat
- Buergers Power PointDokumen16 halamanBuergers Power PointYan VencerBelum ada peringkat
- Nephrotic SyndromeDokumen20 halamanNephrotic Syndromeami5687Belum ada peringkat
- Deficient Knowledge: Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Care Plans (NCP)Dokumen3 halamanDeficient Knowledge: Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Care Plans (NCP)Vincent Paul SantosBelum ada peringkat
- NCP FinalDokumen4 halamanNCP FinalKathrina CraveBelum ada peringkat
- B NCP On and Off Fever 2b ImproveddocxDokumen6 halamanB NCP On and Off Fever 2b ImproveddocxKylie CatralBelum ada peringkat
- Ongoing AppraisalDokumen2 halamanOngoing AppraisalLouisa Marie MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Cu 4Dokumen3 halamanCu 4Paul SahagunBelum ada peringkat
- Case Scenario Osteoarthritis Week 16 GerontologDokumen5 halamanCase Scenario Osteoarthritis Week 16 GerontologMary Josette NavarraBelum ada peringkat
- Ectopic PregnancyDokumen65 halamanEctopic PregnancyWen SilverBelum ada peringkat
- Anxiety Disorders PDFDokumen29 halamanAnxiety Disorders PDFKhyle TolentinoBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Bernal Imbalanced Nutrition pt2Dokumen2 halamanNCP Bernal Imbalanced Nutrition pt2Maria CabangonBelum ada peringkat
- Case StudyDokumen41 halamanCase StudyAubrey Ann FolloscoBelum ada peringkat
- NCP GeDokumen14 halamanNCP GeSuluhTriUtomoBelum ada peringkat
- NCP EsrdDokumen2 halamanNCP EsrdAziil LiizaBelum ada peringkat
- CHN FinalsDokumen15 halamanCHN FinalsLyndon SayongBelum ada peringkat
- Health Assessment FHP - Nutrition and MetabolismDokumen25 halamanHealth Assessment FHP - Nutrition and MetabolismKim DajaoBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 3 NCM 112Dokumen4 halamanTopic 3 NCM 112Marielle ChuaBelum ada peringkat
- Guada A. Dumapit RN, ManDokumen18 halamanGuada A. Dumapit RN, ManAnne B. BuenvenidaBelum ada peringkat
- NCP-Drug Study 2Dokumen4 halamanNCP-Drug Study 2hsiriaBelum ada peringkat
- Insulin EffectsDokumen24 halamanInsulin Effectsvag taoBelum ada peringkat
- X. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveDokumen6 halamanX. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveRenea Joy ArruejoBelum ada peringkat
- Non-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The AmericasDokumen2 halamanNon-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The Americaschristian quiaoitBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlansDokumen1 halamanNursing Care Plansapplensweety100% (2)
- Case Scenario For Group 2Dokumen8 halamanCase Scenario For Group 2nikki sabsBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen4 halamanDrug StudyJames Lavarias SuñgaBelum ada peringkat
- Grand Rounds Concept MapDokumen3 halamanGrand Rounds Concept Mapapi-307132210Belum ada peringkat
- Practical Nursing Diploma Program Pre-Clinical Nursing Care Research Assignment "Prep and Plan"Dokumen7 halamanPractical Nursing Diploma Program Pre-Clinical Nursing Care Research Assignment "Prep and Plan"Jeremy ThomasBelum ada peringkat
- Ugib NCPDokumen5 halamanUgib NCPJhuRise Ann Mangana100% (1)
- NCPDokumen10 halamanNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaBelum ada peringkat
- "The Catholic Liturgical Calendar": The Catholic Doors Ministry Presents The Bible CourseDokumen13 halaman"The Catholic Liturgical Calendar": The Catholic Doors Ministry Presents The Bible CourseNefre Dayap DarrocaBelum ada peringkat
- PhylumDokumen1 halamanPhylumNefre Dayap DarrocaBelum ada peringkat
- Structure: Chemistry Formaldehyde GlycolaldehydeDokumen6 halamanStructure: Chemistry Formaldehyde GlycolaldehydeNefre Dayap DarrocaBelum ada peringkat
- Elementary Graph Theory: Robin Truax March 2020Dokumen15 halamanElementary Graph Theory: Robin Truax March 2020Jefferson WidodoBelum ada peringkat
- TDC Calculation For The Determination of Drill Bit PerformanceDokumen3 halamanTDC Calculation For The Determination of Drill Bit Performancejanuar baharuliBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiology QuestionsDokumen5 halamanMicrobiology QuestionsNaeem AminBelum ada peringkat
- List Lagu EnglishDokumen7 halamanList Lagu EnglishRyn ZulfanBelum ada peringkat
- B.ing Wajib - XI IPA1-2Dokumen3 halamanB.ing Wajib - XI IPA1-2iwan fals NurjaniBelum ada peringkat
- Table of Content and PrefaceDokumen5 halamanTable of Content and PrefaceHaiderEbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Septage Management Guide 1Dokumen43 halamanSeptage Management Guide 1Ria Tiglao FortugalizaBelum ada peringkat
- SRS Cheat CodesDokumen9 halamanSRS Cheat CodesnurhayatiBelum ada peringkat
- AP Physics Test: Electricity and Magnetism-Solutions: Multiple Choice QuestionsDokumen6 halamanAP Physics Test: Electricity and Magnetism-Solutions: Multiple Choice QuestionsChen JohnBelum ada peringkat
- Atomic Structure RevisionDokumen4 halamanAtomic Structure RevisioncvBelum ada peringkat
- Exercises PDFDokumen39 halamanExercises PDF910220Belum ada peringkat
- CMC 2023 Senior Category Question BankDokumen5 halamanCMC 2023 Senior Category Question BankNikita AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 - Nervous ReviewerDokumen18 halamanChapter 8 - Nervous Reviewerchristian anchetaBelum ada peringkat
- GalvInfoNote 1 4Dokumen4 halamanGalvInfoNote 1 4rplata63Belum ada peringkat
- Jeppview For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitDokumen12 halamanJeppview For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitNguyen MinhBelum ada peringkat
- TM 55 1520 400 14 PDFDokumen227 halamanTM 55 1520 400 14 PDFOskar DirlewangerBelum ada peringkat
- SLC Past and Future Hustrulid KvapilDokumen26 halamanSLC Past and Future Hustrulid KvapilkinsaeyaBelum ada peringkat
- BJ SurfactantsDokumen2 halamanBJ SurfactantsAquiles Carrera100% (2)
- Scripture Passages Suitable For Lectio Divina: 1 John 4:7-11Dokumen2 halamanScripture Passages Suitable For Lectio Divina: 1 John 4:7-11Victor AugustoBelum ada peringkat
- OSC - 2015 - Revised - Oct (Power Cables) PDFDokumen118 halamanOSC - 2015 - Revised - Oct (Power Cables) PDFIván P. MorenoBelum ada peringkat
- Animal Cells PDFDokumen4 halamanAnimal Cells PDFFalah HabibBelum ada peringkat
- 2018-Me-184 MMDokumen28 halaman2018-Me-184 MMKhizer Nauman RanaBelum ada peringkat
- AlasDokumen3 halamanAlasdara HinariBelum ada peringkat
- British Vs American English - CrosswordDokumen3 halamanBritish Vs American English - Crosswordlkham enkhsaikhanBelum ada peringkat
- Customer - Reprint DhoniDokumen1 halamanCustomer - Reprint DhoniBaljit SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Wanderer Above The Sea of FogDokumen5 halamanWanderer Above The Sea of FogMaria Angelika BughaoBelum ada peringkat
- Teff Type-I Sourdough To ProduDokumen21 halamanTeff Type-I Sourdough To ProdudanaBelum ada peringkat
- HVT DS HAEFELY RIC 422 Reference Impulse Calibrator V2004Dokumen4 halamanHVT DS HAEFELY RIC 422 Reference Impulse Calibrator V2004leivajBelum ada peringkat
- "Automatic Tyre Pressure Inflation System": Bachelor of TechnologyDokumen41 halaman"Automatic Tyre Pressure Inflation System": Bachelor of Technologymd washiqeBelum ada peringkat