Anatomy and Physiology Hmole
Diunggah oleh
Eunice CasaclangDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Anatomy and Physiology Hmole
Diunggah oleh
Eunice CasaclangHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth. External Female Reproductive System Escutcheon - the distribution of pubic hair Mons Veneris/Pubis - is the adipose tissue lying above the pubic bone of adult females, anterior to the pubic symphysis. The mons pubis forms the anterior portion of the vulva. Clitoris - is a sexual organ that is present only in female mammals. In humans, the clitoris is the most sensitive erogenous zone of the female and the primary cause of female sexual pleasure Skenes gland (Para urethral gland) - are glands located on the anterior wall of the vagina, around the lower end of the urethra. They drain into the urethra and near the urethral opening and may be near or a part of the G-Spot. These glands are surrounded with tissue (which includes the part of the clitoris) that reaches up inside the vagina and swells with blood during sexual arousal. Vestibule Bartholins gland (Vulvo vaginal gland) - are two glands located slightly posterior and to the left and right of the opening of the vagina. They secrete mucus to lubricate the vagina and are homologous to bulbourethral glands in males. Hymen - is a membrane that surrounds or partially covers the external vaginal opening. It forms part of the vulva, or external genitalia. The size of the hymenal opening increases with age. Fourchette / frenulum labiorum pudendi - is a frenulum where the labia minora meet posteriorly. The fourchette may be torn during delivery due to the sudden stretching of the vulval orifice, or during intercourse. Frenulum - is a small fold of tissue that secures or restricts the motion of a mobile organ in the body. In females, genital frenula include the frenulum clitoridis of the clitoris and the frenulum labiorum pudendi (aka fourchette) where the labia minora meet at the back. Labia minora - are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginalopening, situated between the labia majora (outer labia, or outer lips). Inner lips vary widely in size, colour, and shape from woman to woman. Labia majora - are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineumand form the lateral boundaries of the pudendal cleft, which contains the labia minora, interlabial sulci, clitoral hood, clitoral glans, frenulum clitoridis, the Hart's Line, and the vulval vestibule, which contains the external openings of the urethra and the vagina. Perineum - is a region of the body including the perineal body and surrounding structures. There is some variability in how the boundaries are defined, but the term generally includes the genitals and anus.
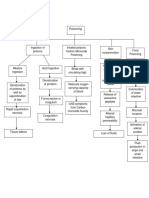
Anus - is the external opening of the rectum. Like other animals, its closure is controlled by sphincter muscles.Feces are expelled from the body through the anus during the act of defecation, the primary function of the anus. Internal Female Reproductive System Fundus - is the top portion, opposite from the cervix. Corpus Isthmus ovarian ligament fallopian tube 4 parts of fallopian tube Interstitial-1 Isthmus-2 (tubal ligation) Ampulla-5 (site of fertilization) Infandibulum-2 Uterus Head- fundus Body- corpus Neck- isthmus Corpus- 3 layers Endometrium Myometrium Perimetrium Isthmus- 3 parts Internal os Cervical canal External os
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hydatidiform MoleDokumen18 halamanHydatidiform Molejean thereseBelum ada peringkat
- Uterine RuptureDokumen19 halamanUterine RuptureAna Denise Quinajon0% (1)
- Gestational Trophoblastic Diseases Hydatiform MoleDokumen40 halamanGestational Trophoblastic Diseases Hydatiform MoleL3SBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDokumen4 halamanNormal Spontaneous Deliveryvivian magnoBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Threatened AbortionDokumen5 halamanNCP Threatened AbortionKceey CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Ectopic PregnancyDokumen26 halamanEctopic PregnancyCHryz TinBelum ada peringkat
- CP Hydatidiform MoleDokumen13 halamanCP Hydatidiform Molesweetheart_joannieBelum ada peringkat
- Ahmed Mohamed Abdel Rahim Rammah: Senior Registrar Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Al - Adan Hospital, KuwaitDokumen32 halamanAhmed Mohamed Abdel Rahim Rammah: Senior Registrar Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Al - Adan Hospital, Kuwaithossam626Belum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Abortion Case Study (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Dokumen4 halamanPathophysiology of Abortion Case Study (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Raiden VizcondeBelum ada peringkat
- 10.theories of LaborDokumen18 halaman10.theories of LaborJulia Ramos100% (1)
- And Vaginal Bleeding (In Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy)Dokumen9 halamanAnd Vaginal Bleeding (In Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy)Clareen JuanicoBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study (Placenta Previa)Dokumen5 halamanCase Study (Placenta Previa)Jai - HoBelum ada peringkat
- ETHICO OutlineDokumen5 halamanETHICO Outline'emotera' Gudbai DotaBelum ada peringkat
- Prob With The PowerDokumen4 halamanProb With The PowerPauline Navarro100% (1)
- High Risk PregnancyDokumen14 halamanHigh Risk PregnancyJezrael PueblosBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 109 (PRELIMS) - Lesson 3Dokumen17 halamanNCM 109 (PRELIMS) - Lesson 3nianBelum ada peringkat
- Uterine MyomaDokumen45 halamanUterine MyomaAndiniMayudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Hydatidiform MoleDokumen10 halamanHydatidiform MoleLisa TurnerBelum ada peringkat
- Abruptio PlacentaDokumen4 halamanAbruptio PlacentaChelzie LasernaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care of A Family Experiencing A Complication of Labor or BirthDokumen111 halamanNursing Care of A Family Experiencing A Complication of Labor or BirthEvery Youth MattersBelum ada peringkat
- Hydatidiform Mole AnahistoDokumen11 halamanHydatidiform Mole AnahistoIanMayBelum ada peringkat
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) Part I: Molar PregnancyDokumen88 halamanGestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) Part I: Molar Pregnancyhafidzz1100% (1)
- Spontaneous AbortionDokumen8 halamanSpontaneous Abortionsaber_fate_11Belum ada peringkat
- Problems of The PassengerDokumen9 halamanProblems of The PassengerDanah Grace SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Physiological changes in pregnancy: Respiratory, nervous, and musculoskeletal systemsDokumen9 halamanPhysiological changes in pregnancy: Respiratory, nervous, and musculoskeletal systemsAyazBelum ada peringkat
- Problems With The PowersDokumen5 halamanProblems With The PowersAlexander Ruiz Queddeng100% (1)
- Theories of Labor: Prepared By: Ronarica B. Diones, R.N., R.MDokumen17 halamanTheories of Labor: Prepared By: Ronarica B. Diones, R.N., R.MDee BorreroBelum ada peringkat
- Theories of LabourDokumen22 halamanTheories of LaboursubashikBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care of Induction and Augmentation of LaborDokumen17 halamanNursing Care of Induction and Augmentation of LaborZyrene RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE 5 POSTPARTUM NRG 203 REDOBLE TANUTAN CHAVEZ and FELEODokumen24 halamanMODULE 5 POSTPARTUM NRG 203 REDOBLE TANUTAN CHAVEZ and FELEONyze GarrixBelum ada peringkat
- Pa Tho Physiology of Uterine MyomaDokumen2 halamanPa Tho Physiology of Uterine Myomaghettodawg187100% (7)
- Pathophysiology AbrasionDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology AbrasionVito VitoBelum ada peringkat
- Myoma CaseDokumen111 halamanMyoma Caseapi-1976296750% (2)
- Nursing Care Management - 107: de La Salle Lipa College of NursingDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Management - 107: de La Salle Lipa College of NursingThe Blue and Gold RvdBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 109 High Risk Newborn To MaturityDokumen74 halamanNCM 109 High Risk Newborn To MaturityMantilla, Kristina Cassandra A.Belum ada peringkat
- The Incompetent Cervix 2Dokumen30 halamanThe Incompetent Cervix 2api-3705046100% (3)
- 1.1 Pathophysiology of Ectopic Pregnancy BSN 2C FinalDokumen3 halaman1.1 Pathophysiology of Ectopic Pregnancy BSN 2C FinalArianne Rose Afable PagulayanBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of PoisoningDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of PoisoninggoyaBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment of The BreastDokumen11 halamanAssessment of The BreastSIR ONEBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 107 5M Case Analysis PDFDokumen9 halamanNCM 107 5M Case Analysis PDFKisha BethelBelum ada peringkat
- CAJA, RENZO GABRIEL, BSN 2-1 NCM109-Midterm ModuleDokumen14 halamanCAJA, RENZO GABRIEL, BSN 2-1 NCM109-Midterm ModuleRenzo GabrielBelum ada peringkat
- "Uterine Leiomyoma " A Case Study: Saint Mary's University School of Health and Natural SciencesDokumen75 halaman"Uterine Leiomyoma " A Case Study: Saint Mary's University School of Health and Natural SciencesKyla CarbonelBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Teaching Plan 2Dokumen7 halamanSample Teaching Plan 2Tanya WilliamsBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Related To Psychological and Physiologic Changes of PregnancyDokumen6 halamanNursing Care Related To Psychological and Physiologic Changes of PregnancyKristineeeBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study HELLPDokumen7 halamanCase Study HELLPJovirtBelum ada peringkat
- Care of The Mother and The Fetus During The Prenatal Period (Part 2)Dokumen20 halamanCare of The Mother and The Fetus During The Prenatal Period (Part 2)Austine James Sabenicio PantiloBelum ada peringkat
- Premature Rupture of MembraneDokumen66 halamanPremature Rupture of MembranePriscilla Marie Macasaddug100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Ectopic PregnancyDokumen3 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of Ectopic PregnancyNepfrisia AsmadBelum ada peringkat
- Genetic testing and counseling for maternal and child healthDokumen2 halamanGenetic testing and counseling for maternal and child healthReyna Chame GarcinezBelum ada peringkat
- PartographDokumen3 halamanPartographAlliana O. BalansayBelum ada peringkat
- 16 Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDokumen46 halaman16 Amniotic Fluid EmbolismAhmed TarigBelum ada peringkat
- Female Reproductive SystemDokumen69 halamanFemale Reproductive Systemenam professorBelum ada peringkat
- Female Reproductive Anatomy GuideDokumen3 halamanFemale Reproductive Anatomy GuidearzeManzanoBelum ada peringkat
- Sex Organs of The Human FemaleDokumen17 halamanSex Organs of The Human FemaleTaniya DwiputriBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive System: External Generative OrgansDokumen28 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive System: External Generative OrgansAlmira Gamao100% (1)
- Structures in The External Female Genitalia WordDokumen3 halamanStructures in The External Female Genitalia WordMark Matthew Guadalupe100% (1)
- The Female Reproductive SystemDokumen25 halamanThe Female Reproductive SystemIan Mizzel A. Dulfina100% (1)
- Presentation On: Female Reproductive SystemDokumen54 halamanPresentation On: Female Reproductive SystemLetsShop BbsrBelum ada peringkat
- Female Reproductive System Functions and AnatomyDokumen67 halamanFemale Reproductive System Functions and AnatomyPaul AndersonBelum ada peringkat
- Hospital Management SystemDokumen46 halamanHospital Management SystemDushyant Singh93% (15)
- 02 1975 Act DdbiaDokumen13 halaman02 1975 Act DdbiaChuah C. KenBelum ada peringkat
- Stunting in IndonesiaDokumen218 halamanStunting in IndonesiaPratamaOktaRickyBelum ada peringkat
- History of Physical Education in PakistanDokumen47 halamanHistory of Physical Education in PakistanayazlashariBelum ada peringkat
- Digestive System Parts PacketDokumen2 halamanDigestive System Parts PacketRusherBelum ada peringkat
- What To Do When You Dont Know What To DoDokumen118 halamanWhat To Do When You Dont Know What To DoRoxanne FreytesBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy Trains 3rd Edition Emag 1Dokumen62 halamanAnatomy Trains 3rd Edition Emag 1Dibyendu BanerjeeBelum ada peringkat
- PhD Fluid MechanicsDokumen4 halamanPhD Fluid MechanicsGooftilaaAniJiraachuunkooYesusiinBelum ada peringkat
- DSMDokumen2 halamanDSMOtilia EmaBelum ada peringkat
- Laura Mitchell - An Introduction To Orthodontics-Oxford University Press (2013) PDFDokumen326 halamanLaura Mitchell - An Introduction To Orthodontics-Oxford University Press (2013) PDFGavrilescu Mihai84% (25)
- Ruhs College of Nursing Sciences, Jaipur: Assignment ON Sampling TechniquesDokumen13 halamanRuhs College of Nursing Sciences, Jaipur: Assignment ON Sampling TechniquesDr-Sanjay SinghaniaBelum ada peringkat
- Gamble J Sped854 m8 Philosophy2Dokumen5 halamanGamble J Sped854 m8 Philosophy2api-295546890Belum ada peringkat
- NUR1204-RLE - Group 4 - Home Visit Activity (HTP and HVP)Dokumen16 halamanNUR1204-RLE - Group 4 - Home Visit Activity (HTP and HVP)Jayvee BillonesBelum ada peringkat
- SPECIAL WORKSHOP ANNOUNCEMENT-with Keshe NotesDokumen4 halamanSPECIAL WORKSHOP ANNOUNCEMENT-with Keshe NotesAhmad AriesandyBelum ada peringkat
- Carrillo & Associates, Inc: Rosa Antonia Carrillo, MSODDokumen3 halamanCarrillo & Associates, Inc: Rosa Antonia Carrillo, MSODalberto1954Belum ada peringkat
- # Category Image Product Name Producer Package Hs Code Remark Key FeaturesDokumen9 halaman# Category Image Product Name Producer Package Hs Code Remark Key Featuresiq_dianaBelum ada peringkat
- Alywn Cosgrove Real World Fat Loss PDFDokumen75 halamanAlywn Cosgrove Real World Fat Loss PDFJM Gym Manticao100% (1)
- Briovent VentilatorDokumen10 halamanBriovent VentilatorPurchase DepartmentBelum ada peringkat
- OSHA Standard For Fixed Ladders SummaryDokumen12 halamanOSHA Standard For Fixed Ladders SummarysesabcdBelum ada peringkat
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Section 1 - Product InformationDokumen2 halamanMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Section 1 - Product Informationmohamed AdelBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Answer On A Separate Sheet of Paper. Then Check Your Answers. Follow The ExamplesDokumen5 halaman4 Answer On A Separate Sheet of Paper. Then Check Your Answers. Follow The ExamplesAndrea chaparroBelum ada peringkat
- RMT TrainningDokumen2 halamanRMT TrainningDita Nadya RizkitaBelum ada peringkat
- FM 999-3 Counter-Zombie Operations at The Fireteam Level v1.1Dokumen16 halamanFM 999-3 Counter-Zombie Operations at The Fireteam Level v1.1Arthur BarieBelum ada peringkat
- Truvivity by NutriliteDokumen10 halamanTruvivity by Nutriliteโยอันนา ยุนอา แคทเธอรีน เอี่ยมสุวรรณBelum ada peringkat
- Q1 Test in Mapeh 6Dokumen4 halamanQ1 Test in Mapeh 6Say RizBelum ada peringkat
- Maybank MNC CompleteDokumen37 halamanMaybank MNC CompleteRobbie Ravin0% (1)
- PLR CourseDokumen43 halamanPLR CourseTaniya ChatterjeeBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Exam Budding ScientistsDokumen3 halaman2 Exam Budding ScientistsWassila Nour100% (1)
- Advances in Rapid Detection Methods For Foodborne PathogensDokumen16 halamanAdvances in Rapid Detection Methods For Foodborne PathogensƠi XờiBelum ada peringkat
- Masonry QuizDokumen12 halamanMasonry QuizJoanne Jose Castro0% (1)