Drug Study
Diunggah oleh
sarah1217Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Drug Study
Diunggah oleh
sarah1217Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
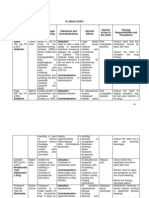
DRUG STUDY Drug Name Paracetam ol Classificati on Analgesics (NonOpioid) & Antipyretic s Dosa ge 500 mg Mode of Action Paracetamol
exhibits analgesic action by peripheral blockage of pain impulse generation. It produces antipyresis by inhibiting the hypothalamic heatregulating centre. Its weak antiinflammatory activity is related to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis in the CNS. Indication Mild to moderate pain and f ever Contraindic ation Contraindica ted in patients hypersensiti ve to drug Drug Interaction Reduced absorption of cholestyramine wit hin 1 hr of admin. Accelerated absorption with metoclopramide. Decreased effect with barbiturates, carbama zepine, hydantoins, rifampicin and sulfinpyrazone. Paracetamol may increase effect of warfarin. Potentially Fatal: Paracetamol increases the risk of liver damage in chronic alcoholics. Increased risk of toxicity with other hepatotoxic drugs or drugs which induce microsomal enzymes Side Effects Nausea, allergic reactions, skin rashes, acute renal tubular necrosis. Potentially Fatal: Very rare, blood dyscrasias (e.g. thrombocyto penia, leucopenia, neutropenia, agranulocyto sis); liver damage Nursing Responsibilities Do not exceed the recommend d dosage Avoid using multiple preparations containing acetaminophen. Carefully check all OTC products. Give drug with food if GI upset occurs. Discontinue drug if hypersensitivity reactions occur. Teaching Point: Do not take for longer than 10 days. Take the drug only for complaints indicated it is not an antiinflammatory agent Avoid the use of other over-thecounter preparations. They may contain acetaminophen, and serious over dosage may occur. Report rash, unsual bleeding or bruising, yellowing of skin or eyes, changes in voiding pattern.
Drug Name Clindamyci n
Classificati on Antibiotics
Dosag e 300 mg
Mode of Action Clindamycin inhibits protein synthesis by reversibly binding to the 50S subunit of the ribosomal thus blocking the transpeptidati on or translocation reactions of susceptible organisms resulting to stunted cell growth.
Indication Severe ana erobic infections Prophylaxis of endocar ditis Toxic shock syndrome Acne
Contraindicati on Contraindicate d in patients hypersensitive to drug or lincomycinuse cautiously in patients with renal or hepatic disease, asthma, history of GI disease, or significant allergies
Drug Interaction Increased neuromuscu lar blockade with neuromuscu lar agents Decreased GI absorption with kaolin, aluminum salts
Side Effects CNS: headache CV: Thrombophlebitis EENT: pharyngitis GI: abdominal pain, Anorexia, bloody or tarry stools ,constipation, diarrhea , dysphagia , esophagitis, flatulence, nausea, psuedome mbranuscolitis, unpleasant or bitter taste, vomiting. GU: UTI HEMATOLOGIC: Eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia, Transientleukopenia SKIN: maculopapular rash, urticaria OTHER: anaphylaxis, erythema
Nursing Responsibilities Assess patients infection before and regularly throughout therapy-before giving first dose, obtain specimen for culture and sensitivity test, and begin therapy pending results. Monitor renal, hepatic, and hematopoetic functions during prolonged therapy.-be alert for adverse reactions and drug interactions Question patient for history of allergies, particularly to clindamycin, lincomycin, and aspirin. Avoid concurrent use of neuromuscular blocking agents. Monitor bowel activity, stool consistency; report diarrhea promptly due to potential for serious colitis. Assess skin for rash with topical application. Assess for superinfection: severe diaarhea, genital/anal pruritus, increase fever, and change of oral mucosa.
Drug Name Hydrocrotis one
Classificatio n Adrenocorti cal steroid Corticostero id Glucocortico id
Dosa ge 100 mg
Mode of Action Enters target cells and binds to cytoplasm ic receptors; initiates many complex reactions that are responsibl e for its antiinflammat ory, immunos uppressiv e and salt retaining actions.
Indication Replacemen t therapy in adrenocor tical insufficiency As supplement in adrenal insufficiency during minor surgery under general anaesthesia Acute adrenocortic al insufficiency Soft tissue inflammatio n Joint inflammatio ns
Contraindi cation Viral/funga l infections, tubercular or syphilitic lesions, bacterial infections unless used in conjunctio n with appropriat e chemother apy.
Drug Interaction Thiazides may enhance hyperglycaemia and hypokalaemia caused by corticosteroids. Increased incidence of peptic ulcer or GI bleeding with concurrent NSAIDs admin. Response to anticoagulants altered. Dose of antidiabetics and antihypertensives needs to be increased. Decreases serum conc of salicylates and antimuscarinic agents. Ethanol may enhance gastric mucosal irritation. Reduced efficacy with concurrent use ofcarbamazepine, phenytoin, primidone, barbiturates and rifampicin. Mutual inhibition of metabolism between ciclospori n and
Side Effects Sodium and fluid retention. Potassium and calcium depletion. Muscle wasting, weakness, osteoporosis. GI disturbances and bleeding. Increased appetite and delayed wound healing. Bruising, striae, hirsutism, acne, flushing. Raised intracranial pressure, headache, depression, psychosis, menstrual irregularities. Hyperglycaemia, glycosuria, DM, obesity, moonface, buffalo hump. Suppression of pituitaryadrenocortical system. Increased susceptibility for infection. Potentially
Nursing Responsibilities Establish baseline and continuing data on BP, weight, fluid and electrolyte balance, and blood glucose. Lab tests: Periodic serum electrolytes blood glucose, Hct and Hgb, platelet count, and WBC with differential. Be alert to signs of hypocalcemia onitor for persistent backache or chest pain; compression and spontaneous fractures of long bones and vertebrae present hazards. Monitor for and report changes in mood and behavior, emotional instability, or psychomotor activity, especially with long-term therapy. Be alert to possibility of masked infection and delayed healing Patient & Family Education Expect a slight weight gain with improved appetite. After dosage is stabilized, notify physician of a sudden slow but steady weight increase [2 kg (5 lb)/wk]. Avoid alcohol and caffeine; may contribute to steroid-ulcer development in long-term
corticosteroids increase plasma conc of both drugs. Enhanced effect in women taking oestrogens or oral contraceptives.
Fatal: Abrupt withdrawal leading to acute adrenal insufficiency. Rapid IV Inj may cause CV collapse.
therapy. Do not ignore dyspepsia with hyperacidity. Report symptoms to physician and do NOT self-medicate to find relief. Do NOT use aspirin or other OTC drugs unless prescribed specifically by the physician. Note: A high protein, calcium, and vitamin D diet is advisable to reduce risk of corticosteroidinduced osteoporosis. Notify physician of slow healing, any vague feeling of being sick, or return to pretreatment symptoms. Do not abruptly discontinue drug; doses are gradually reduced to prevent withdrawal symptoms. Report exacerbation of disease during drug withdrawal.
Drug Name Ciprofloxa cin
Classification Antibacterial Fluoroquinol one
Dosa ge 400 mg
Mode of Action Bactericida l; interferes with DNA replication in susceptible bacteria preventing cell reproducti on.
Indication For the treatment of infections caused by susceptible gramnegative bacteria Treatment of uncomplica ted UTIs Treatment of nosocomial pneumonia Lower respiratory infections
Contraindicat ion Contrainticat ed with allergy to ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin or other fluoroquinolo nes, pregnancy, lactation.
Drug Interaction Decreased absorption with concurrent sucralfate, magnesium-aluminum antacids, calcium, iron, zi nc and multivitamins. Increased methotrexate a ndcaffeine levels when taken concurrently with ciprofloxacin. Probenecid reduces renal clearance of ciprofloxacin. Potentiates oral anticoagulants and glibenclamide. Concurrent use with corticosteroids may increase tendon rupture. Concurrent use with ciclosporin may cause transient increases in serum creatinine. CNS excitation may occur with concurrent admin of quinolones and NSAIDs. Serum concentrations of theophyllineare markedly elevated when co-administered with ciprofloxacin; monitor serum levels of theophylline. Potentially Fatal: Concurrent use with tizanidine can cause marked elevation in
Side Effects GI disturbances; headache, tremor, confusion, convulsions; rashes; joint pain; phototoxicity. Transient increases in serum creatinine. Haematological, hepatic and renal disturbances. Vasculitis, pseudomembran ous colitis and tachycardia. Phototoxicity. Potentially Fatal: Anaphylact oid reaction; cardiopulmonary arrest.
Nursing Responsibilities Report tendon inflammation or pain. Cipro needs to be discontinued. Lab tests: Culture and sensitivity tests should be done prior to initial dose. Treatment may be implemented pending results. Monitor urine pH; it should be less than 6.8, especially in the older adult and patients receiving high dosages of ciprofloxacin, to reduce the risk of crystalluria. Monitor I&O ratio and patterns: Patients should be well hydrated; assess for S&S of crystalluria. Patient & Family Education Immediately report tendon inflammation or pain. Cipro should be discontinued. Fluid intake of 23 L/d is advised, if not contraindicated. Report sudden, unexplained joint pain. Restrict caffeine due to the following effects (e.g., nervousness,
serum levels of tizanidine; avoid concurrent usage. Click to view more ciprofloxacin Drug Interactions
insomnia, anxiety, tachycardia). Use caution with hazardous activities until reaction to drug is known. Drug may cause light-headedness
Drug Name Ketorolac
Classification Antipyretic Nonopioid analgesic NSAID
Dosage 30 mg
Mode of Action Antiinflammatory and analgesic activity; inhibits prostaglandin and leukotriene synthesis.
Indicati on Short term manage ment of pain.
Contraindication Hypersensitivity to aspirin or other NSAIDs, asthma. Hypovolaemia or dehydration. Do not give postoperatively to patients with high risk of haemorrhage. History of peptic ulcer or coagulation disorders. Nasal polyps, angioedema, bronchospasm. Labour. Moderate to severe renal impairment. GI bleeding, cerebrovascular bleeding. As prophylactic analgesic before surgery. Pregnancy, lactation.
Drug Interaction Increased risk of nephrotoxici ty with other toxins. Increased risk of bleeding with anticoagula nts
Side Effects GI ulcer, bleeding and perforation, drowsiness, rash, bronchospasm, hypotension, psychosis, dry mouth, fever, bradycardia, chest pain, dizziness, headache, sweating, oedema, pallor, liver function changes. Transient stinging and local irritation (ophthalmic). Potentially Fatal: Anaphylaxi s. Severe skin reactions. MI, stroke, GI bleeding.
Nursing Responsibilities Patients who have asthma, aspirin-induced allergy, and nasal polyps are at increased risk for developing hypersensitivity reactions. Assess for rhinitis, asthma, and urticaria. Assess pain (note type, location, and intensity) prior to and 1-2 hr following administration. Ketorolac therapy should always be given initially by the IM or IV route. Oral therapy should be used only as a continuation of parenteral therapy. Caution patient to avoid concurrent use of alcohol, aspirin, NSAIDs, acetaminophen, or other OTC medications without consulting health care professional. Effectiveness of therapy can be demonstrated by decrease in severity of pain. Patients who do not respond to one NSAIDs may respond to another.
Drug Name Benzydamine Hydrochloride
Classification Nonsteroidal AntiInflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) Mouth/Throat Preparations
Dosage 2 spray
Mode of Action Benzydamine belongs to a family of medicines known as nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They work to reduce pain and inflammation in the body by reducing the production of hormone-like substances that promote the inflammatory response.
Indication Relief of painful conditions of the oral cavity including tonsillitis, sor e throat, radiation mucositis, aphthous ulcers, post-orosurgical & periodontal procedures; for pharyngitis, swelling & inflammatory conditions. DifflamC:Antiseptic.
Contraindica tion Severe hepatic or renal impairment. Sensitization reaction w/ soln. Appropriate antibacterial therapy should be considered in bacterial infection complication s. Excessive lozenge consumption may have laxative effect. Pregnancy.
Drug Interaction There are no known drug interactions with benzydamin e
Side Effects Oral, numbness; dryness or thirst, tingling, warm feeling in mouth, altered sense of taste.
Nursing Responsibilities Do not exceed 12lozenges a day. Do not take Difflam Sugar-Free Lozenges continuously for more than seven days
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDokumen1 halamanCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GDokumen9 halamanDrug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GggalicinaoBelum ada peringkat
- AtroventDokumen1 halamanAtroventSheri490100% (1)
- Xylocard PiDokumen11 halamanXylocard PiRamakant SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- FlagylDokumen3 halamanFlagylAdrianne BazoBelum ada peringkat
- BrivaracetamDokumen110 halamanBrivaracetamBendisDacicaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug DilantinDokumen1 halamanDrug DilantinSrkocherBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Analysis CefoxitinDokumen2 halamanDrug Analysis CefoxitinNika LoBelum ada peringkat
- Generic Name: BudesonideDokumen8 halamanGeneric Name: BudesonidemeangelmeBelum ada peringkat
- Drug AdvilDokumen1 halamanDrug AdvilDiana Laura LeiBelum ada peringkat
- Miglitol (Glyset)Dokumen1 halamanMiglitol (Glyset)EBelum ada peringkat
- Propofol Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanPropofol Drug Studygersalia.christiennikkiBelum ada peringkat
- MorphineDokumen1 halamanMorphineCassie100% (3)
- DiflucanDokumen1 halamanDiflucanSheri490Belum ada peringkat
- Antimalarial DrugsDokumen7 halamanAntimalarial DrugsHilmanBelum ada peringkat
- Anticholinergics Study Drug ListDokumen1 halamanAnticholinergics Study Drug ListDrima Edi100% (1)
- Ertapenem (Invanz)Dokumen1 halamanErtapenem (Invanz)Adrianne BazoBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study KeterolacDokumen2 halamanDrug Study KeterolacKillerBall RegioBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen5 halamanDrug StudyRai D. MacapantonBelum ada peringkat
- LevaquinDokumen1 halamanLevaquinKatie McPeek100% (1)
- FlagylDokumen2 halamanFlagylKatie McPeek100% (1)
- IndomethacinDokumen9 halamanIndomethacinQuiKe PvBelum ada peringkat
- RifampinDokumen3 halamanRifampinZenit DjajaBelum ada peringkat
- Daptomycin (Cubicin)Dokumen1 halamanDaptomycin (Cubicin)Adrianne BazoBelum ada peringkat
- DoxycyclineDokumen18 halamanDoxycyclineSabab MunifBelum ada peringkat
- PhenytoinDokumen5 halamanPhenytoinRhawnie B. GibbsBelum ada peringkat
- Indacaterol GlycopyrroniumDokumen1 halamanIndacaterol GlycopyrroniumNeulAskiel FloresBelum ada peringkat
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyDokumen8 halamanEMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyShaine WolfeBelum ada peringkat
- AmloDokumen1 halamanAmloamy navajaBelum ada peringkat
- DRUG StudyDokumen6 halamanDRUG StudyJheryck SabadaoBelum ada peringkat
- Penicillin VDokumen3 halamanPenicillin Vapi-3797941Belum ada peringkat
- Artesunat Injection 2009Dokumen4 halamanArtesunat Injection 2009Franca ImadiyiBelum ada peringkat
- Midazolam FinalDokumen2 halamanMidazolam FinalAhmad AbqariBelum ada peringkat
- Zofran IVPDokumen1 halamanZofran IVPAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Levothyroxine - WikipediaDokumen9 halamanLevothyroxine - WikipediaRoxana FrincuBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study - PiptazDokumen1 halamanDrug Study - PiptazMutya XDBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study On EPINEPHRINEDokumen6 halamanDrug Study On EPINEPHRINEshadow gonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- Asthma and Other Respiratory Medications DefindDokumen4 halamanAsthma and Other Respiratory Medications DefindKiran ManojBelum ada peringkat
- CiprofloxacinDokumen2 halamanCiprofloxacinNika Joy Cabrera AlarconBelum ada peringkat
- Coreg (Carvedilol)Dokumen1 halamanCoreg (Carvedilol)Adrianne BazoBelum ada peringkat
- Haloperidol PDFDokumen1 halamanHaloperidol PDFAda AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- Reglan Drug CardDokumen4 halamanReglan Drug CardAdrianne BazoBelum ada peringkat
- Intake & Output Monitoring Sheet: 11 PM 11-7 1000 ML 0 550 ML 0 0Dokumen2 halamanIntake & Output Monitoring Sheet: 11 PM 11-7 1000 ML 0 550 ML 0 0Renea Joy ArruejoBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study - CapDokumen5 halamanDrug Study - CapABARAJBelum ada peringkat
- CHH Drug Study Week 3Dokumen21 halamanCHH Drug Study Week 3maryxtine24Belum ada peringkat
- Salbuterol Generic NameDokumen4 halamanSalbuterol Generic NamejunieBelum ada peringkat
- Triamcinolone (Topical) - Drug InformationDokumen5 halamanTriamcinolone (Topical) - Drug InformationMauricio Sv0% (1)
- NEUROPHARMACOLOGYDokumen36 halamanNEUROPHARMACOLOGYDebika DasBelum ada peringkat
- Generic Name T Rade Name Classification Minitran Anti Angina NitroglycerinDokumen1 halamanGeneric Name T Rade Name Classification Minitran Anti Angina NitroglycerinChristopher LeeBelum ada peringkat
- (Product Name) MR Tablet 30mg (Product Name) MR Tablet 60mgDokumen10 halaman(Product Name) MR Tablet 30mg (Product Name) MR Tablet 60mggmsanto7Belum ada peringkat
- Drug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramDokumen3 halamanDrug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramJear RomeroBelum ada peringkat
- EzetimibeDokumen3 halamanEzetimibeapi-3797941Belum ada peringkat
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDokumen3 halamanName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31Belum ada peringkat
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDokumen19 halamanDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeDokumen9 halamanDrugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeKevin Sam AguirreBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study 68-75Dokumen8 halamanDrug Study 68-75joshua_santiago_5Belum ada peringkat
- Drug Study QiDokumen6 halamanDrug Study QiKevin Sam AguirreBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen9 halamanDrug StudyOdarp PradzBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen6 halamanDrug StudytrinaLCBelum ada peringkat
- Rekapan Belanja JKNDokumen5 halamanRekapan Belanja JKNAPOTEK PUSKESMAS MALEBERBelum ada peringkat
- Primary Tooth Pulp Therapy - Dr. Elizabeth BerryDokumen52 halamanPrimary Tooth Pulp Therapy - Dr. Elizabeth BerryMihaela TuculinaBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Management and Strategic Planning:: Organization's Strategic PlanDokumen7 halamanPerformance Management and Strategic Planning:: Organization's Strategic PlanSara AbidBelum ada peringkat
- Declaration Page Sample Homeowners 12Dokumen1 halamanDeclaration Page Sample Homeowners 12Keller Brown JnrBelum ada peringkat
- English Quarterly TestDokumen3 halamanEnglish Quarterly TestEdmon FabregasBelum ada peringkat
- DefibrillatorDokumen2 halamanDefibrillatorVasanth VasanthBelum ada peringkat
- Stepanenko DermatologyDokumen556 halamanStepanenko DermatologySanskar DeyBelum ada peringkat
- Emissivity Table E4Dokumen11 halamanEmissivity Table E4Mekro Permana PinemBelum ada peringkat
- Articulo de Las 3 Tesis Por BrowDokumen30 halamanArticulo de Las 3 Tesis Por BrowJHIMI DEIVIS QUISPE ROQUEBelum ada peringkat
- Classical and Operant Conditioning ExamplesDokumen6 halamanClassical and Operant Conditioning ExamplesPersephone355100% (1)
- Assignment 2 ME 326Dokumen10 halamanAssignment 2 ME 326divided.symphonyBelum ada peringkat
- MDB Specs PDFDokumen9 halamanMDB Specs PDFAbdElrahman AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- 742210V01Dokumen2 halaman742210V01hakim_zadehBelum ada peringkat
- AIPMT 2009 ExamDokumen25 halamanAIPMT 2009 ExamMahesh ChavanBelum ada peringkat
- Datasheet Cofraplus 60Dokumen2 halamanDatasheet Cofraplus 60Žarko JanjićBelum ada peringkat
- PYC 1501 Basic Psychology - PersonalityDokumen15 halamanPYC 1501 Basic Psychology - Personalityektha_nankoomar91100% (3)
- Strep Throat FactsDokumen2 halamanStrep Throat FactsFactPaloozaBelum ada peringkat
- GLYSANTIN+G48+bg+IN 000000000030667689 SDS GEN US en 8-1Dokumen11 halamanGLYSANTIN+G48+bg+IN 000000000030667689 SDS GEN US en 8-1Ali RidloBelum ada peringkat
- Chem Sba 2019-2020Dokumen36 halamanChem Sba 2019-2020Amma MissigherBelum ada peringkat
- Akin To PityDokumen356 halamanAkin To PityPaul StewartBelum ada peringkat
- Medicina 57 00032 (01 14)Dokumen14 halamanMedicina 57 00032 (01 14)fauzan nandana yoshBelum ada peringkat
- PCB Engraver Operator Manual PDFDokumen41 halamanPCB Engraver Operator Manual PDFmyoshkeuBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 8: Separation DesignDokumen45 halamanLecture 8: Separation DesignRavi Kiran MBelum ada peringkat
- Service Manual - DM0412SDokumen11 halamanService Manual - DM0412SStefan Jovanovic100% (1)
- BMC Brochure WebDokumen4 halamanBMC Brochure WebVikram Pratap SinghBelum ada peringkat
- CV Ilham AP 2022 CniDokumen1 halamanCV Ilham AP 2022 CniAzuan SyahrilBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamental Unit of Life 1-25Dokumen25 halamanFundamental Unit of Life 1-25Anisha PanditBelum ada peringkat
- NICUDokumen15 halamanNICUkavyarkrnagarBelum ada peringkat
- Revised Man As A Biological BeingDokumen8 halamanRevised Man As A Biological Beingapi-3832208Belum ada peringkat