Types of Graphs That Can Be Used For Data Presentation
Diunggah oleh
drjatrikDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Types of Graphs That Can Be Used For Data Presentation
Diunggah oleh
drjatrikHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Q7.
Describe the various types of graphs that can be used for data presentation
Presentation graphs are key to effective visualisation, and can demonstrate quantitative data in an effective and engaging way. There are basically 2 basic kinds of graphics namely Charts which show how much and diagrams that sow how. Charts are most useful for research and diagrams are least useful. The various charts used in report writing: Line Chart Bar Chart Pie Chart Stratum Chart Scatter diagram Pictogram
Line Chart Shows information over a period of tie. Time change is shown from left to right on horizontal X-axis; Change in quantity from bottom up on vertical Y-axis. It is a two-dimesional chart. When more than one variable is presented each line can be a different colour. The number of items hat can be compared on one chart is limited. It is best used to demonstrate a trend over time. With a line chart, you can show two variables at the same time, as well as reveal the relationship between them. They can demonstrate both a comparison between data sets, and a comparison between trends in data sets.
Bar Chart Popular because it is simple and easy to create and interpret. Vertical or horizontal bars are used to represent frequencies and percentage numbers. Vertical bars work well to demonstrate data such as cost and value. Horizontal bars are a fantastic way to present an absolute value of time, for example the length it takes to complete a particular task. Length of the bars represent the quantities they stand for. Clustered bar charts represent 2 or more quantities in the same chart. Cross hatching or different colours distinguish different kinds of information. Bilateral column charts show plus and minus differences. Titles of the bar are shown on the top or bottom; good for showing percentage change. Stacked column Charts show comparison of subdivisions of the column. The bar chart allows presenters to demonstrate absolute data values, and allows direct comparison between data values and data sets. This works particularly well when comparing the same variable, for example costs in different departments within an organisation. Even better, the bar chart can be used to demonstrate an increase or decrease in these values, and not just a static viewpoint. The bar chart allows the presenter to go into great level of detail in a very simple way.
Pie Chart Circle divided intao sections, each section represents a portion of the total.. Area represented is proportional to the size of the item. Excellent for showing the decomposing of a total quantity into its components. The pie chart can only be used for direct comparisons between a single linked data set. However, while pie charts can only be used to show one data set, they can show multiple points within it. You could show, for example, that company X has a 75% market share, whilst company Y only has 10%. The pie chart
is a really good comparison tool, but it never shows absolute value just proportional value. Pie charts are often viewed as being the boring chart.
STRATUM CHART 2 dimensional chart with time along its horizontal x-axis and values of the item plotted on the vertical Y axis. . The area of the graph is divided into several horizontal layers strata, one layer corresponding to each item. The width of each stratum represents the relative magnitude of the corresponding item at that time.
SCATTER DIAGRAM This diagram shows whether any relationship exists between two variables under consideration. In the scatter diagram if the points are closer to the straight line to be drawn, we conclude there is a strong relationship between the variables. @ types of information: visually determine if the two variables are related. If related, what kind of line describes the relationship linear or curvilinear. Scatter charts are useful when presenting a complete data set. That data set could show a trend, or an absence of a trend. These charts are typically used when there are lots of data points, so that the viewer can then establish whether theres a relationship between the data points or not.
PICTOGRAM This is a special type of bar chart which uses pictures instead of rectangular lines. A Pictograph (picture used as writing pictures which resemble what they signify) is an ideogram (symbols which represent ideas) that conveys its meaning through its pictorial resemblance to a physical object.
Pictogram graphs are simple graphs like bar charts except they use a number of little pictures to show how many items there are in each row. Pictograms can take the form of diagrams to represent statistical data and can be varied in color, size or number to represent change. Pictograms are language insensitive but not always easy to design a good pictogram. They are easy to read, visually appealing and handle large data sets easily using keyed icons. However it is hard to quantify partial icons which must be of a consistent size. Pictogram is best only for 2 6 categories and is simplistic.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Rumus Calculation SeparatorDokumen21 halamanRumus Calculation SeparatorAffian WidjanarkoBelum ada peringkat
- Dispatch GuideDokumen30 halamanDispatch Guidepaker28Belum ada peringkat
- 51 Point Aws Security Configuration Checklist PDFDokumen7 halaman51 Point Aws Security Configuration Checklist PDFSarita GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Building a Data Pipeline With Pentaho - From Ingest to AnalyticsDokumen18 halamanBuilding a Data Pipeline With Pentaho - From Ingest to AnalyticsDeni DianaBelum ada peringkat
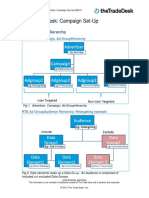
- The Trade DeskDokumen13 halamanThe Trade DeskAmpLiveBelum ada peringkat
- Toc From Ssim 2022 En-1Dokumen5 halamanToc From Ssim 2022 En-1mohamed galalBelum ada peringkat
- Essential IT controls for risk managementDokumen196 halamanEssential IT controls for risk managementvishal jalanBelum ada peringkat
- SQL Inception: Dive Deeper Into The Data Dreamscape: Author: Andres ScrofinaDokumen53 halamanSQL Inception: Dive Deeper Into The Data Dreamscape: Author: Andres ScrofinaMansi MaheshwariBelum ada peringkat
- Swings Lab AssignmentDokumen12 halamanSwings Lab AssignmentPiyush KhalateBelum ada peringkat
- M.E. EXAM Time TableDokumen7 halamanM.E. EXAM Time Tablepa390786Belum ada peringkat
- Inview message and variable triggeringDokumen2 halamanInview message and variable triggeringGabriel David Paez CamposBelum ada peringkat
- Instructions for Indoor Pentathlon Competition CandidatesDokumen2 halamanInstructions for Indoor Pentathlon Competition CandidatesSudeepa HerathBelum ada peringkat
- This Study Resource Was: Activity: Meme-CreationDokumen2 halamanThis Study Resource Was: Activity: Meme-CreationRye FelimonBelum ada peringkat
- Power Off Reset Reason BackupDokumen5 halamanPower Off Reset Reason BackupDȃ̈niȇ̈r RṏdríguezBelum ada peringkat
- GPON ONU FHR 1100 GZB 40Mbps 1G EthernetDokumen1 halamanGPON ONU FHR 1100 GZB 40Mbps 1G EthernetMarketing SatcomBelum ada peringkat
- UAS B InggrisDokumen9 halamanUAS B InggrisAstri Irma YunitaBelum ada peringkat
- Python For S60 3rd EditionDokumen9 halamanPython For S60 3rd EditionShabeerBelum ada peringkat
- E1 Install GuideDokumen31 halamanE1 Install GuideRahul JaiswalBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of MatlabDokumen69 halamanBasics of MatlabsoumenchaBelum ada peringkat
- Openshift Container Platform 4.4: ArchitectureDokumen54 halamanOpenshift Container Platform 4.4: ArchitecturebbierrBelum ada peringkat
- Full Stage Web Developer + MernDokumen3 halamanFull Stage Web Developer + MernkjckjBelum ada peringkat
- Q.1 (A) An Algorithm Takes 0.5Ms For Input Size 100. How Long Will It Take For Input Size 500 If The Running Time Is - I. Quadratic Ii. NlognDokumen3 halamanQ.1 (A) An Algorithm Takes 0.5Ms For Input Size 100. How Long Will It Take For Input Size 500 If The Running Time Is - I. Quadratic Ii. Nlognharshaahuja92Belum ada peringkat
- CP49E Proc Manual PDFDokumen24 halamanCP49E Proc Manual PDFmdobrica100% (1)
- Test Design Techniques: Istqb Certified Tester - Foundation LevelDokumen112 halamanTest Design Techniques: Istqb Certified Tester - Foundation LevelAnonymous Uk3rVZDVFBelum ada peringkat
- Referencia Manual PostgreSQL PDFDokumen334 halamanReferencia Manual PostgreSQL PDFSergio AugustoBelum ada peringkat
- MATH308 Cheat Sheet 9Dokumen5 halamanMATH308 Cheat Sheet 9Melbely BaduaBelum ada peringkat
- Physio Arm Control For Patient Using IOT TechnologyDokumen5 halamanPhysio Arm Control For Patient Using IOT TechnologyIJRASETPublicationsBelum ada peringkat
- As NZS 2485-1995 Medical Equipment - Single-Use Winged Intravenous Devices (Sterile) For General Medical UseDokumen8 halamanAs NZS 2485-1995 Medical Equipment - Single-Use Winged Intravenous Devices (Sterile) For General Medical UseSAI Global - APACBelum ada peringkat
- The Guide To Moble Game Monetization StrategiesDokumen18 halamanThe Guide To Moble Game Monetization StrategiesBuckyBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Conservation Building Code For Residential BuildingsDokumen23 halamanEnergy Conservation Building Code For Residential BuildingsAnonymous Qm0zbNkBelum ada peringkat