Science Synthesis III
Diunggah oleh
lala0483Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Science Synthesis III
Diunggah oleh
lala0483Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
GRADE FIRST PROPERTIES OF WATER
THE STUDENTS WILL READ AND ANSWER ORAL QUESTIONS
THE SUN
GRADE SECOND
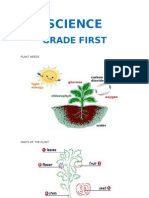
TYPES OF PLANTS
Ferns Ferns are an ancient family of plants. Scientists have found fern fossils from the beginning of the Mesozoic era, 360 million years ago. Ferns are older than land animals and older than dinosaurs. They were living on earth 200 million years before flowering plants evolved. As we know them now, most ferns are leafy plants that grow in moist areas under forest trees.
CONCEPTUALIZATION Plant Plants are a major group of life forms and include familiar organisms such as trees, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. About 350,000 species of plants, defined as seed plants, bryophytes, ferns and fern allies, are estimated to exist currently. As of 2004, some 287,655 species had been identified, of which 258,650 are flowering and 15,000 bryophytes. Green plants, sometimes called metaphytes, obtain most of their energy from sunlight via a process called photosynthesis. We are going to meet two classifications: 1. Classes of plants according to their size. There are three main types of plants Trees The trees are larger plants that exist. They come in many different shapes and sizes, from small fruit trees until sequoias, that the trees are larger, since some of them measuring 84 meters high and has more than 3500 years. The trees also are different from other plants because they have a single stem, called trunk, which is hard and woody. A large number of species of trees lose their leaves with the arrival of cold winter. They do this to protect themselves from the cold and not freeze leaves them with frost. In the spring, it will sprout new leaves by all its branches. I call deciduous trees. By name a few examples, have the sheet expires almond, elm and birch. Other species of trees do not lose their leaves during the winter, but that will renew throughout the year. I call evergreen trees. This is the case of pine, fir, oak or olive. The bushes They are smaller than plant trees, but larger than herbs. They have several stems that some are woody shrubs. Like the trees, some lose their leaves in winter. There are also adapted to different climates. Some may resist frost of winter; others bear
large periods of drought, while others are adapted to live in very warm areas, and so on. There are numerous species of shrubs; some of them are roses, rockrose and aulaga. The herbaceous plants The herbs are small plants out of the ground a few them have a short life for one or two years. Most soil of the wild grass. Others are grown to provide food for humans or also caring as ornamental plants for their beauty. They are wheat, poppy or parsley. 2. Plants without flowers and flowering plants Plants without flowers Many plants do not produce flowers at any point in their lives. In this group of plants are called in Botany plants cryptogams. His way is to reproduce by spores. The best known of the plants that have no flowers are mosses, ferns and algae. It is the SECONDplant began to exist and lived in times that there were still not human beings. They usually live in forests and very humid because they need to have their water swimming spores to reproduce. The mosses are the most primitive land plants and easiest way. They are small plants that live in very humid and shady, because not tolerate direct sunlight. They can be found in the soil, under the shade of rain forests, but always in areas umbra. The ferns are also very old plant. For 300 million years ferns were much more abundant than now. Some were as large as huge trees and forests were authentic. His remains and buried putrefaction have led, over millions of years, coal. Also need to live in areas of high humidity and cool. centimetres. Most of planet is covered with animals, and some were herbaceous plants
Algae are a group of plants that live in water. Many scientists doubt that belong to the plant kingdom, as no show all the features and functions of the plant. Of the algae come the rest of the plants. They were the origin of plants because, over millions of years, some species on earth leading to other plants as mosses and ferns. Algae grow on the seabed or glued to the rocks and there seas, rivers, lakes and ponds. They have very different shapes and colours. They are quite different to the rest of plants, as they have no root or stem since living in water, no need for these bodies to absorb. They made photosynthesis, and some of them are microscopic. An example of what we can see algae in the ponds, lakes, rivers and especially in the sea, where there are many species of colours green, yellow, blue or red. Plants with flowers Most of the plant reproduces by flowers. In Botany plant these plants are called "phanerogams." For them it is not essential that there is water to reproduce, so it can grow for areas that are not wet. In flower plant has its reproductive organs. The flowers are formed the fruits and seeds, which are necessary for a plant of this kind is played.
Some plants produce flowers once or twice each year, such as orange or jasmine, others produce flowers only once in his whole life. The pita, for example, is a plant with thorns, which grows wild throughout the area around the Mediterranean. Supports the drought storing water in its thick leaves. Even 20 or 25 years does not produce flowers and dies after flowering. The flowering plants are divided into two main groups: The gymnosperms have no fruits to protect the seed. Its flowers are very simple and often go unnoticed in our view. They are gymnosperms, for example, pine, fir and cypress. It is the oldest seed plants. The angiosperm plants are more recent and more evolved. They have flowers that are often complex striking our view. The seeds are covered by a fruit that protects them. They are the power supply of humans and many mammals. There is also collected a large number of raw materials and natural products. The jazmines, roses, wheat and oak are angiosperms. REMEMBER
Plants make their own food Plants, like animals, need nourishment. They also need to breathe. Plant nutrition is very different from animal nutrition. The most important difference is that plants do not need to get their food from their surroundings. Instead, they make their own food. Food is made in the green parts of the plants, mainly in the leaves. Plant respiration is also different from animal respiration. Plants breathe in the air or underwater, depending on where they live. The leaves of the plant are responsible for respiration.
How plants get nourishment Plants get nourishment in the following way: First, the roots absorb water and nutrients from the soil. The mixture of water and nutrients that flows into the plant is called raw-sap. Plants turn the raw sap into refined sap in the leaves. Refined sap is a mixture of water and plant food. Leaves need sunlight to turn raw sap into refined sap. Finally, the refined sap is transported to all parts of the plant.
GROW OF THE PLANTS
Seed A seed is a small embryonic plant enclosed in a covering called the seed coat, usually with some stored food. It is the product of the ripened ovule of gymnosperm and angiosperm plants which occurs after fertilization and some growth within the mother plant. The formation of the seed completes the process of reproduction in seed
plants (started with the development of flowers and pollination), with the embryo developed from the zygote and the seed coat from the integuments of the ovule. Seeds have been an important development in the reproduction and spread of flowering plants, relative to more primitive plants like mosses, ferns and liverworts, which do not have seeds and use other means to propagate themselves. This can be seen by the success of seed plants (both gymnosperms and angiosperms) in dominating biological niches on land, from forests to grasslands both in hot and cold climates. The term seed also has a general meaning that predates the above anything that can be sown i.e. "seed" potatoes, "seeds" of corn or sunflower "seeds". In the case of sunflower and corn "seeds", what is sown is the seed enclosed in a shell or hull, and the potato is a tuber. Plant Propagation Plant propagation is defined as the process of reproducing or creating a new plant or seedling. Like all other living organisms in Nature, plants must reproduce to survive. Nature affords a variety of ways to do this in the plant world. Different species will propagate or reproduce in different ways. And, unlike the animal world, many plants will reproduce in multiple ways. Plant propagation is an important part of gardening, whether outdoors or with your indoor houseplants. When you have a great plant, and you want to create a new one "just like it" for yourself or a friend, you need to know about plant propagation. Seed Production Seeds are by far the most common means of plant propagation. The vast majority of plants in the world produce seeds. The seeds are produced in the fruit of a plant or in the flower. In nature the seeds dry out in autumn and then spend the winter in or on the ground. They awaken and sprout in the spring as a young seedling. Seeds are cast about by nature in a variety of ways. Some seeds fall to the ground, and new offspring sprout up right near the location of the mother plant. Other seeds are cast far distances by floating through the air. Good examples of these are dandelions and poplar trees. Other plants use animals to help spread their seeds in a wide area. Berries for example pass though the digestive system of birds, and are deposited long distances away. Other seeds are contained in burrs that attach themselves to an animals fur, and are carried for miles before being cast off by their unsuspecting transportation. The number of seeds produced is usually proportional to the seeds survival rate. Thats why some plants produce thousands of seeds, as only a few ultimately find a suitable place to germinate. Seeds are generally easy to collect and store away for next year. In todays world of mass production, only a few varieties of a species are readily available in seed stores, online, and in catalogs. Heirloom seed sources and keeping your own seeds are a great way of retaining less common varieties that may carry unique features or qualities. Those unique qualities will make your garden stand out to both the casual observer and the garden experts. Example: Fruits Cuttings and Rooting Plants This is the second most common form of plant propagation. But, it is sometimes the most difficult. Sure, there are lots of plants that you can easily and successfully propagate by cuttings. Then, there are others that are more difficult. A good example of this are roses, which require a more controlled environment and protection during the "cutting" stage. A good candidate for cuttings, is a healthy, growing plant, one that has not gone dormant in the fall. Cut the end of a stem, generally three to four inches long. Look for a stem that
does not have a flower or a flower bud. Remove any flowers and buds, and the bottom leaves. There should be four to six healthy leaves on the cutting. Some cuttings need to be placed in water to allow roots to form. Others, are placed in moist soil. Care must be taken to make sure the tender new roots do not dry out. After a healthy new root system is formed, you can then transplant your cutting into a container or into your garden. Some plants, like African Violets, work well with leaf cuttings. The leaf is either placed in water to root, or placed directly into moist soil. Some leaf cuttings will grow pinned to the surface of the soil. The new plants will root from the veins where they contact the moist soil. Example: Geranium Bulb A wide variety of flowers grow from bulbs and corms. The original bulb grows smaller bulbs as offshoots. Pull bulbs in the summer after the plant has died back. Separate the smaller bulbs from the mother bulb. Example: Tulip.
PLANTS REPRODUCTION
Vegetative reproduction is asexual reproductionother terms that apply are vegetative propagation or vegetative multiplication. Vegetative growth is enlargement of the individual plant; vegetative reproduction is any process that results in new plant "individuals" without production of seeds or spores.
Plants reproduction Non-flowering plants Some plants don't produce flowers and seeds. Plants such as ferns and mosses are called nonflowering plants and produce spores instead of seeds. There is also another group called the Fungi, that include mushrooms, and these also reproduce by spores. We often think of these individuals as "non photosynthetic plants" when in fact they belong to their very own group or kingdom. Spores are microscopic specks of living material. Ferns produce their spores on the undersides of the leaves (fronds). You may have seen them. They are the brown "spots" or "pads" on the bottom of the leaves. If you have access to a microscope, use it to look at the spores. You will find them to be a variety of shapes and unique to each kind of fern. Plants from parts is a form of asexual or vegetative propagation. This process is sometimes called cloning because every new plant is exactly like the parent. One type of cloning uses cuttings--parts of plants that grow into new plants. Both stems and leaves can be used as cuttings. Another kind of cloning is grafting--the joining
together of two plants into one. Other kinds of cloning use bulbs or tubers--underground parts that make new plants. Flowering plants
Pollination is very important. It leads to the creation of new seeds that grow into new plants. But how does pollination work? Well, it all begins in the flower. Flowering plants have several different parts that are important in pollination. Flowers have male parts called stamens that produce a sticky powder called pollen. Flowers also have a female part called the pistil. The top of the pistil is called the stigma, and is often sticky. Seeds are made at the base of the pistil, in the ovule. To be pollinated, pollen must be moved from a stamen to the stigma. When pollen from a plant's stamen is transferred to that same plant's stigma, it is called self-pollination. When pollen from a plant's stamen is transferred to a different plant's stigma, it is called cross-pollination. Cross-pollination produces stronger plants. The plants must be of the same species. For example, only pollen from a daisy can pollinate another daisy. Pollen from a rose or an apple tree would not work.
GRADE THIRD ANIMAL CLASSIFICATION ECOSYSTEMS
How we classify animals We classify animals, or put them into groups, in order to study them. We put animals with similar characteristics in the same group. The most common classification divides animals into two groups: vertebrates and invertebrates.
CONCEPTUALIZATION We can classify the animals according to the type of food they eat. There are three basic classifications: herbivores, carnivores and omnivores. HERBIVORES: Eat plants cows and horses are herbivores. CARNIVORES: eat other animals, lions, wolves and dogs are examples of carnivores. OMNIVORES: Eat both meat and plants. Bears, chimpanzees and humans are all omnivores. Like the people, animals have to digest the food they eat. The digestive system is responsible for digestion. Vertebrates, such as cats and humans, have complex digestive systems. Invertebrates , such as worms have more simple digestive systems. REMEMBER Most animals can eat many different foods. If one type of food becomes scarce, the can eat other things. EXAMPLE: A CHIMPANZEE DIET Chimpanzees basically eat plants. These apes eat the leaves and fruit of the many plants that grow in the areas where they live. However, sometimes chimpanzees eat meat. A pack of chimpanzees will hunt and kill small monkeys. Afterwards, they all share the meat.
ECOSYSTEMS
The ecosystem is the central concept of ecology. The word ecology is derived from the Greek word oikos meaning place. Ecology therefore, studies places and what happens in them, taking places to be natural spaces. The most basic concepts of this science focus on observation of the environment and discovery of the needs of and the relationships between living things. Conceptualization Animals and plants live together. Plants need light and water to live. Some plants, like the beech tree, need a lot of water. Others like cactus need little water. As a result, beech tree grow in wet areas and cactus in dry ones. Different animals live in different environments too, for example, bears live in cool, wet places, and camels live in hot, dry places. The place where a plant or animal lives is called its habitat. Animals and plants that need the same amount of heat, light and water share the same habitat. For example, beech trees and bears share the same habitat; beech trees and camels do not
GRADE FOURTH MATTER ENERGY
Everything we see is made of matter. For example, the sun, the water, rocks, plants, the human body and the things we build are made of matter. This is why they have shape, weight, color and specific temperature. Since everything is made of matter, all things have mass, volume and density. Mass, volume and density are general properties of matter. We can observe and measure objects by comparing them with a fixed amount. This amount is called a unit. For example, if you want to know tall you are, you compare your height with a fixed measurement: the meter. CONCEPTUALIZATION When you measure mass, volume and density, you have the matter, so is important to compare everything to know it. Mass: is the amount of matter in an object. For example a steel nail has more matter than a steel pin. Weight is a measure of the earth`s force of attraction, or gravity, on an object. Weight depends of mass. Therefore, weight also tell us how much matter there is in an object. Volume: is the amount of the space an objects occupies, volume is measured in litters (l) and cubic meters (m3), but these are large units of measurement. So we often use smaller measurements, like cubic millimeters (mm3), centiliters (cl) and millimeters (ml). Density: density is the relationships between mass volume. If we compare two objects with the same mass but different volumes, the object with less volume is denser than the object with more volume. The states of matter. Matter can exist in three states: solid, liquid or gaseous. Pieces of iron or rock are examples of matter in the solid state. Water, oil and alcohol are matter in liquid state. Air is gaseous state. The solid state. Solid objects have constant volume and shape. Their shape and volume do not change when we put them in a different container. Other solids are elastic, like rubber. When we apply a force to them, their shape changes. When we stop applying the force, they change back to their original shape. Other solids are fragile, like glass. They brake easily. Other solid are plastic, like clay. When we apply a force of them, their shape change, when we stop applying the force, they maintain their new shape. The liquid state. Have a constant volume, but no shape of their own. Water in a bottle has the shape of the bottle. If we put the water of the bottle and into a jug, the shape of water changes, but the volume is the same. Liquids are fluids. This means that they can pass through any opening in a solid body. They can flow through tubes. The gaseous state. Gases change volume and shape. if we burst a balloon, the air that was inside the balloon expands into the whole room. Before we burst the balloon, the air had the shape of the balloon, now it has the shape and the volume of the room. CHANGES IN A MATTER: all the matter around us is constantly undergoing change. Matter can undergo two types of change, physical change and chemical change. When the matter undergoes a physical change, the substances that it is made up Stay the same. When matter undergoes a chemical change, the substances change into different substances. For example, when paper burns, is turns into ash. Paper and ash are different substances. Physical changes. These are examples of physical change. Change of state: for example, water changes state when it turns into steam as it boils.
Changes in shape: include the division of an object into smaller parts. For example we grind coffee beans into a powder to make coffee. Changes in size: size changes and fermentation are examples of chemical change. Combustion and fermentation. Combustion: occurs when we woods burn and fermentation occurs when the sugar turns in alcohol.
TYPES OF ENERGY
The focus of study in this unit is energy. Even thought the concept of energy is a complex one, many aspects can be understood by students at this age. Energy is necessary are constantly changing. Sometimes they change places, such as when an object falls to the ground. Sometimes the object`s shape or appearance changes, such as when a plant grows. Sometime an object undergoes a change of state, such as when butter melts. We can`t see the energy, we can only see the changes energy produces. Different forms of energy. There are many different forms of energy, such as kinetic, chemical, electrival an heat energy.
Movement produces kinetic energy, for example a ball has energy when we throw it. Food, batteries and fuel contain chemical energy. The body needs the energy in the batteries produces electricity. Fuels produce het and light when the burn. Electric current provides electrical energy. A bulb and a motor work with electrical energy. Heat energy is the energy hot objects transfer to cold objects. Light and sound are also forms of energy.
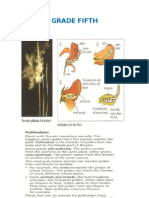
GRADE FIFTH MATTER ENERGY
Everything we see is made of matter. For example, the sun, the water, rocks, plants, the human body and the things we build are made of matter. This is why they have shape, weight, color and specific temperature. Since everything is made of matter, all things have mass, volume and density. Mass, volume and density are general properties of matter. We can observe and measure objects by comparing them with a fixed amount. This amount is called a unit. For example, if you want to know tall you are, you compare your height with a fixed measurement: the meter. CONCEPTUALIZATION When you measure mass, volume and density, you have the matter, so is important to compare everything to know it. Mass: is the amount of matter in an object. For example a steel nail has more matter than a steel pin. Weight is a measure of the earth`s force of attraction, or gravity, on an object. Weight depends of mass. Therefore, weight also tell us how much matter there is in an object. Volume: is the amount of the space an objects occupies, volume is measured in litters (l) and cubic meters (m3), but these are large units of measurement. So we often use smaller measurements, like cubic millimeters (mm3), centiliters (cl) and millimeters (ml). Density: density is the relationships between mass volume. If we compare two objects with the same mass but different volumes, the object with less volume is denser than the object with more volume. The states of matter. Matter can exist in three states: solid, liquid or gaseous. Pieces of iron or rock are examples of matter in the solid state. Water, oil and alcohol are matter in liquid state. Air is gaseous state. The solid state. Solid objects have constant volume and shape. Their shape and volume do not change when we put them in a different container. Other solids are elastic, like rubber. When we apply a force to them, their shape changes. When we stop applying the force, they change back to their original shape. Other solids are fragile, like glass. They brake easily. Other solid are plastic, like clay. When we apply a force of them, their shape change, when we stop applying the force, they maintain their new shape. The liquid state. Have a constant volume, but no shape of their own. Water in a bottle has the shape of the bottle. If we put the water of the bottle and into a jug, the shape of water changes, but the volume is the same. Liquids are fluids. This means that they can pass through any opening in a solid body. They can flow through tubes. The gaseous state. Gases change volume and shape. if we burst a balloon, the air that was inside the balloon expands into the whole room. Before we burst the balloon, the air had the shape of the balloon, now it has the shape and the volume of the room. CHANGES IN A MATTER: all the matter around us is constantly undergoing change. Matter can undergo two types of change, physical change and chemical change. When the matter undergoes a physical change, the substances that it is made up Stay the same.
When matter undergoes a chemical change, the substances change into different substances. For example, when paper burns, is turns into ash. Paper and ash are different substances. Physical changes. These are examples of physical change. Change of state: for example, water changes state when it turns into steam as it boils.
Changes in shape: include the division of an object into smaller parts. For example we grind coffee beans into a powder to make coffee. Changes in size: size changes and fermentation are examples of chemical change. Combustion and fermentation. Combustion: occurs when we woods burn and fermentation occurs when the sugar turns in alcohol.
TYPES OF ENERGY
The focus of study in this unit is energy. Even thought the concept of energy is a complex one, many aspects can be understood by students at this age. Energy is necessary are constantly changing. Sometimes they change places, such as when an object falls to the ground. Sometimes the object`s shape or appearance changes, such as when a plant grows. Sometime an object undergoes a change of state, such as when butter melts. We can`t see the energy, we can only see the changes energy produces. Different forms of energy. There are many different forms of energy, such as kinetic, chemical, electrival an heat energy.
Movement produces kinetic energy, for example a ball has energy when we throw it. Food, batteries and fuel contain chemical energy. The body needs the energy in the batteries produces electricity. Fuels produce het and light when the burn. Electric current provides electrical energy. A bulb and a motor work with electrical energy. Heat energy is the energy hot objects transfer to cold objects. Light and sound are also forms of energy.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Social Synthesis IIIDokumen6 halamanSocial Synthesis IIIlala0483Belum ada peringkat
- Homewrok Blog IIIDokumen2 halamanHomewrok Blog IIIlala0483Belum ada peringkat
- Jueves de PruebaDokumen10 halamanJueves de Pruebalala0483Belum ada peringkat
- Science Ii Term-Taller de Acompañamiento Parte IiDokumen3 halamanScience Ii Term-Taller de Acompañamiento Parte Iilala0483Belum ada peringkat
- Science Ii Term-Taller de AcompañamientoDokumen2 halamanScience Ii Term-Taller de Acompañamientolala0483Belum ada peringkat
- Math Ii Term-Taller de AcompañamientoDokumen3 halamanMath Ii Term-Taller de Acompañamientolala0483Belum ada peringkat
- Social Ii Term-Taller de AcompañamientoDokumen7 halamanSocial Ii Term-Taller de Acompañamientolala0483Belum ada peringkat
- English Synthesis IIDokumen19 halamanEnglish Synthesis IIlala0483Belum ada peringkat
- Taller de Acompañamiento Ii QuintoDokumen3 halamanTaller de Acompañamiento Ii Quintolala0483Belum ada peringkat
- Science Synthesis II 5Dokumen5 halamanScience Synthesis II 5lala0483Belum ada peringkat
- Science Synt II 4Dokumen6 halamanScience Synt II 4lala0483Belum ada peringkat
- Science Synthesis IIDokumen22 halamanScience Synthesis IIlala0483Belum ada peringkat
- Science and Social Synthesis IIDokumen28 halamanScience and Social Synthesis IIlala0483Belum ada peringkat
- Body Parts: Grade 1Dokumen2 halamanBody Parts: Grade 1lala0483Belum ada peringkat
- Homeworks BlogDokumen2 halamanHomeworks Bloglala0483Belum ada peringkat
- Homework Feb 20-25: Colegio Gimnasio Campestre San SebastiánDokumen3 halamanHomework Feb 20-25: Colegio Gimnasio Campestre San Sebastiánlala0483Belum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Aaryan International School Class-XII Subject-Biology (Chapter 2)Dokumen37 halamanAaryan International School Class-XII Subject-Biology (Chapter 2)Akshit Sharma VIII Diasy Roll no 6Belum ada peringkat
- Bio Enzyme2.0Dokumen17 halamanBio Enzyme2.0Mgps100% (3)
- 1 - Lecture - Seed Definition - 14.8.19Dokumen18 halaman1 - Lecture - Seed Definition - 14.8.19NAVEEN KUMAR100% (1)
- Lettuce: Planting Dates Types and VarietiesDokumen4 halamanLettuce: Planting Dates Types and VarietiesZineil BlackwoodBelum ada peringkat
- Training Manual On HDP PlacementDokumen18 halamanTraining Manual On HDP PlacementAklilu GullaBelum ada peringkat
- 7 Steps To Make A Living On A Small FarmDokumen41 halaman7 Steps To Make A Living On A Small FarmAndrés Suárez100% (10)
- Importation Into New Zealand of Processed Animal Feeds of Plant OriginDokumen26 halamanImportation Into New Zealand of Processed Animal Feeds of Plant Originfarizan rashid BBTBelum ada peringkat
- Elaeagnus Pungens - Thunb.: Search For PlantDokumen4 halamanElaeagnus Pungens - Thunb.: Search For PlantmarionunBelum ada peringkat
- Plant PropagationDokumen16 halamanPlant PropagationBhim JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- Vascular Epiphytes - General Biology and Related Biota (Cambridge Tropical Biology Series) (PDFDrive)Dokumen370 halamanVascular Epiphytes - General Biology and Related Biota (Cambridge Tropical Biology Series) (PDFDrive)CrystalBelum ada peringkat
- Primary Checkpoint - Science (0843) November 2008 Paper 1Dokumen16 halamanPrimary Checkpoint - Science (0843) November 2008 Paper 1Tumwesigye robert100% (1)
- Five Farming Technologies Tackle Climate-Change Threats - WSJDokumen7 halamanFive Farming Technologies Tackle Climate-Change Threats - WSJHumberto RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- Development Difuse Light StorageDokumen9 halamanDevelopment Difuse Light Storagekang_eebBelum ada peringkat
- Functions of Phosphorus in PlantsDokumen2 halamanFunctions of Phosphorus in Plantspemanr1914Belum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of The Coffee Fruit and BeanDokumen3 halamanAnatomy of The Coffee Fruit and BeanmileabadBelum ada peringkat
- In-Vitro Cultivation of PaphiopedilumDokumen15 halamanIn-Vitro Cultivation of PaphiopedilumRadman-Petkovski100% (1)
- AtonikDokumen162 halamanAtonikTawana BrownBelum ada peringkat
- Seed Dormancy and GerminationDokumen19 halamanSeed Dormancy and GerminationJoshua RomeroBelum ada peringkat
- Management Methods of Crop Diseases: Complete TermDokumen217 halamanManagement Methods of Crop Diseases: Complete TermJiru AlemayehuBelum ada peringkat
- 2ND Periodical Test in Science 6 With Tos KeyDokumen15 halaman2ND Periodical Test in Science 6 With Tos KeyNoemi Lyn CastilloBelum ada peringkat
- Visayas State University: Post Harvest and Seed Technology A. Seed TechnologyDokumen2 halamanVisayas State University: Post Harvest and Seed Technology A. Seed TechnologyFranz Joseph NayreBelum ada peringkat
- PETKUS Chemical BatchTreater C50Dokumen2 halamanPETKUS Chemical BatchTreater C50igbnsBelum ada peringkat
- The Value of Using Good SeedsDokumen2 halamanThe Value of Using Good SeedsalmorsBelum ada peringkat
- Test Reproduction Flowering Plants-AnswerDokumen11 halamanTest Reproduction Flowering Plants-AnsweressunBelum ada peringkat
- AsafoetidaDokumen12 halamanAsafoetidaSrivani GayathriBelum ada peringkat
- Manual For Mango ProductionDokumen9 halamanManual For Mango ProductionFrench Neco TupasBelum ada peringkat
- 01 RRL Rice Production Practices PDFDokumen64 halaman01 RRL Rice Production Practices PDFCepriano CentinoBelum ada peringkat
- Agrifarming - In-Growing Curry Leaf Plant From Cuttings Seed Kadi Patta PDFDokumen7 halamanAgrifarming - In-Growing Curry Leaf Plant From Cuttings Seed Kadi Patta PDFMoolam RaoBelum ada peringkat
- Sitophilus OryzaeDokumen4 halamanSitophilus OryzaevermaiprBelum ada peringkat
- Ipil IpilDokumen12 halamanIpil Ipilthechezzmazter100% (1)