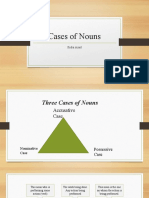
Nominative Case
Diunggah oleh
Liezel Mae FloresDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Nominative Case
Diunggah oleh
Liezel Mae FloresHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Nominative Case Nouns and pronouns in the nominative case, also called the subjective case, are used
as the subjects of clauses. A noun is said to be in the Nominative case if it is the subject of a verb. (SUBJECT is the person or the thing who or which carries out the action of the verb in the sentence)
Examples
Objective case (or Accusative case):
Nouns or pronouns are said to be in Objective cases if they are the direct objects of verbs or if they are the objects of preposition. (Direct object is the person or the thing upon whom or upon which the action of the verb is carried out).
Examples:
I met your sister. Your sister is in objective case. The vendors sell mangoes. Mangoes is in objective case. The book is on the table. Table is in objective case. It is object of the preposition on. This is one of my policies. Policies is in objective case. It is object of the preposition of.
Dative case
Mr. Ram is an intelligent boy. Mr. Ram is a proper noun in Nominative case. The painter paints the portraits. The painter is a common noun in Nominative case. I am buying vegetables for my family. I is a pronoun in Nominative case.
Possessive case (Genitive case):
A noun is said to be in possessive case, if it denotes possession or ownership. A noun or pronoun in the possessive case is governed by the noun that follows it.
Examples:
This is your pencil. (Your is in possessive case. It is our idea. Our is in possessive case. Johns sister has been hospitalized. Johns is in possessive case.
A noun is said to be in dative case if it is the Indirect object of the verb. (Indirect object of the verb is the noun for whom or for which the action of the verb is carried out). There should not be a preposition before the indirect object because in that case it will be the object of that preposition.
Examples:
The teacher gave the students few exercises. Students is in dative case. It is the indirect object of the verb give. The Postman brought me a letter. Me is in dative case. Get him a pen. Him is in dative case.
Vocative case:
A noun or a pronoun is said to be in Vocative case if it is used to call (or to get the attention of) a person or persons.
Examples:
Mr. Bill, students are waiting for you in the main hall. Mr. Bill is in vocative case. You there, stand up. You is in vocative case. Brother, a letter for you. Brother is in vocative case. Chairman, all the letters are posted two days ago. Chairman is in vocative case. An appositive is a noun, noun phrase, or noun clause which follows a noun or pronoun and renames or describes the noun or pronoun. A simple appositive is an epithet like Alexander the Great. Appositives are often set off by commas.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Webster's Word Power Essential Students' Companion: General Knowledge of the English LanguageDari EverandWebster's Word Power Essential Students' Companion: General Knowledge of the English LanguageBelum ada peringkat
- NOUN-CASES Is Another Topic Which Comes Under NOUN. The CASE of A Noun Tells UsDokumen4 halamanNOUN-CASES Is Another Topic Which Comes Under NOUN. The CASE of A Noun Tells UsMujahidBelum ada peringkat
- Noun CasesDokumen5 halamanNoun CasesAbbas EmadBelum ada peringkat
- Cases and Genders of Nouns PDFDokumen3 halamanCases and Genders of Nouns PDFKa ZheBelum ada peringkat
- Noun CasesDokumen3 halamanNoun CasesShehryar Khattak75% (4)
- Eight Parts of SpeechDokumen7 halamanEight Parts of SpeechAnji DudigamBelum ada peringkat
- Nouns: What Is A Noun?Dokumen4 halamanNouns: What Is A Noun?Jughead MithyBelum ada peringkat
- Definition: The Object Is The Person or Thing Affected by The ActionDokumen25 halamanDefinition: The Object Is The Person or Thing Affected by The Actionsudheesh_kalraBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of The Sentence, Object and Subject PronounDokumen11 halamanParts of The Sentence, Object and Subject PronounMåyi Muñoz ArayąBelum ada peringkat
- A01 Act#1 IBALEDokumen6 halamanA01 Act#1 IBALELester IbaleBelum ada peringkat
- What Is The Objective Case?Dokumen11 halamanWhat Is The Objective Case?Ikra MalikBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of SentenceDokumen11 halamanParts of SentenceUrwa Tul WosqaBelum ada peringkat
- Grammar - Parts of SpeechDokumen17 halamanGrammar - Parts of Speechcaptainnkumar1043100% (1)
- Engpro4 Reviewer MidtermDokumen27 halamanEngpro4 Reviewer MidtermAlyanna ManaloBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 1Dokumen34 halamanLesson 1OET STUDYMATERIALBelum ada peringkat
- Personal PronounsDokumen5 halamanPersonal PronounsmiszphoenixBelum ada peringkat
- Pronouns: Presented By: Jelly Ann Q. Fernan Jenny Rose A. Redove BSED English 2Dokumen26 halamanPronouns: Presented By: Jelly Ann Q. Fernan Jenny Rose A. Redove BSED English 2Jonalyn BatallerBelum ada peringkat
- Gen Ed - EnglishDokumen315 halamanGen Ed - EnglishJayson BoteBelum ada peringkat
- Cases of Nouns: Sidra AsadDokumen7 halamanCases of Nouns: Sidra AsadAbdul Haseeb ChBelum ada peringkat
- Verbs: Transitive and Intransitive VerbsDokumen8 halamanVerbs: Transitive and Intransitive VerbsOubiri HouriaBelum ada peringkat
- File 2Dokumen23 halamanFile 2PopBelum ada peringkat
- Nominative & Objective Case NounsDokumen4 halamanNominative & Objective Case NounsKim Jong In100% (1)
- PronounsDokumen32 halamanPronounsArianna NicoleBelum ada peringkat
- Noun, Pronoun, AdjectiveDokumen24 halamanNoun, Pronoun, AdjectiveZhiHui TayeBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of Speech I: Nouns and PronounsDokumen25 halamanParts of Speech I: Nouns and PronounsnatashavermaBelum ada peringkat
- Cases of PronounsDokumen2 halamanCases of Pronouns혜은Belum ada peringkat
- Guion Del ExamenDokumen2 halamanGuion Del ExamenJuan QuintanaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4Dokumen15 halamanUnit 4THEODOROS SORVATZIOTISBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 12: Noun Clauses: Definition of "Clause"Dokumen8 halamanChapter 12: Noun Clauses: Definition of "Clause"Nga ThuyBelum ada peringkat
- Before Studying, The Following Words Should Be Aware Of:: ? ? How To Build Adjective Clause: Two Simple Sentences Are Combined: ExampleDokumen25 halamanBefore Studying, The Following Words Should Be Aware Of:: ? ? How To Build Adjective Clause: Two Simple Sentences Are Combined: ExamplesjkhappsBelum ada peringkat
- Demonstrative PronounsDokumen3 halamanDemonstrative PronounsAliana SyakirahhBelum ada peringkat
- BasicDokumen97 halamanBasicViviana Moreno NavarroBelum ada peringkat
- M2 PronounDokumen57 halamanM2 PronounR BeBelum ada peringkat
- Pronoun 2.0Dokumen10 halamanPronoun 2.0Norielyn DamasoBelum ada peringkat
- English 1Dokumen43 halamanEnglish 1Zenia GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- 8parts of SpeechDokumen23 halaman8parts of SpeechSophia AbatayBelum ada peringkat
- PronounsDokumen4 halamanPronounschilufyampundu03Belum ada peringkat
- Accusative and DativeDokumen12 halamanAccusative and DativeketapBelum ada peringkat
- Cases of Nouns and PronounsDokumen4 halamanCases of Nouns and PronounsSal TellezBelum ada peringkat
- Intermediate C Noun and Noun PhraseDokumen9 halamanIntermediate C Noun and Noun PhraseFauss ForeverBelum ada peringkat
- ASM Inglés Sem 17Dokumen9 halamanASM Inglés Sem 17E.F C.L.Belum ada peringkat
- Adjective ClausesDokumen16 halamanAdjective ClausesEstefane Abigail OyBelum ada peringkat
- ENGLISH Subject Object PredicateDokumen50 halamanENGLISH Subject Object PredicateLauriz Dillumas Machon100% (1)
- Personal Pronoun Is The Pronoun Used To Stand For The NounDokumen41 halamanPersonal Pronoun Is The Pronoun Used To Stand For The NounHaris HarahapBelum ada peringkat
- Structures of Eng FinalsDokumen27 halamanStructures of Eng FinalsLeirhana VeilaBelum ada peringkat
- PronounsDokumen4 halamanPronounsMecislavs GrigorcuksBelum ada peringkat
- PRONOUNS DefinitionDokumen8 halamanPRONOUNS Definitionfliptong1973100% (2)
- English Proficiency: Different Types of PronounsDokumen10 halamanEnglish Proficiency: Different Types of Pronounschampaigne fiona sabalzaBelum ada peringkat
- Cases of Pronouns Special Problems of PronounsDokumen26 halamanCases of Pronouns Special Problems of PronounsReshnee TabañagBelum ada peringkat
- Lets Learn PronounsDokumen3 halamanLets Learn PronounsAllen AdrienBelum ada peringkat
- GRAMMARDokumen19 halamanGRAMMARcheng09Belum ada peringkat
- University of Technology - English - Language - First - Year - 2018 - 2019Dokumen47 halamanUniversity of Technology - English - Language - First - Year - 2018 - 2019Sajad HayderBelum ada peringkat
- Eng 100 Reviewer PrelimDokumen16 halamanEng 100 Reviewer Prelimjamille consingBelum ada peringkat
- Nouns and Prnouns Written Report - Structure of English (Group 2)Dokumen13 halamanNouns and Prnouns Written Report - Structure of English (Group 2)MatthewUrielBorcaAplacaBelum ada peringkat
- M7-Ugtv - PPT - Bahasa Inggris 1 Dan Tata Bahasa 1Dokumen25 halamanM7-Ugtv - PPT - Bahasa Inggris 1 Dan Tata Bahasa 1Aline TriciaBelum ada peringkat
- Subject Pronoun: (Subjective Case)Dokumen5 halamanSubject Pronoun: (Subjective Case)Arun KumarBelum ada peringkat
- PARTS OF SPEECH ProjectDokumen13 halamanPARTS OF SPEECH ProjectSãéèďBelum ada peringkat
- Bahasa Inggris 1: Prodi D3 Manajemen Informatika Fakultas Ilmu Terapan Universitas TelkomDokumen31 halamanBahasa Inggris 1: Prodi D3 Manajemen Informatika Fakultas Ilmu Terapan Universitas TelkomAnik DarwatiBelum ada peringkat
- Nouns: Nouns Are Words That Indicate A Person, Place, or ThingDokumen3 halamanNouns: Nouns Are Words That Indicate A Person, Place, or ThingTRONG DANG QUANGBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A PronounDokumen9 halamanWhat Is A PronounM Bisri MustofaBelum ada peringkat
- HousekeepingDokumen2 halamanHousekeepingLiezel Mae FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Quality Culture: Changing Hearts, Minds, and AttitudesDokumen18 halamanQuality Culture: Changing Hearts, Minds, and AttitudesLiezel Mae FloresBelum ada peringkat
- AcknowledgeDokumen1 halamanAcknowledgeLiezel Mae FloresBelum ada peringkat
- BSPDokumen2 halamanBSPLiezel Mae FloresBelum ada peringkat
- ECONOMICSDokumen113 halamanECONOMICSLiezel Mae FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Pre ColonialDokumen11 halamanPre Colonialkathyrin100% (2)
- Table of Content1Dokumen10 halamanTable of Content1Liezel Mae FloresBelum ada peringkat
- SeizureDokumen7 halamanSeizureLiezel Mae FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Management or Sales TraineesDokumen17 halamanManagement or Sales TraineesLiezel Mae FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Incentives As A Motivational Tool For The Employees of ChowkingDokumen1 halamanIncentives As A Motivational Tool For The Employees of ChowkingLiezel Mae FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Binary Number and Its F (X)Dokumen14 halamanBinary Number and Its F (X)Mhaykan's DaughterBelum ada peringkat
- SeizureDokumen7 halamanSeizureLiezel Mae FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 12 - Using English Grammar by Azar PDFDokumen28 halamanChap 12 - Using English Grammar by Azar PDFAbelardo Hutagalung0% (1)
- German ArticlesDokumen4 halamanGerman ArticlesNoman0% (1)
- Figure of SpeechDokumen12 halamanFigure of SpeechShirley Espeña PadolinaBelum ada peringkat
- Ordinea Cuvintelor in Limba EnglezaDokumen4 halamanOrdinea Cuvintelor in Limba EnglezaLorealBelum ada peringkat
- Word Order 1Dokumen30 halamanWord Order 1AgungBelum ada peringkat
- My ResearchDokumen103 halamanMy Researchmusic2850Belum ada peringkat
- 1988 Sass B The Genesis of The AlphabetDokumen5 halaman1988 Sass B The Genesis of The AlphabetencarnichiBelum ada peringkat
- The Old English Period (449-1100)Dokumen1 halamanThe Old English Period (449-1100)byron_castro_22Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan in English-Cases of Personal PronounsDokumen6 halamanLesson Plan in English-Cases of Personal PronounsSheyn Benito100% (2)
- Subject Pronouns PowerPoint NotesDokumen18 halamanSubject Pronouns PowerPoint NotesThena Axiotis100% (1)
- English 101: Grammar & Reading 2008Dokumen71 halamanEnglish 101: Grammar & Reading 2008A. AkbariBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabification in ArabicDokumen22 halamanSyllabification in ArabicAbdelaadim BidaouiBelum ada peringkat
- Present Simple - Present ProgressiveDokumen32 halamanPresent Simple - Present ProgressiveJéssica Katherine Santoyo VillegasBelum ada peringkat
- An From Oxford Student Guide To Indonesian GrammarDokumen5 halamanAn From Oxford Student Guide To Indonesian GrammarHenda SBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Bing PeminatanDokumen7 halamanTugas Bing PeminatanGhina SalsabillaBelum ada peringkat
- Morphology (Linguistics) : HistoryDokumen6 halamanMorphology (Linguistics) : HistoryBrizZeida LópezBelum ada peringkat
- VerbsDokumen56 halamanVerbsAditya PabbarajuBelum ada peringkat
- French Notes Sem5Dokumen35 halamanFrench Notes Sem5akshitBelum ada peringkat
- Summary Language Change 206-218Dokumen4 halamanSummary Language Change 206-218Saya KenzaBelum ada peringkat
- Linguistic Phonetics and PhonologyDokumen3 halamanLinguistic Phonetics and PhonologyShane Lex De JesusBelum ada peringkat
- English Language Society Yearly Activities 2018 by Teacher FieraDokumen39 halamanEnglish Language Society Yearly Activities 2018 by Teacher FieraSuhaini Abidin100% (1)
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDokumen3 halamanDirect and Indirect SpeechAdinda DestriBelum ada peringkat
- Gluck Isha EthimologyDokumen7 halamanGluck Isha EthimologylynnsimhaserfatyhakimBelum ada peringkat
- Languages - (eBook-PDF) Greek Language - AdjectivesDokumen8 halamanLanguages - (eBook-PDF) Greek Language - Adjectivesdanutza277Belum ada peringkat
- The Morpho-Syntax of Sentential Negation in Rural Jordanian ArabicDokumen11 halamanThe Morpho-Syntax of Sentential Negation in Rural Jordanian ArabicJOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN LINGUISTICSBelum ada peringkat
- Indirect Questions at Work + QuizDokumen5 halamanIndirect Questions at Work + QuizManuel PargaBelum ada peringkat
- Tema 21Dokumen6 halamanTema 21Jose S HerediaBelum ada peringkat
- Su YuYing J 201211 PHD ThesisDokumen193 halamanSu YuYing J 201211 PHD ThesisJenna StevensBelum ada peringkat
- (Jakob Wisse) Ethos and Pathos From Aristotle TO CICERONDokumen384 halaman(Jakob Wisse) Ethos and Pathos From Aristotle TO CICERONLetícia Pimenta50% (2)
- Kinyarwanda Lessons - Betty Ellen Cox - Gakuba FaustinDokumen133 halamanKinyarwanda Lessons - Betty Ellen Cox - Gakuba Faustinunfo100% (3)
- Summary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDari EverandSummary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (4)
- Stonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonDari EverandStonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (21)
- Body Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.Dari EverandBody Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (81)
- Writing to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllDari EverandWriting to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (83)
- Wordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageDari EverandWordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguagePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (429)
- How Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideDari EverandHow Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideBelum ada peringkat
- 1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundDari Everand1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (13)
- How to Read a Book: The Classic Guide to Intelligent ReadingDari EverandHow to Read a Book: The Classic Guide to Intelligent ReadingPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (26)
- Surrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandSurrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- The Practice of Poetry: Writing Exercises From Poets Who TeachDari EverandThe Practice of Poetry: Writing Exercises From Poets Who TeachBelum ada peringkat
- Writing Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsDari EverandWriting Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsBelum ada peringkat
- Idioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsDari EverandIdioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (7)
- The Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageDari EverandThe Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguagePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (916)
- Learn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachDari EverandLearn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (81)
- How To Get Your Point Across In 30 Seconds Or LessDari EverandHow To Get Your Point Across In 30 Seconds Or LessPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (308)
- Abominations: Selected Essays from a Career of Courting Self-DestructionDari EverandAbominations: Selected Essays from a Career of Courting Self-DestructionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Spanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesDari EverandSpanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Learn German with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: German Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachDari EverandLearn German with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: German Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (151)
- Learn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachDari EverandLearn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (15)
- Win Every Argument: The Art of Debating, Persuading, and Public SpeakingDari EverandWin Every Argument: The Art of Debating, Persuading, and Public SpeakingPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (78)
- The Art of Writing: Four Principles for Great Writing that Everyone Needs to KnowDari EverandThe Art of Writing: Four Principles for Great Writing that Everyone Needs to KnowPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (21)
- Summary: Read People Like a Book: How to Analyze, Understand, and Predict People’s Emotions, Thoughts, Intentions, and Behaviors: How to Be More Likable and Charismatic, Book 9 By Patrick King: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDari EverandSummary: Read People Like a Book: How to Analyze, Understand, and Predict People’s Emotions, Thoughts, Intentions, and Behaviors: How to Be More Likable and Charismatic, Book 9 By Patrick King: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisBelum ada peringkat
- The Emotional Craft of Fiction: How to Write the Story Beneath the SurfaceDari EverandThe Emotional Craft of Fiction: How to Write the Story Beneath the SurfacePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (35)
- How to Write a Sentence: And How to Read OneDari EverandHow to Write a Sentence: And How to Read OnePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (115)