Manual Wireless
Diunggah oleh
azszahDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Manual Wireless
Diunggah oleh
azszahHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
WEP Key Configuration for Fedora / RedHatYour WEP key can be temporarily added to your NIC configuration from
the command line, using the iwconfig command. Be su re that there are no colons or any other non-hexadecimal characters between the characters of the key. There should be ten characters in total: iwconfig eth0 key 967136deac The same rules (no colons or non-hexadecimals between the ten total characters) apply when using the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts files to add encryption: # # File: ifcfg-eth0 # DEVICE=eth0 IPADDR=192.168.1.100 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 ONBOOT=yes BOOTPROTO=static TYPE=Wireless MODE=Managed ESSID=homenet KEY=967136deac WEP Key Configuration for Debian / UbuntuIn Debian / Ubuntu systems configuratio n requires the addition of a valid wireless-key parameter, alongside the wireles s-essid parameter, in the /etc/network/interfaces file. # # File: /etc/network/interfaces # # The primary network interface auto eth1 iface eth1 inet static address 192.168.1.100 netmask 255.255.255.0 wireless-key 967136deac wireless-essid homenet In this example our WEP key of 967136deac and the ESSID of homenet have been use d and will become utilized once the eth1 wireless interface is activated. The iwlist CommandThe iwlist command can provide get further information related to not just the NIC, but the entire network, including the number of available frequency channels, the range of possible data rates, and the signal strength. T his example uses the command to verify the encryption key being used by the NIC, which can be very helpful in troubleshooting security related difficulties on y our network. [root@bigboy tmp]# iwlist key ... ... eth0 2 key sizes : 40, 104bits 4 keys available : [1]: 9671-36DE-AC (40 bits) [2]: off [3]: off [4]: off
Current Transmit Key: [1] Security mode:open ... ... [root@bigboy tmp]# ShareFacebookTwitterDeliciousDiggGoogle BookmarksGoogle BuzzMySpaceStumbleUponRe dditMessengerVodpodYahoo BookmarksBeboMister-WongWordPressGoogle ReaderOrkutXING EvernoteNetvibes ShareStrandsPosterousBusiness ExchangeArtoTipdSmakNewsPlurkAIMY ahoo MessengerIdenti.caMozillacaBlogger PostTypePad PostBox.netNetlogTechnorati FavoritesCiteULikeJumptagsHemidemiFunPInstapaperPhoneFavsXerpiNetvouzWinkDiigoBi bSonomyBlogMarksTailrankStartAidKledyKhabbrMeneameYoolinkBookmarks.frTechnotizie NewsVineMultiplyFriendFeedPlaxo PulsePingSquidooProtopage BookmarksBlinklistFave sYiGGWebnewsSegnaloPushaYouMobSlashdotFarkAllvoicesJamespotImera BrazilTwiddlaLi nkaGoGounalogHuggDiglogNowPublicTumblrLiveJournalCurrentHelloTxtSpurlYampleOnevi ewLinkatopiaSimpyLinkedInBuddyMarksAsk.com MyStuffViadeoMapleWistsConnoteaBackfl ipMyLinkVaultSiteJotSphinnDZoneCare2 NewsHyvesSphereBitty BrowserGabbrSymbaloo F eedsTagzaFolkdNewsTrustAmazon Wish ListPrintFriendlyRead It LaterTuentiEmailRedi ff MyPageGoogle GmailYahoo MailHotmailAOL MailAny email AddToAny by Lockerz Ubuntu Linux Tutorials,Howtos,Tips & News | Oneiric,Natty,Maverick HomeForum Free Ubuntu E-BooksSubmit ArticleTop PostsUbuntu HostingContactAboutSubscribeSit emapPrivacy PolicySearchSponsor Ubuntu Server GUI Categories Backup Free Books General Monitoring Networking News Package Mgmt Security Server Sponsor Login/Register Register Log in Archives Select Month November 2011 October 2011 September 2011 August 2011 July 2011 Ju ne 2011 May 2011 April 2011 March 2011 February 2011 January 2011 December 2010 November 2010 October 2010 September 2010 August 2010 July 2010 June 2010 May 20 10 April 2010 March 2010 February 2010 January 2010 December 2009 November 2009 October 2009 September 2009 August 2009 July 2009 June 2009 May 2009 April 2009 March 2009 February 2009 January 2009 December 2008 November 2008 October 2008 S eptember 2008 August 2008 July 2008 June 2008 May 2008 April 2008 March 2008 Feb ruary 2008 January 2008 December 2007 November 2007 October 2007 September 2007 August 2007 July 2007 June 2007 May 2007 April 2007 March 2007 February 2007 Jan uary 2007 December 2006 How To Troubleshoot Wireless Network Connection in Ubuntu March 29, 2008 Networking Email This Post Share22If you're new here, you may wan t to subscribe to my RSS feed and if you have questions related to your ubuntu s ystem post question to our forums. Thanks for visiting! {lang: 'en-GB'}
In setting up their wireless connection for the first time, Im discovering many individuals having problems connecting through Network Manager or other GUI wire less connection tools. In fact my Network Manager is intermittently buggy, conne cting sometimes and not others. This guide benefits all users in case the GUI to ols are not working, and is useful for testing a wireless connection during init ial installation of wireless drivers since it provides for good debugging output . Unencrypted/ WEP / WPA connections will be covered in this guide Pre-requisites 1. Properly installed network driver -- This guide can be used to troubleshoot d river installation to see if it is properly functioning 2. The ESSID of your router must be broadcasted and not hidden 3. Knowlege of your wireless cards driver (please see Prerequisite #4 to determi ne driver). Those using the r8187/r818x driver please see the end of the guide 4. Knowledge of your wireless cards Interface Name - The user must know the prope r interface of the wireless connection (wlan0, eth1, rausb1, etc). To discover t his information, at command line type lshw -C network There may be multiple interfaces listed, however look under the section appropri ate to your wireless device for the line labeled logical name. Here is an exampl e *-network description: Wireless interface product: BCM4306 802.11b/g Wireless LAN Controller vendor: Broadcom Corporation physical id: 0 bus info: pci@06:00.0 logical name: wlan0 version: 03 serial: 00:12:17:35:17:10 width: 32 bits clock: 33MHz capabilities: bus_master cap_list ethernet physical wireless configuration: broadcast=yes driver=ndiswrapper+lsbcmnds driverversion=1.48rc1+C isco-Linksys ,LLC.,02/1 ip=192.168.1.101 latency=64 multicast=yes wireless=IEEE 802.11g resources: iomemory:3c000000-3c001fff irq:11 In the example above the interface name is wlan0. I will refer to the interface name throughout the rest of this guide as [interface]. For people first setting up their connection, please note that the above also li sts the driver used for the network card. In the example above, the driver used is ndiswrapper. If your network device comes back UNCLAIMED or there is no drive r listed, then you have not correctly installed the driver for your device. You must review the procedures for installation of your wireless driver. For those wanting to use static IP addresses, please see section at bottom of gu ide regarding configuration for static IP addresses Unencrypted Connection
All commands typed at the command line: sudo sudo sudo sudo sudo sudo ifconfig dhclient ifconfig iwconfig iwconfig dhclient [interface] down -r [interface] [interface] up [interface] essid ESSID_IN_QUOTES [interface] mode Managed [interface]
WEP Connection You must have either your 64bit or 128 bit HEX Key or the ASCII Equivalent of yo ur HEX Key. sudo ifconfig [interface] down sudo dhclient -r [interface] sudo ifconfig [interface] up sudo iwconfig [interface] essid ESSID_IN_QUOTES sudo iwconfig [interface] key HEX_KEY <<<-------- If using ASCII Equivalent, thi s is s:ASCII_KEY (please make note of the prefix s:) ****Additional Comand that may be needed -- sudo iwconfig [interface] key open < <<----See note below sudo iwconfig [interface] mode Managed sudo dhclient [interface] ***The security mode may be open or restricted, and its meaning depends on the c ard used. With most cards, in open mode no authentication is used and the card m ay also accept non-encrypted sessions, whereas in restricted mode only encrypted sessions are accepted and the card will use authentication if available. WEP Key and special characters If your WEP key has some special characters in it. You might receive the error m essage $ sudo iwconfig eth0 key s:KGhSRaS{G!#[ sudo iwconfig eth0 key s:KG"hSRaS{Gsudo iwconfig eth0 key s:KG"hSRaS{G[ ..... $sudo dhclient eth0 Sending on Socket/fallback DHCPDISCOVER on eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval DHCPDISCOVER on eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval DHCPDISCOVER on eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval DHCPDISCOVER on eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval No DHCPOFFERS received. No working leases in persistent database - sleeping.
4 10 14 3
You need to escape the special characters with a \ and it works $sudo iwconfig eth0 key s:KG\"hSRaS\{G\!\#\[ WPA Connection - WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK For uses of Ra-based chipsets: rt61, rt73, rt2500 please skip directly to the WP A Section entitled WPA with Ra based chipsets Requirements: In most cases the wpa_supplicant package is required in order to c
onnect via WPA. If you have a working ethernet or unencrypted/WEP wireless conne ction, this package may be installed via: sudo aptitude install wpasupplicant If only wireless is available, I would recommend that an unencrypted connection first by established and tested first before directly proceeding to make a WPA c onnection. WPA adds another layer of complexity. Creation of /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf file At command line: gksu gedit /etc/wpa_supplicant.confInside the file add the following for WPA(1): ap_scan=1 ctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant network={ ssid="ESSID_IN_QUOTES" scan_ssid=0 proto=WPA key_mgmt=WPA-PSK psk="ASCII PSK Password in Quotes" pairwise=TKIP group=TKIP } For WPA(2) ctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant network={ ssid="ESSID_IN_QUOTES" psk="ASCII PSK Password in Quotes" key_mgmt=WPA-PSK proto=RSN pairwise=CCMP } ***Word of caution -- In some cases I have found WPA(2) to have different settin gs than the above. Some Broadcom cards use the pairwise/group TKIP cipher for WP A2 rather than CCMP. I would suggest all initially use WPA(1) and then later con vert to WPA2 since some variations to the above may be needed Connect via command line sudo ifconfig [interface] down sudo dhclient -r [interface] sudo wpa_supplicant -w -D[****see footer below***] -i[interface] -c/etc/wpa_supp licant.conf -dd sudo ifconfig [interface] up sudo iwconfig [interface] mode Managed sudo dhclient [interface] ***footer The value listed here is dependent on the driver you have installed. Typing man wpa_supplicant at command line will give you the full gamut of choices however a quick reference ndiswrapper=wext (use wext and not ndiswrapper despite what documentation might
suggest) ath_pci = madwifi ipw2100/2200=ipw WPA with Ra Based Chipsets Ra cards do not require the wpa_supplicant package to use WPA. Here is how to co nnect from the command line with these cards WPA(1) sudo sudo sudo sudo sudo sudo sudo sudo ifconfig [interface] down dhclient -r [interface] ifconfig [interface] up iwconfig [inteface] essid ESSID_IN_QUOTES iwpriv [interface] set AuthMode=WPAPSK iwpriv [interface] set EncrypType=TKIP iwpriv [interface] set WPAPSK=YOUR_WPA_PSK_KEY dhclient [interface]
A successful connection in all cases will results in this user@computer:~$ sudo dhclient wlan0 There is already a pid file /var/run/dhclient.pid with pid 134993416 Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Client V3.0.4 Copyright 2004-2006 Internet Systems Consortium. All rights reserved. For info, please visit http://www.isc.org/sw/dhcp/ Listening on LPF/wlan0/00:12:17:35:17:10 Sending on LPF/wlan0/00:12:17:35:17:10 Sending on Socket/fallback DHCPDISCOVER on wlan0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 4 DHCPDISCOVER on wlan0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 7 DHCPDISCOVER on wlan0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 7 DHCPOFFER from 192.168.1.1 DHCPREQUEST on wlan0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 DHCPACK from 192.168.1.1 bound to 192.168.1.101 -- renewal in 299133 seconds. The computer in this example has received an IP address of 192.168.1.101 Users of RTL 8180, RTL8185, RTL 8187 using the built in native r8187 / r818x dri vers By default the r8187 and r818x drivers are blacklisted due to a know bug. These drivers are usuable however with a twist to the above methods If you want to try using these drivers, please load the kernel modules: sudo modprobe r818x sudo modprobe r8187 These drivers require a bogus or extra letter be suffixed to the essid name in o rder for these drivers to work For example if your are trying to connect to a router with essid=Router, at he c ommand line you would type essid=Routerx. Notice the extra x or bogus character. I have provided an example using the unencrypted connection procedure below, ho wever this extra character needs to be used if attempting to connect to all netw
ork types (unencrypted/ WEP / WPA) sudo sudo sudo sudo sudo sudo ifconfig dhclient ifconfig iwconfig iwconfig dhclient [interface] down -r [interface] [interface] up [interface] essid Routerx [interface] mode Managed [interface]
If these drivers work for you, and you would like these drivers to load automati cally at startup for you, avoiding to have to type sudo modprobe everytime, plea se edit your blacklist file gksu gedit /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist And comment out (or prefix the following lines with a # sign). You want the foll owing lines to appear as below: #blacklist r8187 #blacklist r818x Static IP Addresses Im going to give an example of how to configure your interface using a static IP address using an unencrypted wireless connection. The two lines highlighted bel ow however can be used with WEP and WPA connections. Values in italics must be c ustomized to meet your particular situation sudo sudo sudo sudo sudo sudo sudo ifconfig [interface] down dhclient -r [interface] ifconfig [interface] 192.168.1.100 netmask 255.255.255.0 up route add default gw 192.168.1.1 iwconfig [interface] essid ESSID_IN_QUOTES iwconfig [interface] mode Managed dhclient [interface]
If when using static IP addresses you are getting a problem with name resolution , you will have to specifiy specific dns (domain name servers) in order to trans late URLs to IP addresses. Unfortunately there is not an easy way to configure t his from the command line. This requires that you edit the /etc/resolv.conf file and manually enter the domain name server(s) you want to use. In many cases use rs can specifiy their router, their internet service providers dns servers, or u se opendns (or use all three). Please note that changes made to the /etc/resolv. conf file will not be retained between reboots. To make the nameservers permanen t, the /etc/dhcp3/dhclient.conf file needs to be edited sudo gedit /etc/resolv.confand add the nameservers you want to use, one to a lin e, in the following format. nameserver [nameserver] You can add as many as you want but most isps normally provide two (primary and secondary). Useful Wireless connection Commands ifconfig - lists IP address (similar to ipconfig in Windows) iwlist scan - shows wireless networks that are available in the area along with basic encryption information
lshw -C network - Shows interface and driver associated with each networking dev ice lspci -nn - Shows hardware connected to the pci bus lsusb - Shows USB connected hardware lshw -C usb - Additional info on USB related hardware (good for USB dongles) cat /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist - List modules that will not be loaded by the Oper ating System at boot time lsmod - lists currently loaded kernel modules. (Example usage - lsmod | grep ndi swrapper) route -n - Lists kernel IP routing table -- Good for troubleshooting problems wi th the gateway (netstat -rn = equivalent command) sudo route add default gw 192.168.1.1 - Example of how to set the default gatewa y to 192.168.1.1 sudo route del default gw 192.168.1.1 - Example of how to delete the default gat eway setting sudo modprobe ***** - Loads the kernel module **** . (Example usage - sudo modpr obe ndiswrapper, sudo modprobe r818x, sudo modprobe ath_pci) sudo modprobe -r **** - Unloades the kernel module ****. (Example usage - sudo m odprobe -r ndiswrapper) sudo ifup/ifdown - Brings up/down the interface and clears the routing table for the specified interface sudo ifconfig up/down - Brings up/down the interface for the specified interface sudo dhclient - Request IP address from DNS server for specified interface sudo dhclient -r - Release IP address associated with specified interface sudo iptables -L - Lists firewall rules dmesg | more - Lists boot log -- good for troubleshooting problems with modules/ drivers not being loaded uname -r - Displays kernel version /etc/iftab (Feisty and pre-releases (Edgy, etc)) - /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persiste nt-net.rules (Gutsy) - File which assigns logical names (eth0, wlan0, etc) to MA C addresses cat /etc/resolv.conf - Lists DNS servers associated with network connections (Ne twork Manager) /etc/dhcp3/dhclient.conf - File which sets or modifies dns (domain name servers) settings Credit goes kevdog
Related posts WiFi Radar - Simple tool to Manage Wireless Profiles (23) Wicd - Wired and Wireless Network manager for Ubuntu (35) Update IP addresses at dynamic DNS services Using ddclient (17) UFW (Uncomplicated firewall) For Ubuntu Hardy (25) Ubuntu Networking Configuration Using Graphical Tool (21) Ubuntu Networking Configuration Using Command Line (119) Ubuntu Network Troubleshooting Tips (3) How to install ATI Video Card in you linux SystemHow to get a Canon all-in-one p rinter working with Ubuntu 38 Comments to How To Troubleshoot Wireless Network Con nection in Ubuntu Ashwin Shah says: July 24, 2010 at 12:22 am If the machine does not connect wirelessly, you need to perform a network servic e restart and make sure that you are logged in via root [Reply] 1nS3cur3-I7 says: August 5, 2010 at 3:02 pm Ashwin Shah You may try doing that one time to configure from GUI, but always logging in as root is a security and a stability risk. It tends to slowly screw up xserver, an d allows all kinds of other fun nasty things to happen. As a security consultant , I had to say that this is horrible advice without clarification. [Reply] Kelso says: August 5, 2010 at 8:33 pm Thank you! This saved me so much time also avoided looking like an idiot after re formatting the wifes computer to ubuntu [Reply] William says: December 15, 2010 at 3:38 am Thank you sooo much this saved me! [Reply] Chris Calle says: January 15, 2011 at 1:26 am *FIX* For setting a STATIC IP: DO NOT include the sudo dhclient [interface] command located at the end because it will automatically issue you an IP Not the one you are trying to set. Hope this helps [Reply] Chris Calle says: January 15, 2011 at 1:54 am Assuming you drivers and hardware are working --This should make life easier. --Type this:
$sudo nano /usr/bin/staticweb.sh --ENTER LINES w/ appropriate info: sudo ifconfig [interface] down sudo dhclient -r [interface] sudo ifconfig [interface] [static IP] netmask 255.255.255.0 up sudo route add default gw 192.168.1.1 sudo iwconfig [interface] essid ESSID_IN_QUOTES sudo iwconfig [interface] mode Managed sleep 10 ping -c 3 google.com ifconfig [interface] --SAVE FILE and EXIT EDITOR --Make sure the file is in /usr/bin/ $sudo chmod a+x /usr/bin/staticweb.sh $cd ~ --LOCATE AND EDIT ALIAS FILE: $ls -a --EITHER .bashrc or .bash_aliases IS THE FOLDER $sudo nano .bashrc --LOOK FOR ALIASES: example: alias NAME=command --ADD YOUR ALIAS: alias staticweb=staticweb.sh --SAVE AND EXIT EDITOR $. .bashrc DONE! With all that you should be able to just type staticweb (without the quotes) into the command line and it will trigger the static-ip shell script you just wrote a nd do all the work in one single command. The end of the script will ping google.com and display the status of your networ k just to make sure you are connected to the web and that you IP address is what it should be. If your network connection is local only, just change the ping command from googl e.com to your gateway (192.168.1.1 in most cases) [Reply] ihaq2 says: October 2, 2011 at 12:56 pm ok, i installed last version of ubuntu yesterday and wireless worked ok. today i t doesn;t work at all - the system doesnt find any connections and there are at l east 10 around. when i type lshw -C network it returns PCI (sysfs) What should I do to wifi again? [Reply]
Jack says: October 8, 2011 at 3:47 pm I remove STA wireless driver, and i can connect internet. [Reply] Older commentsLeave a Reply Click here to cancel reply. Name (required) Mail (will not be published) (required) Website
Notify me of followup comments via e-mail
Click to cancel reply How to install ATI Video Card in you linux SystemHow to get a Canon all-in-one p rinter working with Ubuntu Free Ubuntu E-Book A Complete Beginner's Manual for Ubuntu 10.10 (Maverick Meerkat) Getting Started with Ubuntu 10.10 (Maverick Meerkat) is a comprehensive beginner s guide for the Ubuntu operating system. Download Now RSS Feed UbuntuGeek on Twitter
Mobile Antivirus Web Hosting Data Recovery HP Coupons Codes Data recovery RAID Recovery Support Ubuntugeek Amount $: 5.00 10.00 25.00 50.00 100.00 Website(Optional):
Favourite Sites My Daily Tech Tips Windows Reference Debian Admin DebianHelp
SuSe Linux Tutorials Ubuntux Tuxmachines Unixmen Arabic ubuntu support Recent entries How to set gvim as default text editor instead of gedit on ubuntu 11.10 Linux Essentials - Restart the Desktop Environment without closing any windows Purgeconfig A safer way to reset configuration files How to install freetuxtv on ubuntu 11.10 using PPA Rodent - Advanced User file manager for Linux systems Recent comments Lou: I was in the same boat. Change the file p0key: @AndoniCipi - Thank you for the instruct joe: Thanks! That really helped me. :) Al An: Doesnt work with IBM SK-8809 hotkey set Al An: Doesn't work with IBM SK-8809 hotkey set Popular posts Speed Up Firefox web browser (224) iPhone Tethering on Ubuntu 9.10 (Karmic) (175) Send and Receive Your Hotmail messages through Evolution (156) How to Install Java Runtime Environment (JRE) in Ubuntu (151) Atheros AR5007 wireless with madwifi on Ubuntu 8.04 (Hardy heron) (144) 2006-2011 All rights reserved. Ubuntu Geek${sspl}${SSPL}
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Labor Rate For Ducting WorksDokumen1 halamanLabor Rate For Ducting Worksbhh0% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Kromrey Converter Plans r1 - DMR10Dokumen16 halamanKromrey Converter Plans r1 - DMR10bertosam100% (3)
- Ashrae Cooling and Heating Load Calculation ManualDokumen2 halamanAshrae Cooling and Heating Load Calculation ManualTorus Engenharia0% (1)
- Math G7 - Probability and StatisticsDokumen29 halamanMath G7 - Probability and StatisticsLeigh YahBelum ada peringkat
- Well Control: BOP Accumulator Unit (Koomey Unit)Dokumen12 halamanWell Control: BOP Accumulator Unit (Koomey Unit)faraj100% (1)
- ANA Cordon and Search TTP DeliverableDokumen33 halamanANA Cordon and Search TTP DeliverablejpgvenancioBelum ada peringkat
- Fixed Platforms, Walkways, Stairways and Ladders-Design, Construction and InstallationDokumen7 halamanFixed Platforms, Walkways, Stairways and Ladders-Design, Construction and InstallationgeofounBelum ada peringkat
- Nutrition 3Dokumen2 halamanNutrition 3azszahBelum ada peringkat
- Respiration 1Dokumen5 halamanRespiration 1azszah100% (1)
- Nutrition 3Dokumen4 halamanNutrition 3azszahBelum ada peringkat
- Markah Midterm PSK 5 BiruniDokumen1 halamanMarkah Midterm PSK 5 BiruniazszahBelum ada peringkat
- Sulit: © Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama PenuhDokumen4 halamanSulit: © Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama PenuhazszahBelum ada peringkat
- Sulit: © Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama PenuhDokumen4 halamanSulit: © Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama PenuhazszahBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Division1Dokumen6 halamanCell Division1azszahBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Division2Dokumen5 halamanCell Division2azszahBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Division2Dokumen5 halamanCell Division2azszahBelum ada peringkat
- Nutrition 2Dokumen7 halamanNutrition 2azszahBelum ada peringkat
- Ese I Nutrition Ked Ah 08Dokumen2 halamanEse I Nutrition Ked Ah 08azszahBelum ada peringkat
- Nutrition 3Dokumen2 halamanNutrition 3azszahBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical 4Dokumen3 halamanChemical 4azszahBelum ada peringkat
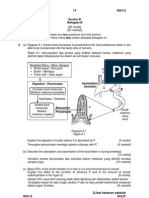
- 17 Moz@C: (40 Marks) Answer Only Two Question From This SectionDokumen4 halaman17 Moz@C: (40 Marks) Answer Only Two Question From This SectionazszahBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical 1Dokumen4 halamanChemical 1azszahBelum ada peringkat
- CellDokumen4 halamanCellazszah100% (1)
- Biologi Pertengahan Tahun 2010Dokumen12 halamanBiologi Pertengahan Tahun 2010azszahBelum ada peringkat
- Confidential: ATP SynthetaseDokumen5 halamanConfidential: ATP SynthetaseazszahBelum ada peringkat
- Cell StructureDokumen8 halamanCell StructureazszahBelum ada peringkat
- CellDokumen4 halamanCellazszah100% (1)
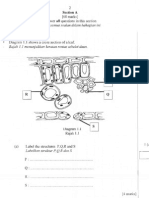
- Jnwuh Semua Socilan Ckilam H Zhugiun Ini: (60 Marks) Answer Questions in This SectionDokumen5 halamanJnwuh Semua Socilan Ckilam H Zhugiun Ini: (60 Marks) Answer Questions in This SectionazszahBelum ada peringkat
- Trial Bio SPM SBP 2010Dokumen78 halamanTrial Bio SPM SBP 2010Rozaini Othman75% (8)
- Yearly Plan Biology Form 5Dokumen34 halamanYearly Plan Biology Form 5azszahBelum ada peringkat
- Ramalan 2012.odtDokumen2 halamanRamalan 2012.odtazszahBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Scoring Check List Student's Name: Class: Instrument: TitleDokumen16 halamanBiology Scoring Check List Student's Name: Class: Instrument: TitleazszahBelum ada peringkat
- Trial Bio SPM SBP 2010Dokumen78 halamanTrial Bio SPM SBP 2010Rozaini Othman75% (8)
- Yearly Plan Biology Form 5Dokumen33 halamanYearly Plan Biology Form 5azszahBelum ada peringkat
- Yearly Plan Biology Form 5Dokumen34 halamanYearly Plan Biology Form 5azszahBelum ada peringkat
- Investigating Anaerobic Respiration in YeastDokumen3 halamanInvestigating Anaerobic Respiration in Yeastazszah88% (17)
- Schnider Limit SwitchDokumen9 halamanSchnider Limit SwitchSyed AsadullahBelum ada peringkat
- Benling Falcon electric scooter specs and featuresDokumen2 halamanBenling Falcon electric scooter specs and featuresanu swamiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapters 1 and 3: ARM Processor ArchitectureDokumen44 halamanChapters 1 and 3: ARM Processor ArchitectureTwinkle RatnaBelum ada peringkat
- 20 Questions On Aircraft Asked in Indian Air Force InterviewDokumen9 halaman20 Questions On Aircraft Asked in Indian Air Force InterviewPreran PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- GAZT E-invoice Data DictionaryDokumen119 halamanGAZT E-invoice Data Dictionarysahira TejadaBelum ada peringkat
- Dell Wireless Card Guide AddendumDokumen6 halamanDell Wireless Card Guide AddendumwazupecBelum ada peringkat
- Srinivas ReportDokumen20 halamanSrinivas ReportSrinivas B VBelum ada peringkat
- Tst170 03 RUP Testing DisciplineDokumen26 halamanTst170 03 RUP Testing DisciplineMARYMP88Belum ada peringkat
- Gas Pressure Regulator Installation InstructionsDokumen10 halamanGas Pressure Regulator Installation Instructionssayem biswasBelum ada peringkat
- Suzuki 660 K6aDokumen88 halamanSuzuki 660 K6aJames Wayne BarkerBelum ada peringkat
- Training Estimator by VladarDokumen10 halamanTraining Estimator by VladarMohamad SyukhairiBelum ada peringkat
- Ie0if32023001028 Rev01Dokumen92 halamanIe0if32023001028 Rev01fernando choqueBelum ada peringkat
- Liftformslabconstruction 160907075019 PDFDokumen12 halamanLiftformslabconstruction 160907075019 PDFishikaBelum ada peringkat
- Project ScopeDokumen2 halamanProject ScopeRahul SinhaBelum ada peringkat
- Emision StandardsDokumen4 halamanEmision StandardsAshish RoongtaBelum ada peringkat
- 300G IM SettingsSheets 20160122Dokumen27 halaman300G IM SettingsSheets 20160122zeljkoradaBelum ada peringkat
- Tips For Internship ReportDokumen1 halamanTips For Internship ReporthummayounnasirBelum ada peringkat
- 2Dokumen5 halaman2madonnaBelum ada peringkat
- BW17V1D24Dokumen5 halamanBW17V1D24Lye YpBelum ada peringkat
- Hybrid Inverter SPH Series Technical SpecificationDokumen2 halamanHybrid Inverter SPH Series Technical SpecificationJulio CesarBelum ada peringkat
- Computer LiteracyDokumen5 halamanComputer LiteracyMazaasach MazaBelum ada peringkat
- Powercell PDX Brochure enDokumen8 halamanPowercell PDX Brochure enFate Laskhar VhinrankBelum ada peringkat