Argentina - Anatomy of A Financial Crisis
Diunggah oleh
Vijay Krishnan AnantharamanDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Argentina - Anatomy of A Financial Crisis
Diunggah oleh
Vijay Krishnan AnantharamanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Argentina: Anatomy of a Financial Crisis
Argentina: Anatomy of Financial Crisis
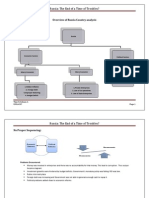
Constitutional Problem: Provinces allowed to take loans while Central Government has to collect taxes inorder to repay them
Emerging markets Scenario: There was high inflow of Capital from foreign iinvestors, so economy became overdependent on this source
Emerging markets: high risk of Banking crisis (when there is potential run on bank deposits), Currency Crisis(Sharp devaluation of Currency.
Contagion Effect: The currency crisi occurs due to irrational behaviours of the investors. This highlight the need for stringent regulations!
Tax Collection: Has been very ineffective.
Government vulnerable to External Shocks (Oil Shocks, Real Devaluation)
High level of foreign Debt. high external debt to export ratio of 400% Debt to GDP rose to 41.4% ; Projected GDP of 2.5% but sctuall -5.0%
Political Factors: High Corruption Levels, Ministry of Econoy turning against the president, two cabinet ministers resigning on corruption charges
Labor reforms: Health care programs and benefi cost a lot to the fiscal deficit
Pension reform: 45% of federal budget went to pensions
Privatization- Lead to the formation of two-tier economy: those exposed to international competion and those shielded by government
Banking sector: Return on Assets greater then 10%, return on Equity -0.7& Sovereign bonds used as debt instruments, Ineffective Swaps
Vijay Krishnan A DM14257
Page 1
Argentina: Anatomy of a Financial Crisis
Alternate Solutions
Basic Restructuring of Constitution
Less Dependancy on foreign capital / Strong regulations to prevent Capital Fleeing
Effective ways of collecting taxes, spending consciously on pension plans
Regulated Privatization, Central Bank to follow Macroeconmic policies
Vijay Krishnan A DM14257
Page 2
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Joint Ventures in China - How To Deal With ThemDokumen4 halamanJoint Ventures in China - How To Deal With ThemVijay Krishnan AnantharamanBelum ada peringkat
- The Indian Telecom Industry and The Role of Indian Government AgenciesDokumen30 halamanThe Indian Telecom Industry and The Role of Indian Government AgenciesVijay Krishnan AnantharamanBelum ada peringkat
- The Glastonbury FestivalDokumen2 halamanThe Glastonbury FestivalVijay Krishnan AnantharamanBelum ada peringkat
- Vietnam - Market Entry DecisionsDokumen1 halamanVietnam - Market Entry DecisionsVijay Krishnan AnantharamanBelum ada peringkat
- British AirwaysDokumen3 halamanBritish AirwaysVijay Krishnan AnantharamanBelum ada peringkat
- Cadbury-Design of Product and ServiceDokumen5 halamanCadbury-Design of Product and ServiceVijay Krishnan Anantharaman100% (12)
- Transforming Korea - Finanical Crisis and Institutional ReformDokumen2 halamanTransforming Korea - Finanical Crisis and Institutional ReformVijay Krishnan AnantharamanBelum ada peringkat
- Russia - The End of A Time of Troubles - 2Dokumen2 halamanRussia - The End of A Time of Troubles - 2Vijay Krishnan AnantharamanBelum ada peringkat
- Mexico - Crisis and CompetetivenessDokumen2 halamanMexico - Crisis and CompetetivenessVijay Krishnan AnantharamanBelum ada peringkat
- Russia 1994Dokumen2 halamanRussia 1994Vijay Krishnan AnantharamanBelum ada peringkat
- Russia - The End of A Time of Troubles - 1Dokumen2 halamanRussia - The End of A Time of Troubles - 1Vijay Krishnan AnantharamanBelum ada peringkat
- China - To Get Rich Is GloriousDokumen2 halamanChina - To Get Rich Is GloriousVijay Krishnan AnantharamanBelum ada peringkat
- Remaking The Rainbow Nation - South Africa 2002Dokumen2 halamanRemaking The Rainbow Nation - South Africa 2002Vijay Krishnan AnantharamanBelum ada peringkat
- Brazil Confronts An Interdependent WorldDokumen2 halamanBrazil Confronts An Interdependent WorldVijay Krishnan AnantharamanBelum ada peringkat
- Brazil 2003 - Inflation Targeting and Debt DynamicsDokumen2 halamanBrazil 2003 - Inflation Targeting and Debt DynamicsVijay Krishnan AnantharamanBelum ada peringkat
- V Jayadevan MethodDokumen10 halamanV Jayadevan MethodVijay Krishnan AnantharamanBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)