Surgery Y3 Mynotes
Diunggah oleh
ismah_haron_1Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Surgery Y3 Mynotes
Diunggah oleh
ismah_haron_1Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Bedside notes
Dr sunet weight loss, appetite and fever. Different way to check axillary lymph. Pain radiating example is gall stone pain radiated to the tip of scapula from right hypocondrium, referred because of sharing same nerve root between viscera and somatic and migrating example is acute appendicitis pain from periumbilicus to right iliac fossa because same embryonic origin. Others are lymph nodes, cns examination, current treatment and basic science. 22/09/10 Dr Ghassan Summary about the history taking and clinical examination. History SYMPTOMS while c. examination SIGNS. Diseases according to age and sex Age Female (breast lump) Male 20 Fibroadenoma 30 Fibroadenosis 40 Breast cancer Gall stone is more common in female while in male the peptic ulcer is more common if pt came with upper abdominal pain. Examine the pain site and its related lymph nodes. Urine bag oliguria less than 400ml/day 1cc/hr/day of normal urine output Cervical superior lymph nodes deep cervical chain posterior lymph nodes Axillary central, humeral, subscapular, pectoral and parastenal lymph nodes Inguinal horizontal (umbilicus, genitalia, buttock and back)and vertical chain from lower limb 24/09/10 Dr Sunet - Renal stone - Gall stone and acute pancreatitis - Prepyloric ulcer - Acute appendicitis Questions: 1. Pain (referred, radiating and migrating) 2. Colicky pain on off, 1 min in, 10 min gone and intestinal obstruction 3. Strangury: slow and painful discharge of urine due to urethra and bladder spasm 4. Nocturia: excessive urination at night 5. Dysuria: painful/difficulty during micturition 6. Hematuria: blood in the urine 7. Frequency: urination at short interval w/o increase in daily volume intake or urine output due to reduce bladder capacity
Surgery posting Y3
27/09/10 Clinic with Dr Ghassan 1. Hemorrhoids - 4 stage of it I with bleeding, II bleeding and prolapsed but return back itself, III bleeding and prolapsed and need to be push to return it back, IV bleeding, prolapsed and strangulated 2. Inguinal hernia - Cause divided to 2: I because of straining, lifting heavy things, to forceful coughing, II due to abdominal muscle weakness congenital, surgery, pregnancy 3. Thyroid problem - It may enlarge during pregnancy but it will be diffuse. But it also can be nodular in multiple pregnancies. - It may also diffusely enlarge if eating cabbage, in IDA and - Symptoms include palpitation, swelling on neck, increase appetite, loss weight, prefer cold weather - Signs are tachycardia, sweating and warm hand, and enlargement of thyroid, lid retraction, lid lag and exophthalmos. - Thyroid may move during swallowing
CASES
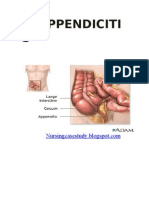
22/09/10 Appendicitis a. Inflammation to the vermiform appendix b. Clinical features: pain migrated from periumbilicus to right iliac fossa region, ass with nausea/vomiting and low grade fever, Rovsings sign and rebound tenderness c. Cx: appendix abscess and mass, perforation and peritonitis 24/09/10 Prepyloric ulcer a. Peptic ulcer: type I(gastric),II(gastric and duodenal aka prepyloric) and atypical ulcer b. Gastric ulcer: CF epigastric pain exaggerated by foods, causing weight loss and anorexia c. Prepyloric ulcer: CF ep relieved by food and pain may also be felt at the central back, more cyclical and ass with nausea d. Atypical ulcer mostly due to hypergastrinemia and ectopic gastric secretion e. Cx: GIT bleeding, IDA, perforation and obstruction because of scarring f. Drugs: antacids, antihistamine, PPI 28/09/10 1. Motorbike accident inquiry of small bowel injury 2. Bowel obstruction due to past colorectal surgery 06/10/09 1. Jaundice Serum bilirubin level is more than 40mmol
Surgery posting Y3
Etiology: a. Pre hepatic more destruction of RBC b. Hepatic unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin c. Post hepatic intraluminal, intramural and extrinsic compression 2. Gall stone aka cholelithiasis a. Risk factor female, fat, fertile, forty and fair b. Types of stone mix, cholesterol and pigment c. Clinical features biliary colic (intermittent epigastric and RUQ pain, nausea and vomiting), acute cholecystitis (RUQ, right flank and back pain, fever and anorexia) and chronic cholecystitis 3. Stone in CBD aka choledocolithiasis a. Types primary and secondary stone b. Clinical features obstructive jaundice (yellowish coloration of skin and sclera, tea colored urine, pale stool, itchiness, epigastric pain, fever, nausea and anorexia), ascending cholangitis (obstructive jaundice, fever and RUQ pain) and acute pancreatitis 4. Acute pancreatitis (>55 years old) a. Etiology trauma, neoplastic (tumor of head of pancreas), infection (mumps and CMV), and others (drug related, gall stone, alcohol and hyperlipidemia) b. Clinical features fever, epigastric pain radiated to back, severe nausea and vomiting, hypotension, tachycardia and dehydration
My EOP notes
1. Perforated peptic ulcer a. Symptoms sudden onset epigastric/generalized abdominal pain, hematemesis, melena, altered consciousness b. Signs signs of shock (tachycardia, low pulse volume, low BP, pallor), abdomen less move with respiration, rigid abdomen, tenderness on palpation on upper abdomen/generalized, shifting dullness, absent bowel sound c. Differential diagnosis ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm, acute pancreatitis, acute cholecystitis, trauma and stomach ca?, esophageal varices d. Investigation FBC, RF, DPL, CT scan and serum amylase, CXR, AXR, e. Management stabilized pt (O2, IV fluid, analgesia, NBM, NG tube, parenteral nutrition), investigation, manage f. Surgical option suture, excision and suture and gastectomy, peritoneal toilet g. Complication of surgical abscess, bleeding, stricture, small stomach syndrome, nutritional problem, surgical infection, recurrent ulcer and 2. Stomach ca - Spread of tumor: direct (pancreas, liver), lymphatic (Virchows LN, troissier sign), blood borne to liver and transperitoneal umbilicus and ovaries 3. Description on stoma bag
Surgery posting Y3
4. 5. 6. 7.
Transparent/not Site Content (fluid/feces) Sprouting Typeeg: end loop etc Complication: infection, healthy/gangrene etc Breast carcinoma Vitiligo: white depigmentation of skin, associated with diabetes, hashimoto disease, Addisons disease, syphilis etc Lower git bleeding: common cause is diverticular disease at right colon and angiodysplasia at left and sigmoid colon.rectal bleeding???????? Spleen injury - Abdominal aorta celiac trunk spleenic artery
OSCE 1. Per rectal examination - Explain: insert finger in anus - Permission, clean hand and wear glove - Inspection - Lubricate finger - Insert, squeeze, feel post and ant - Look at finger - Swap lubricant from patient perianal region - Finding: rectal tumor, BPH, tenderness - Contraindication: fissure in ano and abscess 2. Fluid and electrolytes - Crystalloid: NS, 5% dextrose, dextrose saline and Hartmann/Ringers lactate (Na, K, Cl, Ca and lactate) - Colloid (blood, albumin and gelatin) - Gelatin will stay in intravascular compartment to pulling fluid from extravascular compartment 3. Surgical hemostasis - Direct pressure - Packing - Surgical option: artery forceps, electrocautery and clamping 4. Blood transfusion - Indication: traumatic accident with blood loss, severe burn, blood loss during major surgery, post operative anemia, loss to much blood because peptic ulcer bleeding - Preparation: donor, hospital etc and recipient? - Donor: fit, healthy - Hospital etc: anticoagulant added to blood and screening test (ABO typing, Rh, HIV, Hep B, Treponema pallidum)
Surgery posting Y3
- Complication: acute hemolysis and transmitted infection 5. Skin lesion - Epidermis (include melanocyte), dermis and subcutaneous tissues - Basal cell carcinoma: ulcers at face, roll edge, causes are expose to UV, irridation and genetic, treatment are excision, cryosurgery and radiation - Squamous cell carcinoma: similar to above, except angry looking ulcer with bleeding and everted edge. Easily metastases than BCC - Maglinant melanoma: tumor of melanocytes. Based on A B C D criteria, asymmetry border color and discharge. Types are superficial spreading, nodular maglinant, lentigo maglina and acral lentigonous. Treatment are excision, chemotherapy and radiation - Cyst: epidermoid (scrotal), dermoid (midline) and trichilemmal (female scalp)
Surgery posting Y3
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Postpartum Psychiatric Disorders: By: Ismah Haron Ruzanna Rosslan Noraini TukiranDokumen7 halamanPostpartum Psychiatric Disorders: By: Ismah Haron Ruzanna Rosslan Noraini Tukiranismah_haron_1Belum ada peringkat
- ENT - Anat - Oral Cavity & PharynxDokumen25 halamanENT - Anat - Oral Cavity & Pharynxismah_haron_1Belum ada peringkat
- Management of Upper Urinary Tract Obstruction: By: Siti Nurulismah BT Che HaronDokumen12 halamanManagement of Upper Urinary Tract Obstruction: By: Siti Nurulismah BT Che Haronismah_haron_1Belum ada peringkat
- Discussion: By: Siti Nurulismah BT Che HaronDokumen18 halamanDiscussion: By: Siti Nurulismah BT Che Haronismah_haron_1Belum ada peringkat
- Ophthal Red Eye-conjuctivitis&SchDokumen15 halamanOphthal Red Eye-conjuctivitis&Schismah_haron_1Belum ada peringkat
- Chronic Complications: By: Siti Nurulismah BT Che HaronDokumen16 halamanChronic Complications: By: Siti Nurulismah BT Che Haronismah_haron_1Belum ada peringkat
- O&g - Case - Pih, PPDokumen19 halamanO&g - Case - Pih, PPismah_haron_1Belum ada peringkat
- Medicine Yr3 NotesDokumen3 halamanMedicine Yr3 Notesismah_haron_1Belum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Case Study AppendectomyDokumen40 halamanCase Study AppendectomyArmin Joseph Pepito0% (1)
- A Revision of Aleurodicus Douglas With Two New Genera Proposed For Paleotropical Natives An Identification Guide To World GeneraDokumen100 halamanA Revision of Aleurodicus Douglas With Two New Genera Proposed For Paleotropical Natives An Identification Guide To World GeneraJulian LeonardoBelum ada peringkat
- Surgical JaundiceDokumen35 halamanSurgical JaundiceIbsa ShumaBelum ada peringkat
- Nephrology Underpinning For The Young DoctorsDokumen7 halamanNephrology Underpinning For The Young DoctorsMahmoud DiaaBelum ada peringkat
- Liver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorDokumen22 halamanLiver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorJorie RocoBelum ada peringkat
- (Gastrointestinal Function) Analysis Report Card: Actual Testing ResultsDokumen2 halaman(Gastrointestinal Function) Analysis Report Card: Actual Testing ResultsShashikanth RamamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- In Same A A: Richmond, VrginiaDokumen11 halamanIn Same A A: Richmond, VrginiaRizky AmaliahBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Abdomen CausesDokumen5 halamanAcute Abdomen CausesSheetal DherangeBelum ada peringkat
- Casting and Restraining of AnimalsDokumen5 halamanCasting and Restraining of Animalsmuzammilhussain512786Belum ada peringkat
- Common Hernia TypesDokumen3 halamanCommon Hernia TypesulyaBelum ada peringkat
- Bagi 173-Original Article-1952-4-10-20200625Dokumen6 halamanBagi 173-Original Article-1952-4-10-20200625True DamageBelum ada peringkat
- Case History FormatDokumen10 halamanCase History FormatSafiaSamBelum ada peringkat
- Scan Report PDFDokumen1 halamanScan Report PDFsrikanth PosaBelum ada peringkat
- PASIEN DIGESTIF OHO - 2 Januari 2019 (R1, R2B, R3, R4B)Dokumen2 halamanPASIEN DIGESTIF OHO - 2 Januari 2019 (R1, R2B, R3, R4B)Wahyu Hendra PrabowoBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary System PDFDokumen27 halamanUrinary System PDFfiona100% (3)
- Abdominal InjuriesDokumen52 halamanAbdominal InjuriesVeerabhadra RadhakrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Im - Chronic Kidney Disease - Dr. Lorna Wong - March 20 2021Dokumen107 halamanIm - Chronic Kidney Disease - Dr. Lorna Wong - March 20 2021Christine MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Importance of Strengthening Your Core MusclesDokumen6 halamanImportance of Strengthening Your Core Musclesallan_apduaBelum ada peringkat
- Pilatesmakale PDFDokumen9 halamanPilatesmakale PDFOzkan AltunBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Jan 08 Abdominals PDFDokumen9 halaman10 Jan 08 Abdominals PDFprofines2051Belum ada peringkat
- Nutrition in Human, NoteDokumen7 halamanNutrition in Human, NoteMaheen Farhan VII-G-BBelum ada peringkat
- 11.3 Questions Kidney and OsmoregulationDokumen3 halaman11.3 Questions Kidney and OsmoregulationAnne Margaret LorenzenBelum ada peringkat
- LacfelinumkentDokumen5 halamanLacfelinumkentCristinaBelum ada peringkat
- Dogfish Shark DissectionDokumen4 halamanDogfish Shark Dissectionapi-318665838100% (3)
- Mcqs RenalDokumen19 halamanMcqs RenaldevdsantoshBelum ada peringkat
- Investigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceDokumen38 halamanInvestigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceUjas PatelBelum ada peringkat
- The Acute Abdomen DR Dwicha SPBKBDDokumen41 halamanThe Acute Abdomen DR Dwicha SPBKBDAgung HaryantoBelum ada peringkat
- Biliary Obstruction Workup: Laboratory StudiesDokumen3 halamanBiliary Obstruction Workup: Laboratory StudiesResiden PatKlinBelum ada peringkat
- Idcases: Case ReportDokumen3 halamanIdcases: Case ReportPeko PekoBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of GallbladderDokumen14 halamanAnatomy of GallbladderSamridhi DawadiBelum ada peringkat