Rotational Symmetry Definition
Diunggah oleh
api-174638550Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Rotational Symmetry Definition
Diunggah oleh
api-174638550Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Rotational Symmetry Definition
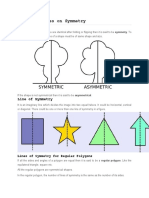
Rotational Symmetry Definition Generally speaking, an object with rotational symmetry is an object that looks the same after a certain amount of rotation. An object may have more than one rotational symmetry; for instance, if reflections or turning it over are not counted, the triskelion appearing on the Isle of Man's flag (see opposite) has three rotational symmetries (or "a threefold rotational symmetry"). More examples may be seen below. The degree of rotational symmetry is how many degrees the shape has to be turned to look the same on a different side or vertex. It can not be the same side or vertex. In another meaning of the word, the rotation group of an object is the symmetry group within E+(n), the group of direct isometries; In other words, the intersection of the full symmetry group and the group of direct isometries. For chiral objects it is the same as the full symmetry group.
Know More About :- Derivative Sec x
Tutorcircle.com
PageNo.:1/4
Laws of physics are SO(3)-invariant if they do not distinguish different directions in space. Because of Noether's theorem, rotational symmetry of a physical system is equivalent to the angular momentum conservation law. See also Rotational invariance. A geometrical figure is in Rotational Symmetry, when we say that after rotating a figure by a certain angle, the figure looks same as before. Let us look at the Rotation Symmetry of an Equilateral Triangle. By rotating the equilateral triangle, we observe that the triangle looks exactly similar when it is rotated by 120 degrees, so the rotational symmetry will be at 120 degrees, 240 degrees and 360 degrees and then one rotation cycle is completed. Now, we come to the conclusion that a figure can look symmetrical 3 times when it completes one rotation. Thus, the order of rotation of the equilateral triangle will be 3. On the other hand, if we look at the Isosceles Triangle or the Scalene Triangle, we observe that figure does not look same at any angular rotation, but after completing the rotation of 360 degrees it looks as it is. So the order of rotation is 1 and the angle of rotation is 360 degrees. Have a look on another geometrical figure, say a Square. A square after the rotation of 90 degrees, take the exact shape, so the angle of the rotation of the square will be 90 degrees, 180 degrees, 270 degrees and 360 degrees. Thus we can say that the order of rotation of the square will be 4. Similarly, the order of rotation of the Rectangle will be 2 and the angle of rotation of the rectangle is 180 degrees.
Learn More :- Rationalize The Denominator Calculator
Tutorcircle.com
PageNo.:2/4
Once we know the order of rotation of any figure, we can find the angle of rotation by applying the formula 360 / order of rotation. By applying the same formula we say for equilateral triangle angle of rotation = 360 / 3 = 120 degrees. For a square angle of rotation = 360 / 4 = 90 degrees and for the rectangle angle of rotation = 360 / 2 = 180 degrees.
Tutorcircle.com
PageNo.:3/4 PageNo.:2/3
ThankYouForWatching
Presentation
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- What Is Rotational Symmetry?Dokumen7 halamanWhat Is Rotational Symmetry?Anna LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Maths SymmetryDokumen1 halamanMaths Symmetrynick merryBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal ChemistryDokumen6 halamanCrystal ChemistryMithra LakshmiBelum ada peringkat
- 2D Symmetry Line SymmetryDokumen1 halaman2D Symmetry Line SymmetryManoj RatnayakeBelum ada peringkat
- Symmetry Operation: 2-Fold Rotation AxisDokumen5 halamanSymmetry Operation: 2-Fold Rotation Axisabid55Belum ada peringkat
- SymmetryDokumen16 halamanSymmetryGiulia Galli LavigneBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal SymmetryDokumen50 halamanCrystal Symmetryfatih muhammadBelum ada peringkat
- Electron Diffraction and Imaging Lecture - Symmetry in 1-D CrystalsDokumen27 halamanElectron Diffraction and Imaging Lecture - Symmetry in 1-D CrystalsKuthuraikaranBelum ada peringkat
- Geometric Designs - SymmetryDokumen13 halamanGeometric Designs - Symmetrymeth lazaroBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE Year 10 Core S 28.2 28.3 Lesson 72Dokumen18 halamanIGCSE Year 10 Core S 28.2 28.3 Lesson 72jonathan abi raadBelum ada peringkat
- Rotations and Rotational SymmetryDokumen9 halamanRotations and Rotational SymmetrycrystalMorgan123Belum ada peringkat
- RotationalDokumen2 halamanRotationalMansi PopliBelum ada peringkat
- Class 7 Math Notes Chapter 14 SymmetryDokumen6 halamanClass 7 Math Notes Chapter 14 SymmetryManishBelum ada peringkat
- RotationDokumen1 halamanRotationSangeethaBelum ada peringkat
- 7 Symmetry and Group TheoryDokumen19 halaman7 Symmetry and Group TheoryMainak SamantaBelum ada peringkat
- Electron Diffraction and Imaging LectureDokumen31 halamanElectron Diffraction and Imaging LectureKuthuraikaranBelum ada peringkat
- Frenkel Introduction To Langlands ProgramDokumen46 halamanFrenkel Introduction To Langlands ProgramFernando Conde-Pumpido VelascoBelum ada peringkat
- GeneralPhysics1 G12 Q2 Mod1 Rotational Kinematics AndRotational Dynamics Week1Dokumen21 halamanGeneralPhysics1 G12 Q2 Mod1 Rotational Kinematics AndRotational Dynamics Week1Cristina SacayananBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Mineralogy and CrystallographyDokumen64 halamanPrinciples of Mineralogy and CrystallographyCamille RaboBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5Dokumen18 halamanChapter 5Note SuwansomphongBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 7 Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion Revision NotesDokumen132 halamanCBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 7 Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion Revision Notesrazi sharifBelum ada peringkat
- MSC Solid State Physics Lecture#3Dokumen17 halamanMSC Solid State Physics Lecture#3Shehzad AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Week 5 Lesson 1Dokumen7 halamanPhysics Week 5 Lesson 1Gabriel SantiagoBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm Module For GeologyDokumen37 halamanMidterm Module For GeologyJohnny King ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Elementary Knowledge On Symmetry Elements of Crystallographic SystemsDokumen6 halaman1 Elementary Knowledge On Symmetry Elements of Crystallographic SystemsSORIANO, JEZEREEL JOYCE A.Belum ada peringkat
- Rotational MotionDokumen12 halamanRotational Motionsanderstoby44Belum ada peringkat
- Trigonometric Functions & Angle RelationshipsDokumen34 halamanTrigonometric Functions & Angle RelationshipsJohnny Siason100% (1)
- Introduction and Symmetry Operations: This Page Last Updated On 27-Aug-2011Dokumen10 halamanIntroduction and Symmetry Operations: This Page Last Updated On 27-Aug-2011imprincesssBelum ada peringkat
- (ENM012 AY22-23) W2 - Trigonometric Functions - D - 2Dokumen28 halaman(ENM012 AY22-23) W2 - Trigonometric Functions - D - 2Jaxon Riego100% (1)
- 1 Elementary Knowledge On Symmetry Elements of Crystallographic SystemsDokumen6 halaman1 Elementary Knowledge On Symmetry Elements of Crystallographic SystemsAngel Bren TambioBelum ada peringkat
- Laws of Crystal SymmetryDokumen1 halamanLaws of Crystal SymmetrySheng NabatBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Crystallography AhmadhDokumen12 halamanAssignment Crystallography AhmadhAhmadhAzharBelum ada peringkat
- Paper of The Circular Motion and Gravitation: Lecturer: Dr. Sc. Syahril, S.Si, MTDokumen25 halamanPaper of The Circular Motion and Gravitation: Lecturer: Dr. Sc. Syahril, S.Si, MTIndriiBelum ada peringkat
- 1 IntrosymmetryDokumen9 halaman1 IntrosymmetryFrancBelum ada peringkat
- What are Eigen Values? - Explained SimplyDokumen2 halamanWhat are Eigen Values? - Explained Simplyir123Belum ada peringkat
- TrigonometryDokumen65 halamanTrigonometryChristine BalladBelum ada peringkat
- Symmetry ElementsDokumen7 halamanSymmetry ElementsMithra LakshmiBelum ada peringkat
- Rotational Kinematics ExplainedDokumen27 halamanRotational Kinematics ExplainedStephen AbadinasBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Module 8: TrigonometryDokumen19 halamanMaths Module 8: TrigonometryDie A MuslimahBelum ada peringkat
- Module 8 - Rotation of Rigid BodiesDokumen11 halamanModule 8 - Rotation of Rigid BodiesAllen Simon BaulaBelum ada peringkat
- Rotation: / Æksi Z/ Earth Sun Orbital Gravity Mathematically Rigid Body TranslationDokumen1 halamanRotation: / Æksi Z/ Earth Sun Orbital Gravity Mathematically Rigid Body TranslationAniket SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson: Quarter 2 - Module: 1: Stem - Gp12Rediia-1 Stem - Gp12Rediia-3Dokumen8 halamanLesson: Quarter 2 - Module: 1: Stem - Gp12Rediia-1 Stem - Gp12Rediia-3Mildred Joy CudpayasBelum ada peringkat
- Euclidean Transformations Affine Transformation Projective TransformationsDokumen11 halamanEuclidean Transformations Affine Transformation Projective TransformationsSatish KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Angular Acceleration - College PhysicsDokumen1 halamanAngular Acceleration - College PhysicsPola RismaBelum ada peringkat
- How The Train TurnsDokumen4 halamanHow The Train Turnsmrana_56Belum ada peringkat
- Improper Rotation: 1 Three DimensionsDokumen3 halamanImproper Rotation: 1 Three DimensionsManuel MensaBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Symmetry ElementsDokumen16 halamanCrystal Symmetry Elementsmithunesh 07Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 (Rotational Motion)Dokumen37 halamanChapter 8 (Rotational Motion)Mehwish IsrarBelum ada peringkat
- Bhs Inggris YogiDokumen7 halamanBhs Inggris YogiArtemisBelum ada peringkat
- Gen. Physics 1 Worksheet on Rotational Equilibrium and DynamicsDokumen26 halamanGen. Physics 1 Worksheet on Rotational Equilibrium and DynamicsFranchezca CoronadoBelum ada peringkat
- General Physics 1: Quarter 2 - Module 1Dokumen30 halamanGeneral Physics 1: Quarter 2 - Module 1Jheremy Charles Morales MorteraBelum ada peringkat
- PDF DocumentDokumen11 halamanPDF DocumentNhey VergaraBelum ada peringkat
- Celestial Coordinate Systems: Craig Lage Department of Physics, New York University, Csl336@nyu - EduDokumen6 halamanCelestial Coordinate Systems: Craig Lage Department of Physics, New York University, Csl336@nyu - EduvenikaBelum ada peringkat
- Molecular Symmetry Elements and OperationsDokumen19 halamanMolecular Symmetry Elements and OperationsMd Mehrab Alam ShayikhBelum ada peringkat
- New MicrDokumen8 halamanNew Micrdarshgupta71Belum ada peringkat
- Polygons and QuadrilateralsDokumen4 halamanPolygons and QuadrilateralsDaniel DowdingBelum ada peringkat
- Angle Measurement in TrigonometryDokumen118 halamanAngle Measurement in TrigonometryJohn Eman LacambraBelum ada peringkat
- Motion Characteristics For Circular MotionDokumen101 halamanMotion Characteristics For Circular MotionMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Random LecturesDokumen30 halamanRandom LecturesTrisha KayeBelum ada peringkat
- Grouped Frequency DistributionDokumen4 halamanGrouped Frequency Distributionapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Scalar FunctionDokumen4 halamanScalar Functionapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Parametric EquationDokumen4 halamanParametric Equationcircleteam123Belum ada peringkat
- Curve Fitting AlgorithmDokumen4 halamanCurve Fitting Algorithmapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Nonlinear SystemsDokumen4 halamanNonlinear Systemsapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Cyclic QuadrilateralDokumen4 halamanCyclic Quadrilateralapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Area TrapezoidDokumen4 halamanArea Trapezoidapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Hyperbola EquationDokumen4 halamanHyperbola Equationapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Real Number PropertiesDokumen4 halamanReal Number Propertiesapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Solve My Math ProblemDokumen4 halamanSolve My Math Problemapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Define Scalar MultiplicationDokumen4 halamanDefine Scalar Multiplicationapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- How To Do Pre AlgebraDokumen4 halamanHow To Do Pre Algebraapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- The Exponential FunctionDokumen4 halamanThe Exponential Functionapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Definition GeometryDokumen4 halamanDefinition Geometryapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Augmented MatricesDokumen4 halamanAugmented Matricesapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen4 halamanUntitledapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- DiameterDokumen4 halamanDiameterapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Cosine LawsDokumen4 halamanCosine Lawsapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- The Law of CosinesDokumen4 halamanThe Law of Cosinesapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Algebra SolverDokumen4 halamanAlgebra Solverapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Range MathsDokumen4 halamanRange Mathsapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Binomial Distribution ProblemsDokumen4 halamanBinomial Distribution Problemsapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Precalculus FunctionsDokumen4 halamanPrecalculus Functionsapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- How To Find The Equation of A LineDokumen4 halamanHow To Find The Equation of A Lineapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen4 halamanUntitledapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Types of GraphDokumen4 halamanTypes of Graphapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Periodic FunctionDokumen4 halamanPeriodic Functionapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Math ProblemsDokumen4 halamanMath Problemsapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- Define ScalarDokumen4 halamanDefine Scalarapi-174638550Belum ada peringkat
- 7 Statistical Thermodynamics-IIDokumen30 halaman7 Statistical Thermodynamics-IICahyarani ParamestiBelum ada peringkat
- Tabletop Simulator Script ObjectDokumen10 halamanTabletop Simulator Script ObjectMichael MelloBelum ada peringkat
- Normo 2021 Extension 2 Mathematics TrialDokumen13 halamanNormo 2021 Extension 2 Mathematics TrialSuleyman KumsuzBelum ada peringkat
- As-NZS 1102-102-1997 Graphical Symbols For Electrotechnical Documentation.Dokumen46 halamanAs-NZS 1102-102-1997 Graphical Symbols For Electrotechnical Documentation.mario100% (2)
- Lecture 2 - Process Control (P1)Dokumen30 halamanLecture 2 - Process Control (P1)Elia SaadBelum ada peringkat
- Aerial Robotics Lecture 3A - 1 2-D Quadrotor ControlDokumen5 halamanAerial Robotics Lecture 3A - 1 2-D Quadrotor ControlIain McCullochBelum ada peringkat
- 2020-04-28 - QX Simulator - EQC - w2Dokumen38 halaman2020-04-28 - QX Simulator - EQC - w2Aritra SarkarBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-3 Soil Permeability and SeepageDokumen24 halamanChapter-3 Soil Permeability and SeepageLemiBelum ada peringkat
- Phasor Circuit Analysis: Phasor Diagrams, Voltage and Current DivisionDokumen8 halamanPhasor Circuit Analysis: Phasor Diagrams, Voltage and Current DivisionDavis LiangBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamic ProcessesDokumen13 halamanThermodynamic ProcessesS Jayasuriya100% (1)
- Teori BDokumen3 halamanTeori BmulyanaBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Fusion in Stars Forms ElementsDokumen3 halamanNuclear Fusion in Stars Forms ElementsEunice AcunaBelum ada peringkat
- Beam Behavior in Nearfield of Vibrating PistonDokumen12 halamanBeam Behavior in Nearfield of Vibrating PistonNothing ConnoisseurBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 48 Applications of Matrices and Determinants: EXERCISE 201 Page 545Dokumen32 halamanChapter 48 Applications of Matrices and Determinants: EXERCISE 201 Page 545Sadio Abdi NasirBelum ada peringkat
- FINAL MW LAB Manual 2019Dokumen89 halamanFINAL MW LAB Manual 2019op thakurBelum ada peringkat
- AlternatorDokumen3 halamanAlternatorshekharpremsureBelum ada peringkat
- Importance & Impact of Stress Intensification Factor (SIF) : A PresentationDokumen8 halamanImportance & Impact of Stress Intensification Factor (SIF) : A Presentationcasaean100% (1)
- PROBLEM SET HydraulicsDokumen1 halamanPROBLEM SET HydraulicsErika Rose LaronBelum ada peringkat
- Eca 1Dokumen47 halamanEca 1Ahmed SohailBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies - Deformation of BodiesDokumen49 halamanMechanics of Deformable Bodies - Deformation of Bodiesmechabuild.engineeringBelum ada peringkat
- The Paradox of Fourier Heat EquationDokumen7 halamanThe Paradox of Fourier Heat EquationAngélica RuizBelum ada peringkat
- Phys2 Week2 Error AnalysisDokumen9 halamanPhys2 Week2 Error AnalysisSahirBelum ada peringkat
- PeDokumen72 halamanPeRakesh NairBelum ada peringkat
- Partial Safety Factors For Homogeneous Reliability of Nonlinear Reinforced Concrete ColumnsDokumen20 halamanPartial Safety Factors For Homogeneous Reliability of Nonlinear Reinforced Concrete ColumnsEman SalehBelum ada peringkat
- MECH 390 - PRACTICE 1 - FALL 2011Dokumen5 halamanMECH 390 - PRACTICE 1 - FALL 2011Abeer AlnaqbiBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Cellular AutomataDokumen91 halaman4 Cellular AutomataSayed ElSheikhBelum ada peringkat
- Ball Drop ActivityDokumen4 halamanBall Drop ActivityKogilan ChitranBelum ada peringkat
- 3.5 Deformation Potential PDFDokumen6 halaman3.5 Deformation Potential PDFJesus AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Design of Transmission LinesDokumen9 halamanMechanical Design of Transmission LinesPathum SudasingheBelum ada peringkat