Disaster Management
Diunggah oleh
Neha DingwaniDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Disaster Management
Diunggah oleh
Neha DingwaniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Disaster Management Introduction Natural calamities causing heavy loss to life, crops and structures are referred to as disaster.
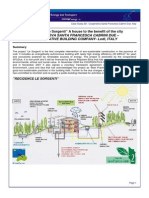
It is difficult to predict when and to what extent disaster is going to occur. Hence countries and societies take up several methods to monitor, assess and manage a disaster situation. Information and Communication technologies have foremost use at each stage. Description This project is about assessment of river flood using Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), Grid Computing and Geo synchronous SATellite (GSAT) technology. When a flood occurs an aircraft fitted with a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is flown over the flood affected region. The SAR is capable of capturing the data about the flood site even in rough weather conditions (cloud, fog, dim light). Typically, if the aircraft flies over the flood region and collects raw data for about half an hour, several snapshots (SAR raw data) are obtained, spanning the length of the river (say 100 200km). These SAR raw data sets need to be processed to obtain an understandable image (resultant image) of the region. This requires provisioning of significant compute and storage resources at short notice. This project exemplifies how the high speed network and HPC clusters & storage are useful to solve such a problem in near real time. The project was conceptualized in 2006 between Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) and Space Application Center (SAC), under the GARUDA grid and the major components were identified. The major components are
data acquisition raw data transmission & scheduling of data processing raw data processing on GARUDA back transmission & geospatial visualization of results
DM-SAR (Disaster Management Synthetic Aperture Radar) sensor, fitted on an aircraft, captures the raw data. SAC is incharge of the data acquisition. The raw data thus obtained was sent to GARUDA grid computing resources for processing. C-DAC gridenabled the program for raw data processing, on the GARUDA grid. Communication channels between SAC and CDAC include high speed Layer 2/3 MPLS Virtual Private Network at 100Mbps as well as GSAT3 Satellite terminals. Data transmission via both 1 Mbps Satellite links and 100Mbps terrestrial links have been tested and analyzed. The data transmission and job scheduling required interfacing the Satellite grid
(SATGrid) with GARUDA grid. Thus, the SATGrid and GARUDA have been successfully interfaced. GANESH scheduler developed by SAC has been used to schedule the jobs from SAC to GARUDA. Specific interfaces required to connect GARUDA with GANESH have been developed by C-DAC. The data processing job execution / submission has been successfully tested via Satellite and terrestrial links. Raw data of different resolutions (1m, 5m and 10m) have been processed on GARUDA. The processing time has been compared with that taken on Altix 32-way SMP at SAC. A 9GB raw data processing taking about 6 and half hours on 32 CPU Itanium-2 Altix was observed to reduce to 54 minutes using 272 CPUs of an Intel Xeon cluster. Specialized geospatial visualization software has been deployed by C-DAC at specific locations using which experts are able to collaborate for decision making. Publications 1. Pankaj Ojha, Mangala N, Prahlada Rao B.B, Manavalan R, Tapan Mishra, V.Manavala Ramanujam, Haresh Bhat, Pankaj Ojha, Mangala N, Prahlada Rao B.B, Manavalan R, Tapan Mishra, V.Manavala Ramanujam, Haresh Bhat, "Disaster Management & Assessment System Using Interfaced Satellite and Terrestrial Grids" "Disaster Management & Assessment System Using Interfaced Satellite and Terrestrial Grids", Workshop on Grid and Utility Computing, International Conference on High Performance Computing, December 2008, India 2. Pankaj Ojha, Ms. Mangala N ,Dr. Prahlad Rao, R.Manavalan, Dr. Tapan Mishra, V.Manavala Ramanujam, Haresh Bhat, Grid Enabled Workflow For Management & Disaster Assesment System At Satellite And Terrestrial Grid (GE-MINDA), National Conference on Emerging trends in Computing and Communication, December 2008, National Institute of Technology, Hamirpur, India 3. V Manavala Ramanujam, Tapan Misra, DMSAR Processing Software Implementation, National Symposium On Advances In Remote Sensing Technology And Applications With Special Emphasis On Microwave Remote Sensing, Indian Society of Remote Sensing (ISRS), December 18-20, 2008, India 4. R.Manavalan, V.Manavala Ramanujam, Tapan Misra, Garuda Flood Assessment System (G-FAS) ,International Symposium for Research Scholars on Metallurgy, Materials Science and Engineering, December 10-12, 2008, India
DISASTER MANAGEMENT: Flood assessment is one of the challenging applications of multi-disciplinary disaster management system. Disaster Management using Synthetic Aperture Radar (DMSAR) is a project to delineate the distribution of open water flood data of a flood affected region, captured using an airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar for Disaster Management. DMSAR is a collaborative project between ISROs Space Application Center (SAC) and C-DAC. The Flood Assessment System comprises of Data Acquisition using airborne synthetic aperture radar, Raw Data Processing and finally Remote Visualization of image. The data of the flood affected area is acquired by an airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) fitted to the belly of an airplane. This raw data is voluminous and requires vast computational power for processing. Hence, the raw data is processed concurrently at different HPC clusters of Garuda in SPMD manner. The outputs are merged and the resultant image is shared for remote collaborative visualization from different locations of the Garuda grid. By parallelizing and running the raw data processing using Garudas HPC resources the processing time significantly improved (from nearly 30 hrs using single CPU to less than half an hour using 368 CPUs)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Project Management GUIDE 2020: Revision 1Dokumen27 halamanProject Management GUIDE 2020: Revision 1lorranaBelum ada peringkat
- Geometric Tracking Control of A Quadrotor UAV On SEDokumen6 halamanGeometric Tracking Control of A Quadrotor UAV On SEnaderjsaBelum ada peringkat
- Appendix F Sample Erosion and Sediment Control PlanDokumen11 halamanAppendix F Sample Erosion and Sediment Control Planjhj01Belum ada peringkat
- TAFJ-AS JBossInstall v5.2 EAP PDFDokumen33 halamanTAFJ-AS JBossInstall v5.2 EAP PDFrameshBelum ada peringkat
- Earthquake EssayDokumen1 halamanEarthquake EssayAnsir Yaqoob100% (1)
- Scheme of Work Writing Baby First TermDokumen12 halamanScheme of Work Writing Baby First TermEmmy Senior Lucky100% (1)
- Questionnaire of Measuring Employee Satisfaction at Bengal Group of IndustriesDokumen2 halamanQuestionnaire of Measuring Employee Satisfaction at Bengal Group of IndustriesMuktadirhasanBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Biomechanical Basis of Extraction Space Closure - Pocket DentistryDokumen5 halaman6 Biomechanical Basis of Extraction Space Closure - Pocket DentistryParameswaran ManiBelum ada peringkat
- PyramidsDokumen10 halamanPyramidsapi-355163163Belum ada peringkat
- Material Balance in Froth Flotation (Excel File Additional Document)Dokumen4 halamanMaterial Balance in Froth Flotation (Excel File Additional Document)joseph kafumbila100% (1)
- Method Statement For FDTDokumen7 halamanMethod Statement For FDTMs UndergroundBelum ada peringkat
- Mr. Edel B. Paclian, LPT Ms. Janny Ame Narral, LPT Master of Arts in EducationDokumen34 halamanMr. Edel B. Paclian, LPT Ms. Janny Ame Narral, LPT Master of Arts in EducationEdel Borden PaclianBelum ada peringkat
- Oil SeparatorDokumen7 halamanOil Separatorbookslover1Belum ada peringkat
- Case Study Sustainable ConstructionDokumen5 halamanCase Study Sustainable ConstructionpraisethenordBelum ada peringkat
- Reflection EssayDokumen3 halamanReflection Essayapi-451553720Belum ada peringkat
- PsiRun SheetsDokumen3 halamanPsiRun SheetsalemauBelum ada peringkat
- Talon Star Trek Mod v0.2Dokumen4 halamanTalon Star Trek Mod v0.2EdmundBlackadderIVBelum ada peringkat
- Fun33 LCNVDokumen6 halamanFun33 LCNVnehalBelum ada peringkat
- Name: Period: Date:: Math Lab: Explore Transformations of Trig Functions Explore Vertical DisplacementDokumen7 halamanName: Period: Date:: Math Lab: Explore Transformations of Trig Functions Explore Vertical DisplacementShaaminiBelum ada peringkat
- Mini Test PBD - SpeakingDokumen4 halamanMini Test PBD - Speakinghe shaBelum ada peringkat
- Neil Bryan N. Moninio: Professional GoalDokumen3 halamanNeil Bryan N. Moninio: Professional GoalNeil Bryan N. MoninioBelum ada peringkat
- Third Periodical Assessment Test (Pat 3) Grade 8 - MathematicsDokumen10 halamanThird Periodical Assessment Test (Pat 3) Grade 8 - Mathematicswerdubob100% (1)
- NSTP ReportDokumen8 halamanNSTP ReportMary Grace MendeBelum ada peringkat
- Is Euclidean Zoning The New Pig in The Parlor?: The Coming of Age of Form-Based Zoning (Damon Orobona)Dokumen19 halamanIs Euclidean Zoning The New Pig in The Parlor?: The Coming of Age of Form-Based Zoning (Damon Orobona)Damon Orobona100% (1)
- WSDL Versioning Best PracticesDokumen6 halamanWSDL Versioning Best Practiceshithamg6152Belum ada peringkat
- PYTHONBOOKDokumen32 halamanPYTHONBOOKJyotirmay SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Andrew Haywood CV 2010Dokumen6 halamanAndrew Haywood CV 2010Dobber0Belum ada peringkat
- (SQP2) Sample Question Paper 2Dokumen2 halaman(SQP2) Sample Question Paper 2Vraj M BarotBelum ada peringkat
- Mcob OcDokumen19 halamanMcob OcashisBelum ada peringkat
- Power Meditation: by Mahaswami MedhiranandaDokumen7 halamanPower Meditation: by Mahaswami Medhiranandaanhadbalbir7347Belum ada peringkat