How To Answer Biology SPM Papers
Diunggah oleh
Cikgu A. KamilDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
How To Answer Biology SPM Papers
Diunggah oleh
Cikgu A. KamilHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
How to Answer Biology SPM Papers How to Answer Biology SPM Papers BIOLOGY 1 1.
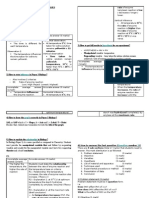
Read the entire question and all the answer choices before deciding on the answer. 2. Mark your answer clearly on the Objective Answer Sheet. 3. If you cannot answer a question, go on to the next question. Remember to come back to this question later. This will prevent you from wasting precious time. 4. Go through your answers after you have finished. You might want to change some of your answers BIOLOGY 2 - STRUCTURED QUESTIONS 1. Write neatly and clearly. 2. Be brief and to the point it is not necessary to repeat the question. 3. Show your working for any calculation work. (Write down the formula, substitute the values into the formula, complete the calculation) 4. Use a pencil to draw diagrams or graphs. 5. Label diagram and graphs clearly. 6. Use the marks allocated to determine how much you should write. One mark is allocated for one point. 7. Use the instruction guide to answer the questions. BIOLOGY 2 - ESSAY QUESTIONS 1. Read all the questions before choosing those that you want to answer. 2. Re-read the chosen questions carefully to make sure you are interpreting them correctly. 3. You may explain your answer using appropriate diagrams (be sure to label all diagrams), equations, graphs, tables or any other suitable methods. 4. Give your answers according to the key instruction words. Use the INSTRUCTION GUIDE below. 5. You may give your answer in point form. Check the number of points in your answer with the number of marks allocated for the question. (One point is usually allocated one mark). If possible give one or two more points than the maximum marks allocated. INSTRUCTION GUIDE AND RESPONSE Key instruction word Answer What is ? Give the actual name. Spelling for scientific terms and names must be accurate. How many .Give the quantity, no need for calculation calculate Show the workings of your calculation and the final answer Name Give the correct name, scientific
names must be underlined State Just give the fact. No explanations or descriptions needed. List State the facts in point form. Define Define the term clearly and completely. Why Give the reasons How Explain step by step how it takes place Compare Give the similarities and differences explicitly. Use a table. What are the differences Give the differences explicitly. Use a table. Describe Tell the story, an account of, state the main points of the topic. No elaborate explanation of why and how is necessary Discuss Give your opinion from different aspects, viewpoints or arguments. Contrast / Distinguish Give the differences only. Evaluate Give the positive and negative aspects. Explain Clarify what, how or why. State the fact followed by a few sentences to elaborate it. Illustrate Explain or clarify by using diagrams, drawings or figures. Outline Briefly give the important points. Summarize Present concisely all main points. Tick ( ) in the box Tick ( ) in the box, DO NOT use a cross ( ). Example for Describe and Explain Describe the graph As the temperature increase from 0 oC to 40 oC , the rate of enzyme activity also increases. The rate of enzyme activity is maximum at 40 oC . As the temperature increases above 40 oC , the rate of enzyme activity decreases. Explain the graph As the temperature increase from 0 oC to 40 oC , the rate of enzyme activity also increases . At these temperatures, the enzyme is more active as the temperature increases because
8 the rate of collision between the enzymes and the substrate molecules increases with the increase of temperature. The rate of enzyme activity is maximum at 40 oC because this temperature is optimum for the enzyme to function. As the temperature increases above 40 oC, the rate of enzyme activity decreases because the enzymes begin to denature due to the high temperature. PAPER 3 : QUESTION 1 The following scientific skills are tested in Question 1: 1. OBSERVATION QUESTION : State two observations. ANSWER : Write down what can be observed only. Do not do any analysis, comparison or conclusion. For most experiments, the observation can be written in the form: The .(responding variable) .. at ..(manipulated variable) is (state reading of measuring instrument) ( Write the observation for the highest and lowest value of the responding variable.) Example: The time taken for the starch to be completely hydrolysed at 5 oC is 45 minutes. The time taken for the starch to be completely hydrolysed at 40 oC is 5 minutes. 2. INFERENCE State one inference which corresponds to each observation. An inference is a brief explanation of the observation, based on scientific knowledge which you already know. Example: 10 The time taken for starch to be completely hydrolysed at 5 oC is 45 minutes because the low temperature causes the enzymes to react slowly with the substrate. The time taken for starch to be completely hydrolysed at 5 oC is 5 minutes because the higher temperature causes the enzymes to react quickly with the substrate. 3. MEASURING AND USING NUMBERS Record the reading of thermometer, stopwatch, ruler etc. from the given diagram. 4. COMMUNICATING Construct the table with the manipulated variable as the first column and the responding variable as the second column.
Data derived or calculated from the second column can be added to the third column. Show the calculations in the third column itself. Units of measurements should be written together with table titles, not with readings. Example Temperature / oC Time for starch to be completely hydrolysed / min Rate of reaction / min -1 5 10 1/10 = 0.1 15 5 1 / 5 = 0.2 30 2 1 / 2 = 0.5 11 5. INTERPRETING DATA Explain / state the relationship between manipulated and responding variables as obtained from a graph of the results. Example: As the temperature increases from 5 oC to 45 oC, the time taken for the complete hydrolysis of starch decreases from 45 minutes to 5 minutes. 6. CONTROLLING VARIABLES Variables State the variable Describe how you control the variables Use action words and name the instruments used MANIPULATED Temperature Use / . Use a thermometer to measure the temperature of the water bath and add ice or warm water to maintain the temperature of the water bath. Place the test tubes in the different water baths. RESPONDING Time taken for complete hydrolysis of starch Record / measure using . Record the time taken for the enzyme substrate mixture to lose its blue colour. CONTROLLED
Concentration of enzyme Use the same/ Maintain Use the same amount of enzyme ( 1 ml) in each of the experiment. 12 7. MAKING HYPHOTHESIS Able to state the hypothesis correctly based on the following criteria: State the manipulated variable State the responding variable Relate the manipulated variable and the responding variable (do not use vague relationships like affects or influence or changes with). Commit to using terms like: increases with / decreases with . 8. PREDICTING QUESTION : If the experiment is repeated .., predict the observation ANSWER : Give a value or relevant statement e.g. the (responding variable) will be higher / lower than (the value in the first experiment) followed by a the reason EXAMPLE: What will the rate of transpiration be at fan speed 3, if the experiment is repeated in the dark? The transpiration rate at fan speed 3 will be less then (value recorded) because the stomata is closed in the dark and less water will be loss through them. 13 9. DEFINING OPERATIONALLY Give a definition based on the context of the experiment. EXAMPLE 1: An experiment is carried out to investigate photosynthesis and the number of bubbles released is counted. The operational definition of photosynthesis would then be: Photosynthesis is the process where green plants release bubbles in the presence of light, carbon dioxide and water. EXAMPLE 2: An experiment is carried out to investigate photosynthesis and leaves are tested with iodine solution for the presence of starch. The operational definition of photosynthesis would be: Photosynthesis is the process where green leaves in the presence of light, carbon dioxide and water, produce starch which turns iodine solution dark blue.
EXAMPLE 3: An experiment is carried out to investigate transpiration under different fan speeds. The operational definition of transpiration would be: Transpiration is the process where a plant loses water to the surrounding which is indicated by the movement of water or air bubble in the capillary tube and is affected by speed of the air current. (You should include the variables in the context of the experiment / experimental conditions and .) 14 10. CLASSIFYING Group the materials or apparatus listed using a table with the headings provided. Group them according to their function in the experiment. 15 11. USING SPACE-TIME RELATIONSHIP State the changes of the responding variable with time. Use relationship words like increases with / decreases with / remains constant with / increases proportionately with / etc. Do not use neutral relationship terms like affects / influences / changes with. 16 PAPER 3 : QUESTION 2 This question tests students ability to plan an experiment in a given format. Students must have all of the following : 1. Problem statement 2. Aim of investigation 3. Variables 4. Hypothesis 5. List of apparatus and materials 6. Technique used 7. Experimental procedure or method 8. Presentation of data 9. Conclusion 1. PROBLEM STATEMENT Must be written in the form of a question End with a question mark. Eg. Does pH affect the activity of amylase? 2. OBJECTIVE Write down the objective as given in the question. Eg. To investigate the effect of pH on the activity of amylase? 17
3. VARIABLES : Write down 3 variables. (Manipulated variable, responding variable and controlled variable. The controlled variable must be one that will affect the outcome of the experiment if not kept constant.) 4. HYPOTHESIS Able to state the hypothesis correctly based on the following criteria: State the manipulated variable State the responding variable Relate the manipulated variable and the responding variable 5. MATERIALS AND APPARATUS List down all the materials and apparatus used. 6. TECHNIQUE In a complete sentence, write down what is observed or measured (include the instrument used). State the specific name of the technique where applicable. Example : (i) Measure and record the volume of fruit juices needed to decolorize blue DCPIP , using a syringe. 18 (ii)Measure and record the initial and final temperature of the water in the boiling tube using a thermometer. 7. PROCEDURE Write down each step clearly and systematically. Your steps should include: Steps where you describe how apparatus and materials are handled. Steps where you describe how the controlled variable is maintained Steps where you describe how the manipulated variable is altered Steps where you describe how the responding variable is measured and the instrument to be used. Precautionary steps which ensure safety / improve accuracy of readings. (write the steps as a set of instructions or direct speech and not in passive speech) 8. PRESENTATION OF DATA Construct the table with the correct titles and units. Leave the table blank. The experiment is not carried out yet, so the
results are not yet available. 9. CONCLUSION Repeat or modify the hypothesis sentence. You may then write whether the hypothesis is accepted or rejected.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Biology Summaries: CO MethaneDokumen25 halamanBiology Summaries: CO MethaneMariam Abdel-RazekBelum ada peringkat
- Security Integrity Quality IELTSDokumen40 halamanSecurity Integrity Quality IELTSahmed127Belum ada peringkat
- Test ConstructionDokumen19 halamanTest ConstructionMilainBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan Observed 23072014Dokumen4 halamanLesson Plan Observed 23072014redbeatnikBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 3 Biology Answering TechniquesDokumen3 halamanPaper 3 Biology Answering Techniquesriyashree100% (1)
- Pre A1 Starters 2018 Reading and Writing Part 5Dokumen7 halamanPre A1 Starters 2018 Reading and Writing Part 5Jim JiménezBelum ada peringkat
- PTE Repeat Sentence Tips and Tricks PDFDokumen4 halamanPTE Repeat Sentence Tips and Tricks PDFMarven Carmona AsetreBelum ada peringkat
- TP Lesson Plan SampleDokumen10 halamanTP Lesson Plan Sampleasmaa elsawaf100% (1)
- Assessing Speaking: Musfera Nara Vadia 1300925 K4-13Dokumen30 halamanAssessing Speaking: Musfera Nara Vadia 1300925 K4-13Rizky HarmiyantiBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Linguistic PPDokumen12 halamanAssignment Linguistic PPNur Farahain NordinBelum ada peringkat
- Create Your Development PortfolioDokumen6 halamanCreate Your Development PortfoliobiljanamarijaBelum ada peringkat
- Second Language Classroom Observation QuestionsDokumen2 halamanSecond Language Classroom Observation QuestionsApplecart23Belum ada peringkat
- Che 4 BookDokumen423 halamanChe 4 BookAnonymous PMF8IpBtfBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan - TP5Dokumen4 halamanLesson Plan - TP5AhsunAli100% (1)
- IELTS Writing Task 1: How to Answer Process Questions in 5 StepsDokumen10 halamanIELTS Writing Task 1: How to Answer Process Questions in 5 StepsJames DSBelum ada peringkat
- CHEM 1113 Syllabus SP15Dokumen8 halamanCHEM 1113 Syllabus SP15Alex Bernier100% (1)
- Oxfordtefltrinity Diptesol Lesson Plan Pro Forma: Grammar: Vocabulary: Pronunciation: SkillsDokumen6 halamanOxfordtefltrinity Diptesol Lesson Plan Pro Forma: Grammar: Vocabulary: Pronunciation: SkillsJem BurtonBelum ada peringkat
- TKT Workshop ScheduleDokumen2 halamanTKT Workshop ScheduledaemynBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To EmSATDokumen2 halamanIntroduction To EmSATAreen AlhazaymehBelum ada peringkat
- PT3 Listening Sample Test - Key PDFDokumen2 halamanPT3 Listening Sample Test - Key PDFAmad AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Public Speaking CriteriaDokumen2 halamanPublic Speaking CriteriaS TANCREDBelum ada peringkat
- The End of 'Chalk and Talk' PDFDokumen4 halamanThe End of 'Chalk and Talk' PDFchew shally100% (1)
- CELT Booklet 2017 2018Dokumen21 halamanCELT Booklet 2017 2018Marisa ConstantinidesBelum ada peringkat
- Reorder Paragraph Prediction FileDokumen3 halamanReorder Paragraph Prediction FileShaikh Hafizur RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- True, False, Not Given PDFDokumen2 halamanTrue, False, Not Given PDFangel lou aguitongBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Chinese As A Second Language 0523/03 May/June 2021Dokumen6 halamanCambridge IGCSE™: Chinese As A Second Language 0523/03 May/June 2021For GamingBelum ada peringkat
- English As A Second Language Stage 9 Scheme of Work 2018 - tcm143-353988Dokumen68 halamanEnglish As A Second Language Stage 9 Scheme of Work 2018 - tcm143-353988Aizat Zulhilmi YusupBelum ada peringkat
- Authentic MaterialDokumen2 halamanAuthentic MaterialAna MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Ielts Test: Test Format - Speaking 11-14 MinutesDokumen18 halamanIelts Test: Test Format - Speaking 11-14 MinutesVinycius AzevedoBelum ada peringkat
- Internship ReportDokumen5 halamanInternship Reportspeedyshipman50% (6)
- H. D. Brown'S Principles For Teaching Listening Skills: Slides by Daniel Beck (Aka Samuraitheologian)Dokumen36 halamanH. D. Brown'S Principles For Teaching Listening Skills: Slides by Daniel Beck (Aka Samuraitheologian)briliyansaBelum ada peringkat
- Viva PPT GuidleinsDokumen2 halamanViva PPT GuidleinsDharmender SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Exam Thread: Paper 1 Tasks 1 & 2 and Paper 2 Tasks 2 & 3: The Distance Delta Module OneDokumen28 halamanExam Thread: Paper 1 Tasks 1 & 2 and Paper 2 Tasks 2 & 3: The Distance Delta Module OneAlexBelum ada peringkat
- Test Specification Table Mid TermDokumen5 halamanTest Specification Table Mid TermAnonymous c1jnt37Belum ada peringkat
- Post Lesson EvaluationDokumen2 halamanPost Lesson EvaluationpandreopBelum ada peringkat
- Trial SBP SPM 2013 Biology SKEMA K3Dokumen12 halamanTrial SBP SPM 2013 Biology SKEMA K3Cikgu Faizal100% (1)
- SPM Chemistry Answering Technique PDFDokumen12 halamanSPM Chemistry Answering Technique PDFAriss LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Answering Techniques Based On The Latest SPM Examination FormatDokumen13 halamanAnswering Techniques Based On The Latest SPM Examination FormatYeap Jing HuiBelum ada peringkat
- Post Lesson ReflectionDokumen8 halamanPost Lesson Reflectionapi-430394514Belum ada peringkat
- Task Based ApproachDokumen3 halamanTask Based ApproachTina Galgotia100% (1)
- General Strategy For ListeningDokumen8 halamanGeneral Strategy For ListeningAnonymous PbCsXeZBelum ada peringkat
- India English Celta Application FormDokumen3 halamanIndia English Celta Application FormSharoon Rubinstein0% (1)
- Exam Thread: Further Work On Paper 1 Tasks 1, 2 & 3 and Paper 2 Tasks 1 & 4Dokumen42 halamanExam Thread: Further Work On Paper 1 Tasks 1, 2 & 3 and Paper 2 Tasks 1 & 4AlexBelum ada peringkat
- Primary School English Language CurriculumDokumen21 halamanPrimary School English Language CurriculumOllynda Bell Ann100% (1)
- PPP Method - Group 6Dokumen26 halamanPPP Method - Group 6Lê Nguyễn Trúc AnBelum ada peringkat
- Grammar Zero To Hero: Pte UniverseDokumen10 halamanGrammar Zero To Hero: Pte UniverseRuqia KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Pte EssentialDokumen2 halamanPte EssentialIshvinder SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Graphics and DesignDokumen23 halamanEngineering Graphics and DesignYadana1Belum ada peringkat
- Arizona State University Tesol 1Dokumen6 halamanArizona State University Tesol 1Catarina NizaBelum ada peringkat
- Module Two - Docx - 1607439360085 PDFDokumen11 halamanModule Two - Docx - 1607439360085 PDFAlliyahBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge English Placement Test (CEPT) : Reading TasksDokumen9 halamanCambridge English Placement Test (CEPT) : Reading TasksLestariBelum ada peringkat
- TKT-What Is A SyllableDokumen3 halamanTKT-What Is A SyllableSam ClarkBelum ada peringkat
- TP 4 Lesson PlanDokumen5 halamanTP 4 Lesson PlanAnaAleksicBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanLesson PlanBienzel NaadatBelum ada peringkat
- TKT Module 3Dokumen11 halamanTKT Module 3Татьяна АндрющенкоBelum ada peringkat
- Rating Scales and Checklists for Research Data CollectionDokumen8 halamanRating Scales and Checklists for Research Data Collectionaditi 0Belum ada peringkat
- Project management methods and market analysisDokumen3 halamanProject management methods and market analysisMR. DEVASHISH GAUTAMBelum ada peringkat
- Q&A in Answering Techniques for Biology Paper 3Dokumen11 halamanQ&A in Answering Techniques for Biology Paper 3Ng Wan LinBelum ada peringkat
- How To Answer SPM Biology Paper 1 2 3 by Kenneth NG Edited May 2009Dokumen20 halamanHow To Answer SPM Biology Paper 1 2 3 by Kenneth NG Edited May 2009Boon Kiat Teh90% (10)
- Answering Techniques For SPM Biology Paper 3Dokumen6 halamanAnswering Techniques For SPM Biology Paper 3Ck Yong100% (6)
- Amazing Math Trick 12461Dokumen23 halamanAmazing Math Trick 12461CRPF SchoolBelum ada peringkat
- Kertas 3 Biology Anchor ChecklistDokumen3 halamanKertas 3 Biology Anchor ChecklistCikgu A. KamilBelum ada peringkat
- Idm PatchDokumen1 halamanIdm PatchCikgu A. KamilBelum ada peringkat
- k1 Biologi Trial Kedah 2015Dokumen27 halamank1 Biologi Trial Kedah 2015Cikgu A. KamilBelum ada peringkat
- Skema K 3 Biologi Kedah 2015Dokumen12 halamanSkema K 3 Biologi Kedah 2015Cikgu A. KamilBelum ada peringkat
- www.crackingpatching.com.txtDokumen1 halamanwww.crackingpatching.com.txtCikgu A. KamilBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Experiment List Form 4&5Dokumen2 halamanBiology Experiment List Form 4&5Cikgu A. Kamil100% (4)
- k2 Biologi Trial Kedah 2015Dokumen22 halamank2 Biologi Trial Kedah 2015Cikgu A. KamilBelum ada peringkat
- JAWAPANOTI2MTK1JPNT201Dokumen1 halamanJAWAPANOTI2MTK1JPNT201Cikgu A. KamilBelum ada peringkat
- Img 20140425 0003Dokumen1 halamanImg 20140425 0003Heather HooverBelum ada peringkat
- Calon SPM 2013Dokumen16 halamanCalon SPM 2013Cikgu A. KamilBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 4Dokumen46 halamanScience Form 4Cikgu A. KamilBelum ada peringkat
- Peperiksaan Percubaan PMR 2013 Peratus A + B Bagi Tingkatan: T3 SemuaDokumen5 halamanPeperiksaan Percubaan PMR 2013 Peratus A + B Bagi Tingkatan: T3 SemuaCikgu A. KamilBelum ada peringkat
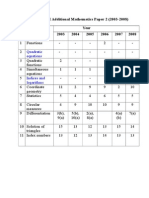
- Analysis of SPM Additional Mathematics Paper 2 (2003-2008) Form 4 Topics Year 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008Dokumen2 halamanAnalysis of SPM Additional Mathematics Paper 2 (2003-2008) Form 4 Topics Year 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008Cikgu A. KamilBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 3Dokumen42 halamanScience Form 3Cikgu A. KamilBelum ada peringkat
- HistoryDokumen18 halamanHistoryBắp NgọtBelum ada peringkat
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDokumen593 halamanHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDokumen593 halamanHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- The Effect of Different Quantities of Water Intake On Urine OutputDokumen2 halamanThe Effect of Different Quantities of Water Intake On Urine OutputCikgu A. Kamil33% (3)
- Biology Form 4 Compilation of ExperimentsDokumen28 halamanBiology Form 4 Compilation of Experimentsriyashree50% (4)
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDokumen593 halamanHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDokumen593 halamanHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDokumen593 halamanHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- The Effect of Air Movement On The Rate of TranspirationDokumen4 halamanThe Effect of Air Movement On The Rate of TranspirationCikgu A. Kamil76% (17)
- International Standard: Norme InternationaleDokumen11 halamanInternational Standard: Norme InternationaleApa DiaBelum ada peringkat
- Heinz Bloch - Compressor Technology Advances - Beyond (2021)Dokumen492 halamanHeinz Bloch - Compressor Technology Advances - Beyond (2021)caapasa100% (1)
- CCSI Buried DoubleJacket 12 G 652 D DGK Rev0Dokumen2 halamanCCSI Buried DoubleJacket 12 G 652 D DGK Rev0Bilal AlifBelum ada peringkat
- CM015 DS 01 2Dokumen2 halamanCM015 DS 01 2Mohamed BeheiryBelum ada peringkat
- Separation and Purification: Test Yourself 3.1 and 3.2 (Page 39)Dokumen2 halamanSeparation and Purification: Test Yourself 3.1 and 3.2 (Page 39)khalil rehmanBelum ada peringkat
- LeTID: Light and Elevated Temperature Induced DegradationDokumen15 halamanLeTID: Light and Elevated Temperature Induced DegradationShubham KumarBelum ada peringkat
- (BS EN 1346 - 2007) - Adhesives For Tiles. Determination of Open Time.Dokumen10 halaman(BS EN 1346 - 2007) - Adhesives For Tiles. Determination of Open Time.BardhBelum ada peringkat
- Preformed Expansion Joint Filler For Concrete (Bituminous Type)Dokumen5 halamanPreformed Expansion Joint Filler For Concrete (Bituminous Type)CPA BTKBelum ada peringkat
- Comp Chem8Dokumen134 halamanComp Chem8Dr. Partha Sarathi SenguptaBelum ada peringkat
- Tds Dep 455sDokumen3 halamanTds Dep 455sA MahmoodBelum ada peringkat
- Naming CompoundsDokumen84 halamanNaming CompoundsangelaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Selection of Heat Treatment and Aluminizing Sequence For Rene 77 SuperalloyDokumen4 halaman1 Selection of Heat Treatment and Aluminizing Sequence For Rene 77 SuperalloyEnary SalernoBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal Dan Resume Pemanfaatan Modifikasi Pati - Oktariananda - E1G020085Dokumen10 halamanJurnal Dan Resume Pemanfaatan Modifikasi Pati - Oktariananda - E1G020085Oktarian NandaBelum ada peringkat
- Edco Incinerator Plant 2: Refractory Lining at IncineraterDokumen1 halamanEdco Incinerator Plant 2: Refractory Lining at IncineraterNic RicBelum ada peringkat
- MAN 0604-03-En Zetasizer Advance Series GuideDokumen120 halamanMAN 0604-03-En Zetasizer Advance Series GuideLaras NovitasariBelum ada peringkat
- Chem 1 Lecture NotesDokumen87 halamanChem 1 Lecture NotesGlenn ClementeBelum ada peringkat
- Fifty Years of The VEPR ModelDokumen13 halamanFifty Years of The VEPR ModelPriyabrata DashBelum ada peringkat
- Iso 14644-17-2021Dokumen34 halamanIso 14644-17-2021dukeplusBelum ada peringkat
- XTH Term 1 Syllabus (2023-2024)Dokumen4 halamanXTH Term 1 Syllabus (2023-2024)Akshat JainBelum ada peringkat
- Demulsifiers For Simulated Basrah Crude OilDokumen107 halamanDemulsifiers For Simulated Basrah Crude OilTuan Yusoff100% (2)
- Qcs 2010 Part 8.07 Glass Reinforced PlasticsDokumen5 halamanQcs 2010 Part 8.07 Glass Reinforced PlasticsRotsapNayrbBelum ada peringkat
- 0255E - Human Albumin SolutionDokumen3 halaman0255E - Human Albumin Solutiondannny_mejiaaBelum ada peringkat
- Product Data: CompositionDokumen2 halamanProduct Data: Compositionsriatul2006Belum ada peringkat
- Kompleksometri ObatDokumen13 halamanKompleksometri ObatBakhitah NurulBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Entrance Test 2Dokumen3 halamanChemistry Entrance Test 2Eljesa LjusajBelum ada peringkat
- Mg (OH) 2 + MgSO4 + H2O体系的相关系和热力学建模及其对氢氧化镁硫酸盐水泥的影响Dokumen14 halamanMg (OH) 2 + MgSO4 + H2O体系的相关系和热力学建模及其对氢氧化镁硫酸盐水泥的影响jordan jackBelum ada peringkat
- Bioflavonoids From the Leaves of Ficus Deltoidea Jack With Α-glucosidase InhibitionDokumen10 halamanBioflavonoids From the Leaves of Ficus Deltoidea Jack With Α-glucosidase InhibitionLife HistoryBelum ada peringkat
- Lewis Structure and Chemical BondingDokumen36 halamanLewis Structure and Chemical BondingAlyssa Crizel CalotesBelum ada peringkat
- CLS-Science ELS Workbook 8Dokumen5 halamanCLS-Science ELS Workbook 8lsavaglia1990Belum ada peringkat
- Determination of Hardness of Water and WastewaterDokumen5 halamanDetermination of Hardness of Water and WastewaterThato NkhemeBelum ada peringkat