Install and Configure DHCP Server in Win Server 2003 Step by Step Guide
Diunggah oleh
bapibapunDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Install and Configure DHCP Server in Win Server 2003 Step by Step Guide
Diunggah oleh
bapibapunHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Install and Configure DHCP Server in Win server 2003 Step By Step Guide
Windows-Server-2003 Add comments
Feb
252008
A DHCP Server assigns IP addresses to client computers. This is very often used in enterprise networks to reduce configuration efforts. All IP addresses of all computers are stored in a database that resides on a server machine.
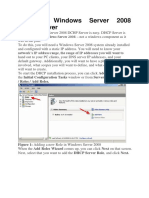
Installing DHCP Server is very easy in win server 2003 First you need to go to Start>All Programs>Administrative Tools>Manage Your Server
Here you need to select Add or remove a role
Verify the following steps click on Next
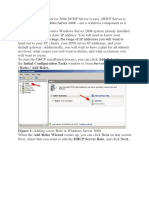
Select Server Role as DHCP Server option click on Next
Summary selection click on Next
Installing DHCP Server in progress
Now this will prompt new scope welcome scree click next
A scope is a collection of IP addresses for computers on a subnet that use DHCP. enter the name and description of your scope click next
Now you need to define the range of addresses that the scope will distribute across the network,the subnet mask for the IP address . Enter the appropriate details and click next.
Enter the IP address range that you want to exclude and click on next
Select lease duration how long a client can use an IP address assigned to it from this scope. It is recommended to add longer leases for a fixed network (in the office for example) and shorter leases for remote connections or laptop computers and click next
You are given a choice of whether or not you wish to configure the DHCP options for the scope now or later.You can select Yes,I want to radion button and click next
Enter the router, or gateway, IP address click next. The client computers will then know which router to use and click next
Enter the DNS and domain name settings can be entered. The DNS server IP address will be distributed by the DHCP server and given to the client click next
If you have WINS setup then here is where to enter the IP Address of the WINS server. You can just input the server name into the appropriate box and press Resolve to allow it to find the IP address itself click next
Now you need to activate this scope now and click next
DHCP Server new scope installation was finished and click finish
Now your server is now a DHCP server message and click finish
Configuring DHCP Now you need to go to Start>Administrative Tools>DHCP
Right Click on your server click on Authorize your DHCP Server
Authorization completed now your DHCP server is up and running
DHCP servers permit you to reserve an IP address for a client. This means that the specific network client will have the same IP for as long as you wanted it to. To do this you will have to know the physical address (MAC) of each network card. Enter the reservation name, desired IP address, MAC address and description choose whether you want to support DHCP or BOOTP and press add. The new reservation will be added to the list.
Thats it it is very easy to configure DHCP server in win server 2003 now you can configure your windows client pc to check your dhcp server is working or not.
How do I... Install and configure a DHCP server in Windows Server 2008?
By Steven Warren April 29, 2008, 12:22 PM PDT
Takeaway: DHCP is an invaluable service when you have a network larger than a handful of computers. Microsoft Windows Server 2008s built-in DHCP server allows Windows machines to obtain their IP addresses and network settings automatically, which can vastly simplify network configuration. Steven
Warren describes how to install and configure a DHCP server in Windows Server 2008, and explores some of the advanced features DHCP has to offer. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is an invaluable service when you have a network larger than a handful of computers. Its also a standard component of enterprise networks and sub networks. Microsoft Windows Server 2008s built-in DHCP server allows Windows machines (and any other TCP/IP-based machines and devices) to obtain their IP addresses and network settingsautomatically, which can vastly simplify network configuration. In this document, well discuss how to install and configure a DHCP server in Windows Server 2008, and well explore some of the advanced features DHCP has to offer. This blog post is also available as a TechRepublic gallery and TechRepublic download.
Create a plan
Before you configure your DHCP server, it is a good idea to have all your ducks in a row. Prepare and have all the necessary information up front before sitting down and configuring your server. For example, you may need to know:
The scope of IP addresses that your server will manage (e.g., 192.168.1.50 to 192.168.1.200). Which machines require static IP addresses (i.e., those machines such as servers and routers that will not use DHCP to receive their IP addresses but will be set manually). Which network information you want to send out to DHCP clients when they get their IP addresses (e.g., the addresses for your default gateway, DNS servers, and WINS servers). It is much easier to configure your DHCP server with this information in hand rather than scrambling for it at implementation time.
Installing DHCP
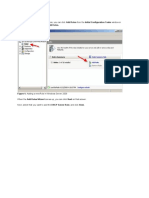
Installing a DHCP server in Windows 2008 is a snap. They created a very simple wizard that walks you through the entire process. Follow me on this journey. To install a DHCP server from the Control Panel, follow these steps: 1. From the Start menu, select | Control Panel | Administrative Tools | Server Manager. 2. Expand and click Roles (Figure A). 3. Choose Add Roles and follow the wizard by selecting the DHCP role (Figure B). 4. A new DHCP wizard appears to help you configure a DHCP server.
Figure A
Server Manager
Figure B
Add Roles Wizard
In the previous release of Windows, a wizard did not appear to walk you through creating a DHCP server. Windows Server 2008 has really simplified this process by allowing you to configure a DHCP server in roughly seven steps. Of course, you can still manage your DHCP server from the DHCP Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in or delete and create scopes on the fly. Lets continue on through the wizard. Your network cards and static IP addresses are automatically detected and you can choose how DHCP will service clients on different subnets, as shown inFigure C.
Figure C
Choose your static IP addresses to service DHCP clients
On the next window (Figure D), you can specify the applicable DNS server(s) to be used with DHCP when an address is assigned. Figure E displays where you would enter the applicable WINS servers if you require it on your network.
Figure D
Enter your DNS server IP address
Figure E
Enter your WINS server IP address
About scopes
When you create a scope, you must select the range of IP addresses and you must specify the appropriate scope options to include. These options are what we were referring to above when we mentioned that you can assign other network information to your clients at the time they are given an IP address. There are two types of scope options: Global and Scope. Global options are propagated to all the scopes that you create on that DHCP server, while Scope options are only for the individual scope that you are working with. For example, if you have different scopes for several different subnets and each subnet will have a different default gateway but will share the same DNS servers, you would want to set the DNS servers as a Global option while the default gateways would be set separately in each scope as a Scope option. On the DHCP scope window, you will create your scope. Depending on the size of your network and the amount of users that will be assigned IP addresses, some thought must be given to the parameters of your scope selections. In my example (Figure F), I created a simple scope.
Figure F
Creating your scope
The subnet type dropdown allows you to choose wireless as well (Figure G). It defaults to 24 hours. If you want to activate the scope when the wizard is complete, click the Activate this scope checkbox. If you leave it empty, you must activate the scope in the DHCP Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in.
Figure G
You can add multiple scopes before continuing the wizard
With Windows Server 2008, if you have a router (Figure H) that supports and is configured to take advantage of IPv6, you can enable this functionality on your network.
Figure H
Enable IPv6 stateless mode
Authorizing the DHCP server and activating scopes
In previous versions of Windows Server, you had to install and configure your DHCP server and then authorize it in the DHCP MMC snap-in. Authorizing your DHCP server allows you to prevent hackers from configuring rogue DHCP servers. In Windows Server 2008, you have the ability to either authorize the server in the Wizard or authorize it after the fact in the DHCP MMC-snap-in (Figure I).
Figure I
Authorizing your DHCP server
You are now ready to review (Figure J) and confirm your settings before applying your DHCP settings (Figure K).
Figure J
Reviewing your DHCP configuration before applying
Figure K
DHCP installation in progress
Once you have installed the DCHP server, you can manage it from the DHCP MMC snap-in (Figure O) located in Administrative tools. On this screen you can create additional exclusions and reservations.
Adding reservations
In addition to specifying exclusions, you can add reservations to your DHCP server. By adding a reservation, you ensure that a machine always receives the same IP address from the DHCP server. 1. Right-click on Reservations and choose new reservation. 2. Enter a friendly name for the reservation and the IP address you want to assign to the computer or device. 3. Enter the MAC address of the computer or device. (For Windows machines, you can find the MAC address by running ipconfig/all from the command prompt of the machine.) 4. Enter a description and then choose the following reservation type: DHCP, BOOTP (going across a router), or both, as shown in Figure L. Click Add.
Figure L
Adding a reservation
Adding exclusions
In addition to specifying reservations, you can add exclusions to your DHCP server (Figure M). By adding exclusions, you ensure that machines never receive a DHCP lease for that range of IP addresses. This is very useful to block IP addresses for your servers and routers.
Figure M
Adding an exclusion
In order to add Exclusions, right-click on Address Pools and choose New Exclusion Range as shown in Figure N and Figure O.
Figure N
IP address Exclusion range
Figure O
DCHP MMC snap-in
Troubleshooting DHCP
After configuring DHCP, the easiest way to troubleshoot it is to use Ipconfig from a command prompt. To view all TCP/IP information on a machine just type ipconfig/all. To release a DHCP lease, type ipconfig/release; to renew a lease, type ipconfig/renew.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Installing DHCP ServerDokumen11 halamanInstalling DHCP ServerSiThuBelum ada peringkat
- DHCP DefinitionDokumen44 halamanDHCP DefinitionAbdoo GerbayeBelum ada peringkat
- Configuration Tasks Window or From Server Manager À Roles À Add RolesDokumen13 halamanConfiguration Tasks Window or From Server Manager À Roles À Add RolesMaxi FrankBelum ada peringkat
- Install Windows Server 2008 DHCP in 10 StepsDokumen13 halamanInstall Windows Server 2008 DHCP in 10 Stepssambradshaw945Belum ada peringkat
- DHCP Configuration Step by StepDokumen20 halamanDHCP Configuration Step by StepshekharrawathotmailBelum ada peringkat
- How To Setup and Configure A Domain Controller On Windows Server 2008 R2Dokumen23 halamanHow To Setup and Configure A Domain Controller On Windows Server 2008 R2AmrinderSinghBelum ada peringkat
- Installing & Configuring Basic DHCP Server On Windows 2003: Assigning The Server A Static IP AddressDokumen11 halamanInstalling & Configuring Basic DHCP Server On Windows 2003: Assigning The Server A Static IP AddressAnonymous PDGLsjN1Q5Belum ada peringkat
- Install and Configure DHCP in Windows Server 2019 StepDokumen43 halamanInstall and Configure DHCP in Windows Server 2019 StepAnji NeyuluBelum ada peringkat
- DHCPDokumen89 halamanDHCPgurucharannayakBelum ada peringkat
- Setting Up A DHCP Server in Windows 2003Dokumen7 halamanSetting Up A DHCP Server in Windows 2003Jalel Bejo GudinaBelum ada peringkat
- How To Install DHCP Server in Windows Server 2003Dokumen8 halamanHow To Install DHCP Server in Windows Server 2003P Vipin McitpBelum ada peringkat
- DHCPDokumen33 halamanDHCPzahirhussiansBelum ada peringkat
- Installing Windows Server 2008 DHCP Server: / Roles / Add RolesDokumen2 halamanInstalling Windows Server 2008 DHCP Server: / Roles / Add Rolesthess22Belum ada peringkat
- Configure DHCP Server in Windows 2000Dokumen18 halamanConfigure DHCP Server in Windows 2000Rajesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- DHCP Server ConfigurationDokumen9 halamanDHCP Server ConfigurationTan TaroBelum ada peringkat
- DHCP Server Setup Guide - Configure IP Addresses, DNS, and MoreDokumen8 halamanDHCP Server Setup Guide - Configure IP Addresses, DNS, and MoreTHIRUNEELAKANDANBelum ada peringkat
- DHVP ServerDokumen2 halamanDHVP Serverthess22Belum ada peringkat
- Al-Quds University Computer Engineering Student: Mohammad Zeidan ID: 21411566 DR - Rushdi Hammamreh MR - Alaa El-Aaraj Experiment 5: DHCP SERVERDokumen16 halamanAl-Quds University Computer Engineering Student: Mohammad Zeidan ID: 21411566 DR - Rushdi Hammamreh MR - Alaa El-Aaraj Experiment 5: DHCP SERVERZeidan MohammadBelum ada peringkat
- Technical QuestionsDokumen21 halamanTechnical Questionsboopathi84Belum ada peringkat
- DHCP in Windows Server 2008 R2: How To Install ItDokumen9 halamanDHCP in Windows Server 2008 R2: How To Install ItkakayaBelum ada peringkat
- DHCP BasicDokumen20 halamanDHCP Basicsabakh bhattiBelum ada peringkat
- IP Address Tcp/IpDokumen12 halamanIP Address Tcp/Ipapi-19820097Belum ada peringkat
- DHCP Installation ProcessDokumen13 halamanDHCP Installation ProcessShahil AftabBelum ada peringkat
- Tasksheet 5 Install and Configure DHCP RoleDokumen8 halamanTasksheet 5 Install and Configure DHCP RoleElma Clarissa ToscanoBelum ada peringkat
- DHCP OverviewDokumen3 halamanDHCP OverviewAkash PhoenixBelum ada peringkat
- 3.2-1 Install and Configure DHCPDokumen57 halaman3.2-1 Install and Configure DHCPMaykel Uryeta MamitzBelum ada peringkat
- Safe and Reliable Configuration. DHCP Minimizes Configuration Errors Caused by Manual IPDokumen3 halamanSafe and Reliable Configuration. DHCP Minimizes Configuration Errors Caused by Manual IPtitassarkerBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 6: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP (Part1)Dokumen51 halamanLesson 6: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP (Part1)Mahmmoud MahdiBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCPDokumen23 halamanDynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCPUchi RomeoBelum ada peringkat
- TVL - CSS12 - Q2 - M7Dokumen10 halamanTVL - CSS12 - Q2 - M7fast6Belum ada peringkat
- Install and Configure DHCP on Windows 2000Dokumen3 halamanInstall and Configure DHCP on Windows 2000Arjun KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Operating System Lab Project ReportDokumen15 halamanOperating System Lab Project ReportTahmid Ahmed NuhashBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1 - Implementing Advanced Network ServicesDokumen66 halamanModule 1 - Implementing Advanced Network ServicesEricPattersonBelum ada peringkat
- DHCPDokumen2 halamanDHCPkarthysBelum ada peringkat
- Unit - I - Unit-V Notes - Basic IP ServicesDokumen271 halamanUnit - I - Unit-V Notes - Basic IP ServicesYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCABelum ada peringkat
- Knowledge Byte: CollaborateDokumen21 halamanKnowledge Byte: CollaborateR. Azhar KusumaBelum ada peringkat
- 3.2-1 Install and Configure DHCPDokumen57 halaman3.2-1 Install and Configure DHCPMichael John ClarkeBelum ada peringkat
- How To Configure Linux DHCP ServerDokumen7 halamanHow To Configure Linux DHCP ServerprimaryBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 11Dokumen12 halamanLab 11Travis Jon Wheelwright83% (12)
- DHCPDokumen17 halamanDHCPElson RealistaBelum ada peringkat
- Configure DHCP Server Role and Scopes in Windows ServerDokumen5 halamanConfigure DHCP Server Role and Scopes in Windows ServerJalel Bejo GudinaBelum ada peringkat
- Installing DHCP ServerDokumen14 halamanInstalling DHCP ServerbebibooBelum ada peringkat
- Deploying DHCP: in This ChapterDokumen8 halamanDeploying DHCP: in This ChapterEmilio CobradorBelum ada peringkat
- Tle-12 q1 Las Css Wk8day1Dokumen7 halamanTle-12 q1 Las Css Wk8day1marivic itongBelum ada peringkat
- Configure Windows Server 2008 R2Dokumen55 halamanConfigure Windows Server 2008 R2rommelBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 4 CCNDokumen7 halamanLab 4 CCNAreeba NoorBelum ada peringkat
- DHCP Scopes and ExclusionsDokumen4 halamanDHCP Scopes and ExclusionsDavid LlanesBelum ada peringkat
- Windows 2000 Configure DHCP ServerDokumen10 halamanWindows 2000 Configure DHCP ServerTRAIAN LĂZĂRICĂBelum ada peringkat
- DHCP ImpDokumen38 halamanDHCP ImpAnonymous NeRBrZyAUbBelum ada peringkat
- DHCP SRV 2.4 ReadmeDokumen3 halamanDHCP SRV 2.4 ReadmeDerek VanderkrukBelum ada peringkat
- QuestionsDokumen10 halamanQuestionsHari ShankerBelum ada peringkat
- Configuring A DHCP ScopeDokumen3 halamanConfiguring A DHCP ScopeIndra KiranBelum ada peringkat
- Answer:: Networking Interview QuestionsDokumen10 halamanAnswer:: Networking Interview QuestionsramBelum ada peringkat
- TC2461en-Ed02 Deployment Guide For Smart DeskPhone 8088 NOE With Windows Server 2016Dokumen39 halamanTC2461en-Ed02 Deployment Guide For Smart DeskPhone 8088 NOE With Windows Server 2016Asnake TegenawBelum ada peringkat
- Configure DHCP, IIS, DNS and NAT in Windows Server 2016Dokumen17 halamanConfigure DHCP, IIS, DNS and NAT in Windows Server 2016gokuBelum ada peringkat
- Automating IP Address Assignment with DHCPDokumen22 halamanAutomating IP Address Assignment with DHCPJeisson Andres CortesBelum ada peringkat
- DHCP Deep DiveDokumen9 halamanDHCP Deep DiveGaurav NayakBelum ada peringkat
- DHCP QuestionDokumen9 halamanDHCP QuestionLalit KaushikBelum ada peringkat
- 360deployment v73 621040Dokumen100 halaman360deployment v73 621040bapibapunBelum ada peringkat
- Article On Unix For Oracle DBADokumen7 halamanArticle On Unix For Oracle DBASwapnil YeoleBelum ada peringkat
- Organizational Behavior FundamentalsDokumen14 halamanOrganizational Behavior FundamentalsSamuel WeeBelum ada peringkat
- Asst Account Application FormDokumen2 halamanAsst Account Application FormbapibapunBelum ada peringkat
- The Practice of TratakaDokumen7 halamanThe Practice of TratakaNRV APPASAMY100% (2)
- Pineapple Peel Extract vs Calamansi Extract Stain RemoverDokumen13 halamanPineapple Peel Extract vs Calamansi Extract Stain RemoverShebbah MadronaBelum ada peringkat
- The Definitions of CurriculumDokumen27 halamanThe Definitions of CurriculumAngie Bern LapizBelum ada peringkat
- Wjec A Level Maths SpecificationDokumen50 halamanWjec A Level Maths SpecificationastargroupBelum ada peringkat
- Trigonometry Ted Sundstrom and Steven SchlickerDokumen430 halamanTrigonometry Ted Sundstrom and Steven SchlickerhibiskusologjiaBelum ada peringkat
- LCCC Campus MapDokumen1 halamanLCCC Campus MapmatsciBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Thinking Portfolio AssignmentDokumen8 halamanCritical Thinking Portfolio Assignmentapi-334295481Belum ada peringkat
- Background and Introduction of The ProblemDokumen48 halamanBackground and Introduction of The ProblemElizebethBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd Year-Industrial Training Letter SampleDokumen3 halaman3rd Year-Industrial Training Letter SampleSai GowthamBelum ada peringkat
- David Sosa - The Import of The Puzzle About BeliefDokumen31 halamanDavid Sosa - The Import of The Puzzle About BeliefSr. DanieoBelum ada peringkat
- Validating and Using The Career Beliefs Inventory: Johns Hopkins UniversityDokumen12 halamanValidating and Using The Career Beliefs Inventory: Johns Hopkins Universityyinyang_trBelum ada peringkat
- English Language and Applied Linguistics Textbooks Lo Res USDDokumen61 halamanEnglish Language and Applied Linguistics Textbooks Lo Res USDJames Blackburn Quéré Cutbirth100% (2)
- Data Pre Processing in WEKADokumen5 halamanData Pre Processing in WEKAPrashant SunejaBelum ada peringkat
- Space Systems and Space Subsystems Fundamentals Course Sampler 140211082630 Phpapp02Dokumen42 halamanSpace Systems and Space Subsystems Fundamentals Course Sampler 140211082630 Phpapp02danielBelum ada peringkat
- Peak Performance Cricket ExtractDokumen5 halamanPeak Performance Cricket ExtractRui CunhaBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 3 DiscussionDokumen2 halamanLab 3 DiscussionMarlee WhiteBelum ada peringkat
- Impact of K-Pop Music On The Academic PDokumen29 halamanImpact of K-Pop Music On The Academic Pdave tayron paggao100% (1)
- Struts HTML Checkbox enDokumen4 halamanStruts HTML Checkbox enjudesahayarajBelum ada peringkat
- 2.01-Motion in A Straight Line-HWDokumen2 halaman2.01-Motion in A Straight Line-HWNirmal gkBelum ada peringkat
- Personal Philosophy of Education-Exemplar 1Dokumen2 halamanPersonal Philosophy of Education-Exemplar 1api-247024656Belum ada peringkat
- HA200Dokumen4 halamanHA200Adam OngBelum ada peringkat
- Affine CipherDokumen3 halamanAffine CipheramitpandaBelum ada peringkat
- Political Philosophy of J S MillDokumen9 halamanPolitical Philosophy of J S MillRajkumar SunnyBelum ada peringkat
- Training Program On: Personality Development Program and Workplace SkillsDokumen3 halamanTraining Program On: Personality Development Program and Workplace SkillsVikram SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Reservoir Characterization 3 LoggingDokumen47 halamanReservoir Characterization 3 LoggingMohamed AbdallahiBelum ada peringkat
- Accomplishment in ScinceDokumen21 halamanAccomplishment in ScinceChristine CanoyBelum ada peringkat
- Manuel Quezon's First Inaugural AddressDokumen3 halamanManuel Quezon's First Inaugural AddressFrancis PasionBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Literature in English Tips + AdviseDokumen2 halamanSPM Literature in English Tips + AdviseJessica NgBelum ada peringkat
- Well Logging 1Dokumen33 halamanWell Logging 1Spica FadliBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Political SubjectDokumen7 halamanWhat Is A Political SubjectlukaBelum ada peringkat