Automobile Lab Experiment No
Diunggah oleh
psmonu54Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Automobile Lab Experiment No
Diunggah oleh
psmonu54Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Automobile Lab Experiment No.
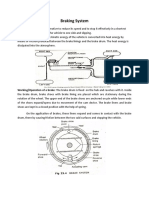
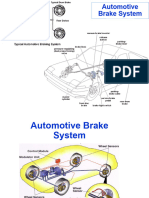
Experiment: - Repair of brakes (hydraulic brakes) a) b) c) d) Adjusting the brakes. Overhauling of brakes. Bleeding of brakes. Testing of brakes
Objective: - After doing the above experiment, students will be able to a) Acquire the knowledge of adjusting the brakes b) Will be in a position to open the entire brake system, identify the defective parts and replace them. c) Will be in a position to assemble all parts of the system. d) Will be in a position of knowing the process of bleeding and also in a position to do the same. e) Will be in a position to test the effectiveness of brakes. ADJUSTMENT OF BRAKES:-
When pedal is pressed to apply brake, there should be at least 1/2 inch free pedal movement before breaking action starts. This may vary from company to company. The brakes are adjusted as per the above mentioned recommendation before they are ready to use. This is done by following a definite procedure. a) List the wheels by screw jack. b) Loosen the lock nut for the forward brake shoe and keep it in this position. c) Turn the eccentric with other wrench towards the front of automobile till the brake shoe touches the drum.
d) Release the eccentric while turning the wheel with one hand, till wheel turns freely. e) Hold the eccentric in this position and tighter the lock nut. f) Repeat the same operation to adjust other shoe, but turn the eccentric in the backward direction of the vehicle. g) Above procedure is repeated for all the four wheels. Power Brake Booster The power brake booster is mounted on the firewall directly behind the master cylinder and, along with the master cylinder, is directly connected with the brake pedal. Its purpose is to amplify the available foot pressure applied to the brake pedal so that the amount of foot pressure required to stop even the largest vehicle is minimal. Power for the booster comes from engine vacuum. The automobile engine produces vacuum as a by-product of normal operation and is freely available for use in powering accessories such as the power brake booster. Vacuum enters the booster through a check valve on the booster. The check valve is connected to the engine with a rubber hose and acts as a one-way valve that allows vacuum to enter the booster but does not let it escape. The booster is an empty shell that is divided into two chambers by a rubber diaphragm. There is a valve in the diaphragm that remains open while your foot is off the brake pedal so that vacuum is allowed to fill both chambers. When you step on the brake pedal, the valve in the diaphragm closes, separating the two chambers and another valve opens to allow air in the chamber on the brake pedal side. This is what provides the power assist. Power boosters are very reliable and cause few problems of their own; however, other things can contribute to a loss of power assist. In order to have power assist, the engine must be running. If the engine stalls or shuts off while you are driving, you will have a small reserve of power assist for two or three pedal applications but, after that, the brakes will be extremely hard to apply and you must put as much pressure as you can to bring the vehicle to a stop. OVERHAULING OF THE BRAKES:It requires:-
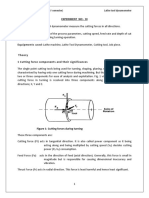
1. Dismantling of breaks- i.e. removal of tyres, brake drum, removal of wheel cylinder, brake shoes & master cylinder. 2. Checking of all the above components. 3. Removal of faulty parts and replacement by new parts. 4. Fixing of new brake lining on the brake shoes after removal of the old one. 5. Replacement of piston and diaphragms in all wheel cylinders. These parts are available in the name of wheel cylinder kit. 6. Replacement of piston and diaphragms in master cylinder. 7. To assemble all the parts, fixing of the wheel drum and fitment of the tyre. 8. To carry out bleeding of the brakes to remove any air bubbles present in the pipeline. 9. To carry out the adjustment of the brakes and brake paddle. The brake paddle should have a free play of half inch. 10.Testing of brakes, if on testing any defect is noticed, then to rectify the same.
Testing Of Brake:1. After minor adjustment of brakes or brakes overhauling, the brakes are tested on roads. The vehicles brakes are applied on dry road at moderate speed and then checked for the following :a) Effective braking distance the vehicle should stop within a reasonable distance of about 1 foot. b) Pulling of brake on one side when brakes are applied vechiles should not be put on one side. If it is so, the readjustment of the brake is to be done. c) Dragging of brakes. d) Brake paddle hardness brake paddle should be soft enough to press it. If it is hard, the brake linkages are to be checked. e) Chattering of brakes when brakes are applied, the brake should not chatter. If ant noise is noticed then brakes are applied, then there is something loose in the drum.
If everything is OK the brakes are OK. If any further defect are noticed then the same should be rectified and the vehicle is retested for a effective braking.
BLEEDING OF BRAKES:-
When air enters, into the brake system and any brake line is disconnected, bleeding of brakes has to be done. Since air is compressible so any presence of air inside brake lining does not allow to transmit brake force to apply brakes. Therefore, the system must be free from presence of air. Bleeding is the process of removal of air from the braking system.
Bleeding Procedure:-
Following steps are followed for bleeding of brakes :
(a) Remove all dirt from the master cylinder filler plug. Then fill the master cylinder upto lower edge of the filler neck by removing the filler plug. (b) Clean all the bleeding connections provided on all wheel cylinders. (c) After this bleeder hose and fixture is connected to that wheel cylinder which has longest brake line. The other rend of bleeder hose is placed in a glass jar, and submerge this end in the brake fluid. (d) How bleeder valve is opened by half to three quarter turn. (e) Then press the foot pedal and allow it to return back slowly. (f) This pumping action must be continued till all the air along with some brake fluid comes out through bleeding hose. (g) After this bleeding operation is carried out on all wheel cylinders. This completes the bleeding operation. At the end master cylinder is filled with brake fluid to required level.
Anti-Lock Brakes (ABS) The most efficient braking pressure takes place just before each wheel locks up. When you slam on the brakes in a panic stop and the wheels lock up, causing a screeching sound and leaving strips of rubber on the pavement, you do not stop the vehicle nearly as short as it is capable of stopping. Also, while the wheels are locked up, you loose all steering control so that, if you have an opportunity to steer around the obstacle, you will not be able to do so. Another problem occurs during an extended skid is that you will burn a patch of rubber off the tire, which causes a
"flat spot" on the tread that will produce an annoying thumping sound as you drive. Anti-lock brake systems solve this lockup problem by rapidly pumping the brakes whenever the system detects a wheel that is locked up. In most cases, only the wheel that is locked will be pumped, while full braking pressure stays available to the other wheels. This effect allows you to stop in the shortest amount of time while maintaining full steering control even if one or more wheels are on ice. The system uses a computer to monitor the speed of each wheel. When it detects that one or more wheels have stopped or are turning much slower than the remaining wheels, the computer sends a signal to momentarily remove and reapply or pulse the pressure to the affected wheels to allow them to continue turning. This "pumping" of the brakes occurs at ten or more times a second, far faster then a human can pump the brakes manually. If you step on the brakes hard enough to engage the anti-lock system, you may feel a strong vibration in the brake pedal. This is a normal condition and indicates that the system is working, however, it can be disconcerting to some people who don't expect it. If your vehicle has anti-lock brakes, read your owner's manual to find out more about it. The system consists of an electronic control unit, a hydraulic actuator, and wheel speed sensors at each wheel. If the control unit detects a malfunction in the system, it will illuminate an ABS warning light on the dash to let you know that there is a problem. If there is a problem, the anti-lock system will not function but the brakes will otherwise function normally.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Chapter10 BrakesDokumen31 halamanChapter10 BrakesShreyas IyengarBelum ada peringkat
- ATT Brakes - Example TextbookDokumen15 halamanATT Brakes - Example TextbookSooraj KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Brake Operating SystemDokumen18 halamanBrake Operating SystemWoong-Sub LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic Braking SystemDokumen16 halamanElectromagnetic Braking SystemGallant Info100% (1)
- To Study About Various Types of Braking SystemDokumen24 halamanTo Study About Various Types of Braking SystemRavi Donga100% (1)
- Unit 6 61 Hydraulic BrakesDokumen7 halamanUnit 6 61 Hydraulic BrakesAnand Kumar JhaBelum ada peringkat
- Electro Magnetic BrakingDokumen19 halamanElectro Magnetic BrakingCUBE Engineering SolutionsBelum ada peringkat
- Excellent Module No 2 CoompleteDokumen38 halamanExcellent Module No 2 CoompleteVaibhav Vithoba NaikBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment No. 08: ObjectiveDokumen5 halamanExperiment No. 08: ObjectiveMoiz AamirBelum ada peringkat
- CBLM Brake SystemDokumen15 halamanCBLM Brake Systemace ebradoBelum ada peringkat
- Braking SystemDokumen11 halamanBraking Systemvenkat sai100% (1)
- To Whom It May ConcernDokumen96 halamanTo Whom It May ConcernKamal SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Study and Demonstration of Automobile Brakes MechanicalDokumen9 halamanStudy and Demonstration of Automobile Brakes MechanicalSANURASAGARBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 10 Position and Warning SystemsDokumen14 halamanCHAPTER 10 Position and Warning Systemsখালিদহাসান80% (5)
- How The Braking System WorksDokumen3 halamanHow The Braking System WorksCristian ÂČBelum ada peringkat
- Automotive Brakes: Prepared By: Bibhuti Bhusan Samantaray Asst. Professor, GEC 9439373223Dokumen45 halamanAutomotive Brakes: Prepared By: Bibhuti Bhusan Samantaray Asst. Professor, GEC 9439373223Ajit100% (1)
- Automotive Brake SystemDokumen42 halamanAutomotive Brake SystemTanzim Rafat AyonBelum ada peringkat
- Automotive Brake SystemDokumen45 halamanAutomotive Brake SystemImrul Kayesh AruBelum ada peringkat
- How Brakes WorkDokumen7 halamanHow Brakes WorkAnonymous LFgO4WbIDBelum ada peringkat
- Automotive Brake SystemDokumen39 halamanAutomotive Brake Systemjubaer ahmed50% (4)
- Hydraulic BrakeDokumen5 halamanHydraulic BrakenvjkhfghfBelum ada peringkat
- Internal Expanding BrakeDokumen11 halamanInternal Expanding BrakeGirish Sahare100% (1)
- Van Training HandbookDokumen20 halamanVan Training HandbookMitch PolonskyBelum ada peringkat
- Brakes: Question: How Does A Brake System Inspection Work?Dokumen3 halamanBrakes: Question: How Does A Brake System Inspection Work?Muhammad SiddiqueBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 5Dokumen34 halamanUnit 5A ABHISHEK MARSHALLBelum ada peringkat
- 2.experiment No2 SfbaksjfbkajfDokumen6 halaman2.experiment No2 Sfbaksjfbkajfpratik thakareBelum ada peringkat
- Keshav ProjectDokumen24 halamanKeshav ProjectkeshavjhaBelum ada peringkat
- Air Brake PROJECT REPORTDokumen52 halamanAir Brake PROJECT REPORTChockalingam Athilingam72% (18)
- Braking SystemDokumen19 halamanBraking SystemArvind YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Nikhil. P. Katti Department of Mechanical Engineering IV SemesterDokumen4 halamanNikhil. P. Katti Department of Mechanical Engineering IV SemesterNikhil KattiBelum ada peringkat
- Antilock Brake Systems (ABS)Dokumen30 halamanAntilock Brake Systems (ABS)pRAMOD g pATOLEBelum ada peringkat
- Braking SystemDokumen22 halamanBraking SystemSIDBelum ada peringkat
- 12H Frein TestDokumen13 halaman12H Frein TestaniriBelum ada peringkat
- Braking System-By GirlsDokumen23 halamanBraking System-By Girlskrish0690Belum ada peringkat
- Seminar Presentation: Braking System, TyreDokumen28 halamanSeminar Presentation: Braking System, TyreGuru MaheshBelum ada peringkat
- Suspension SystemDokumen50 halamanSuspension Systemgemrief5Belum ada peringkat
- Title:-Off Road VehicleDokumen6 halamanTitle:-Off Road VehicleSunil PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Presentation Sample ABS BrakesDokumen5 halamanTechnical Presentation Sample ABS BrakesrinirajBelum ada peringkat
- SynopsisDokumen8 halamanSynopsismanoj kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Preface: Practical Knowledge Leads A Man To Perfection'Dokumen15 halamanPreface: Practical Knowledge Leads A Man To Perfection'Arpan SaxenaBelum ada peringkat
- Federal University of Technology Minna in Affiliation With Federal College of Education (Tech) AkokaDokumen13 halamanFederal University of Technology Minna in Affiliation With Federal College of Education (Tech) AkokaChandra SekarBelum ada peringkat
- To Study About Various Types of Braking System: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDokumen22 halamanTo Study About Various Types of Braking System: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleBhavik GattaniBelum ada peringkat
- Braking System InformationDokumen30 halamanBraking System InformationLala GuanyesBelum ada peringkat
- Study of Braking SystemDokumen7 halamanStudy of Braking SystemVishal ChauhanBelum ada peringkat
- Abs BleedingDokumen15 halamanAbs BleedingJarmo JuvonenBelum ada peringkat
- COMPLETE Report (Braking Department)Dokumen30 halamanCOMPLETE Report (Braking Department)Dinie Abdullah ZamawiBelum ada peringkat
- Project PBLDokumen19 halamanProject PBLAdam LuqmanBelum ada peringkat
- Anti-Lock Braking System: ComponentsDokumen3 halamanAnti-Lock Braking System: ComponentsMasum ParvezBelum ada peringkat
- Anti-Lock Braking SystemDokumen17 halamanAnti-Lock Braking SystemDhananjay Titarmare100% (1)
- Hydraulic Brake: Braking Brake Fluid Ethylene GlycolDokumen6 halamanHydraulic Brake: Braking Brake Fluid Ethylene GlycolVijayakumar NatarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Autonext Study Material 3 (Brakes)Dokumen11 halamanAutonext Study Material 3 (Brakes)SouravBelum ada peringkat
- Brake Hydraulics: Dual-Circuit Braking SystemDokumen22 halamanBrake Hydraulics: Dual-Circuit Braking SystemJithin RajBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar Report On ABSDokumen25 halamanSeminar Report On ABSAshik AssimBelum ada peringkat
- Abs TechnologyDokumen14 halamanAbs Technologyanime landBelum ada peringkat
- AT 8004 NGHV Unit 5Dokumen6 halamanAT 8004 NGHV Unit 5Ashwin NarendranBelum ada peringkat
- Sloane's New Bicycle Maintenance ManualDari EverandSloane's New Bicycle Maintenance ManualPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Production Engg Lab Manual (V Semester) Lathe Tool DynamometerDokumen4 halamanProduction Engg Lab Manual (V Semester) Lathe Tool Dynamometerpsmonu54Belum ada peringkat
- MCQ On Six SigmaDokumen5 halamanMCQ On Six Sigmapsmonu5450% (2)
- Response Table For Analyze Taguchi Design: Learn More About Minitab 18Dokumen11 halamanResponse Table For Analyze Taguchi Design: Learn More About Minitab 18psmonu54Belum ada peringkat
- Q.1 Define Rapid Prototyping. What Are The Roles of Prototype inDokumen1 halamanQ.1 Define Rapid Prototyping. What Are The Roles of Prototype inpsmonu54Belum ada peringkat
- APT ProgramDokumen5 halamanAPT Programpsmonu54Belum ada peringkat
- Objective Q JigDokumen1 halamanObjective Q Jigpsmonu54Belum ada peringkat
- Gate QuesDokumen5 halamanGate Quespsmonu54Belum ada peringkat
- Foundary NotesDokumen13 halamanFoundary Notespsmonu540% (1)
- Advances in Automobiles With Nanomaterials: A ReviewDokumen7 halamanAdvances in Automobiles With Nanomaterials: A Reviewpsmonu54Belum ada peringkat
- ListDokumen2 halamanListpsmonu54Belum ada peringkat
- Study of Automobile ValveDokumen6 halamanStudy of Automobile Valvepsmonu54Belum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Engineering Department December 2019 Djf5042 - Industrial Robotics (End of Chapter 1)Dokumen3 halamanMechanical Engineering Department December 2019 Djf5042 - Industrial Robotics (End of Chapter 1)YING AEISYAHBelum ada peringkat
- CC1 - AssignmentDokumen1 halamanCC1 - AssignmentAssiah AndreaBelum ada peringkat
- Online Meeting With Clients: Project GuideDokumen16 halamanOnline Meeting With Clients: Project GuideGovindaram RajeshBelum ada peringkat
- TechRef 3-W-Transformer 3phaseDokumen40 halamanTechRef 3-W-Transformer 3phaseTorrez JeanBelum ada peringkat
- Cosc - 1436 - Fall 16 - Dalia - Gumeel-CDokumen6 halamanCosc - 1436 - Fall 16 - Dalia - Gumeel-CBenBelum ada peringkat
- CIM For Enterprise Integration (IEC) 61968Dokumen53 halamanCIM For Enterprise Integration (IEC) 61968Igor SangulinBelum ada peringkat
- Online Recruitment SystemDokumen42 halamanOnline Recruitment SystemTanmay Abhijeet74% (19)
- Download, Upload, Delete Files From FTP Server Using C#Dokumen9 halamanDownload, Upload, Delete Files From FTP Server Using C#Henrique PereiraBelum ada peringkat
- An Efforts Estimate For Agile ProjectsDokumen11 halamanAn Efforts Estimate For Agile ProjectsflytosantyBelum ada peringkat
- Kmu Cat Rollnoslip 263112Dokumen1 halamanKmu Cat Rollnoslip 263112Saeed AkhtarBelum ada peringkat
- Commutation Circuits SCR PDFDokumen2 halamanCommutation Circuits SCR PDFRhondaBelum ada peringkat
- K.Surya Rao: Curriculum VitaeDokumen6 halamanK.Surya Rao: Curriculum Vitaenaveen_spy122Belum ada peringkat
- Itc e Choupal PPT Final 111114132618 Phpapp01Dokumen30 halamanItc e Choupal PPT Final 111114132618 Phpapp01pks009Belum ada peringkat
- Lab Manual Exp 3 - Gas Temperature Process ControlDokumen8 halamanLab Manual Exp 3 - Gas Temperature Process ControlAhmad DanialBelum ada peringkat
- SANOG35 Tutorial Programming and Python For Network Engineers PDFDokumen138 halamanSANOG35 Tutorial Programming and Python For Network Engineers PDFPhuwanart PhiBelum ada peringkat
- Image2CAD AdityaIntwala CVIP2019Dokumen11 halamanImage2CAD AdityaIntwala CVIP2019christopher dzuwaBelum ada peringkat
- Reference Manual (0.8.0) (2022.04.16) : OpencoreDokumen111 halamanReference Manual (0.8.0) (2022.04.16) : OpencorevalakiakinemtevagyBelum ada peringkat
- 125 DoDokumen81 halaman125 DoĐình Tuấn NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- 31.33.00010 31-JAN-2023 31-JAN-2023 Closed A318, A319, A320, A321, A330, ... 23-71, 31-33, 31-36, ... External QAR 3TU/2TV Installation/removalDokumen107 halaman31.33.00010 31-JAN-2023 31-JAN-2023 Closed A318, A319, A320, A321, A330, ... 23-71, 31-33, 31-36, ... External QAR 3TU/2TV Installation/removalNaixBelum ada peringkat
- ASR9000xr Understanding SNMP and TroubleshootingDokumen56 halamanASR9000xr Understanding SNMP and TroubleshootingDharmendraBelum ada peringkat
- Ubuntu OpenStack Fundamentals TrainingDokumen6 halamanUbuntu OpenStack Fundamentals TrainingAnupriya DayaratneBelum ada peringkat
- Guide: Overclocking FX-8350 To 4.8GHz On Crosshair V Formula-ZDokumen7 halamanGuide: Overclocking FX-8350 To 4.8GHz On Crosshair V Formula-ZBobapatatasBelum ada peringkat
- Ncpre BombayDokumen5 halamanNcpre BombaySingh SranBelum ada peringkat
- Home Automation Using Android And: Raspberry Pi (Literature Review)Dokumen11 halamanHome Automation Using Android And: Raspberry Pi (Literature Review)Shubham TogargeBelum ada peringkat
- A5.28 and A5.18 - ER70S-GDokumen10 halamanA5.28 and A5.18 - ER70S-GSurat ButtarasriBelum ada peringkat
- David Hatcher Childress Technology of The GodsDokumen2 halamanDavid Hatcher Childress Technology of The GodsLeonardoBelum ada peringkat
- Erc111 DKRCC - Es.rl0.e3.02 520H8596Dokumen24 halamanErc111 DKRCC - Es.rl0.e3.02 520H8596Miguel BascunanBelum ada peringkat
- Drive Passenger BusDokumen7 halamanDrive Passenger BusJason MandelaBelum ada peringkat
- Welcome Letter - RobotStudio School Edition - 107670Dokumen1 halamanWelcome Letter - RobotStudio School Edition - 107670Meche HerztBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco Configure Cisco Meeting Server and CUCMDokumen11 halamanCisco Configure Cisco Meeting Server and CUCMandreicainBelum ada peringkat