Critical Care Medicine Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal Medicine
Diunggah oleh
abimorgJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Critical Care Medicine Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal Medicine
Diunggah oleh
abimorgHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Critical Care Medicine
Certification Examination Blueprint What Does the Examination Cover? The examination is designed to evaluate the extent of the candidate's knowledge and clinical judgment in the areas in which a critical care physician should demonstrate a high level of competence. Expertise in the broad domain of critical care medicine, and the diagnosis and treatment of both common and rare conditions that have important consequences for patients, will be assessed. Examination content is consistent with a pre-established blueprint, or table of specifications. The blueprint is developed by the Subspecialty Board on Critical Care Medicine and is reviewed and revised annually to ensure that it is current. In addition, practicing critical care medicine trainees, and training program directors are surveyed periodically to provide feedback on the blueprinting process. The blueprint is used as a guide in developing the examination. The majority of questions (over 75 percent) are based on patient presentations occurring in settings that reflect current medical practice. Questions requiring simple recall of medical facts are in the minority; the majority of questions require integration of information from several sources, prioritization of alternatives, and/or utilization of clinical judgment in reaching a correct conclusion. Some questions require interpretation of pictorial material, such as ultrasound scans, magnetic resonance imaging scans, electrocardiograms, radiographs, computed tomograms, radionuclide scans, and photomicrographs. Topics covered may include the following: Airway maintenance and management of mechanical ventilation Interpretation of data from hemodynamic monitoring devices Medical problems related to burns and acute illness Postoperative medical management, which frequently involves consultation by the internist Indications for and complications of surgical procedures Drug metabolism, toxicity, and excretion in acute illness Administrative and management principles and techniques General internal medicine as encountered in the practice of critical care medicine (including some general pediatrics with an emphasis on adolescent medicine)
The content areas covered and their relative proportions on the exam are as follows: Medical Content Category Renal/Endocrine/Metabolism Cardiovascular Disorders Pulmonary Disease Infectious Disease Gastrointestinal Disorders Neurologic Disorders Hematologic/Oncologic Disorders Surgical/Trauma/Transplantation Pharmacology/Toxicology Research/Administration/Ethics Total Relative Percentage 15% 17.5% 20% 12% 5.5% 9.5% 5.5% 7.5% 5% 2.5% 100%
Content Outline of the Certification Examination This content outline describes a typical Critical Care Medicine Certification Examination; actual content on a specific examination may vary. Each medical content category from the examination blueprint is listed in boldface below, along with target blueprint percentage and total number of questions in the category. Within each category, the approximate distribution of questions in specified areas is also listed.
Medical Content Category (Relative Percentage) Renal/Endocrine/Metabolism (15%) Sodium/water balance Potassium disorders Acid-base disorders Calcium/phosphate/magnesium/ammonia disorders Diabetes (excluding DKA) and energy metabolism Thyroid disorders Adrenal disorders Pituitary abnormalities Tumor-related syndromes Acute renal failure Nutritional support
Number of Questions 30 as follows: 4 2 9 2 2 1 2 1 1 4 2
Cardiovascular Disorders (17.5%) Acute coronary syndromes Arrhythmias Congestive heart failure Hemodynamic monitoring Advanced cardiac life support Vascular disorders Valvular heart disease Pericardial disease Myocardial disease
35 as follows: 4 4 6 9 2 4 2 2 2
Medical Content Category (Relative Percentage) Pulmonary Disease (20%) Pulmonary physiology/pathophysiology Diagnostic and therapeutic procedures Mechanical ventilation Airway disease Parenchymal lung disease Pulmonary vascular disorders Pleural disorders Hemoptysis Sleep disorder breathing Infectious Disease (12%) Systemic infections Central nervous system infections Head, neck, and upper airway infections Cardiovascular infections Gastrointestinal and intra-abdominal infections Genitourinary tract infections Soft tissue, bone, and joint infections Non-vascular transcutaneous catheters (intracranial, transhepatic, peritoneal, nephrostomy) Antimicrobial therapy and resistance Immunocompromised hosts Other special hosts Virulence factors, toxins, and bioweapons Hospital epidemiology and infection control
Number of Questions 40 as follows: 4 3-4 12 3-4 10-11 4 1-2 1 1 24 as follows: 3 3 2 2 2 2 1 1 2 2 1 2 1
Gastrointestinal Disorders (5.5%) Esophagus Stomach Small bowel Large bowel Liver Pancreas Gallbladder
11 as follows: 2 1 1 2 3 1 1
Medical Content Category (Relative Percentage) Neurologic Disorders (9.5%) Brain death Cerebral vascular disease Seizures, status epilepticus, subclinical status, myoclonus Neurogenic pulmonary edema Neuromuscular diseases Increased intracranial pressure and hydrocephalus Head trauma Spinal cord injury and neurogenic shock Encephalopathy/coma/delirium Pain control, sedation, and neuromuscular blockade
Number of Questions 19 as follows: 1 5 1 1 2 1 1-2 2 1 4
Hematologic/Oncologic Disorders (5.5%) Red blood cell diseases White blood cell diseases Platelet disorders Coagulopathies Hypercoagulable states Transfusion medicine Solid tumors Oncologic syndromes Bone marrow transplant Complications of immunosuppressive drugs and chemotherapy
11 as follows: 0-1 1-3 1-3 1-3 1-3 1-3 0-1 0-1 0-1 0-1
Surgical/Trauma/Transplantation (7.5%) Cardiovascular/vascular Abdominal/gastrointestinal Obstetric/genitourinary Skin and soft tissues/extremities Environmental injury Postoperative management (general) Trauma Transplantation
15 as follows: 2 2 0-1 0-1 6-7 0-1 2-3 0-1
Medical Content Category (Relative Percentage) Pharmacology/Toxicology (5%) Basic pharmacologic principles Drug interactions Common adverse drug interactions and allergic reactions Toxicology, drug overdose, and poisoning
Number of Questions 10 as follows: 0-1 0-2 3-4 3-4
Research/Administration/Ethics (2.5%) Intensive care unit (ICU) administration Continuous quality improvement/patient safety Staffing issues Economic considerations Medicolegal interactions Ethical considerations Medical research Teaching and education Psychosocial issues
5 as follows: 0-1 0-1 0-1 0-1 0-1 2-3 1-2 0-1 0-1
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Genetic Diagnosis of Endocrine DisordersDari EverandGenetic Diagnosis of Endocrine DisordersRoy E. WeissBelum ada peringkat
- Nephrology Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen4 halamanNephrology Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Internal Medicine: What Does The Examination Cover?Dokumen8 halamanInternal Medicine: What Does The Examination Cover?hiloneBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Chemistry, Immunology and Laboratory Quality Control: A Comprehensive Review for Board Preparation, Certification and Clinical PracticeDari EverandClinical Chemistry, Immunology and Laboratory Quality Control: A Comprehensive Review for Board Preparation, Certification and Clinical PracticeBelum ada peringkat
- Geriatric Medicine Certification Examination Blueprint - ABIMDokumen7 halamanGeriatric Medicine Certification Examination Blueprint - ABIMabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Anesthesia Complications in the Dental OfficeDari EverandAnesthesia Complications in the Dental OfficeRobert C. BosackBelum ada peringkat
- Hematology Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen3 halamanHematology Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Blood and Marrow Transplantation Long-Term Management: Prevention and ComplicationsDari EverandBlood and Marrow Transplantation Long-Term Management: Prevention and ComplicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Oncology Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen4 halamanMedical Oncology Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism - American Board of Internal Medicine - ABIMDokumen3 halamanEndocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism - American Board of Internal Medicine - ABIMabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Hospital Medicine Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen4 halamanHospital Medicine Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Rare and Complex UrologyDari EverandRare and Complex UrologyJen TidmanBelum ada peringkat
- Interventional Cardiology Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen3 halamanInterventional Cardiology Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Interventional Cardiology Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen3 halamanInterventional Cardiology Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint - ABIMDokumen4 halamanGastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint - ABIMabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- IM HandbookaDokumen378 halamanIM HandbookakkBelum ada peringkat
- IM HandbookDokumen430 halamanIM HandbookPhil ChanBelum ada peringkat
- AKT Syllabus PDFDokumen9 halamanAKT Syllabus PDFZaheer AliBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Care NursingDokumen20 halamanCritical Care NursingEdwin Delos Reyes AbuBelum ada peringkat
- Thomas M. de Fer Thomas Ciesielski The Washington Manual Internship Survival Guide 2019Dokumen516 halamanThomas M. de Fer Thomas Ciesielski The Washington Manual Internship Survival Guide 2019Aitzaz AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Internal Medicine - Promotion Exam Blueprint v.2Dokumen6 halamanInternal Medicine - Promotion Exam Blueprint v.2Naz Al-ShahraniBelum ada peringkat
- CTCAE 4.03 2010-06-14 QuickReference 5x7Dokumen196 halamanCTCAE 4.03 2010-06-14 QuickReference 5x7Andreea ZaharieBelum ada peringkat
- Ebook Medicine in A Day Revision Notes For Medical Exams Finals Ukmla and Foundation Years PDF Full Chapter PDFDokumen67 halamanEbook Medicine in A Day Revision Notes For Medical Exams Finals Ukmla and Foundation Years PDF Full Chapter PDFregina.white324100% (26)
- Intensive Care Medicine Notes March 20131 PDFDokumen364 halamanIntensive Care Medicine Notes March 20131 PDFMd ShafayetBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohol Withdrawal and Upper Intestinal BleedingDokumen14 halamanAlcohol Withdrawal and Upper Intestinal Bleedingsupraja.bommalaBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Problems Associated With Aging ProcessDokumen28 halamanClinical Problems Associated With Aging Processهنادي رازمBelum ada peringkat
- ABIMDokumen3 halamanABIMMohamed KhattabBelum ada peringkat
- Heart Failure: Abdul Hafiz AliasDokumen19 halamanHeart Failure: Abdul Hafiz AliasAbdul Hafiz Alias100% (5)
- Surgery Facts and Figures by James Green, Saj Wajed Z LiborgepubDokumen908 halamanSurgery Facts and Figures by James Green, Saj Wajed Z LiborgepubMahmoud AbouelsoudBelum ada peringkat
- Comlex ContentDokumen2 halamanComlex Contentkaml20Belum ada peringkat
- Update To ProtocolsDokumen192 halamanUpdate To ProtocolsJody MeadsBelum ada peringkat
- Pre Anesthetic EvaluationDokumen67 halamanPre Anesthetic EvaluationdrvithalkBelum ada peringkat
- Study of Etiology LALAJUNDokumen3 halamanStudy of Etiology LALAJUNDavid Al HavizBelum ada peringkat
- Medicine in A Day Revision Notes For Medical Exams Finals Ukmla and Foundation Years 1St Edition Armbruster Full ChapterDokumen68 halamanMedicine in A Day Revision Notes For Medical Exams Finals Ukmla and Foundation Years 1St Edition Armbruster Full Chapterjames.fowler901100% (4)
- EM Clinical GuidelinesDokumen310 halamanEM Clinical GuidelineszianchaBelum ada peringkat
- Or AssignmentDokumen3 halamanOr AssignmentMelissa Joy DollagaBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Care MedicineDokumen2 halamanCritical Care Medicinesaif aliBelum ada peringkat
- Preoperative Optimization and RiskDokumen12 halamanPreoperative Optimization and RiskREY GARCIA DARIELA DEL VALLEBelum ada peringkat
- Tsegeee PDFDokumen5 halamanTsegeee PDFAsnakeBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosis and Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease: Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines NetworkDokumen41 halamanDiagnosis and Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease: Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network'-dooublleaiienn Itouehh IinBelum ada peringkat
- Hot Topics 4e MRCGPDokumen13 halamanHot Topics 4e MRCGPgautambob29% (7)
- Website Exam Guidance v2012Dokumen8 halamanWebsite Exam Guidance v2012GiacenBelum ada peringkat
- Contents - Critical Care MedicineDokumen6 halamanContents - Critical Care MedicinemohammadasadBelum ada peringkat
- BMJ CCFDokumen94 halamanBMJ CCFaliakbar178Belum ada peringkat
- Blueprint - Internal MedicineDokumen1 halamanBlueprint - Internal MedicineQQQQBelum ada peringkat
- Delirium: EpidemiologyDokumen8 halamanDelirium: EpidemiologyNunuBelum ada peringkat
- Refractory Epilepsy Diagnosis and Management: Local Experience at National Guard Hospital in Jeddah, KSADokumen18 halamanRefractory Epilepsy Diagnosis and Management: Local Experience at National Guard Hospital in Jeddah, KSAOmar MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Perioperative Management of The Geriatric PatientDokumen19 halamanPerioperative Management of The Geriatric PatientJunita Ratna SariBelum ada peringkat
- Autonomy:: Great Deal of Autonomy Very Limited AutonomyDokumen1 halamanAutonomy:: Great Deal of Autonomy Very Limited AutonomyIsmail LubisBelum ada peringkat
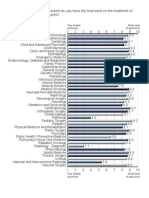
- Knowledge, Attitude and Practice of Physicians in The Treatment of Hypertension in North-Central NigeriaDokumen6 halamanKnowledge, Attitude and Practice of Physicians in The Treatment of Hypertension in North-Central NigeriaIline MichaelaBelum ada peringkat
- Neurological Complications of Surgery and AnaesthesiaDokumen14 halamanNeurological Complications of Surgery and Anaesthesiarian rantungBelum ada peringkat
- Ircmj 17 06 20705 PDFDokumen7 halamanIrcmj 17 06 20705 PDFUchi SuhermanBelum ada peringkat
- MCI SyllabusDokumen6 halamanMCI SyllabusloocasjBelum ada peringkat
- Pat PortfolioDokumen24 halamanPat Portfolioapi-283407010Belum ada peringkat
- CPG in Heart FailureDokumen62 halamanCPG in Heart FailureCoffee TeeBelum ada peringkat
- Kvit Noac Bleeding Real LifeDokumen6 halamanKvit Noac Bleeding Real LifeLovadi Emese IldikóBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Medicine BlueprintDokumen1 halamanAcute Medicine BlueprintKo KhiBelum ada peringkat
- Final Report of The Committee On Recognizing New and Emerging Disciplines in Internal Medicine (NEDIM) - 2Dokumen8 halamanFinal Report of The Committee On Recognizing New and Emerging Disciplines in Internal Medicine (NEDIM) - 2abimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Policies and Procedures Certification August 2012 ABIMDokumen20 halamanPolicies and Procedures Certification August 2012 ABIMabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Nephrology Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - ABIMDokumen4 halamanNephrology Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - ABIMabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Number of Candidates Certified Annually by The American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen7 halamanNumber of Candidates Certified Annually by The American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Perspectives On Gastroenterology Board Certification: Meeting The Challenge To Keep CurrentDokumen2 halamanPerspectives On Gastroenterology Board Certification: Meeting The Challenge To Keep CurrentabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- ABIM MOC - Helping Physicians - IMPROVE QUALITY CAREDokumen8 halamanABIM MOC - Helping Physicians - IMPROVE QUALITY CAREabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- First-Time Taker Pass Rates - Maintenance of Certification - American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen1 halamanFirst-Time Taker Pass Rates - Maintenance of Certification - American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance of Certification Program Completion Rates (February 2012) - American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen2 halamanMaintenance of Certification Program Completion Rates (February 2012) - American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- ABIM HIPAA BUSINESS ASSOCIATE AGREEMENT ADDENDUM TO THE AMERICAN BOARD OF INTERNAL MEDICINE’S APPLICATION FOR CONTINUOUS PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATIONS FOR ADMISSION TO CERTIFICATION EXAMINATIONSDokumen3 halamanABIM HIPAA BUSINESS ASSOCIATE AGREEMENT ADDENDUM TO THE AMERICAN BOARD OF INTERNAL MEDICINE’S APPLICATION FOR CONTINUOUS PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATIONS FOR ADMISSION TO CERTIFICATION EXAMINATIONSabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Developmental Milestones For Internal Medicine Residency TrainingDokumen13 halamanDevelopmental Milestones For Internal Medicine Residency TrainingabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Interventional Cardiology Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen3 halamanInterventional Cardiology Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- ABIM Diabetes PIM™ Practice Improvement Module Measures CatalogueDokumen30 halamanABIM Diabetes PIM™ Practice Improvement Module Measures CatalogueabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- MAINTENANCE OF CERTIFICATION Oncologists - American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen4 halamanMAINTENANCE OF CERTIFICATION Oncologists - American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Infectious Disease Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen8 halamanInfectious Disease Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Internal Medicine Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen8 halamanInternal Medicine Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Hospice and Palliative Medicine Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen3 halamanHospice and Palliative Medicine Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Hospital Medicine Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen4 halamanHospital Medicine Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Hospital Medicine Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen4 halamanHospital Medicine Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Non-Standard Subspecialty Disciplines Recognized For The Purpose of J-1 Visa Sponsorship - American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen3 halamanNon-Standard Subspecialty Disciplines Recognized For The Purpose of J-1 Visa Sponsorship - American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Interventional Cardiology Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen3 halamanInterventional Cardiology Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Hematology Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineDokumen3 halamanHematology Certification Examination Blueprint - American Board of Internal MedicineabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroenterology Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - ABIMDokumen4 halamanGastroenterology Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - ABIMabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Geriatric Medicine Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - ABIMDokumen7 halamanGeriatric Medicine Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint - ABIMabimorgBelum ada peringkat
- Medicine Malaysia (Cardiology 1)Dokumen12 halamanMedicine Malaysia (Cardiology 1)dr1lostBelum ada peringkat
- Exam #4 Study Blueprint 2019Dokumen2 halamanExam #4 Study Blueprint 2019Stephanie DeeBelum ada peringkat
- Basic EKG RefresherDokumen210 halamanBasic EKG RefresherAaron D. Phoenix100% (6)
- Infective EndocarditisDokumen10 halamanInfective EndocarditisShrests SinhaBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Life Support (BLS) Primary Survey For Respiratory ArrestDokumen6 halamanBasic Life Support (BLS) Primary Survey For Respiratory ArrestRifqi MuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Microbiology Resident's HandbookDokumen191 halamanMedical Microbiology Resident's HandbookSrinivas RajanalaBelum ada peringkat
- The Impact of Dominant Ventricular Morphology On The Early Postoperative Course After The Glenn ProcedureDokumen7 halamanThe Impact of Dominant Ventricular Morphology On The Early Postoperative Course After The Glenn ProcedureEitan KeizmanBelum ada peringkat
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDokumen57 halamanCongenital Heart DiseaseAparna RawatBelum ada peringkat
- CV (Dr. Mayada Farag)Dokumen3 halamanCV (Dr. Mayada Farag)ABC XYZBelum ada peringkat
- Dysrhythmias: Normal Electrical ActivityDokumen32 halamanDysrhythmias: Normal Electrical ActivityLarisse de LeonBelum ada peringkat
- FRS Eng 2017 Fnl1Dokumen1 halamanFRS Eng 2017 Fnl1M Fathur Arief KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- Unipulse 400Dokumen6 halamanUnipulse 400Eliel VelasquezBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiology Study Guide Handout PDFDokumen86 halamanCardiology Study Guide Handout PDFStarr Newman100% (1)
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs FinalDokumen31 halamanAntiarrhythmic Drugs FinalAmanuel Maru50% (2)
- ECG WorksheetDokumen3 halamanECG WorksheetElaiza UyBelum ada peringkat
- Mcqs Pediatric Cardiology EmergencyDokumen29 halamanMcqs Pediatric Cardiology EmergencyOmed M. AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac Valve Surgery: DR - Med. Dr. Yanto Sandy Tjang, SPBTKV (K), Mba, MPH, MSC, DSC, PHD, Fics, FetcsDokumen20 halamanCardiac Valve Surgery: DR - Med. Dr. Yanto Sandy Tjang, SPBTKV (K), Mba, MPH, MSC, DSC, PHD, Fics, FetcsnoviBelum ada peringkat
- ECG QuizDokumen6 halamanECG QuizIsland Rae100% (1)
- Bifascicular Block - LITFL - ECG Library DiagnosisDokumen10 halamanBifascicular Block - LITFL - ECG Library DiagnosisKARTHICK GBelum ada peringkat
- Arrhythmia 6 YrDokumen72 halamanArrhythmia 6 YrPiyush MalikBelum ada peringkat
- 10.1007@s10554 020 01913 6Dokumen10 halaman10.1007@s10554 020 01913 6Bosman AriestaBelum ada peringkat
- 2015 The ECG Handbook of Contemporary Challenges PDFDokumen246 halaman2015 The ECG Handbook of Contemporary Challenges PDFFercho MedBelum ada peringkat
- ECG Monitoring in TheatreDokumen17 halamanECG Monitoring in TheatrePhani NadellaBelum ada peringkat
- London Core Review Course - (Thurs 18 May - Sun 21 May 2017) - TimetableDokumen5 halamanLondon Core Review Course - (Thurs 18 May - Sun 21 May 2017) - Timetablelondon_core_reviewBelum ada peringkat
- JAMA 1998: Physicians Disciplined For Sex-Related OffensesDokumen6 halamanJAMA 1998: Physicians Disciplined For Sex-Related OffensesThe National DeskBelum ada peringkat
- DIET in Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokumen3 halamanDIET in Chronic Kidney Diseaseatul_desai_3Belum ada peringkat
- Cara Membaca EKG Lengkap PAluDokumen214 halamanCara Membaca EKG Lengkap PAluGiriBelum ada peringkat
- RCP Consultant Physicians Working With PatientsDokumen266 halamanRCP Consultant Physicians Working With PatientsalaaBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiopulmonary Arrest Simulation LabDokumen3 halamanCardiopulmonary Arrest Simulation LabJessica Mason100% (2)
- Study of Renal Profile in Obese Hypertensive Patients: Nani Kazi DesharDokumen16 halamanStudy of Renal Profile in Obese Hypertensive Patients: Nani Kazi DesharBipin SunarBelum ada peringkat