4 Chris Palma LLarkin
Diunggah oleh
christopherDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
4 Chris Palma LLarkin
Diunggah oleh
christopherHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
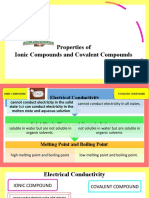
Chris Palma Period 2 11 5 12 Ionic Vs Covalent bonding Lab investigation Introduction: Atoms are found in the period table
with a total of eight valence electrons. They bond covalently or ionicly to form an octect or a full shell. They bond because an anion with a negative charge attracts cations with a positive charge. This allows the particles to share or transfer electrons successfully. The electrons will only be transferred correctly if the octect is formed. Without these the atoms wouldnt become stable. Hypothesis: Table 1: the expected results of testing five different chemicals Compounds to tested Chemical Formula Hypothesis1: Ionic Hypothesis 2: High or covalent or low melting points? Distilled water Sodium Chloride Sucrose (shugar) Dextrose Sodium Chloride H20 NaCl C6H22O11 C6H12O6 NaSo6 covalent ionic covalent covalent ionic low high low low high No yes no no yes Hypothesis 3: will it conduct electricity?
Procedures: Part I. Melting point and strength of bonds 1. fold aluminum foil into a square that will neatly fit on the ring-stand. place a sample or each of the 4 different compounds(water is already melted) on your square of aluminum foil (all 4 at the same time). be careful not to mix them up & keep track. Carefully place the tray on the ring stand and heat with the Bunsen burner ( no longer than 1 2 min).
2.
Chris Palma Period 2 11 5 12 3. Immediately begin recording your detailed observations , keeping track of the order in which the samples melt (or dont melt if thats the case)-which ones have strong bonds and which have weak. Allow the square of foil to cool and then wash it of into the sink.
4.
PARTII. Electrical Conductivity 1. Weigh an approximately 0.1 gram of each sample compound in different wells of a plate(make sure to zero the well plate on the balance) Test the dry compounds for conductivity with the tester . Record your observations (yes or No). Add enough drops of distilled to the well to dissolve the compounds as best you can . Test the solution for conductivity with the tester. Record your observations (Yes and no0. Make sure to wash the conductivity tester with distilled water after every use. Repeat for all of the sample
2.
3.
4.
5. Results:
Table 2: the results of testing five different Chemicals Name/Chemical Formula: Distilled (pure) water/H2O Sodium chloride/NaCl Sucrose(sugar)C12H22O11 Dextrose/ C6H22O11 Sodium Sulfate/NaSO4 : Part I: Melting point (1-5), med. or low ?) I= lowest(already melted) 5 2 3 4 Part II: conducted Electricity (Yes/No) Dry Dissolved no no no no no no yes no no yes Final Conclusion: Ionic or Covalent Bonds Covalent Ionic Covalent Covalent Ionic
From the results, the ionic compounds were those that conducted electricity and had high melting points. However, the covalent compounds have low melting points and dont
Chris Palma Period 2 11 5 12 conduct electricity in water. Sucrose and dextrose were both covalent bonds and were the first two to melt in the buns and burner. After adding distilled water into the compounds they were tested with a tool to check if they conducted electricity but didnt. On the other hand, the two ionic bonds; Sodium Chloride and Sodium sulfate conducted electricity in distilled water and dissolved later on then the covalent bonds. Ionic bonds are formed from metal cations(+) and non-metal anions(-) so when they dissolve in water, electricity can flow through the solution. Additionally, Ionic Bonds are very strong since electrostatic attractions hold cations and anions together. The atoms were able to be determined by figuring out which compounds conducted electricity and by their capacity of high or low melting points. Conclusion: In conclusion the beginning hypothesis was correct because all educated guesses came out to be correct. The prediction was Sodium Chloride and Sodium sulfate were going to be ionic and Sucrose as well as Dextrose was covalent. This was concluded because of their melting points and their ability to conduct electricity
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Final Profect WorkDokumen1 halamanFinal Profect WorkchristopherBelum ada peringkat
- Final ProjectDokumen1 halamanFinal ProjectchristopherBelum ada peringkat
- Final Project WorkDokumen1 halamanFinal Project WorkchristopherBelum ada peringkat
- Mandala 2012 AssignmentDokumen2 halamanMandala 2012 AssignmentchristopherBelum ada peringkat
- Chris Palma Lab ChemistryDokumen1 halamanChris Palma Lab ChemistrychristopherBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Benzene and Its Derivatives: Structure, Naming, ReactionsDokumen5 halamanBenzene and Its Derivatives: Structure, Naming, ReactionsJosephine TeroBelum ada peringkat
- Ch-19 Gas Welding, Gas Cutting & Arc WeldingDokumen184 halamanCh-19 Gas Welding, Gas Cutting & Arc WeldingDivya Soni0% (1)
- LABSA ProposalDokumen10 halamanLABSA ProposalMichelle MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- CAA Guidelines Antibiotic Free Inputs NewDokumen19 halamanCAA Guidelines Antibiotic Free Inputs Newroshan asnotkarBelum ada peringkat
- Pranav ChemicalsDokumen5 halamanPranav ChemicalsPranav ChemicalsBelum ada peringkat
- Earl's Practical Test Part 2 (Lab Report Template) - Dk014Dokumen5 halamanEarl's Practical Test Part 2 (Lab Report Template) - Dk014MALIUS BIN SUNGGI MoeBelum ada peringkat
- Gram Equivalent Concept: Sunil Kumar SinghDokumen9 halamanGram Equivalent Concept: Sunil Kumar Singhnitesh004Belum ada peringkat
- Baranowski2002 - XRF Soil ChemicalDokumen10 halamanBaranowski2002 - XRF Soil ChemicalElisangela SordiBelum ada peringkat
- Caramel OverviewDokumen6 halamanCaramel OverviewPham Thi Cam TuBelum ada peringkat
- Rearrangement ReactionsDokumen7 halamanRearrangement ReactionssantiisantBelum ada peringkat
- Properties of Ionic Compounds and Covalent CompoundsDokumen6 halamanProperties of Ionic Compounds and Covalent Compoundsnoraini nasikinBelum ada peringkat
- Dyeing Lab Department Calculation and Others - TEXTILE TECHNOLOGY ( ) PDFDokumen10 halamanDyeing Lab Department Calculation and Others - TEXTILE TECHNOLOGY ( ) PDFshakilsai100% (1)
- Experiment 15 - UrineDokumen3 halamanExperiment 15 - UrineJesette KhoBelum ada peringkat
- EP Web Catalog CRS PDFDokumen84 halamanEP Web Catalog CRS PDFramaiaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 6Dokumen16 halamanUnit 6alex ortizBelum ada peringkat
- Japanies PharmacopieaDokumen254 halamanJapanies PharmacopieaakramuddaulaBelum ada peringkat
- Exxal 9 Alcohol Product Safety SummaryDokumen3 halamanExxal 9 Alcohol Product Safety SummaryKayalvilli ShanmugamBelum ada peringkat
- Price List Brochure Klin'sDokumen4 halamanPrice List Brochure Klin'sAbdiyasa Dharma InovasiBelum ada peringkat
- Polyester Properties, Preparation and Applications by Hina Yamashita, Yui Nakano PDFDokumen259 halamanPolyester Properties, Preparation and Applications by Hina Yamashita, Yui Nakano PDFVasile LeniucBelum ada peringkat
- Week 2A-Concetration of SolutionDokumen72 halamanWeek 2A-Concetration of SolutionLuke BelmarBelum ada peringkat
- Welding ReportDokumen15 halamanWelding ReportSamBelum ada peringkat
- Batteries: Life Cycle Analysis of Lithium-Ion Batteries For Automotive ApplicationsDokumen15 halamanBatteries: Life Cycle Analysis of Lithium-Ion Batteries For Automotive ApplicationstutywaodeBelum ada peringkat
- PISE1-En-US SiC Block Heat Exchanger - SE SeriesDokumen2 halamanPISE1-En-US SiC Block Heat Exchanger - SE SeriesViajante_santosBelum ada peringkat
- STS Military Catalogue 20190815 WebDokumen40 halamanSTS Military Catalogue 20190815 WebMichał ŚwieradBelum ada peringkat
- Study 3101 w1Dokumen319 halamanStudy 3101 w1Koray SimsekBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Design For Methanol Distillation Unit: February 2021Dokumen51 halamanPlant Design For Methanol Distillation Unit: February 2021maged1998100% (1)
- Xi NM B MT 4 PDFDokumen11 halamanXi NM B MT 4 PDFSatwant KaurBelum ada peringkat
- What is Chemistry? Exploring the Study of MatterDokumen124 halamanWhat is Chemistry? Exploring the Study of Mattermajji satish0% (1)
- Disposal of Poly (Alkene) PlasticsDokumen4 halamanDisposal of Poly (Alkene) PlasticsSonal WanigasooriyaBelum ada peringkat