Blood Supply of Brain
Diunggah oleh
vmagtotoDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Blood Supply of Brain
Diunggah oleh
vmagtotoHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
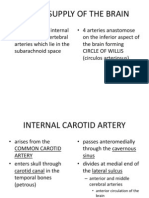
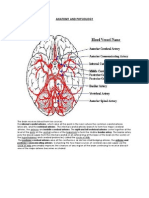
Blood Supply of Brain Supplied by two internal carotid arteries and two vertebral arteries and their branches
anastomose to form the circle of Willis Internal Carotid Artery (ICA) - Begins at bifurcation of common carotid artery where it possesses localized dilatation (carotid sinus) - Terminates as anterior and middle cerebral arteries posterior to the medial end of lateral cerebral sulcus Branches of Cerebral portion 1. Opthalmic Artery - Arises as ICA emerges from cavernous sinus - Supplies eye, other orbital structures. Terminal branches supply frontal area of scalp, ethmoid and frontal sinuses, dorsum of nose 2. Posterior Communicating Artery - Emerges near ICAs terminal bifurcation - Joins posterior cerebral artery (PCA) to form Circle of Willis 3. Choroidal artery - Also emerges near ICAs terminal bifurcation - Enters inferior horn of lateral ventricles and ends in choroid plexus to supply the crus cerebri, lateral geniculate body, optic tract, and internal capsule 4. Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA) - Smaller branch of ICA. Enters longitudinal fissure of cerebrum and is joined to ACA of opposite side by Anterior communicating artery. It curves backward over corpus callosum to anastomose with PCA - Cortical branches supply medial area of cortex up to parieto-occipital sulcus and 1 inch on adjoining lateral surface (leg area of pre-central gyrus) - Central branches help supply parts of lentiform and caudate nuclei and internal capsule 5. Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) - Largest branch - Cortical branches supply entire lateral surface except those supplied by ACA. Thus it supplies all motor area except the leg area - Central branches supply lentiform and caudate nuclei and internal capsule - UMNL/face & UE ang affected pag nagkaproblema
Magtoto
Vertebral Artery - Branch of subclavian artery, ascends neck through transverse foramen of C1-C6 - Lower border of pons, joins vertebral artery of opposite side to form Basilar Artery and ascends in a groove on the anterior surface of pons . it divides into the two posterior cerebral arteries at upper border of pons. - Posterior Cerebral Artery is joined by posterior communicating branch of ICA - Cortical branches inferolateral and medial surfaces of temporal lobe and the lateral and medial surfaces of occipital lobe (Visual cortex) - Central branches supply parts of the thalamus, lentiform nucleus, midbrain, pineal and medial geniculate bodies - Choroidal branch enters inferior horn of lateral ventricle to supply choroid plexus. Also supplies choroid plexus of third ventricle - Blindness pag nagkaproblema sa arteries Circle of Willis - Lies at interpeduncular fossa at base of brain - Formed by anterior communicating artery, ACAs, ICAs, posterior communicating arteries, PCAs, and basilar arteries Arteries to Specific Brain Areas - Corpus Striatum and Internal Capsule supplied by medial and lateral striate central branches of MCA - Thalamus supplied by posterior communicating, basilar, and PCA - Midbrain supplied by PCA, basilar, and superior cerebellar artery - Pons supplied by basilar, anterior, inferior, and superior cerebellar arteries - Medulla oblongata supplied by vertebral, anterior and posterior spinal, posterior inferior cerebellar, and basilar arteries - Cerebellum supplied by superior cerebellar, anterior inferior cerebellar, posterior inferior cerebellar ** Blood supply to the brain sympathetic blood supply which causes vasoconstriction Autoregulation specific amount of blood that goes to the brain - Increase in CO2 and hydrogen(acidic) vasodilation - Decrease in O2 Cerebral blood flow 15% of Cardiac output, 50-60mL/100g of brain tissue/min Cerebral ischemia 5-10s: unconscious; 1min: neuronal function; 4mins: irreversible changes Cerebral angiography
Magtoto
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Blood Supply of The BrainDokumen11 halamanBlood Supply of The Brainneleh grayBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of Blood VesselDokumen3 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of Blood Vesselneleh grayBelum ada peringkat
- CVADokumen13 halamanCVAAmlan jyoti thanapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Presented By: VIVEK DEVDokumen38 halamanPresented By: VIVEK DEVFranchesca LugoBelum ada peringkat
- Musculoskeletal SystemDokumen19 halamanMusculoskeletal SystemDani Anyika100% (1)
- Spinal Cord and Spinal NervesDokumen67 halamanSpinal Cord and Spinal NervesRAVISHBelum ada peringkat
- Superficial and Deep ReflexesDokumen28 halamanSuperficial and Deep ReflexesShilpa SBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiorespiratory AssessmentDokumen7 halamanCardiorespiratory AssessmentmalarvelykBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BRAINDokumen5 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of The BRAING FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Approach To A Patient With ParaplegiaDokumen31 halamanApproach To A Patient With ParaplegiaFaisal Qureshi75% (4)
- By Sweta Kumari Summer Project-II Submitted ToDokumen22 halamanBy Sweta Kumari Summer Project-II Submitted ToSudarshanKumar0% (1)
- Spinal Cord Injury: Mrs. Zaida ZaracenaDokumen36 halamanSpinal Cord Injury: Mrs. Zaida ZaracenaArdhel LoslosoBelum ada peringkat
- Rehabilitation in Spinal Cord InjuryDokumen2 halamanRehabilitation in Spinal Cord InjuryAudry ArifinBelum ada peringkat
- Final Coma StimulationDokumen23 halamanFinal Coma StimulationpreetisagarBelum ada peringkat
- Motor Neuron DiseaseDokumen8 halamanMotor Neuron DiseaseyigoBelum ada peringkat
- Transverse MyelitisDokumen19 halamanTransverse MyelitisAnonymous YHQmN8a01100% (1)
- Muscular DystrophyDokumen64 halamanMuscular DystrophysridharBelum ada peringkat
- Coma Stimulation PDFDokumen2 halamanComa Stimulation PDFCarrie100% (1)
- Spinal Cord InjuryDokumen49 halamanSpinal Cord InjuryIis Rica MustikaBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of Spinal Cord Injuries - PhysiopediaDokumen20 halamanOverview of Spinal Cord Injuries - PhysiopediaRaina Ginella DsouzaBelum ada peringkat
- Tuberculosis of SpineDokumen11 halamanTuberculosis of SpineSepti RahadianBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Minute Walk TestDokumen3 halaman6 Minute Walk Testrk_s7Belum ada peringkat
- Research Methodology: For All Physiotherapy and Allied Health Sciences StudentsDokumen1 halamanResearch Methodology: For All Physiotherapy and Allied Health Sciences StudentsProductivity 100Belum ada peringkat
- Origin & Conduction of Cardiac Impulse: Dr.S.Brinda MD Associate Professor PhysiologyDokumen36 halamanOrigin & Conduction of Cardiac Impulse: Dr.S.Brinda MD Associate Professor PhysiologyAtchaya ThillainatarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Dysphagia ManagementDokumen21 halamanDysphagia ManagementSooraj A. O.100% (1)
- Heart Sounds: They Are The Sounds Produced by The Mechanical Activities of The Heart During Each Cadiac CycleDokumen19 halamanHeart Sounds: They Are The Sounds Produced by The Mechanical Activities of The Heart During Each Cadiac Cyclevishnudurga100% (1)
- MPT SyllabusDokumen72 halamanMPT SyllabusRupsa MajumderBelum ada peringkat
- Vitiligo PPT (1) .PPTX LectureDokumen35 halamanVitiligo PPT (1) .PPTX LectureVinay DhranaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment ON Chest Physiotherapy: Sri Guru Ram Das Nursing Institute Pandher, AmritsarDokumen13 halamanAssignment ON Chest Physiotherapy: Sri Guru Ram Das Nursing Institute Pandher, AmritsarPawan BatthBelum ada peringkat
- Total Knee ReplacementDokumen99 halamanTotal Knee ReplacementGandis Ayu WardaniBelum ada peringkat
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDokumen29 halamanCerebrovascular AccidentMarites GalvezBelum ada peringkat
- Arterial Line Arterial LineDokumen13 halamanArterial Line Arterial LineLinamaria Lozano100% (1)
- Bicipital TendonitisDokumen2 halamanBicipital TendonitisJ Cheung100% (2)
- PTCADokumen51 halamanPTCAJasmin Jacob100% (1)
- Growth and Development of ChildrenDokumen108 halamanGrowth and Development of Childrenabdisalaan hassanBelum ada peringkat
- Tx3: Bobath'S Neurodevelopmental Treatment: PT Applications Team DLSMHSI CRS PT Department AY 2018-2019Dokumen4 halamanTx3: Bobath'S Neurodevelopmental Treatment: PT Applications Team DLSMHSI CRS PT Department AY 2018-2019Pauline JaleaBelum ada peringkat
- Middle Cerebral ArteryDokumen4 halamanMiddle Cerebral Arterykat9210Belum ada peringkat
- Management of Head InjuryDokumen87 halamanManagement of Head InjurydhabeBelum ada peringkat
- Herpes ZosterDokumen16 halamanHerpes ZosterColleen De la RosaBelum ada peringkat
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDokumen62 halamanCerebrovascular AccidentJaydee DalayBelum ada peringkat
- Geriatric RehabilitationDokumen16 halamanGeriatric RehabilitationAjay DherwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Discuss Surgical Management of Cerebral Palsy - 000Dokumen72 halamanDiscuss Surgical Management of Cerebral Palsy - 000SamBelum ada peringkat
- Lung SurgeriesDokumen43 halamanLung SurgeriesSereinBelum ada peringkat
- Brachial Plexus InjuryDokumen21 halamanBrachial Plexus InjurySemi IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- TuberculomaDokumen7 halamanTuberculomaAdeleBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Vii RehabilitationDokumen28 halamanUnit Vii RehabilitationSamjhana NeupaneBelum ada peringkat
- Chest Physiotherapy - Postural DrainageDokumen2 halamanChest Physiotherapy - Postural DrainageMicah MagallanoBelum ada peringkat
- Muscular DystrophyDokumen3 halamanMuscular Dystrophyderrickmason626Belum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Airway DiseasesDokumen7 halamanPulmonary Rehabilitation: Airway DiseasesshivamptBelum ada peringkat
- Lung Expansion 1Dokumen31 halamanLung Expansion 11trindogg100% (2)
- ParaplegiaDokumen7 halamanParaplegiaRigaga GopiBelum ada peringkat
- Development of HeartDokumen15 halamanDevelopment of Heartash ashBelum ada peringkat
- POMRDokumen9 halamanPOMREva BellaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Eight: Principles, Objectives and General Ap-Proaches Relating To Community-Based RehabilitationDokumen5 halamanChapter Eight: Principles, Objectives and General Ap-Proaches Relating To Community-Based RehabilitationAnandhu GBelum ada peringkat
- Ambulation Aids and Patterns 2018Dokumen59 halamanAmbulation Aids and Patterns 2018venkata ramakrishnaiah100% (1)
- Spinal Cord Injury Description/definitionDokumen2 halamanSpinal Cord Injury Description/definitionAlyzza Gayle AdrianoBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac RehabilitationDokumen28 halamanCardiac Rehabilitationshivalingam20Belum ada peringkat
- Myasthenia Gravis BrochureDokumen2 halamanMyasthenia Gravis BrochureMolly100% (1)
- The Indian Association of Physiotherapists - IAP Constitutions PDFDokumen17 halamanThe Indian Association of Physiotherapists - IAP Constitutions PDFHasan Rahman100% (1)
- HIV-Associated Opportunistic Infections of The CNSDokumen13 halamanHIV-Associated Opportunistic Infections of The CNSmauroignacioBelum ada peringkat
- KumeDokumen28 halamanKumeGrace Clemenia-GrefaldiaBelum ada peringkat
- Ad&d The Book of Lairs IIDokumen97 halamanAd&d The Book of Lairs IIJohn Strickler100% (7)
- Evolution Epidemiology and Etiology of Temporomandibular Joint DisordersDokumen6 halamanEvolution Epidemiology and Etiology of Temporomandibular Joint DisordersCM Panda CedeesBelum ada peringkat
- Duck Rearing and ManagemntDokumen49 halamanDuck Rearing and Managemntkaranpraba1901Belum ada peringkat
- Medical Parasitology: Human ParasitesDokumen30 halamanMedical Parasitology: Human ParasitesElycaBelum ada peringkat
- Trachoma - Background, Pathophysiology, EpidemiologyDokumen3 halamanTrachoma - Background, Pathophysiology, EpidemiologyWiri Resky AmaliaBelum ada peringkat
- LEAPS Fugl-Meyer InstructionsDokumen17 halamanLEAPS Fugl-Meyer InstructionsDaniele Bertolo100% (1)
- Qi Permeating TechniqueDokumen2 halamanQi Permeating TechniquemeneamelaBelum ada peringkat
- Beginner's Guide To Getting Started With DiscusDokumen18 halamanBeginner's Guide To Getting Started With DiscusGary HoustonBelum ada peringkat
- 2.biomekanik Pada Edentulus PenuhDokumen27 halaman2.biomekanik Pada Edentulus PenuhJesica Dwiasta Octaria NainggolanBelum ada peringkat
- The HelpDokumen7 halamanThe HelpRajipah OsmanBelum ada peringkat
- Neuritis in Morbus HansenDokumen32 halamanNeuritis in Morbus HansenSiska IxchaBelum ada peringkat
- Asupan Purin Dan Tingkat Pengetahuan Dengan Kadar Asam Urat Di Puskesmas Rurukan Kota Tomohon Yuli Runtuwene, Rudolf B. Purba, Phembriah S. KerehDokumen11 halamanAsupan Purin Dan Tingkat Pengetahuan Dengan Kadar Asam Urat Di Puskesmas Rurukan Kota Tomohon Yuli Runtuwene, Rudolf B. Purba, Phembriah S. Kerehsiti nurhidayahBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Prelim 3-KeyDokumen3 halamanPractice Prelim 3-KeyLauren PriscoBelum ada peringkat
- RehumaticDokumen3 halamanRehumaticgopscharanBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Molar Distalization: A Critical Analysis: MF Sfondrini V Cacciafesta G SfondriniDokumen13 halamanUpper Molar Distalization: A Critical Analysis: MF Sfondrini V Cacciafesta G SfondriniCypry SchmitzBelum ada peringkat
- Pollen Allergy - Prevention and Natural Remedies - Greater KashmirDokumen3 halamanPollen Allergy - Prevention and Natural Remedies - Greater Kashmirrizan loanBelum ada peringkat
- Reiki Wings - Rinku PatelDokumen82 halamanReiki Wings - Rinku PatelOana Simionescu100% (3)
- Urinary SystemDokumen31 halamanUrinary SystemAyro Business CenterBelum ada peringkat
- Bio Ass I QPDokumen7 halamanBio Ass I QPSwayam GosaviBelum ada peringkat
- Poultry Science and TechnologyDokumen2 halamanPoultry Science and TechnologyPopa Anne MarieBelum ada peringkat
- Vitamins and Minerals: Nutrient (Vitamins) Needed For Key SourcesDokumen4 halamanVitamins and Minerals: Nutrient (Vitamins) Needed For Key SourcesKevin Carl A. CorpuzBelum ada peringkat
- Checklist (PapSmear)Dokumen5 halamanChecklist (PapSmear)Sinung BawonoBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 3rd Edition EllisDokumen8 halamanTest Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 3rd Edition Elliscanebrutalfniy66Belum ada peringkat
- Meat Milk and Fish HygieneDokumen74 halamanMeat Milk and Fish Hygieneransingh100% (1)
- 12-Fancy Birds RearingDokumen45 halaman12-Fancy Birds RearingAnonymous sBJu38BqBelum ada peringkat
- Research Life ScienceDokumen21 halamanResearch Life ScienceKeyth Abegail RendonBelum ada peringkat
- CABERGOLINE Safety2Dokumen6 halamanCABERGOLINE Safety2Kane SmithBelum ada peringkat
- MaternityDokumen91 halamanMaternityAnonymous D8KswoBelum ada peringkat
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDari EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsBelum ada peringkat
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDDari EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDari EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (404)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDari EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (32)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDari EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BePenilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDari EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Dari EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Penilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDari EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (82)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDari EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (4)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (42)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDari EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDari EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesDari EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (1412)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeDari EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (254)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearDari EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (23)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlDari EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (60)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDari EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (8)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Dari EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (110)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDari EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceDari EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern SciencePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (51)
- Summary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDari EverandSummary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (61)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryDari EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (46)