2012-11-28 Solving More Trig Equations and Graphing Sine and Cosine
Diunggah oleh
samjshah0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
3K tayangan7 halamanFor any angle u, it is always true that 2 2 sin ) ( ) ( cos 1 u u + =. Check to see that this is true for 12 / 7 u t =. For the equation sin( ) 0. U = / there are two values of u (for 0 360 o o u s s ) that will make this equation true.
Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniFor any angle u, it is always true that 2 2 sin ) ( ) ( cos 1 u u + =. Check to see that this is true for 12 / 7 u t =. For the equation sin( ) 0. U = / there are two values of u (for 0 360 o o u s s ) that will make this equation true.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
3K tayangan7 halaman2012-11-28 Solving More Trig Equations and Graphing Sine and Cosine
Diunggah oleh
samjshahFor any angle u, it is always true that 2 2 sin ) ( ) ( cos 1 u u + =. Check to see that this is true for 12 / 7 u t =. For the equation sin( ) 0. U = / there are two values of u (for 0 360 o o u s s ) that will make this equation true.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 7
1
Name:_____________________________ Date:__________________ Band:________
Precalculus | Packer Collegiate Institute
Solving More Trig Equations, Graphing Sine and Cosine
Warm Up:
1. (a) For any angle u , it is always true that
2 2
sin ) ( ) ( cos 1 u u + = . Use your calculators in radian mode. Check
to see that this is true for 12 / 7 u t = .
(b) Can you use the unit circle to understand why this is true?
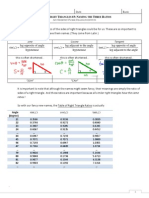
Section 1: Lets get started with another simple basic trig equation.
1. For the equation cos( ) 0.4 u = there are two values of u (for 0 360
o o
u s s ) that will make this equation
true.
What quadrants are the
two angles in? How do you
know?
What is the reference angle
(the angle made to the x-
axis) for these values?
What are the two values of u that make the
equation true?
2. For the equation sin( ) 0.72 u = there are two values of u (for 0 360
o o
u s s ) that will make this equation
true.
What quadrants are the
two angles in? How do you
know?
What is the reference angle
(the angle made to the x-
axis) for these values?
What are the two values of u that make the
equation true?
2
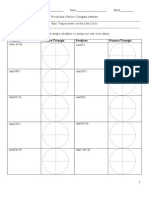
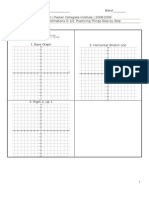
Section 2: Graphing Sine and Cosine and Some of Their Properties
We recently have graphed sine and cosine. It takes the plotting of a lot of points. For us, when we graph sine
and cosine, lets just plot the key points which Ive included below. Each of these key points corresponds to a
point on the unit circle Label the points A, B, C, D, and E on the unit circle.
) si ( n( ) f u u =
t
2
t
2
t
3t
2
2t
1
1
x
y
A
B
C
D
E
) co ( s( ) g u u =
t
2
t
2
t
3t
2
2t
1
1
x
y
A
B
C
D
E
By plotting just these points, it makes our lives much easier!
1. True or False: The sine curve from 0 u t s s is a semicircle.
2. True or False: The important u -values when we plot a standard sine or cosine graph are all multiples
of / 2 t (these are the key points).
3. True or False: The sine and cosine curves continue on in both directions (horizontally) forever!
4. The domain of ) co ( s( ) g u u = is __________________ and the range is ____________________.
5. True or False: The domain and range of ) si ( n( ) f u u = is different than the domain and range
of ) co ( s( ) g u u = .
3
6. True or False: When you shift the graph of ) si ( n( ) f u u = to the right / 2 t units you get the graph of
) co ( s( ) g u u = .
7. True or False: If ) si ( n( ) f u u = , then / 2) cos( ) ( f u t u + = .
8. True or False: If ) si ( n( ) f u u = , then / 2) s( ) ( co f u t u = .
9. True or False: If co ( ) s( ) g u u = , then ) cos( ( ) ) ( g g u t u u = = .
10. True or False: If si ( ) n( ) f u u = , then ( ) ( 2 ) sin( ) f f u t u u = = .
11. True or False: The function co ( ) s( ) g u u = is one-to-one.
Section 3: Graphing Using the Graphing Calculator [be in Radian Mode!]
We can graph trigonometric functions on our graphing calculators but it likes x s and y s, not u s.
So usually to graph something, wed type: into our graphing screen.
So to graph a sine curve, well type: . Be warned Even though it says sin( ) y x = , you should
think of it as ) si ( n( ) f u u = , where the horizontal axis (inputs) are angles, and the vertical axis represents the outputs
to the function.
The graphing calculator is really nice and will even pick a nice window for you. Go to the ZOOM menu, just
click on .
Draw what you see below for sine and cosine.
) si ( n( ) f u u =
) co ( s( ) g u u =
4
1. ZTrig picks a very specific window. What window does it choose?
Xmin: Ymin:
Xmax: Ymax:
Xscl: Yscl:
2. Now change your mode so that you are in degree mode. Regraph the functions, but again use ZTtrig
to choose the window. What is the window now?
Xmin: Ymin:
Xmax: Ymax:
Xscl: Yscl:
Section 4: Even and Odd Functions
Lets review even and odd functions.
Even Function Odd Function
Algebraically, it means that:
Algebraically, it means that:
Graphically, it means that:
Graphically, it means that:
1. Is the graph for the sine function even, odd, or neither? How do you know?
2. Is the graph for the cosine function even, odd, or neither? How do you know?
3. True or False: ) sin( s 3 30 ) 0 in(
o o
=
[if it is false, how could you modify the right hand part of the equation to make it true?]
4. True or False: / 6) c cos( / 6) os( t t =
[if it is false, how could you modify the right hand part of the equation to make it true?]
Rewrite the following:
cos( 6 ) 0
o
= cos( 4 ) 5
o
= sin( 9 ) 0
o
=
cos( 3 / 2) t =
5
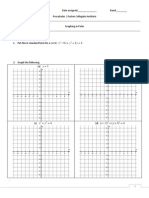
Section 5: Relating Our Basic Trig Equations to Our Graphs
Prelude: One way to solve 2 3 5 1 x x = + is to solve it graphically. We could plot
1 2 3
2 5 1
Y x
Y x
=
= +
on our
calculators and find out the x-value where they intersected! It isnt the fastest way to solve the problem, but
we can.
Use your calculator to do this! The x-value which makes the equation true is: __________________
Relating this to Basic Trig Equations: Recall we already learned to solve basic trig equations algebraically. For
example, we learned how to solve ) c s( . o 0 4 u = with a restricted values foru , like: 3 0 60
o o
u s s .
Now lets solve it graphically. We could plot:
1 cos( )
2 0.4
Y x
Y
=
=
Put your calculator in degree mode and set the window so that it has our restricted u values, and then graph!
We cannot use ZTrig because we only care about our function for specific u values, and ZTrig doesnt know
that! It always uses the same u values.
What variable is X secretly standing in for?
Sketch what you see! Find the points of intersection .
The points of intersection are _________ and __________.
Thus, the solutions to ) c s( . o 0 4 u = (where 3 0 60
o o
u s s ) are: __________ and ___________.
(Did that match up with what you found in Section 1?)
6
1. Use your graphing calculator to find the solution(s) to ) . n( 0 si 6 u = , where 3 0 60
o o
u s s .
Be sure to share what window you used and draw a quick sketch of what your calculator shows you.
Round your answer to the hundredths place.
Fill in window:
Sketch your graph:
Solution(s):
2. Use your graphing calculator to find the solution(s) to 1 cos( ) u = , where 3 2t u t s s .
Be sure to share what window you used and draw a quick sketch of what your calculator shows you.
Round your answer to the hundredths place.
Fill in window:
Sketch your graph:
Solution(s):
3. Use your graphing calculator to find the solution(s) to ) s n( . i 1 2 u = , where 4 90 0 5
o o
u s s .
Be sure to share what window you used and draw a quick sketch of what your calculator shows you.
Round your answer to the hundredths place.
Fill in window:
Sketch your graph:
Solution(s):
4. We havent graphed the tangent function yet. It is cray cray! Use your graphing calculator to find the
solution(s) to ) t n( . a 2 5 u = , where 2 90 70
o o
u s s . Im giving you the window.
Sketch your graph:
Solution(s):
7
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Letter To MoMath BoardDokumen1 halamanLetter To MoMath Boardsamjshah100% (1)
- Y X X Y: Warm Up: Sketch The Graphs Below. (This Is Going To Get You Thinking About Our Next Topic, Parabolas.)Dokumen7 halamanY X X Y: Warm Up: Sketch The Graphs Below. (This Is Going To Get You Thinking About Our Next Topic, Parabolas.)samjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Last TrigDokumen18 halamanLast TrigsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2013-04-19 Assessment On (Polar) Conic BasicsDokumen7 halaman2013-04-19 Assessment On (Polar) Conic BasicssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2017-04-Xx Basic Trigonometric EquationsDokumen14 halaman2017-04-Xx Basic Trigonometric EquationssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2015-04-Xx Similar Right Triangles 2.5 Do NowDokumen2 halaman2015-04-Xx Similar Right Triangles 2.5 Do NowsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 5.8 Radical Eqts and IneqDokumen3 halaman5.8 Radical Eqts and IneqkcarveyBelum ada peringkat
- 4.5: Rational FunctionsDokumen5 halaman4.5: Rational FunctionsRebecka Kermanshahi PetersonBelum ada peringkat
- 2010-03-19 Riemann Program ActivityDokumen4 halaman2010-03-19 Riemann Program ActivitysamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2013-01-31 Cofunctions and An Introduction To Trig IdentitiesDokumen4 halaman2013-01-31 Cofunctions and An Introduction To Trig Identitiessamjshah50% (2)
- Calculus Curriculum For 2009-2010Dokumen7 halamanCalculus Curriculum For 2009-2010samjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Form Right Angles.: Name D BDokumen2 halamanForm Right Angles.: Name D BsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- D Band Groupwork ListDokumen4 halamanD Band Groupwork Listsamjshah100% (1)
- Desmos Low PointsDokumen29 halamanDesmos Low PointssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2012-11-14 Angular and Linear SpeedDokumen2 halaman2012-11-14 Angular and Linear SpeedsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Name D B: EMI Ircle OnjectureDokumen2 halamanName D B: EMI Ircle OnjecturesamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2015-04-xx Similar Right Triangles 3 PDFDokumen8 halaman2015-04-xx Similar Right Triangles 3 PDFsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2017-04-24 Basic Trigonometric EquationsDokumen14 halaman2017-04-24 Basic Trigonometric EquationssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2010-04-26 Drawing Integrals No SolutionsDokumen5 halaman2010-04-26 Drawing Integrals No SolutionssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Based Assessment Mimi, Jill, and Eddie: 1 - Organizing Idea (What Is The Overarching Concept?)Dokumen8 halamanPerformance Based Assessment Mimi, Jill, and Eddie: 1 - Organizing Idea (What Is The Overarching Concept?)samjshahBelum ada peringkat
- PreCalculus Advanced Course Expectations, 2017-2018Dokumen10 halamanPreCalculus Advanced Course Expectations, 2017-2018samjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Quarter 1 Calculus SkillsDokumen1 halamanQuarter 1 Calculus SkillssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2016-10-31 SequencesDokumen26 halaman2016-10-31 SequencessamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Name D B: Quation FOR A IrcleDokumen13 halamanName D B: Quation FOR A IrclesamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Does It Still Hold For A Circle?: G C: A S CDokumen5 halamanDoes It Still Hold For A Circle?: G C: A S CsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2016 10 XX Combinatorial Revelations PDFDokumen8 halaman2016 10 XX Combinatorial Revelations PDFsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Implicit Differentiation VisuallyDokumen6 halamanImplicit Differentiation VisuallysamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2012-11-15 Basic Trigonometry On The Unit Circle PracticeDokumen2 halaman2012-11-15 Basic Trigonometry On The Unit Circle PracticesamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2018-05-Xx Inkblot or Gerrymandered DistrictDokumen2 halaman2018-05-Xx Inkblot or Gerrymandered Districtsamjshah100% (1)
- MAT1033C - 2014-2015 - InstructorDokumen86 halamanMAT1033C - 2014-2015 - InstructorHanzDucNguyen80% (15)
- 2013-02-28 Introduction To PolarDokumen6 halaman2013-02-28 Introduction To PolarsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Slope Stations Lab: Station Description Teacher's Initials SDokumen9 halamanSlope Stations Lab: Station Description Teacher's Initials SheathermkohnBelum ada peringkat
- I T C T C P: Sosceles Riangles AND Ongruent Riangles Hallenge RoblemsDokumen9 halamanI T C T C P: Sosceles Riangles AND Ongruent Riangles Hallenge RoblemssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Ddistance / Dtime: T R T RDokumen2 halamanDdistance / Dtime: T R T RsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Ddistance / Dtime: T R T RDokumen2 halamanDdistance / Dtime: T R T RsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2014-04-11 The Very Big and The Very Small, OptimizationDokumen5 halaman2014-04-11 The Very Big and The Very Small, OptimizationsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Absolute Value Functions - Graphing Calculator ActivityDokumen3 halamanAbsolute Value Functions - Graphing Calculator ActivityheathermkohnBelum ada peringkat
- 2019-10-04 Analyzing Student Created FunctionsDokumen1 halaman2019-10-04 Analyzing Student Created FunctionssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Graphing Sine and CosineDokumen17 halamanGraphing Sine and CosineNiaBelum ada peringkat
- RdkpickleDokumen8 halamanRdkpicklesamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2016 10 XX Combinatorial RevelationsDokumen12 halaman2016 10 XX Combinatorial RevelationssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2016 10 XX Combinatorial RevelationsDokumen12 halaman2016 10 XX Combinatorial RevelationssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2013-03-04 Understanding Polar GraphsDokumen5 halaman2013-03-04 Understanding Polar GraphssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- PBADokumen10 halamanPBAsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Name D B: Ngle Isectors of A RiangleDokumen4 halamanName D B: Ngle Isectors of A RianglesamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2009-09-29 How To Write An Explanation in MathDokumen3 halaman2009-09-29 How To Write An Explanation in MathsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2012-11-26 Solving Basic Trig Equations and Graphing Basic Trig FunctionsDokumen6 halaman2012-11-26 Solving Basic Trig Equations and Graphing Basic Trig FunctionssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 01 Crossed Diagonals (Proof)Dokumen4 halaman01 Crossed Diagonals (Proof)samjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Section 3.2 NotesDokumen2 halamanSection 3.2 NoteskcarveyBelum ada peringkat
- For Full Disclosure, I Don't Really Love The Author of The QuotationDokumen2 halamanFor Full Disclosure, I Don't Really Love The Author of The Quotationsamjshah100% (1)
- 2015-03-30 A Conjecture About Semicircles, Part IIDokumen4 halaman2015-03-30 A Conjecture About Semicircles, Part IIsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2009-11-19 Double Challenge Problems For Basic DerivativesDokumen2 halaman2009-11-19 Double Challenge Problems For Basic DerivativessamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- K K K K K K: Circle EllipseDokumen4 halamanK K K K K K: Circle EllipsesamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 6.6 Analyzing Graphs of Quadratic EqtsDokumen2 halaman6.6 Analyzing Graphs of Quadratic EqtskcarveyBelum ada peringkat
- 2016-10-31 Card Sort For SequencesDokumen2 halaman2016-10-31 Card Sort For SequencessamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2018-03-Xx One Last Derivative... LNDokumen4 halaman2018-03-Xx One Last Derivative... LNsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2018 05 03 Riemann SumsDokumen7 halaman2018 05 03 Riemann Sumssamjshah100% (1)
- 2015-04-Xx Similar Right Triangles 1Dokumen13 halaman2015-04-Xx Similar Right Triangles 1samjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Concept MapDokumen1 halamanConcept MapsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2012-11-19 Constant Multiple and Addition Rules For DerivativesDokumen6 halaman2012-11-19 Constant Multiple and Addition Rules For DerivativessamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2013-02-29 Graphing in PolarDokumen5 halaman2013-02-29 Graphing in PolarsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2017-04-04 Super Large Numbers (Long Block)Dokumen4 halaman2017-04-04 Super Large Numbers (Long Block)samjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Centers of RotationsDokumen9 halamanCenters of RotationssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Online Learning! - Adv. PrecalculusDokumen7 halamanOnline Learning! - Adv. PrecalculussamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- UG Aths: Athematician ATE ANDDokumen9 halamanUG Aths: Athematician ATE ANDsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2010-09-22 Limits Prelude 2Dokumen2 halaman2010-09-22 Limits Prelude 2samjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2013-12-10 Basic Derivatives Multiple MethodsDokumen4 halaman2013-12-10 Basic Derivatives Multiple MethodssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2009-03-31 Function Transformation, Part 3.5Dokumen2 halaman2009-03-31 Function Transformation, Part 3.5samjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2.4-2.5 Review WorksheetDokumen3 halaman2.4-2.5 Review WorksheetkcarveyBelum ada peringkat
- 2013-04-08 A Polar Family of CurvesDokumen1 halaman2013-04-08 A Polar Family of CurvessamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- UG Aths: Time (S) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 PositionDokumen10 halamanUG Aths: Time (S) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 PositionsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- UG Aths: Time (S) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 PositionDokumen10 halamanUG Aths: Time (S) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 PositionsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- HW: PG 333, 14-40 Even. DateDokumen4 halamanHW: PG 333, 14-40 Even. DatekcarveyBelum ada peringkat
- 2013-03-06 Polar Practice Home EnjoymentDokumen3 halaman2013-03-06 Polar Practice Home EnjoymentsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2018 01 31 Popcorn ActivityDokumen4 halaman2018 01 31 Popcorn ActivitysamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Adv. Precalculus Skill List (Ongoing) PDFDokumen2 halamanAdv. Precalculus Skill List (Ongoing) PDFsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 6.3 Solving Quadratics by FactoringDokumen2 halaman6.3 Solving Quadratics by FactoringkcarveyBelum ada peringkat
- 2017-01-30 Bug PathsDokumen10 halaman2017-01-30 Bug PathssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2017-01-30 Bug PathsDokumen10 halaman2017-01-30 Bug PathssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2013-12-02 Product Rule, Why You Should Believe ItDokumen6 halaman2013-12-02 Product Rule, Why You Should Believe ItsamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- All Topic Lists Combined (Geometry 2015-2016)Dokumen14 halamanAll Topic Lists Combined (Geometry 2015-2016)samjshahBelum ada peringkat
- 2012-11-16 Introducting Three New Trigonometric FunctionsDokumen2 halaman2012-11-16 Introducting Three New Trigonometric FunctionssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- MESA White Paper 52 - Smart Manufacturing - Landscape ExplainedDokumen50 halamanMESA White Paper 52 - Smart Manufacturing - Landscape ExplainedAbigail100% (1)
- Graded Unit 1Dokumen38 halamanGraded Unit 1Yen Fa Chen100% (1)
- Discovering Derivative RulesDokumen5 halamanDiscovering Derivative RulesRobert Talbert100% (1)
- Already Have An Account?. Then You'll BeDokumen6 halamanAlready Have An Account?. Then You'll BeheathermkohnBelum ada peringkat
- 2.4-2.5 Review WorksheetDokumen4 halaman2.4-2.5 Review WorksheetkcarveyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 NotesDokumen17 halamanChapter 2 Notessesirekha@gmail.comBelum ada peringkat
- 2019-04-01 Clothesline Math - LogarithmsDokumen12 halaman2019-04-01 Clothesline Math - Logarithmssamjshah0% (1)
- 2018 05 02 Velocity GraphsDokumen7 halaman2018 05 02 Velocity GraphssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- Polar Graph Contest (2017-2018, Adv. Precalculus)Dokumen48 halamanPolar Graph Contest (2017-2018, Adv. Precalculus)samjshah100% (1)
- 2018-04-19 Geometry and Calculus (Long Block) SolutionsDokumen5 halaman2018-04-19 Geometry and Calculus (Long Block) SolutionssamjshahBelum ada peringkat
- François Roche - R&Sie (N) ArchitectsDokumen14 halamanFrançois Roche - R&Sie (N) ArchitectsEmersonAagaardBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Unijunction Transistor (UJT)Dokumen6 halamanWhat Is Unijunction Transistor (UJT)khan yousafzaiBelum ada peringkat
- UCLA - What Statistical Analysis Should I Use - SPSSDokumen54 halamanUCLA - What Statistical Analysis Should I Use - SPSSmllabateBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Image Import, Processing, and Export - MATLAB & Simulink - MathWorks IndiaDokumen5 halamanBasic Image Import, Processing, and Export - MATLAB & Simulink - MathWorks Indiarajivsharma1610Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson 17-Optimization Problems (Maxima and Minima Problems)Dokumen18 halamanLesson 17-Optimization Problems (Maxima and Minima Problems)Jhonnel CapuleBelum ada peringkat
- Thayer Cyber Hacking in Southeast Asia BibliographyDokumen2 halamanThayer Cyber Hacking in Southeast Asia BibliographyCarlyle Alan ThayerBelum ada peringkat
- Cybercrime Tactics and Techniques: Q3 2018: Provided byDokumen27 halamanCybercrime Tactics and Techniques: Q3 2018: Provided byAndres Felipe CameroBelum ada peringkat
- CH 06Dokumen106 halamanCH 06Ray Vega LugoBelum ada peringkat
- 02-Ax 2012 Admin Wkshp-Installation and ConfigurationDokumen59 halaman02-Ax 2012 Admin Wkshp-Installation and Configurationمحمد زكريBelum ada peringkat
- BineshDokumen32 halamanBineshBINESHBelum ada peringkat
- Apply File Io Operation in JavaDokumen18 halamanApply File Io Operation in JavaEdwin LapatBelum ada peringkat
- Homology Modeling: Ref: Structural Bioinformatics, P.E Bourne Molecular Modeling, FolkersDokumen16 halamanHomology Modeling: Ref: Structural Bioinformatics, P.E Bourne Molecular Modeling, FolkersPallavi VermaBelum ada peringkat
- Mukesh Dubey Resume June 2019Dokumen2 halamanMukesh Dubey Resume June 2019Mukesh DubeyBelum ada peringkat
- Fortune - Tafadzwa - Madzivo - Infrastructure & Cyber Security OfficerDokumen4 halamanFortune - Tafadzwa - Madzivo - Infrastructure & Cyber Security OfficerFortune Tafadzwa MadzivoBelum ada peringkat
- Durbin LevinsonDokumen7 halamanDurbin LevinsonNguyễn Thành AnBelum ada peringkat
- eS383P Supported OS EDokumen2 halamaneS383P Supported OS EEmad SaadBelum ada peringkat
- Dyna Line, ButtonsDokumen20 halamanDyna Line, Buttonsgus459Belum ada peringkat
- Clicking Clean 2017Dokumen102 halamanClicking Clean 2017dreams24Belum ada peringkat
- Toastmasters 430A Online Meeting Tips PDFDokumen3 halamanToastmasters 430A Online Meeting Tips PDFHrishikesh ChavanBelum ada peringkat
- Load Management Part 2Dokumen8 halamanLoad Management Part 2MaxiSanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Math PyqDokumen4 halamanMath Pyqsangwan2503banitaBelum ada peringkat
- HP Elitebook 820 g1 Notebook PCDokumen178 halamanHP Elitebook 820 g1 Notebook PCRicardo AlfaroBelum ada peringkat
- RDBMS Lab Cycle 2Dokumen3 halamanRDBMS Lab Cycle 2Harsha VardhanBelum ada peringkat
- InstallationDokumen111 halamanInstallationSuma P RBelum ada peringkat
- Applicationpedia - Snipping Tools To Take A Screenshot On WindowsDokumen9 halamanApplicationpedia - Snipping Tools To Take A Screenshot On WindowsOecil KritingzBelum ada peringkat
- Cyberark Defender: Cyberark Cau201 Version DemoDokumen7 halamanCyberark Defender: Cyberark Cau201 Version DemoHakanBelum ada peringkat
- Amateur Photographer - 11 February 2017Dokumen84 halamanAmateur Photographer - 11 February 2017Aruna Premarathne100% (1)
- A Multi-Sphere Scheme For 2D and 3D PackingDokumen5 halamanA Multi-Sphere Scheme For 2D and 3D PackingArs Santosh KumarBelum ada peringkat