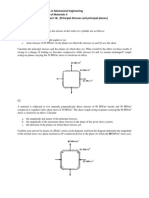
Project
Diunggah oleh
Kiran RockJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Project
Diunggah oleh
Kiran RockHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ABSTRACT:
A foundation is the lowest and supporting layer of a structure.
Shallow foundations Main article: Shallow foundation Shallow foundations, often called footings, are usually embedded about a meter or so into soil. One common type is the spread footing which consists of strips or pads of concrete (or other materials) which extend below the frost line and transfer the weight from walls and columns to the soil or bedrock. Another common type of shallow foundation is the slab-on-grade foundation where the weight of the building is transferred to the soil through concrete slab placed at the surface. Slab-on-grade foundations can be reinforced mat slabs, which range from 25 cm to several meters thick, depending on the size of the building, or post-tensioned slabs, which are typically at least 20 cm for houses, and thicker for heavier structures. Deep foundations Main article: deep foundation A deep foundation is used to transfer the load of a structure down through the upper weak layer of topsoil to the stronger layer of subsoil below. There are different types of deep footings including impact driven piles, drilled shafts, caissons, helical piles, and earth stabilized columns. The naming conventions for different types of footings vary between different engineers. Historically, piles were wood, later steel,reinforced and pre tensioned Monopile foundation Main article: monopole foundation A monopile foundation is a type of deep foundationwhich uses a single, generally largediameter, structural element embedded into the earth to support all the loads (weight, wind, etc.) of a large above-surface structure. A large number of monopile foundations have been utilized in recent years for economically constructing fixed bottom off shore wind forms in shallow-water subsea locations. For example, a single wind form went online in 2008 with over 100 turbines, each mounted on a 4.7-meterdiameter monopile footing in ocean depths up to 18 meters of water. Design: Foundations are designed to have an adequate load capacity with limited settlement by a geotechnical engineer, and the footing itself may be designed structurally by a structural engineer
Inadequate foundations in muddy soils below sea level caused these houses in the Netherlands to subside. The primary design concerns are settlement and bearing capacity. When considering settlement, total settlement and differential settlement is normally considered. Differential settlement is when one part of a foundation settles more than another part. This can cause problems to the structure the foundation is supporting. It is necessary that a foundation not be loaded beyond its bearing capacity or the foundation will "fail".
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Tutorial 1 Properties of MaterialDokumen19 halamanTutorial 1 Properties of MaterialElany WhishawBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Evaluation of Constitutive Soil Models For Predicting Movements Caused by A Deep Excavation in SandDokumen21 halamanEvaluation of Constitutive Soil Models For Predicting Movements Caused by A Deep Excavation in SandAmmar SohailBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Nptel: Design of Offshore Structures - Web CourseDokumen2 halamanNptel: Design of Offshore Structures - Web CourseSumanBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Performance-Based Seismic Design PDFDokumen7 halamanPerformance-Based Seismic Design PDFNicky LimBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering: Suresh R. Dash, L. Govindaraju, Subhamoy BhattacharyaDokumen14 halamanSoil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering: Suresh R. Dash, L. Govindaraju, Subhamoy BhattacharyaKuntal GhoshBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- 220kV Beam - 1Dokumen3 halaman220kV Beam - 1k_arindam1Belum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Set ADokumen12 halamanSet ADan Casurao0% (1)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Behaviour of Sand Confined With Single and Multiple GeocellsDokumen14 halamanBehaviour of Sand Confined With Single and Multiple Geocellssundeep48100% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Extracted Pages From Design of Steel Portal Frames For EuropeDokumen1 halamanExtracted Pages From Design of Steel Portal Frames For EuropeMoussaàb RedaouniaBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Eurocode 2 Part 1,4 - DDENV 1992-1-4-1994 PDFDokumen26 halamanEurocode 2 Part 1,4 - DDENV 1992-1-4-1994 PDFmarineugen0% (1)
- Seismic Analysis of A Reinforced Concrete Building by Response Spectrum MethodDokumen10 halamanSeismic Analysis of A Reinforced Concrete Building by Response Spectrum MethodRahul KumarBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Slab CalculationDokumen18 halamanSlab CalculationREC ALFONSO CINCOBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Deep FoundationsDokumen98 halamanTypes of Deep FoundationsRuli Aprillianto67% (3)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Chapter 11 Rock Support and ReinforcementDokumen35 halamanChapter 11 Rock Support and ReinforcementVu Pham Tien100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- WWW - MINEPORTAL.in: Online Test Series ForDokumen31 halamanWWW - MINEPORTAL.in: Online Test Series ForSheshu BabuBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Tutorial 1B Principal Stresses and PlanesDokumen2 halamanTutorial 1B Principal Stresses and PlanesumarkamranBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Fundamentals of Aircraft Structures: AERO 234Dokumen39 halamanFundamentals of Aircraft Structures: AERO 234roy barmoBelum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- U Seithu Min Edited 2021Dokumen28 halamanU Seithu Min Edited 2021Wint Thu HtunBelum ada peringkat
- Geotecnical FormulaDokumen13 halamanGeotecnical FormulasaitalBelum ada peringkat
- Prestressed Concrete Structures 500 OqaDokumen90 halamanPrestressed Concrete Structures 500 OqasanthiamuthaBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Yield Line Analysis - 1Dokumen19 halamanYield Line Analysis - 1Ahmed NabilBelum ada peringkat
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Bulletin of The New Zealand Society For Earthquake Engineering, Vol. 44, No. 4, December 2011Dokumen15 halamanBulletin of The New Zealand Society For Earthquake Engineering, Vol. 44, No. 4, December 2011atac101Belum ada peringkat
- The Influence of Humidity On The Deformation and Fracture Behaviour of PMMADokumen6 halamanThe Influence of Humidity On The Deformation and Fracture Behaviour of PMMAHoang BuiBelum ada peringkat
- Steel Design Fourth Edition William T Segui Solution Manual 1Dokumen11 halamanSteel Design Fourth Edition William T Segui Solution Manual 1RazaBelum ada peringkat
- Supply and Installation of 5 (SGT 800) Gas Turbine UnitsDokumen3 halamanSupply and Installation of 5 (SGT 800) Gas Turbine UnitssamccoBelum ada peringkat
- SPE 168294 Coiled Tubing Material Selection For Velocity Strings in Sour Brine ServiceDokumen13 halamanSPE 168294 Coiled Tubing Material Selection For Velocity Strings in Sour Brine ServiceJamshed SoomroBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration Analysis of Structure Using Tune Mass DamperDokumen7 halamanVibration Analysis of Structure Using Tune Mass DamperAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Earth Pressure Theories, Effect of Water Table, Layered SoilsDokumen6 halamanEarth Pressure Theories, Effect of Water Table, Layered SoilsRajesh Khadka100% (1)
- CE6102 - 5 - Application of Newton Raphson Techniques To Elasto-Plastic Model With Constant Yield SurfacesDokumen9 halamanCE6102 - 5 - Application of Newton Raphson Techniques To Elasto-Plastic Model With Constant Yield SurfacesandreashendiBelum ada peringkat
- Singly Reinforced BeamDokumen3 halamanSingly Reinforced BeammariyaBelum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)