Hebreo, Arameo, Transliteración
Diunggah oleh
Heriberto MercedesDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Hebreo, Arameo, Transliteración
Diunggah oleh
Heriberto MercedesHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Hebrew Streams
w ww.hebrew-streams.org
Hebrew & Aramaic Transliteration
(Academic & Non-Academic)
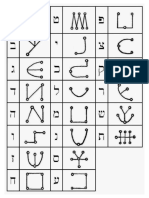
Hebrew Bible (Tanakh or Miqra The Jewish tradition; Old Testament in in Christian tradition) was composed and transmitted in Hebrew, though portions of it are in Aramaic. Hebrew In use from the 2nd millennium B C / E , Hebrew is one of many S(h)emitic languages, a name derived after Shem the son of Noah from whom the majority of peoples speaking these languages were descended (Gen 10:2131). In the 8th cent., it is called the language of Judah (Yehudit, 2 Kgs 18:26) or the language of Canaan (Isa 19:18). It is called Hebrew (Greek, Hebraisti) first in the prologue to Sirach (ca. 130 BC/E). Aramaic Aramaic is related to Hebrew as French is to Italian. It dates back to at least 1,000 BC / E . Its name is taken from the place name Aram, a region known now as Syria and western Iraq. From the 9th or 8th cent. on, Aramaic became the international medium of commerce and diplomacy in the ancient Near East, much as Koin Greek did later in the 4th cent. following Alexander's conquests. In older reference books Aramaic is often called Chaldee or Chaldean, after the ancient Greek name Chaldaios for an area of ancient Babylonia. Biblical Aramaic occurs in four places: (1) two words in Genesis 31:47 (Y e g a r sahadutha); (2) one whole verse in Jeremiah 10:11; (3) two sections in Ezra (4:86:18; 7:1226); and (4) the central portion of Daniel (2:4b7:28). In 2 Kgs 18:26 servants of the Judean king Hezekiah (715-687 BC/E) plead with an Assyrian official not to speak in Hebrew (lit., Judean; Yehudit), but in Aramaic (Aramit), so the common people will not understand. Aramaic words, expressions, and names occur in the Greek New Testament: Ephphatha (Mark 7:34), Gabbatha (John 19:13), Golgotha (Mark 15:22; John 19:17), Marana tha (1 Corinthians 16:22), Rabbouni (Mark 10:51; John 20:16), Siloam (John 9:7); Eloi Eloi lama sabachtani (Matthew 27:46), Talitha cumi (Mark 5:41); Barnabas (Acts 4:36), Kefa or Kephas (=Peter; John 1:42), Tabitha (Acts 9:36, 40). The Pentateuch and portions of the Prophets were translated into Aramaic for Jews who had lost their knowledge of Hebrew. This began perhaps in the second century BC / E , and these paraphrases are called The Targums (translations). The Talmud is bilingual. Its first portion, the Mishnah, exists primarily in Hebrew; the Gemara, or commentary portion on the Mishnah, is mostly Aramaic. This is true for both editions: Babylonian (Bavli; 500 C E / A D ) and Palestinian or Jerusalem (Yerushalmi; 400 CE/AD). Scripts & Samples Over two thousand years ago, the so-called Aramaic Square Script was adopted for Hebrew, so both languages use the same consonant alphabet. Examples of the script from 2,100-year-old fragments from Qumran can be seen at Isaiah 53 at Qumran and The Name at Qumran (PDF). See the transliterated and translated Hebrew texts: Numbers 6:2227; Isaiah 55:811; Psalm 103:814 (PDF). The Tables The following Tables contain two systems of transliteration. Academic Symbols is used by most scholars of Biblical and Ancient Hebrew. The second is called General or Non-Academic. This style is used in nontechnical publications and on this website.
05-10-05
www.hebrew-streams.org
HebrewAramaic Transliteration
Consonants
Hebrew & Aramaic Letter Name
alef beit veit gimel dalet daleth he vav zayin het tet yod kaf, final kaf khaf lamed mem, final mem nun, final nun samekh ayin peh, final peh feh tzaddei, final tzaddei qof resh shin sin tav tav or thav
Sound
silent b v g as in "God" d dh h v z h or ch 2 t y k, kh 3 k l m n s silent p, f f tz or ts as in cats k or q (not qu-) r sh s t
Academic Symbols
1 a b c k 4 t z
1
NonAcademic Symbols
vowel only is voiced b v g d dh h v z h or ch t y k, kh kh l m n s vowel only is voiced p, f f tz or ts k or q r sh s t t or th
)
b b g d d h w z
h9 t[
y k k l m n s
(
p p s[ q r
s] s8
t t
th
/Alef has lost its sound over time. Now only its accompanying vowel is sounded. /Ayin has lost its sound over time. Now only its accompanying vowel is sounded.
2
2 Ch 3 4
as in Lechem, Pesach or Menachemnot as in cherish, choose, church. Kh as in Melekh, Malkhut or Mikhtav (also spelled Melech, Malchut and Michtav).
www.hebrew-streams.org
HebrewAramaic Transliteration
Vowels
Hebrew & Aramaic Vowel Name Sound (American English)
a as in "cat" ah "far" ah eh "met" ei "day" ei ih
"bid"
Academic Symbols
NonAcademic Symbols
a ah ah e ei ei i i i o
patach qametz final qametz he segol tzerei tzerei yod short hiriq
a a4 a4 e e4 e= i i4 i= o o4 o= u u= o] a] e] e]
long hiriq hiriq yod qametz hatuf holem full holem qibbutz shureq hatef qametz hatef patach hatef segol sheva
ee
"bee"
ee oh (in short
unaccented syllable)
oh oh uh full oo fool short "ah" short "a" short "eh" eh or silent
o o u u a a e e or '
Sources
Encyclopdia Judaica (Jerusalem: Keter, 1972), vol. 1, page 90; vol. 8, column 79 Leslie McFall, Hebrew Language, International Standard Bible Encyclopedia (rev. ed., Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1982), 2:65763 Franz Rosenthal, A Grammar of Biblical Aramaic (6th rev. ed., Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag, 1995) SBL [Society of Biblical Literature] Handbook of Style (Peabody, Mass.: Hendrickson, 1999)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The CepherDokumen25 halamanThe CepherPulp Ark74% (222)
- Secrets in The Book of EstherDokumen99 halamanSecrets in The Book of Estherapi-3811809100% (1)
- Yhwh PronouncedDokumen2 halamanYhwh PronouncedRoberto Fortu50% (2)
- Torah 101-Tzav Parsha I. Answers To Study Questions (From Vayikra)Dokumen7 halamanTorah 101-Tzav Parsha I. Answers To Study Questions (From Vayikra)api-204785694100% (1)
- YAH A Name of GodDokumen6 halamanYAH A Name of GodAnselmo ViottiBelum ada peringkat
- (Angelic) MetatronAlphabet - CompleteDokumen15 halaman(Angelic) MetatronAlphabet - CompletePhoenixRising61100% (3)
- Hebrew LettersDokumen14 halamanHebrew Lettersjobster1967100% (2)
- Yichud Hashem: (Unification of The Name of G-D)Dokumen7 halamanYichud Hashem: (Unification of The Name of G-D)liboaninoBelum ada peringkat
- Alefato HebreoDokumen35 halamanAlefato Hebreoqadam guiilenBelum ada peringkat
- The SepherDokumen35 halamanThe SepherRabbi Luis100% (1)
- Brock - Greek Words in Ephrem and NarsaiDokumen11 halamanBrock - Greek Words in Ephrem and NarsaiYIBelum ada peringkat
- Margaret Healy - Shakespeare, Alchemy and The Creative Imagination - The Sonnets and A Lover's Complaint-Cambridge University Press (2011)Dokumen272 halamanMargaret Healy - Shakespeare, Alchemy and The Creative Imagination - The Sonnets and A Lover's Complaint-Cambridge University Press (2011)Renata BragaBelum ada peringkat
- The Lion and The Lamb in Revelation 5Dokumen10 halamanThe Lion and The Lamb in Revelation 5Ertis CeleghiniBelum ada peringkat
- Hebrew in Irish GlossariesDokumen21 halamanHebrew in Irish GlossariesPMBelum ada peringkat
- Hebrew AlphabetDokumen24 halamanHebrew Alphabetdzimmer6Belum ada peringkat
- Puns, Paronomasia, and Word-Play in The Book of MormonDokumen30 halamanPuns, Paronomasia, and Word-Play in The Book of MormonRobert F. Smith100% (1)
- Hebrew VowelsDokumen271 halamanHebrew VowelsHaileleul KassaBelum ada peringkat
- Hebrew Phrasebook - WikitravelDokumen15 halamanHebrew Phrasebook - WikitravelThomas St100% (2)
- Ancient Hebrew MorphologyDokumen22 halamanAncient Hebrew Morphologykamaur82100% (1)
- The Evidence of Perfect and Imperfect PentagramsDokumen47 halamanThe Evidence of Perfect and Imperfect PentagramsRichter, JoannesBelum ada peringkat
- African Origins of The Hebrews by NTR NB Akhu ZP TpyDokumen6 halamanAfrican Origins of The Hebrews by NTR NB Akhu ZP TpyNetjer Neb KD Hartley-elBelum ada peringkat
- A Short Guide to the Pronunciation of New Testament GreekDari EverandA Short Guide to the Pronunciation of New Testament GreekBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Aramaic - John HuehnergardDokumen12 halamanWhat Is Aramaic - John HuehnergardideboerBelum ada peringkat
- Middle East Pbook 1 Hebrew - v1 - m56577569830512329Dokumen16 halamanMiddle East Pbook 1 Hebrew - v1 - m56577569830512329Arabic LanguageBelum ada peringkat
- Hebrew, Aramaic Origins of The New TestamentDokumen7 halamanHebrew, Aramaic Origins of The New TestamentMarius MarioBelum ada peringkat
- Francis Bacon - Critical and Theoretical Perspectives (PDFDrive)Dokumen217 halamanFrancis Bacon - Critical and Theoretical Perspectives (PDFDrive)Markizz10Belum ada peringkat
- Introducing Translating Studies. Brief Chapter 1 To 5.Dokumen28 halamanIntroducing Translating Studies. Brief Chapter 1 To 5.Volando Voy100% (13)
- A Is for Abandon: An English to Biblical Hebrew Alphabet BookDari EverandA Is for Abandon: An English to Biblical Hebrew Alphabet BookBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Why MarYah Is The Aramaic Name For YHWHDokumen16 halamanUnderstanding Why MarYah Is The Aramaic Name For YHWHVineyard StalinBelum ada peringkat
- Mishnaic HebrewDokumen4 halamanMishnaic Hebrewdzimmer6Belum ada peringkat
- What Is The Family Doing 9776Dokumen1 halamanWhat Is The Family Doing 9776MELINA DAYANA CALIZAYA TORRES60% (5)
- Manipravalam-Kesavan V PDFDokumen35 halamanManipravalam-Kesavan V PDFSri Nath100% (1)
- Hebrew and Aramaic As Languages of The ZoharDokumen19 halamanHebrew and Aramaic As Languages of The ZoharErnestoMilotiBelum ada peringkat
- Hebrew New TestamentDokumen14 halamanHebrew New TestamentDavid MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- LiteratureDokumen24 halamanLiteratureJeanette Agpoon AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- The Aramaic Maranatha in 1 Cor 16 22. TRDokumen12 halamanThe Aramaic Maranatha in 1 Cor 16 22. TRartaxerxulBelum ada peringkat
- Urim and Thummim - SandersDokumen24 halamanUrim and Thummim - SandersRaymond de HoopBelum ada peringkat
- Segal An Essay On Euripidean ComedyDokumen10 halamanSegal An Essay On Euripidean ComedyStefano CeccarelliBelum ada peringkat
- Encyclopedia Judaica SvAramaicDokumen35 halamanEncyclopedia Judaica SvAramaicJordan PickettBelum ada peringkat
- WALKER, L. L. Language of AmosDokumen13 halamanWALKER, L. L. Language of AmosFilipe AraújoBelum ada peringkat
- Baruch HaShem - The Pronunciation of YHVHDokumen7 halamanBaruch HaShem - The Pronunciation of YHVHPiet Janse van RensburgBelum ada peringkat
- 2021Dokumen15 halaman2021xdboy2006Belum ada peringkat
- Above Torah: What the New Testament Truly Reveals about "the Law"Dari EverandAbove Torah: What the New Testament Truly Reveals about "the Law"Belum ada peringkat
- Aramaic Idiom and The Son of Man Problem: A Response To Owen and ShepherdDokumen30 halamanAramaic Idiom and The Son of Man Problem: A Response To Owen and ShepherdOlestar 2023-06-22Belum ada peringkat
- A Translation of and Comparison of The Hebrew and Old Greek of Psalms 1-18, Including Other Greek Translations of Psalm 18 by David Bruce GainDokumen17 halamanA Translation of and Comparison of The Hebrew and Old Greek of Psalms 1-18, Including Other Greek Translations of Psalm 18 by David Bruce GainDavid Bruce GainBelum ada peringkat
- Abbreviations SAHDDokumen25 halamanAbbreviations SAHDKlaas SpronkBelum ada peringkat
- On Dual Narratives in The Haggadah: "Davar Acher"Dokumen9 halamanOn Dual Narratives in The Haggadah: "Davar Acher"outdash2Belum ada peringkat
- 1975 Nidntt CryDokumen3 halaman1975 Nidntt Crycatalin barascuBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching English To Hebrew Speakers: IdiomsDokumen4 halamanTeaching English To Hebrew Speakers: Idiomsisrael_cohen_3Belum ada peringkat
- The Hebrew Root: (RomaDokumen18 halamanThe Hebrew Root: (RomaAngela NatelBelum ada peringkat
- MGLHDokumen5 halamanMGLHKlaas SpronkBelum ada peringkat
- Israel EtymologyDokumen3 halamanIsrael Etymologyisrael_cohen_3Belum ada peringkat
- Torah 101-Yitro Parsha I. Answers To Study Questions (Beshallach)Dokumen5 halamanTorah 101-Yitro Parsha I. Answers To Study Questions (Beshallach)api-204785694Belum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen4 halamanUntitledoutdash2Belum ada peringkat
- The So-Called Ostrich in The God Speeches of The Book of Job (Job 39,13-18)Dokumen17 halamanThe So-Called Ostrich in The God Speeches of The Book of Job (Job 39,13-18)aminBelum ada peringkat
- Kasher and Klien TargumDokumen37 halamanKasher and Klien TargumdavidednmBelum ada peringkat
- Rah - StöklDokumen5 halamanRah - StöklTabitha van KrimpenBelum ada peringkat
- KLW Paraq V Davies Cam 2011Dokumen10 halamanKLW Paraq V Davies Cam 2011Klaas SpronkBelum ada peringkat
- A Grammatical Overview of Egyptian and CDokumen34 halamanA Grammatical Overview of Egyptian and CJoão FerrãoBelum ada peringkat
- 34 Genre Without A Name (JJS)Dokumen11 halaman34 Genre Without A Name (JJS)leeBelum ada peringkat
- D .Weissert. 1973. "Alexandrian Analogical Word-Analysis and Septuagint Translation Techniques." Textus, 8, Pp. 31-44.Dokumen22 halamanD .Weissert. 1973. "Alexandrian Analogical Word-Analysis and Septuagint Translation Techniques." Textus, 8, Pp. 31-44.héctor ortegaBelum ada peringkat
- The Old Persian FontDokumen5 halamanThe Old Persian FontGB GilmerBelum ada peringkat
- 21-Aramaic and Iraqi Arabic Aku Maku The Mesopotamian Particles of ExistenceDokumen7 halaman21-Aramaic and Iraqi Arabic Aku Maku The Mesopotamian Particles of ExistenceQmanQBelum ada peringkat
- Biblical Hebrew EMagazine 087Dokumen7 halamanBiblical Hebrew EMagazine 087José PrietoBelum ada peringkat
- Modern Hebrew: Philip Zhakevich and Benjamin KantorDokumen40 halamanModern Hebrew: Philip Zhakevich and Benjamin KantorVicente AlmelaBelum ada peringkat
- NT GreekDokumen141 halamanNT GreekOmid DjalaliBelum ada peringkat
- U3230366 11388 Grammar-EssayDokumen13 halamanU3230366 11388 Grammar-EssayMỹ Linh TrầnBelum ada peringkat
- Creative Writing7 Q2WK8Dokumen6 halamanCreative Writing7 Q2WK8StarlyhtBelum ada peringkat
- Nirmal VermaDokumen8 halamanNirmal Vermagalena.tsvetkovaBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Exercise On Tenses Put The Verbs in Brackets Into Their Correct TensesDokumen3 halamanPractice Exercise On Tenses Put The Verbs in Brackets Into Their Correct TensesTrần Minh SơnBelum ada peringkat
- Azccrs StandardsDokumen41 halamanAzccrs Standardsapi-293876096Belum ada peringkat
- Tales of Demons and Gods 1-109Dokumen930 halamanTales of Demons and Gods 1-109Chan Weigang100% (1)
- Edge of Night - CommentsDokumen5 halamanEdge of Night - Commentsfrangelo85Belum ada peringkat
- Immortal HeroesDokumen21 halamanImmortal HeroesElsie Joy LicarteBelum ada peringkat
- Lyric Sheet: 2020 - Page 1Dokumen2 halamanLyric Sheet: 2020 - Page 1XplciitBelum ada peringkat
- Microsoft Word - Romanticism 19th Century Research Paper P CraneDokumen12 halamanMicrosoft Word - Romanticism 19th Century Research Paper P CranepdcraneBelum ada peringkat
- Forever by His Side 1981 HenryDokumen7 halamanForever by His Side 1981 HenryMathura DasBelum ada peringkat
- The Unknown Citizen OutlineDokumen3 halamanThe Unknown Citizen Outlineapi-265616030Belum ada peringkat
- Life of PiDokumen4 halamanLife of PiAswin P KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Writing Programme Notes: A Guide For Diploma CandidatesDokumen16 halamanWriting Programme Notes: A Guide For Diploma Candidatesapi-312140386Belum ada peringkat
- 19PHD0055 Internal Full Time Department of English School of Social Science and Languages Vellore Institute of Technology VELLORE-632007Dokumen14 halaman19PHD0055 Internal Full Time Department of English School of Social Science and Languages Vellore Institute of Technology VELLORE-632007ManojBelum ada peringkat
- Sar CheviDokumen8 halamanSar Cheviliza buskhrikidzeBelum ada peringkat
- Forms of PoetryDokumen47 halamanForms of Poetrymark johnBelum ada peringkat
- El Escape de Hitler. Patrick BurnsideDokumen7 halamanEl Escape de Hitler. Patrick Burnsidetincho1980Belum ada peringkat
- Canterville Ghost - Oscar WildeDokumen5 halamanCanterville Ghost - Oscar WildeMelvin HumperdinckBelum ada peringkat
- Share QUIZ 1-50 LONG QUIZDokumen2 halamanShare QUIZ 1-50 LONG QUIZAngelineBelum ada peringkat
- Atma Shatkam - 1 Page, IAST, DevanagariDokumen4 halamanAtma Shatkam - 1 Page, IAST, DevanagariWill Wannamaker100% (1)
- Noli Me Tangere - A Diagnosis of Filipino SocietyDokumen1 halamanNoli Me Tangere - A Diagnosis of Filipino SocietyTrina HemedezBelum ada peringkat
- Snow White and The 7 DwarvesDokumen3 halamanSnow White and The 7 DwarvesApril Ann MarabilesBelum ada peringkat