New Text Document
Diunggah oleh
jamesearl_cubillasDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
New Text Document
Diunggah oleh
jamesearl_cubillasHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
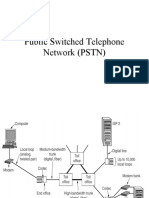
1. a signal which varies between three levels ; bipolar code ;. 2.
its is used to connect computers in the same building or in same area; LAN ;. 3. Digital transmission provided a higher level of signal quality than analog tr ansmission because; repeaters regenerate digital pulses and remove distortion ;. 4. which of the following is not a baseband signal for modulation? ; RF carrier ;. 5.which of the following can be used to demodulate a PAM signal? ; low pass filt er;. 6. A modulation process in which a train of fixed-width pulses is transmitted wh ose polarity indicates whether the demodulator output should rise or fall at eac h pulse ; DM (delta Modulation); 7.a blank system involves switching the carrier wave between two frequencies; FS K;. 8. the simpllankest form of error detection is ; parity;. 9. when a block of data is transmitted, and if no error is detected, a ; is sent back to the transmitter.; A C K;. 10. what do you call the technique that allows correction of data of the receive r?; F E C ;. 11. a PCM transmission requires blank bandwidth than AM transmission; more;. 12. according to the nyquist theorem, the sampling rate that can be used in a pc m system is blank the highest audio frequency; twice;. 13. error checking is accomplished by using blank in computer telephone communic ations; parity;. 14. digital signals; do notprovide a continous set of values, present values as discrete steps, can utilized decimal or binary systems, all of the above;. 15. the event which marked the start of the modern computer age was; development of transistor;. 16. the baud rate; is equal to twice the bandwidth of an ideal channel;. 17. the shannon hartley law; refers to noise;. 18. the code which provides parity check is; ASCII;. 19.forward error correcting code corrects errors by; requiring no part of the si gnal to be retransmitted;. 20. full duplex operation; requires two pairs of cable, can transfer data in bot h directions at once, requires modems at both ends of the circuit, all of the ab ove;. 21. the rs-232 interface; interconnects data sets and transmission circuits;. 22. switching systems; are limited to small data networks;. 23. the data transmission rate of modem is measured in; bits per second;. 24. indicate which of the following is not binary code; morse;. 25. to permit the selection of 1 out of 16 equiprobable events, the number of bi ts required is; 4;. 26. A signal system in which each letter alphabet is represented by a different symbol is not because; noise would introduce too many errors;. 27. the hartley law states that ; the maximum rate of information depends on the channel bandwith;. 28.indicate the false statement. In order to combat noise,; the channel bandwith may be increased;. 29. the most common modulation system used for telegraphy is; frequency shift ke ying;. 30. pulse width modulation may be generated; with mono stable multi-vibrator;. 31. indicate which of the following system is digital? ; pulse code modulation;. 32. quantizing noise occurs in; pulse code modulation;. 33. the modulation system inherently most noise resistant is; pulse code modulat ion;. 34. in order to reduce quantizing noise, one must ; increase the number of stand ard amplitudes;. 35. the hartley shannontheorems sets a limit on the ; maximum capacity of a chan nel with a given noise level;. 36. indicate which of the following pulse modulation system is analog; PWM;. 37. companding is used; to protect small signals in PCM from quantizing distorti
on;. 38. a blank interconnects LAN having identical protocols at the physical and dat a link layers; bridge;. 39. digitizing signal can reduce; distortion;. 40. a digital signal can be changed from a 1 to a 0 by blank; noise;. 41. a regenerative blank converts a degraded pulse into new pulse; repeater;. 42. which of the following multiplexing scheme is easy to implement with digital signals; TDM;. 43. what limits the bandwidth of the channel? ; digital data rate;. 44. which of the following does limit the digital data rate of the channel? ; tr ansmission rate;. 45. the blank equation describes how to obtain ultimate limit for transmission;. 46. digital data can be sent through a channel no matter how low the SNR is, as long as it is not ; Zero;. 47. blank signals must be sampled before they can be sent in digital form. ; ana log;. 48. the blank is equal to half the highest frequency component of analog signal. ; nyquist rate;. 49. aliasing occurs when the sampling rate is. ; too low;. 50. what distortion occurs when the sampling rate is too low? foldover distortio n;. 51. what is the output of a sampler? ; PAM signal;. 52. which of the following is commonly used digital transmssion scheme? ; PCM;. 53. what is the conversion of analog signal sample to a binary number? ; samplin g;. 54. it allows improved dynamic range for a given bandwidth. ; companding;. 55. the companding system used in america is known as ; mu- law companding ;. 56.a type of digital modulation which has only one bit transmitted per cycle. ; Delta Modulation;. 57. the first digital code was the. ; morse code;. 58. in digital transmission, signal degradation can be removed using: ; regenera tive repeater;. 59.Natural sampling does not use: ; a sampling and hold circuit;. 60.which is true about aliasing and foldover distortion? ; they are the same thi ng;. 61. foldover distortion is caused by: ; too few samples per second;. 62. the immediate result of sampling is. ; PAM;. 63. which of the following is considered analog in nature? ; PDM;. 64. pulse time modulation (PTM) is another form of. ; PPM;. 65. a vocoder implements compression by: ; constructing a model of the human voc al system;. 66. manchester coding: ; is a biphase code, has a level transition in the middle of every bit period , provides strong timing information, all of the choices;. 67. which coding scheme requires DC continuity?. ; unipolar NRZ;. 68. compared to PCM, adaptive delta modulation can transmit voice: ; within love r bit rate but the same quality;. 69. in delta modulation, " garnular noise" is produced when: ; the signal does n ot change;. 70. in europe, companding uses: ; the A-Law;. 71. in north america, companding uses: ; the mu-law;. 72.another name for multiplier circuit is. ; balanced modulator;. 73. modems are required to connect computers to telephone lines because. ; the t elephone network will not pass direct current;. 74. the data transmission rate of the modem is measured in.; baud rate;. 75. the word "keying" is still used to denote. ; digital modulation;. 76. which of the following is rarely used for digital communications? ; A S K;. 77. inforamtion capacity is proportional to. ; bandwidth;. 78.a" mark" is . ; a binary one;. 79.which of the following. does not makes efficient use of available bandwidth? ; FSK;.
80. which of the follwong is used extensively in high-frequency radioteletype tr ansmission? ; FSK;. 81. digital amplitude modulation is called. ; QPSK;. 82. QAM uses. ; FM;. 83. what shows the "symbols" used in QAM?. ; phasor diagram constellation diagra m, constellation diagram, truth table, all of the choices;. 84. what is the maximum speed you can get from a telephone line modem? ; 54 kbps ;. 85. DSL carries blank speed data over twisted pair telephone wire ; High;. 86. GMSK means. ; gaussian minimum shift keying;. 87. FSK stands for. ; frequency shift keying;. 88. what is a special case of fsk that achieves the minimum bandwidth possible f or a two frequency FSK system at a given data rate. ; GMSK;. 89. use an audio tone of two or more different frequencies to modulate a convent ional analog transmitterfor data transmission. ; Audio Frequency Shift Keying ( A FSK);. 90. CAP modulkation is avariant of QAM used with ADSL data communication systems . what does CAP mean?. ; carrierless Amplitude phase.. 91. digital modulation scheme that represents a bit pattern by a change in phase from the previous phase. ; delata phase shift keying.. 92. DMT modulation is a modulation scheme for ADSL data communication systems th at uses many carriers at different frequencies, each modulated using QAM. what d oes DMT mean? ; Discrete Multi-tone;. 93. an acronym for modulaot-demodulator, and commonly a device used to enable da ta to be transmitted via an analog channel. ; modem;. 94. a cable used to make a direct connection between two devices usimng thier se rial ports. ; Null modem;. 95. what parameters of a sine-wave carrier can be modulated? ; amplitude, freque ncy, phase, all of the choices;. 96. what signal parameters are varied with QAM? ; amplitude and phase;. 97. why is QAM used more in fixed than in mobile radio systems? ; it requires a high signal-to-noise ratio;. 98. the word gaussian in GMSK refers to. ; shape of a filter that is used before the modulator to reduce the transmiited bandwidth of the signal;.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- CNS-ST3.1Dokumen17 halamanCNS-ST3.1Achilles AldaveBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ in EST by Melvin C. Arceo of PERC DCDokumen35 halamanMCQ in EST by Melvin C. Arceo of PERC DCLocrian IonianBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Analysis of Modulation Techniques in MIMO Rician Channel For WCDMA SystemDokumen4 halamanPerformance Analysis of Modulation Techniques in MIMO Rician Channel For WCDMA SystemIJERDBelum ada peringkat
- Glosario de TCSDokumen4 halamanGlosario de TCSMatias WolfBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Modulation Techniques / MultiplexingDokumen3 halamanDigital Modulation Techniques / MultiplexingYzza Veah Esquivel100% (2)
- Pulse-Code Modulation (PCM) Is A Method Used ToDokumen8 halamanPulse-Code Modulation (PCM) Is A Method Used ToMwesigye KennethBelum ada peringkat
- Data and CommunicationDokumen26 halamanData and CommunicationTahajan M. HadjirulBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 4Dokumen3 halamanAssignment 4Sonal HarshBelum ada peringkat
- Fpga Implementation of Direct Sequence Spread SpectrumDokumen29 halamanFpga Implementation of Direct Sequence Spread SpectrumThirumal ArunBelum ada peringkat
- DRFM Basic PaperDokumen7 halamanDRFM Basic PaperAjinkya Kale100% (1)
- Introduction To Cdma: Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Is A Radically New Concept in WirelessDokumen24 halamanIntroduction To Cdma: Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Is A Radically New Concept in WirelessMohamed Abdel MonemBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Umts Cdma TechDokumen3 halaman5 Umts Cdma TechDiwakar MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Transmittal of Digitally Modulated and Called Digital RadioDokumen1 halamanTransmittal of Digitally Modulated and Called Digital RadiozesleyBelum ada peringkat
- Ilovepdf Merged 2Dokumen150 halamanIlovepdf Merged 2lavadiajhonBelum ada peringkat
- Modemi: (PSTN - Public Snjitched Telephone Netnjork)Dokumen10 halamanModemi: (PSTN - Public Snjitched Telephone Netnjork)Бранислав ЛукићBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Spread Spectrum CommunicationsDokumen20 halamanIntroduction To Spread Spectrum CommunicationsSriramBelum ada peringkat
- Delta Modulation For Voice Transmission: Application Note January 1997 AN607.1Dokumen6 halamanDelta Modulation For Voice Transmission: Application Note January 1997 AN607.1Mac AnciadoBelum ada peringkat
- Answers To NetworkingDokumen6 halamanAnswers To Networkingmohamed turayBelum ada peringkat
- CDMA TechnologyDokumen40 halamanCDMA TechnologyMohammed AatifBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Iii - Part-A: Course Material (Question Bank)Dokumen5 halamanUnit Iii - Part-A: Course Material (Question Bank)Saravana KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Enhancement Techniques in Recent Cdma TechnologyDokumen8 halamanEnhancement Techniques in Recent Cdma TechnologyPrashanth KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Telemetry Assignment: Submitted By: Singh Kushagra Harilal Ei-H 0909732109Dokumen47 halamanTelemetry Assignment: Submitted By: Singh Kushagra Harilal Ei-H 0909732109Shashank SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- Final CdmaDokumen61 halamanFinal Cdma777srisri777Belum ada peringkat
- Modem: What Is A Modem? Types of Modems: Modulator ConvertsDokumen7 halamanModem: What Is A Modem? Types of Modems: Modulator ConvertsthiruBelum ada peringkat
- Data Comm. & NetworkDokumen139 halamanData Comm. & NetworkAkash SachanBelum ada peringkat
- Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)Dokumen60 halamanPublic Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)sainimandyBelum ada peringkat
- Term Paper On CDMADokumen5 halamanTerm Paper On CDMATaufeeq Malik100% (1)
- Introduction To Digital CommunicationsDokumen12 halamanIntroduction To Digital CommunicationsYashwanthReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Data Communication EquipmentDokumen6 halamanData Communication EquipmentCarlo Guzon100% (1)
- What Are LAPD and LAPD ?: Time Diversity Is Used in Digital Communication Systems To Combat That The TransmissionsDokumen8 halamanWhat Are LAPD and LAPD ?: Time Diversity Is Used in Digital Communication Systems To Combat That The TransmissionsVikas MishraBelum ada peringkat
- FM Tranciever AppsDokumen7 halamanFM Tranciever Appsinsomnium86Belum ada peringkat
- PCM, PDH and SDHDokumen58 halamanPCM, PDH and SDHAbdul Wahab67% (3)
- ReviewerDokumen7 halamanReviewerMELANIE LLONABelum ada peringkat
- 3G Overview 2Dokumen298 halaman3G Overview 2sharadrajputanaBelum ada peringkat
- DC Lab ManualDokumen24 halamanDC Lab Manualvidyae100% (2)
- WC-Lect 10 Thu 16 April Part 2Dokumen10 halamanWC-Lect 10 Thu 16 April Part 2Fahad MehmoodBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 5Dokumen23 halamanLec 5Altayeb Ibn AbdulhameedBelum ada peringkat
- ECE - Modems in Data CommunicationDokumen7 halamanECE - Modems in Data CommunicationLLoydDomingoMandocdocBelum ada peringkat
- Cacho, Kathleen Joy C. (Digital Communication SFE Portfolio)Dokumen14 halamanCacho, Kathleen Joy C. (Digital Communication SFE Portfolio)KATHLEEN JOY CACHOBelum ada peringkat
- ESTDokumen11 halamanESTAnthonette PajanoyBelum ada peringkat
- CDMA (IS-95,99) : CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access)Dokumen4 halamanCDMA (IS-95,99) : CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access)Pk_erkaBelum ada peringkat
- 388 Wireless TechnologyDokumen44 halaman388 Wireless TechnologySyed Ali Irfan JaffriBelum ada peringkat
- Ee4105 Wcdma NewDokumen105 halamanEe4105 Wcdma NewJeffGan LkBelum ada peringkat
- ST2153 & ST2154Dokumen53 halamanST2153 & ST2154Pratap SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Data Communications 2 ReviewerDokumen6 halamanData Communications 2 ReviewerRechie VallenteBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Simulation Parameters of Pulse Shaping FIR Filter For WCDMADokumen16 halamanAnalysis of Simulation Parameters of Pulse Shaping FIR Filter For WCDMAavnishBelum ada peringkat
- Code Division Multiple AccessDokumen8 halamanCode Division Multiple AccessDwarak ChaluvadiBelum ada peringkat
- Subcarrier MultiplexingDokumen21 halamanSubcarrier MultiplexingSantosh Kumar100% (1)
- Data and Computer CommunicationsDokumen45 halamanData and Computer Communicationswferry27Belum ada peringkat
- Digital Communication Chapter 11Dokumen5 halamanDigital Communication Chapter 11MIsh GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Design Low Power Physical Layer of NB-IOT LTE Uplink ReceiverDokumen17 halamanDesign Low Power Physical Layer of NB-IOT LTE Uplink Receiversadsadasdsad asdasdaBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Transmission, Multiplexing and T-CarriersDokumen33 halamanDigital Transmission, Multiplexing and T-CarriersMukesh100% (5)
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversDari EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessDari EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2)
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandDari EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandBelum ada peringkat
- Awarded Hydropower 2016-03-31 Grid PDFDokumen43 halamanAwarded Hydropower 2016-03-31 Grid PDFjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Acoustic Communication by Ants: The Journal of The Acoustical Society of America November 2000Dokumen11 halamanAnalysis of Acoustic Communication by Ants: The Journal of The Acoustical Society of America November 2000jamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- Brochure Ecodial-EnDokumen4 halamanBrochure Ecodial-EnMostafa AliBelum ada peringkat
- CSU QC Carmen MangrovesDokumen8 halamanCSU QC Carmen Mangrovesjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- Data 2013 ReviewDokumen8 halamanData 2013 Reviewjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- Enhanced Production and Risk Management in Agriculture (Eprima) Decision Support SystemDokumen26 halamanEnhanced Production and Risk Management in Agriculture (Eprima) Decision Support Systemjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- Narrative Report For Upd Parmap Processing Surigao Del Norte Block 65CdDokumen25 halamanNarrative Report For Upd Parmap Processing Surigao Del Norte Block 65Cdjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- BerkeleyDokumen2 halamanBerkeleysandollarcardBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Acoustic Communication by Ants: The Journal of The Acoustical Society of America November 2000Dokumen11 halamanAnalysis of Acoustic Communication by Ants: The Journal of The Acoustical Society of America November 2000jamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- Sensors: A Qualitative Comparison of Different Logical Topologies For Wireless Sensor NetworksDokumen27 halamanSensors: A Qualitative Comparison of Different Logical Topologies For Wireless Sensor Networksjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S1364815217302384 MainDokumen13 halaman1 s2.0 S1364815217302384 Mainjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- Pcieerd Ar 2016Dokumen82 halamanPcieerd Ar 2016jamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S1364815217302384 MainDokumen13 halaman1 s2.0 S1364815217302384 Mainjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- Specifcations & ApplicationsDokumen15 halamanSpecifcations & Applicationsjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- 8Dokumen4 halaman8jamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- Specifcations & ApplicationsDokumen15 halamanSpecifcations & Applicationsjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- Warping Survey Plans For Visual RepresentationDokumen25 halamanWarping Survey Plans For Visual Representationjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- FWUAV - Checklist of ProceduresDokumen1 halamanFWUAV - Checklist of Proceduresjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- B4304Dokumen9 halamanB4304jamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- Warping FLA Survey Plans For Visual RepresentationDokumen33 halamanWarping FLA Survey Plans For Visual Representationjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- DroneMapper Instructions PDFDokumen20 halamanDroneMapper Instructions PDFjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- 96sep PoorDokumen75 halaman96sep Poorjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- UAS Flight School TrainingDokumen3 halamanUAS Flight School Trainingjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- HCF4094B: 8 Stage Shift and Store Bus Register With 3-State OutputsDokumen13 halamanHCF4094B: 8 Stage Shift and Store Bus Register With 3-State Outputsjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- Dear Bosses and PNP StaffDokumen1 halamanDear Bosses and PNP Staffjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- My Final AlgoDokumen2 halamanMy Final Algojamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- FILELISTDokumen7 halamanFILELISTjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- FILELISTDokumen7 halamanFILELISTjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3television CamerasDokumen18 halamanChapter 3television Camerasjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- 3000 RPMDokumen2 halaman3000 RPMjamesearl_cubillasBelum ada peringkat
- ODA X9 2SL DatasheetDokumen8 halamanODA X9 2SL DatasheetYudy UtamaBelum ada peringkat
- A Tired BrainDokumen3 halamanA Tired BrainSivasonBelum ada peringkat
- 09.tracheostomy Management by Speech Language Pathologists in SwedenDokumen12 halaman09.tracheostomy Management by Speech Language Pathologists in SwedenCarlonchaCáceresBelum ada peringkat
- Upaam 1135891 202105060749199700Dokumen18 halamanUpaam 1135891 202105060749199700Kartik KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Ecotopia Remixed II-FormattedDokumen54 halamanEcotopia Remixed II-FormattedthisisdarrenBelum ada peringkat
- Fret Position Calculator - StewmacDokumen1 halamanFret Position Calculator - StewmacJuan Pablo Sepulveda SierraBelum ada peringkat
- (Eng) Zx890lch 5a Ks En316Dokumen13 halaman(Eng) Zx890lch 5a Ks En316MC TAK LEEBelum ada peringkat
- Ask A Monk EnlightenmentDokumen16 halamanAsk A Monk EnlightenmentPetruoka EdmundasBelum ada peringkat
- Statistics and Probability Module 3Dokumen3 halamanStatistics and Probability Module 3Eftychia LeegleeBelum ada peringkat
- Iron Ore ProcessDokumen52 halamanIron Ore Processjafary448067% (3)
- E-OLSS: Electronic ControlDokumen12 halamanE-OLSS: Electronic ControlSamidiBelum ada peringkat
- Case StudyDokumen61 halamanCase StudyA GBelum ada peringkat
- Apcotide 1000 pc2782Dokumen1 halamanApcotide 1000 pc2782hellmanyaBelum ada peringkat
- 1ST SUMMATIVE TEST FOR G10finalDokumen2 halaman1ST SUMMATIVE TEST FOR G10finalcherish austriaBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise 9 Two Factor Factorial Experiments and Derivation of Expected Mean SquaresDokumen14 halamanExercise 9 Two Factor Factorial Experiments and Derivation of Expected Mean SquaresHasmaye PintoBelum ada peringkat
- Spectroscopy (L-26 To 29)Dokumen81 halamanSpectroscopy (L-26 To 29)Vashistha GargBelum ada peringkat
- Siprotec 7ut82 ProfileDokumen2 halamanSiprotec 7ut82 ProfileOliver Atahuichi TorrezBelum ada peringkat
- 1986 EMT Disruption of Microbial Cells For Intracellular ProductsDokumen11 halaman1986 EMT Disruption of Microbial Cells For Intracellular ProductsLezid CortesBelum ada peringkat
- 9701 w09 QP 21Dokumen12 halaman9701 w09 QP 21Hubbak KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Properties of Matter ReviewDokumen8 halamanProperties of Matter Reviewapi-290100812Belum ada peringkat
- Basses: Pricelist March 2019Dokumen3 halamanBasses: Pricelist March 2019zhaihaijunBelum ada peringkat
- Time Value of Money LectureDokumen54 halamanTime Value of Money LectureRanin, Manilac Melissa SBelum ada peringkat
- Salem RPGDokumen16 halamanSalem RPGabstockingBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Transfer in Cell During Exercise and Oxygen Metabolism and Transport - PalakDokumen85 halamanEnergy Transfer in Cell During Exercise and Oxygen Metabolism and Transport - Palakpalooo4Belum ada peringkat
- Tabel Gsi, RMR, RmiDokumen4 halamanTabel Gsi, RMR, RmiPup BooBelum ada peringkat
- Is 4031 Part 4 - ConsistencyDokumen4 halamanIs 4031 Part 4 - ConsistencyCrypto AbhishekBelum ada peringkat
- Convection Concentric Annulus Vertical Cylinders Filling Porous MediaDokumen17 halamanConvection Concentric Annulus Vertical Cylinders Filling Porous MediakarthikeyanBelum ada peringkat
- LPG GasDokumen39 halamanLPG Gasv prasanthBelum ada peringkat
- Illuminati TruthsDokumen27 halamanIlluminati TruthsDonnaveo ShermanBelum ada peringkat
- Table 1 Minimum Separation DistancesDokumen123 halamanTable 1 Minimum Separation DistancesjhonBelum ada peringkat