U13 Nutrition Vocabulary 111411
Diunggah oleh
pjpooterhootsDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
U13 Nutrition Vocabulary 111411
Diunggah oleh
pjpooterhootsHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Nutrition Vocabulary NUR 101
2011 Prof. A. Fitzgibbon
Nutritive value: the nutrient content of a specified amount of food Ingestion: the act of taking in food or medication Mastication: to chew food Digestion: the conversion of food into absorbable substances in the GI tract; digestion is accomplished through the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into smaller and smaller molecules, with the help of glands located both inside and outside the gut Absorption: the passage of the end products of digestion from the gastrointestinal tract into the blood and lymphatic vessels and the cells of tissues. Absorption of this kind can take place either by diffusion or by active transport Metabolism: the sum of all physical and chemical processes by which a living substance is formed and maintained and by which energy is made available for use by the organism Basal metabolic rate (BMR): the rate of energy utilization in the body required to maintain essential activities such as breathing; the number of calories youd burn over 24 hours while lying down but not sleeping Actual metabolic Rate: estimated by adding the caloric cost of all the activities you engage in throughout the day to your BMR Anabolism: a process in which simple substances are converted by the bodys cells into more complex substances (e.g. building tissue, positive nitrogen balance) Catabolism: a process in which complex substances are broken down into simpler substances (e.g. breakdown of tissue) Caloric Value: the amount of energy that nutrients or foods supply to the body Calorie: a unit of heat energy equivalent to the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1kg of water 1C Food Pyramid: a diagrammatic proportional representation of human nutritional needs updated in 2005 by the U.S. Department of Agriculture to replace the previous food pyramid created in 1992; the "My Pyramid" icon has 6 panels representing grains, vegetables, fruits, milk, meat and beans and fats, sugars, and salts; according to My Pyramid, the majority of servings should come from grains, followed closely by milk, then by vegetables and fruits; meat and beans should be lean and varied; fats, sugars, and salt should be consumed sparingly
Active transport: movement of substances across cell membranes against the concentration gradient Electrolyte: a chemical substance that, when dissolved in water or melted, dissociates into electrically charged particles (ions) and thus is capable of conducting an electric current; the principal positively charged ions in the body fluids (cations) are sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), calcium (Ca2+), and magnesium (Mg2+); the most important negatively charged ions (anions) are chloride (Cl), bicarbonate (HCO3) and phosphate(PO43) Ion: an atom or group of atoms that has acquired an electrical charge through the gain or loss of an electron or electrons Cation: a positively charged ion Anion: a negatively charged ion Diffusion: the mixing of molecules or ions of two or more substances as a result of random motion Osmosis: passage of a solvent through a semipermeable membrane from an area of lesser solute concentration to one of greater solute concentration Hydrostatic Pressure: the pressure a liquid exerts on the side of the container that holds it; also called filtration force
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Elements of HardscapingDokumen57 halamanElements of HardscapingNathar ShaBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Mercedes Benz M272 EngineDokumen28 halamanMercedes Benz M272 EngineJijo Mercy100% (2)
- RAJPUT - Gokul IndustryDokumen76 halamanRAJPUT - Gokul IndustryrajputvjBelum ada peringkat
- Risk Assesment FOR PIPING WORKDokumen1 halamanRisk Assesment FOR PIPING WORKsunil100% (2)
- Booster Mock Test For NEETDokumen15 halamanBooster Mock Test For NEETDrBelum ada peringkat
- Yes Bank FinalDokumen107 halamanYes Bank FinalDrMehul JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- Rangtong Shentong ViewDokumen19 halamanRangtong Shentong Viewlongjim31100% (1)
- Enzymes MCQsDokumen2 halamanEnzymes MCQsNobody's PerfectBelum ada peringkat
- Advent of SkyscrapersDokumen27 halamanAdvent of SkyscrapersJoshua AlboBelum ada peringkat
- Aerial MV Covered Networks: Worth A New Look?: 2. Medium Voltage Overhead Insulated/ Covered LinesDokumen1 halamanAerial MV Covered Networks: Worth A New Look?: 2. Medium Voltage Overhead Insulated/ Covered LinesAnonymous 1AAjd0Belum ada peringkat
- Honda Bikes and ScootersDokumen6 halamanHonda Bikes and ScootersShamrjit AgrahariBelum ada peringkat
- Fuhs - Towards An Integral EpistemologyDokumen39 halamanFuhs - Towards An Integral EpistemologyjmcmichaelBelum ada peringkat
- SAIC N 2023 PreQualTestApplicator&AppProcCastRefract EL Rev2Dokumen3 halamanSAIC N 2023 PreQualTestApplicator&AppProcCastRefract EL Rev2Anonymous S9qBDVkyBelum ada peringkat
- (Complete) BLC 201 Assignment Intro Logistics SCM Sep 2021 - McdonaldDokumen12 halaman(Complete) BLC 201 Assignment Intro Logistics SCM Sep 2021 - McdonaldHf CreationBelum ada peringkat
- Gunny PasteDokumen2 halamanGunny PastejpesBelum ada peringkat
- Catalyst PreparationDokumen15 halamanCatalyst PreparationVISHAL SHARMABelum ada peringkat
- The Guardian Weekly 9-02-2024-2Dokumen64 halamanThe Guardian Weekly 9-02-2024-2krris.galBelum ada peringkat
- User Manual For Emvólio: WWW - Blackfrog.InDokumen22 halamanUser Manual For Emvólio: WWW - Blackfrog.InmariaBelum ada peringkat
- 1mrk508015-Ben B en Auxiliary Signalling and Trippning Relays Rxma 1 Rxma 2 Rxms 1 RXSF 1 Rxme 1 Rxme 18 RXMH 2 RXMDokumen20 halaman1mrk508015-Ben B en Auxiliary Signalling and Trippning Relays Rxma 1 Rxma 2 Rxms 1 RXSF 1 Rxme 1 Rxme 18 RXMH 2 RXMalaa6474794Belum ada peringkat
- International Standard Paper SizesDokumen34 halamanInternational Standard Paper SizesAman KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Nokia 6131 NFCDokumen5 halamanNokia 6131 NFCvetvetBelum ada peringkat
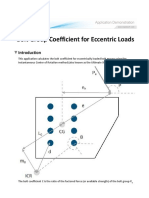
- Bolt Group Coefficient For Eccentric Loads PDFDokumen5 halamanBolt Group Coefficient For Eccentric Loads PDFdvelchevBelum ada peringkat
- Learn Horse Riding: at HPRCDokumen16 halamanLearn Horse Riding: at HPRCAkashBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Welding Defects PDFDokumen12 halamanTypes of Welding Defects PDFDhiab Mohamed AliBelum ada peringkat
- 8 - Precast Concrete Structures-Students PDFDokumen17 halaman8 - Precast Concrete Structures-Students PDFsitehabBelum ada peringkat
- MH2732-Robotics Lab ManualDokumen50 halamanMH2732-Robotics Lab Manualramzi ayadiBelum ada peringkat
- Expansion ScrewsDokumen32 halamanExpansion ScrewsJomar PortadoBelum ada peringkat
- Baluarte BridgeDokumen1 halamanBaluarte BridgeIndra MishraBelum ada peringkat
- DuranDuran OrdinaryWorldDokumen1 halamanDuranDuran OrdinaryWorldEduardo LuzBelum ada peringkat
- Hopf 6870 - 1101Dokumen58 halamanHopf 6870 - 1101macakafkaBelum ada peringkat