I. Postpartal Infections Causes
Diunggah oleh
Joanne GomezDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
I. Postpartal Infections Causes
Diunggah oleh
Joanne GomezHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ANGELES UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION College of Nursing COMPETENCY APPRAISAL II Maternal Nursing I. POSTPARTAL INFECTIONS Causes: A.
Endogenous: Normal Flora B. Exogenous: Anaerobic Strep (Hospital Personnel, Manipulation, Breaks in Aseptic Technique, Coitus, PROM) General Signs and Symptoms: Malaise, Anorexia, Fever, Chills and Headache General Management Monitor VS and temp every 2 4 hrs COMPLETE bed Rest; Position of comfort Proper Nutrition : High calorie; High protein Increased Fluid Intake : 3-4L Encourage frequent voiding. Monitor I/O Analgesics Antipyretics and Antibiotics A. Perineal Infection Pain, heat, pressure in the perineum Inflammation of suture line, 1- 2 inches sloughed Removal of sutures; resuture Hot sitz bath or warm compress B. Endometritis Placental point of entry; Peritonitis and Pelvic Thrombophlebitis Abdominal tenderness, Prolonged severe afterpains Uncontracted (tender and large) uterus, pain Dark brown, foul smelling lochia Ileus Oxytocin administration Fowlers position. Pain management. C. Thrombophlebitis Increased production of clotting factors Femoral Malaise, Chils, Fever + Homans sign Diminished pulses Shiny white skin Pain, stiffness, swelling Pelvic Severe chills Dramatic temp changes Pulmo. Embolism
Superficial Palpable thrombus Pain and Tenderness Warm and Pinkish
Assessment Bed rest, leg elevated Use bed cradles. Hot packs/ Moist heat Elastic stockings. Analgesics. Antibiotics Heparin Na IV Monitor for Pulmonary Embolism
Never massage leg. Avoid crossing legs. Avoid prolonged sitting. Avoid constricting clothes. Avoid pressure behind knees.
D. Mastitis Staph aureus Breasfeeding mothers, 2- 3 weeks Fever, chills, tachycardia, malaise, abdominal pain Reddening, swelling, inflammatory signs Handwashing, breast care Warm water, Or Cold application Let breast milk dry on nipples clean bra Good breastfeeding techniques Manual expression of breast milk Analgesics
Antibiotics
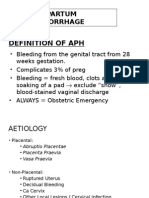
II. BLEEDING/HEMORRHAGE A. First Trimester Bleeding 1. Abortion Types Threatened Signs/ Symptoms Spontaneous vaginal bleed Moderate bright red Low uterine cramping Management CBR 24-48 Coitus Restriction Hormone therapy Monitor V/S Count perineal pads Maintain IV Monitor for hemmorhage RhoGAM Complete VS iNC
Imminent/ Inevitable Missed
Cervical Dilatation and Effacement No inc in FH, FHT 2 wks signs of Abortion 3 or more successive pregnancies
Habitual
2. Ectopic Pregnancy Pregnancy OUTSIDE of UTERUS; Fallopian Tube :AMPULLA Spotting to bleeding: Dark red or brown Ruptures in 12 weeks SEVERE, SHARP, KNIFE LIKE, Lower Quadrant (L/R) Referred shoulder pain Rigid Abdomen Cullens Sign Excruciating pain upon IE Shock Methotrexate MGT: Salpingostomy, Salpingectomy Nursing Care: COMBAT SHOCK B. Second Trimester Bleeding 1. Hydatidiform Mole Chorionic Villi: Proliferation and degeneration Grape like clusters; Antecedent of choriocarcinoma Low SE status with low protein intake <18 yrs old and >35 years old Marked nausea and vomiting Fundic Ht Increase, Weight gain No Fetal Heart Tones th Signs of toxemia before 24 AOG Clear, fluid, grape sized vesicles th nd Vaginal bleeding by 4 wk/2 Tri Bright red/ dark brown, Slight, profuse and intermittent High levels of HCG High levels of HCG Snowstorm pattern on UTZ D&C, Vacuum Aspiration Oxytocin for Contraction MTX HCG monitoring q 1-2 weeks until NORMAL; 1 2 months/year Prophylaxis
2. Incompetent Cervical Os Premature dilation of the cervix Congenital/ Hormonal/Trauma Show and uterine contractions Ruptured membranes Painless cervical dilatation Bed Rest, Hydration, Tocolysis TH Cerclage 14-18 AOG McDonalds: NSD
Shirodkar: CS No coitus, prolonged standing, heavy lifting Monitor for contractions, bleeding and rupture of membranes and signs of infection
C. Third Trimester Bleeding 1. Placenta Previa Improperly implanted Low lying/Partial/Complete Increased Parity Advanced Maternal Age Rapid succession of pregnancies Dx: UTZ PAINLESS BRIGHT RED VAGINAL BLEEDING Uterus is soft, relaxed and non tender Maternal VS, FHT, Fetal Activity IE? Complete Bed Rest , Side Lying Prepare O2 and Blood IV and Tocolytics Hemorrhage, Infection, Prematurity 2. Abruptio Placenta th Premature separation of placenta from uterine wall after 20 week and before delivery Maternal Hypertension Increasing parity, Maternal Age Sudden release of amniotic fluid Short umbilical cord Direct trauma Hypofibrinoginemia Dark red vaginal bleeding, or absence of bleeding SEVERE, SHARP, KNIFE LIKE PAIN, Fundic region Signs of Shock Couvelaire uterus Fetal distress Monitor Maternal V/S, and FHT WOF excessive vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain and increase in fundic height Maintain bedrest. Administer 02, IV, Blood products Trendelenburg position Left lateral position Monitor uterine activity Vaginal delivery Cesarian delivery DIC on the postpartum D. Postpartum Bleeding 1. Early Postpartum Bleeding a. Uterine Atony Overdistention of Uterus CS Placental Accidents Prolonged and Difficult labor WOF increased pulse rate MASSAGE Ice compress, oxytocin administration, empty bladder Bimanual compression Hysterectomy
2. Late a. Retained Placental Fragments Dilatation and Curettage b. Hematoma Ice compress Oral Analgesics Incision and Ligation
III. HIGH RISK PREGNANCY
A. Anemia Iron deficiency Postpartum Infection Fatigue, H/A, Pallor, Tachycardia HgB: < 10 g/dL; Hct: 30% Monitor HgB and Hct every 2 weeks Iron and Folic acid supplements Vitamin C and tea Iron, Folic Acid, Protein Blood Transfusion Oxytocin, with excessive bleeding B. Cardiac Disease Increased plasma volume, cardiac output ND Blood volume at maximum for last weeks of 2 trimester Functional Classification of Cardiac Disease Class I Class II Uncompromised Slightly compromised; slight limitation of physical activity Ordinary physical activity causes sx Markedly compromised ; limitation of physical activity Less ordinary activity causes excessive fatigue, palpitations, dyspnea, or anginal pain Inability to perform any physical activity w/o discomfort Sx of cardiac insufficiency present at rest Cough and respiratory congestion Dyspnea and fatigue Palpitations and tachycardia Peripheral edema Chest pain Respiratory infection Heart failure and pulmonary edema Warn about obesity. Monitor V/S, FHT, Fetal condition Limit physical activity. Stress rest. Monitor for signs of cardiac rest and decompensation. Prevent anemia. Low sodium diet Labor: V/S monitor. Cardiac monitor. External fetal monitor. Bed Rest. Side lying, Head and shoulders elevated.
Class III
Class IV
C. Diabetes Mellitus Maternal glucose crosses, placenta does not. First trimester: maternal insulin needs decrease Second and third: insulin needs increase Placental delivery: abrupt decrease of hormones, decrease insulin requirements Fetus produces own insulin, pulls glucose from mother. Predisposes the mother to hypoglycemic reactions. D. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus ND rd 2 or 3 trimester; Pancreas unable to respond th Screening during 24 28 week AOG 3 OGTT confirmatory After delivery, EUGLYCEMIC state S/sx of Hyperglycemia, Blurred vision, Recurrent UTI and yeast infection, Gestational Hypertension, Polyhydramnios, LGA Dietary changes, Insulin, Exercise: 65 130 mg/dl Monitor serum glucose, urine for glucose and ketones Weight monitoring Proper caloric intake + insulin therapy WOF for complications (Preeclampsia) and Infection Assess Fetal Status and Fetal Compromise Monitor Fetal Status and prepare CS Regulate insulin and provide glucose IV Postpartum Interventions: Observe for hypoglycemia. Reregulate insulin needs after the first day.
Assess dietary needs Monitor for postpartum infection or postpartum hemorrhage
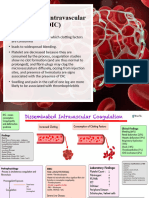
E. Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Causes Abruptio placentae Amniotic fluid embolism Gestational hypertension IUFD Liver disease Sepsis Signs and Symptoms Signs of Bleeding Decreased fibrinogen, plt. Ct, Hct Inc PT, PTT, Clotting Time, Fibrin Degradation products Remove underlying cause. Implement interventions for blood loss. Monitor urine output and maintain at 30 ml/hr. F. Pregnancy Induced Hypertension th nd 24 week 2 week postpartum HYPERTENSION; EDEMA; PROTEINURIA Age ; Multigravida Low Socio economic status Multigravida Co morbidities nd Roll over Test: 28- 32 week of pregnancy Lateral recumbent to supine position; +20 mmHg Mild Preeclampsia 1-5lbs/week Upper Extremity Edema 140/90 (+30 mmhg/15 mmHg) Proteinuria 0.5 gms/liter Severe Preeclampsia 160/110 Proteinuria 5gm/liter , 24 hours Cerebral/Visual disturbances Pulmonary edema/Cyanosis Elev. Liver; Oliguria Aura
ECLAMPSIA: CONVULSIONS; Increased BUN, Uric Acid
Mild Hypertension Monitor BP. Monitor Fetal Activity Rest Periods Lateral Position Anti HPN meds Monitor I/O Evaluate renal fxn
Mild Pre Eclampsia Monitor Neurologic Status Monitor DTR Adequate fluids Monitor for HELLP
Severe Pre Eclampsia MgSO4 Monitor Mg toxicity Prepare for induction of labor
Remain with client. Call for help. Ensure open airway. Turn client to side. O2 at 8-10L/min Monitor FHT Meds for seizures. Complete Bed Rest Diet : High CHON/CHO
ECLAMPSIA Insert oral airway. Suction. Prepare for delivery. Document occurrence.
Mild Preeclampsia Moderate Na Restriction No added salt Fish paste, sauce, canned good
Severe Preeclampsia Salt Poor (3 grams, Na /day)
Diuretics 20-30 ml/hr UO Fatigue and muscle weakness Monitor I/O
K Supplement WOF D-D Interactions
Barbiturates Sedation
Magnesium Sulfate CNS Dep. Vasodilator Cathartic
10gms(RED)
IV. PROBLEMS WITH LABOR AND DELIVERY A. Premature Rupture of Membranes Gestational age determines intervention INFECTION! Fluid pooling in vaginal vault Nitrazine test positive. V/S Monitoring; Fetal Monitoring Avoid vaginal examinations Antibiotics as needed. B. Prolapsed Umbilical Cord Displaced between presenting part and amnion or protruding Compression of cord, fetal circulation compromise Feeling something is coming out Visible/palpable cord FHR is irregular and slow Violent fetal activity Elevate fetal presenting part via finger pressure Extreme Trendelenburg/ Modified Sims/ Knee Chest Oxygen, 8-10 LPM via face mask Monitor fetal heart rate and assess fetal hypoxia IV fluid Prepare for immediate birth. Document event and patient response. C. Precipitous Labor and Delivery Labor < 3 hours Preciptous delivery made available Stay with the client. Keep client calm. Do not keep fetus from being delivered. D. Dystocia Difficult Labor: prolonged and painful Power/Passenger/Passageway Hypotonic/Hypertonic Contractions DHN, infection, Fetal Injury, Death Monitor maternal and fetal well being Administer prophylactic antibiotic. IV, I/O monitoring Instruct on proper breathing Monitor color of amniotic fluid Monitor for cord prolapse after membrane rupture E. Fetal Distress Fetal heart rate < 120 beats/min or >160 bpm Meconium stained amniotic fluid Fetal hyperactivity Severe variable decelerations Late decelerations Lateral Position Oxygen, 8 10 LPM, Face mask Discontinue oxytocin Monitor maternal and fetal status Prepare for cesarean delivery PREPARED BY: J. DELFIN RN, MN
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- ANC, PNC and U5 Children: Dr. Sachin ParmarDokumen52 halamanANC, PNC and U5 Children: Dr. Sachin Parmarsachin parmarBelum ada peringkat
- Case Presentation On Ectopic PregnancyDokumen56 halamanCase Presentation On Ectopic PregnancyElisha Joshi100% (5)
- NCP - HmoleDokumen8 halamanNCP - HmoleChloe Opiña100% (6)
- Lecture 2 Chapter19, 20 High Risk Pregnancy 2015 Student'sDokumen145 halamanLecture 2 Chapter19, 20 High Risk Pregnancy 2015 Student'sKa Reen100% (5)
- 1 Nursing Care of The Pregnant Client Pre Gestational ConditionDokumen134 halaman1 Nursing Care of The Pregnant Client Pre Gestational ConditionVince MatthewBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Pregnancy - 094218Dokumen67 halamanNormal Pregnancy - 094218Beatrice habukuwie BaahBelum ada peringkat
- A CASE REPORT: Hyperthyroidism in PregnancyDokumen46 halamanA CASE REPORT: Hyperthyroidism in PregnancyIrma Permata sariBelum ada peringkat
- Hyperemesis, Hmole, Placenta PreviaDokumen12 halamanHyperemesis, Hmole, Placenta Previadanica grace gubaBelum ada peringkat
- Obstetrics Study Guide 3: Mitra Ahmad Soltani 2008Dokumen172 halamanObstetrics Study Guide 3: Mitra Ahmad Soltani 2008Anonymous N2PHMnTIYLBelum ada peringkat
- PUERPERIUMDokumen38 halamanPUERPERIUMChikky ChikyBelum ada peringkat
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Mrs - Jagadeesw Ari.j M.SC NursingDokumen28 halamanHyperemesis Gravidarum: Mrs - Jagadeesw Ari.j M.SC NursingErika Anne Mercado CadawanBelum ada peringkat
- University of Saint Louis Tuguegarao City, Philippines: Maternal and Child Health NursingDokumen94 halamanUniversity of Saint Louis Tuguegarao City, Philippines: Maternal and Child Health NursingErica Veluz LuyunBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertensive Disorder in Pregnancy Untuk KuliahDokumen78 halamanHypertensive Disorder in Pregnancy Untuk Kuliah404notfoundBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd Lecture Substance Abuse & Gestational Conditions (NCM102)Dokumen14 halaman3rd Lecture Substance Abuse & Gestational Conditions (NCM102)Charmaine MativoBelum ada peringkat
- Gestational Conditions: Mrs. Catherine V. Sta. Monica, RNDokumen140 halamanGestational Conditions: Mrs. Catherine V. Sta. Monica, RNCatherine Villanueva Sta MonicaBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertensive Disorders of PregnancyDokumen46 halamanHypertensive Disorders of PregnancyJagadeeswari JayaseelanBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Pre Gestation and Gestational ConditionsDokumen88 halaman2 Pre Gestation and Gestational Conditionslermacornel61Belum ada peringkat
- Gestational 1Dokumen8 halamanGestational 1RoseAngelyne VicenteBelum ada peringkat
- Ante-Partum HaemorrhageDokumen42 halamanAnte-Partum HaemorrhageSerenna DehalooBelum ada peringkat
- Recitation in MaternalDokumen6 halamanRecitation in MaternalVictoria Eugelio BungalsoBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Hiperemesis GravidarumDokumen34 halaman8 Hiperemesis GravidarumVherty Vhertozt Vuazt100% (1)
- Gyno... PTL & PRODokumen30 halamanGyno... PTL & PROhailemichael chekolBelum ada peringkat
- Prom PPT 2Dokumen31 halamanProm PPT 2NadikBelum ada peringkat
- NURS325 05 Antepartum ComplicationDokumen81 halamanNURS325 05 Antepartum ComplicationaliBelum ada peringkat
- Revised OB Handout Part 2 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherDokumen9 halamanRevised OB Handout Part 2 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherMatelyn OargaBelum ada peringkat
- Pedia AbnormalDokumen34 halamanPedia Abnormallight_tyrBelum ada peringkat
- Kavitha K C - A Case Presentation - Nephrotic SyndromeDokumen27 halamanKavitha K C - A Case Presentation - Nephrotic SyndromeVishesh ParayilBelum ada peringkat
- At I Maternal NewbornDokumen24 halamanAt I Maternal NewbornEunice Cortés100% (2)
- SEMINAR HYPERTENSION DISORDER DURING PREGNANCY ContentDokumen19 halamanSEMINAR HYPERTENSION DISORDER DURING PREGNANCY ContentMonika shankar100% (1)
- 7-Neonatal Surgical EmergenciesDokumen29 halaman7-Neonatal Surgical EmergenciesResti Rangga SusiloBelum ada peringkat
- Preeclampsia EclampsiaDokumen40 halamanPreeclampsia EclampsiaPurnama WatiBelum ada peringkat
- Placenta Abruptio: Maneja, Jan Michael B. BSN 223Dokumen6 halamanPlacenta Abruptio: Maneja, Jan Michael B. BSN 223JiraGonzales100% (1)
- Nursing Care of The High Risk Pregnant Client With Gestational ConditionDokumen55 halamanNursing Care of The High Risk Pregnant Client With Gestational ConditionMarc FresBelum ada peringkat
- OB ComplicDokumen103 halamanOB ComplicmanilynBelum ada peringkat
- What The Bleep?: Common Calls For Junior Doctors in O&G DR Alice KnowlesDokumen43 halamanWhat The Bleep?: Common Calls For Junior Doctors in O&G DR Alice KnowlesAlice KnowlesBelum ada peringkat
- OB High Risk PregnancyDokumen78 halamanOB High Risk PregnancyMaye ArugayBelum ada peringkat
- LR ProtocolDokumen159 halamanLR ProtocolJeevan VelanBelum ada peringkat
- Ectopic PregnancyDokumen32 halamanEctopic Pregnancyyt2zkpkphqBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Nursing Care of The Pregnant Client Pre-Gestational ConditionDokumen6 halaman1 Nursing Care of The Pregnant Client Pre-Gestational ConditionFaith Calimlim100% (1)
- Miscarriage and Its Types: Farhad Ali 15 - 177 3 Year MBBSDokumen21 halamanMiscarriage and Its Types: Farhad Ali 15 - 177 3 Year MBBSmarviBelum ada peringkat
- ANTERPARTAL COMPLICATIONS Women With Preexisting Illness 1Dokumen85 halamanANTERPARTAL COMPLICATIONS Women With Preexisting Illness 1justinekaye diongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Gynae EmerganciesDokumen39 halamanGynae EmerganciesgibreilBelum ada peringkat
- Antenatal Clinic ProtocolDokumen24 halamanAntenatal Clinic ProtocolDivakarpatil MukundraoBelum ada peringkat
- MCN ReviewerDokumen4 halamanMCN ReviewerMaria Arabella LanacaBelum ada peringkat
- 2 - Pre Gestational ConditionDokumen11 halaman2 - Pre Gestational ConditionAngelica Dalit MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of Newborn, - 130319150346Dokumen45 halamanClassification of Newborn, - 130319150346Ez Ball100% (1)
- Dic PihDokumen82 halamanDic PihMatth N. ErejerBelum ada peringkat
- Obstetrics Case TakingDokumen42 halamanObstetrics Case TakingAnusree AnusreervBelum ada peringkat
- Antenatal CareDokumen43 halamanAntenatal CareAyubBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertensive DisordersDokumen25 halamanHypertensive Disorders216 SUDANI BHAVIKA NARSHIBHAIBelum ada peringkat
- Heart Disease and PrenancyDokumen24 halamanHeart Disease and PrenancyzizsatriaBelum ada peringkat
- High Risk Newborns StudentDokumen38 halamanHigh Risk Newborns StudentKeanu Win CatipayBelum ada peringkat
- Abnormal Ob HandoutsDokumen3 halamanAbnormal Ob HandoutsBoy MadBelum ada peringkat
- Pain in PregnancyDokumen60 halamanPain in Pregnancysyirah99Belum ada peringkat
- High Risk Newborn: Dr. H. Usha RaniDokumen28 halamanHigh Risk Newborn: Dr. H. Usha RaniNaresh GadaganiBelum ada peringkat
- Post Abortion CareDokumen35 halamanPost Abortion CareNatukunda DianahBelum ada peringkat
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension: Also Called: Toxemia or Pre-Eclampsia or Gestational HypertensionDokumen22 halamanPregnancy Induced Hypertension: Also Called: Toxemia or Pre-Eclampsia or Gestational HypertensionRhuby Pascual AbenojaBelum ada peringkat
- Pre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandPre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Birth Plan Template - TheInformedBirth PDFDokumen7 halamanBirth Plan Template - TheInformedBirth PDFEr. Nidhi Shah100% (1)
- Critical Thinking AnalysisDokumen7 halamanCritical Thinking AnalysisFlourence ZafranBelum ada peringkat
- Vbac - YurDokumen20 halamanVbac - YurkikiBelum ada peringkat
- Materi 2 & 3 (Filling in Medical Report)Dokumen8 halamanMateri 2 & 3 (Filling in Medical Report)Anggie Rambu100% (1)
- Ectopic Pregnancy and MiscarriageDokumen287 halamanEctopic Pregnancy and Miscarriageera anggoro kusuma ningrumBelum ada peringkat
- Obstructed Labour and The Partogram: EsmoeDokumen89 halamanObstructed Labour and The Partogram: EsmoeLana LocoBelum ada peringkat
- RH Incompatibility and PregnancyDokumen2 halamanRH Incompatibility and PregnancyChelcee MagsinoBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Allylestrenol A Pregnancy-Supporting ProgestoDokumen8 halamanOral Allylestrenol A Pregnancy-Supporting ProgestowaelBelum ada peringkat
- Population Development Division Brho Monitoring and AccomplishmentDokumen3 halamanPopulation Development Division Brho Monitoring and AccomplishmentBarangay UbaliwBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Terms and Definitons Commonly Used in MCNDokumen15 halamanMedical Terms and Definitons Commonly Used in MCNjoemel gregoriBelum ada peringkat
- SecretDokumen1 halamanSecretAyisha LoureliBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 109 Week 7 1Dokumen47 halamanNCM 109 Week 7 1Stephanie Ann ZanoriaBelum ada peringkat
- Embryonic DemiseDokumen80 halamanEmbryonic DemiseDr. mohammed100% (2)
- Factors Affecting Labor.Dokumen2 halamanFactors Affecting Labor.Salman KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Study of Sociodemographic Profile, Maternal, Fetal Outcome in Preeclamptic and Eclamptic Women A Prospective StudyDokumen6 halamanStudy of Sociodemographic Profile, Maternal, Fetal Outcome in Preeclamptic and Eclamptic Women A Prospective StudyHarvey MatbaganBelum ada peringkat
- Terms of Pregnancy (C SU07)Dokumen4 halamanTerms of Pregnancy (C SU07)عبدالرحمن الزيودBelum ada peringkat
- A Journey To Safe Motherhood: Chiranjeevi Yojana GujaratDokumen47 halamanA Journey To Safe Motherhood: Chiranjeevi Yojana GujaratNeeraj SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Classification: Miscarriage or Spontaneous Abortion Is The Spontaneous End of A Pregnancy at ADokumen9 halamanClassification: Miscarriage or Spontaneous Abortion Is The Spontaneous End of A Pregnancy at AAnn GelaBelum ada peringkat
- Why The COVID Jab Should Be Banned For Pregnant WomenDokumen11 halamanWhy The COVID Jab Should Be Banned For Pregnant WomenMarios AshikkisBelum ada peringkat
- Maternal and Child Health Questions W/ RationaleDokumen15 halamanMaternal and Child Health Questions W/ RationaleMaicah ShaneBelum ada peringkat
- Abruptio PlacentaDokumen5 halamanAbruptio PlacentaJuan Carlo Z. SolidumBelum ada peringkat
- Hypothyroidism in Pregnancy: Motherisk RoundsDokumen3 halamanHypothyroidism in Pregnancy: Motherisk RoundsIndrani DasBelum ada peringkat
- Indications and Risks of Vacuum Assisted Deliveries.: OriginalDokumen2 halamanIndications and Risks of Vacuum Assisted Deliveries.: OriginalgagagigoBelum ada peringkat
- Workshop CPD Online IBI - 6 Maret 2021 - Admin PDDokumen68 halamanWorkshop CPD Online IBI - 6 Maret 2021 - Admin PDFahrunisa Cahyaning PertiwiBelum ada peringkat
- Gestational DiabetesDokumen15 halamanGestational DiabetesAbdulJabar RiadhBelum ada peringkat
- Putra Et Al 55-58Dokumen4 halamanPutra Et Al 55-58arga setyo adjiBelum ada peringkat
- EABDokumen12 halamanEABAr Kethees WaranBelum ada peringkat
- Maternity NursingDokumen28 halamanMaternity Nursingja100% (11)
- Gestational ConditionsDokumen148 halamanGestational ConditionsEsvinch EsvinchBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosis and Mangement of Abnormal LabourDokumen55 halamanDiagnosis and Mangement of Abnormal LabourVirda Maharani100% (3)