Diode Characteristic and Biasing
Diunggah oleh
Faye YturraldeHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Diode Characteristic and Biasing
Diunggah oleh
Faye YturraldeHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
College of Engineering Ateneo de Naga University Activity 1 Diode Characteristic and Biasing
Name: Romelyn P. Perez Date Performed: _April 12, 2012_ Section: GEN1______ Date Submitted: Name of Laboratory Partner: _Nikko Alexis C. Peralta______ Laboratory Instructor: _Engr. Anacleto Casimiro___
RESULTS AND ANALYSIS Table 1 Diode Specification Product Number: Continuous Forward Current: Peak Inverse Voltage: IN4001 30A 50V
Table 2 Diode Curve Supply Voltage 0V 0.1V 0.2V 0.3V 0.4V 0.5V 0.6V 0.7V 0.8V 0.9V 1V 1.5V 2V 2.5V 3V Diode Voltage 0 99.812mV 198.546mV 291.136mV 363.792mV 410.551mV 440.473mV 461.316mV 476.971mV 489.384mV 499.615mV 533.677mV 554.527mV 569.515mV 581.2mV Diode and Resistor Current 0 0 0.001471mA 0.008882mA 0.036304mA 0.089484mA 0.15965mA 0.238698mA 0.323186mA 0.410671mA 0.500489mA 0.96656mA 1.446mA 1.931mA 2.419mA Resistor Voltage 0 0 1.454mV 8.864mV 36.208mV 89.449mV 159.527mV 238.684mV 323.029mV 410.616mV 500.385mV 966.323mV 1.445mV 1930mV 2419mV
College of Engineering Ateneo de Naga University
Table 2 Diode Curve
Current (mA)
3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0
V-i plot
Diode Voltage (mV) OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS: Yes, the values remain constant for the diode and transistor. As shown at the graph above, we observed that when the diode voltage is increasing, the diode and resistor current is also increasing. Therefore, the relationship of the Diode and Resistor Current and Diode voltage is directly proportional.
College of Engineering Ateneo de Naga University
Current (mA)
3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0
V-i plot
Resistor Voltage (mV)
OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS: As shown at the graph above, we observed that when the resistor voltage is increasing, the diode and resistor current is also increasing. Therefore, the relationship of the Diode and Resistor Current and Resistor voltage is directly proportional.
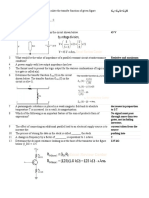
Table 3 Diode Circuit VAB Fig. 2 Fig. 3 Fig. 4 Fig. 5 Fig. 6 Fig. 7 5.02 V 5.02 V -3 V -1V -1 V 1.5V States of Diode On Off Off Off Off On Diode Voltage 0.7 V 5.02V -3 V - 0.535 V -1V 567.715mV Diode Current 4.39mA 0 0 0 0 1.865mA Bias Condition Forward Reverse Reverse reverse Reverse Forward
College of Engineering Ateneo de Naga University Follow-Up Activity Table 4 Faults 1. Normal Condition 2. R3 short 3. R3 open 4. R2 short 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. R2 open R1 short R1 opens D1 open D2 open VO condition (in terms of VCC) VO = 2VDC + D2 - 3D1 4 VO = 2VDC + R1 4 VO = 2VDC + R12D1R1 2 R1 VO = 2VDC + D12D1R1 2 R1 VO = VDC VR1 D1 VO = VDC D1 VO = 0 VO = 0 VO = VDC VR1 D1
OBSERVATION: As we observed in the Table 3, when the state of diode is ON, the bias condition of the diode is forward and there will be current flowing through the diode. But when the state of diode is OFF, the bias condition of the diode is reverse, so the current that flows into the diode is equal to 0 A. In case of two voltage sources the state of diode is depend on the higher voltage, so the bias of the diode can be forward or reverse depend to the polarity of the higher voltage source.
Generalization:
In this activity entitled Diode Characteristic and Biasing, aside from we improve our skill and knowledge in analyzing circuit, I learned and verify the function of a diode in a circuit, and also the importance of knowing the state of diode, because when the state of diode is on, its bias condition is forward and there will be currents across. While, when the state of diode is off, the current across is equal to 0 A. And also the relationship of the voltage and current in a series circuit is directly proportional, when the voltage increases, the current also increases.
College of Engineering Ateneo de Naga University
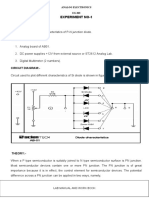
Pre-Lab Measuring the Diode Voltage: Measuring the Diode and Resistor Current:
R1 1k
R1 1k
V1 2.5 V D1 1N4001
XMM1
V1 2.5 V
D1 1N4001
XMM1
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Troubleshooting Electronic Components With The PET BloodhoundDari EverandTroubleshooting Electronic Components With The PET BloodhoundBelum ada peringkat
- 1 PN Junction PDFDokumen4 halaman1 PN Junction PDFAbhishekh TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Electronics LabDokumen60 halamanBasic Electronics Labrahulsingle67% (3)
- PCNSE v9 (2020) PDFDokumen77 halamanPCNSE v9 (2020) PDFFaye Yturralde100% (1)
- Electronic Devices - Circuits Lab ManualDokumen77 halamanElectronic Devices - Circuits Lab ManualpdnkiranBelum ada peringkat
- Elex Pre Board Exam ExcelDokumen9 halamanElex Pre Board Exam ExceluvubwebweBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 1 (Diode Characteristics and Biasing)Dokumen3 halamanActivity 1 (Diode Characteristics and Biasing)Carmelyn BorjaBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics Lab ReportsDokumen46 halamanElectronics Lab ReportsDanilyn Padillo LucioBelum ada peringkat
- Betaizar J Lab2.1Dokumen8 halamanBetaizar J Lab2.1Jay BetaizarBelum ada peringkat
- (ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 1 Final ReportDokumen15 halaman(ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 1 Final ReportLawrence Abram AlcantaraBelum ada peringkat
- 1mechanical Experiment Semiconductor Diode Biasing PracticalDokumen17 halaman1mechanical Experiment Semiconductor Diode Biasing PracticalJeferson RosalesBelum ada peringkat
- Ex 305Dokumen51 halamanEx 305DineshKumarCholkarBelum ada peringkat
- Betaizar J LaboratoryNo1Dokumen7 halamanBetaizar J LaboratoryNo1Jay BetaizarBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 1Dokumen12 halamanExperiment 1Jomar RosalesBelum ada peringkat
- Exp 1Dokumen16 halamanExp 1Jeshua LloreraBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Report#1Dokumen8 halamanLab Report#1Nguyen TranBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 9 The Effects of Diodes and Rectifiers in CircuitsDokumen10 halamanLab 9 The Effects of Diodes and Rectifiers in Circuitsapi-709999921Belum ada peringkat
- Crisostomo Parzuelo Moreno Activity 1Dokumen8 halamanCrisostomo Parzuelo Moreno Activity 1Anna Maria ParzueloBelum ada peringkat
- Lab reportTTDokumen13 halamanLab reportTTPaa Kwesi ArhinfulBelum ada peringkat
- BECE LabManualDokumen15 halamanBECE LabManualDrakie SumanilBelum ada peringkat
- PN Junction Diode1Dokumen17 halamanPN Junction Diode1SURESH SURAGANIBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Manual ECE 1Dokumen15 halamanLab Manual ECE 1Macky Malupangue100% (1)
- BXE Experiment No.3Dokumen8 halamanBXE Experiment No.3DsgawaliBelum ada peringkat
- Bread Board 1 Multimeter 1 DC Power Supply 1 Connecting Cable 2Dokumen6 halamanBread Board 1 Multimeter 1 DC Power Supply 1 Connecting Cable 2Ezedin NegashBelum ada peringkat
- ECN Experiment WorkBookDokumen29 halamanECN Experiment WorkBookAlpesh ThesiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Experimentally Study The IV Curves of DiodeDokumen5 halamanExperimentally Study The IV Curves of DiodeMuhammad Tehreem100% (1)
- Ecb 2182 Electronics and Microprocessors Lab Manual: S.Sadhish Prabhu, Ap/EceDokumen63 halamanEcb 2182 Electronics and Microprocessors Lab Manual: S.Sadhish Prabhu, Ap/EceNeoBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Manual Electronic Devices and Circuits Practical 2Dokumen10 halamanLab Manual Electronic Devices and Circuits Practical 2Engr Zaryab WarraichBelum ada peringkat
- EDC Lab 3Dokumen9 halamanEDC Lab 3Sameer KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Sdc-Labmanual by Prabhu Kumar SurarapuDokumen62 halamanSdc-Labmanual by Prabhu Kumar Surarapuprabhu4scribdBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory Experiment 2Dokumen7 halamanLaboratory Experiment 2PajayBelum ada peringkat
- Characteristics of P-N Junction DiodeDokumen15 halamanCharacteristics of P-N Junction Diodehybe07jiminBelum ada peringkat
- Study of Reverse Charracteristics of Zener DiodeDokumen3 halamanStudy of Reverse Charracteristics of Zener DiodeZealWolfBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics 1Dokumen42 halamanElectronics 1Shanti Emmanuelle EscabarteBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic Devices & Circuits: Laboratory ManualDokumen61 halamanElectronic Devices & Circuits: Laboratory ManualFadila IsmailBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 8Dokumen13 halamanLab 8Richard LangBelum ada peringkat
- V-I Characteristics of PN Junction DiodeDokumen6 halamanV-I Characteristics of PN Junction DiodeAditya GorrepatiBelum ada peringkat
- Expt. No.: 1 PN Junction Diode Characteristics DateDokumen7 halamanExpt. No.: 1 PN Junction Diode Characteristics DateArunMssBelum ada peringkat
- SPH 340 - 206 Lab ManualDokumen83 halamanSPH 340 - 206 Lab Manualwakala manaseBelum ada peringkat
- Diode Test and Familiarization: Table1 1Dokumen3 halamanDiode Test and Familiarization: Table1 1cent carinoBelum ada peringkat
- FullDokumen67 halamanFullKalaiselvan PunniyamoorthyBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics Device Circuit Lab SheetDokumen27 halamanElectronics Device Circuit Lab Sheetjimfinch512Belum ada peringkat
- Lab 1 - Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsDokumen8 halamanLab 1 - Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsMD NAZMUN HASAN NAFEESBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 5Dokumen3 halamanExperiment 5Farhana LisaBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 4 Zener Diode: Data and ResultsDokumen6 halamanExperiment 4 Zener Diode: Data and ResultsCARLO CASTILLOBelum ada peringkat
- Vels Vidhyashram Senior Secondary School: Measuring Current Using Halfwave RectifierDokumen17 halamanVels Vidhyashram Senior Secondary School: Measuring Current Using Halfwave RectifierAryan TengBelum ada peringkat
- List of Experiments: Ee2207 Electronic Devices and Circuits Laboratory (Revised)Dokumen54 halamanList of Experiments: Ee2207 Electronic Devices and Circuits Laboratory (Revised)prakashkumarBelum ada peringkat
- Angel D. Acevedo Ross Intermediate Lab LL Lab Report 1: Specific Charge of Electron E/m Universidad de Puerto Rico: Rio PiedrasDokumen9 halamanAngel D. Acevedo Ross Intermediate Lab LL Lab Report 1: Specific Charge of Electron E/m Universidad de Puerto Rico: Rio PiedrasangelBelum ada peringkat
- EEE 1218 Sessional On Analog Electronics: Date: 23-05-202 Student's Name: Afiat Khan Tahsin Roll: 1907047Dokumen3 halamanEEE 1218 Sessional On Analog Electronics: Date: 23-05-202 Student's Name: Afiat Khan Tahsin Roll: 1907047Afiat KhanBelum ada peringkat
- LAB LEDs and ZenerDokumen12 halamanLAB LEDs and ZenerjosembosemBelum ada peringkat
- Cse Labreport-1Dokumen6 halamanCse Labreport-1SR NibirBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 1 PHYELC - 2Dokumen5 halamanExperiment 1 PHYELC - 2owronrawan74Belum ada peringkat
- 15E282 18lab1Dokumen10 halaman15E282 18lab1Yadhuvanth kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Lab02 Hardware Single Phase Uncontrolled RectifiersDokumen15 halamanLab02 Hardware Single Phase Uncontrolled RectifiersMaryamBelum ada peringkat
- ECE2201 Lab Report 1Dokumen10 halamanECE2201 Lab Report 1jeffclist2Belum ada peringkat
- EL - 124 Electronic Devices & Circuits: Experiment # 06Dokumen10 halamanEL - 124 Electronic Devices & Circuits: Experiment # 06Jawwad IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- KEC151P - Lab - Experiments - UPDATED ONEDokumen34 halamanKEC151P - Lab - Experiments - UPDATED ONEAkshat GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- ElectronicsLab - Manual March2010Dokumen64 halamanElectronicsLab - Manual March2010pnarendrareddy.mscBelum ada peringkat
- EEE 1302 - Experiment 1Dokumen4 halamanEEE 1302 - Experiment 1Sadikul Hasan Mridha Atul (181016024)Belum ada peringkat
- M.ABDULLAH FA19-BEE-110 Electronic 1 Lab 2 PDFDokumen12 halamanM.ABDULLAH FA19-BEE-110 Electronic 1 Lab 2 PDFAtyia JavedBelum ada peringkat
- Discussion:: R1 D. R1 DDokumen3 halamanDiscussion:: R1 D. R1 DHaziq KlBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Report 1. Diode Characteristics HalfDokumen10 halamanLab Report 1. Diode Characteristics HalfayasumireBelum ada peringkat
- KeySecure and Encryption ConnectorsDokumen19 halamanKeySecure and Encryption ConnectorsFaye YturraldeBelum ada peringkat
- Product Life Cycle Announcement: Current SKU Description Replacement SKU DescriptionDokumen1 halamanProduct Life Cycle Announcement: Current SKU Description Replacement SKU DescriptionAlbert Osorio GalegoBelum ada peringkat
- Checkpoint Train4sure 156-315 77 v2018-12-21 by Paul 445q PDFDokumen209 halamanCheckpoint Train4sure 156-315 77 v2018-12-21 by Paul 445q PDFFaye YturraldeBelum ada peringkat
- Review QuestionsDokumen7 halamanReview QuestionsFaye YturraldeBelum ada peringkat
- FMG 5.4 - Exam TopicsDokumen32 halamanFMG 5.4 - Exam TopicsFaye YturraldeBelum ada peringkat
- PoliticsDokumen3 halamanPoliticsFaye YturraldeBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Information Theory: By: Faye Camille P. YturraldeDokumen9 halamanBasics of Information Theory: By: Faye Camille P. YturraldeFaye YturraldeBelum ada peringkat
- Book BindDokumen79 halamanBook BindFaye YturraldeBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory Experiment Control Systems EngineeringDokumen7 halamanLaboratory Experiment Control Systems EngineeringFaye YturraldeBelum ada peringkat
- Logic Circuits and Switching Theory (Laboratory Manual)Dokumen103 halamanLogic Circuits and Switching Theory (Laboratory Manual)Faye Yturralde50% (2)
- PRBS GenerationDokumen10 halamanPRBS GenerationFaye YturraldeBelum ada peringkat
- Eye PatternDokumen7 halamanEye PatternFaye YturraldeBelum ada peringkat
- 1DS20LVS04 1DS20LVS010 Aat-3Dokumen12 halaman1DS20LVS04 1DS20LVS010 Aat-3Sanjay GowdaBelum ada peringkat
- EE537-Spring 2020 Digital Integrated Circuit Design Instructor: Engr. Dr. Nasir MohyuddinDokumen2 halamanEE537-Spring 2020 Digital Integrated Circuit Design Instructor: Engr. Dr. Nasir Mohyuddinuzair ahmadBelum ada peringkat
- Final ExamDokumen14 halamanFinal Exam한지원Belum ada peringkat
- Clipper CircuitsDokumen9 halamanClipper CircuitsMitali SinghBelum ada peringkat
- 74HC373 PhilipsDokumen26 halaman74HC373 Philipsfausto rodolfo yáñez páezBelum ada peringkat
- s9014 Datasheet PDFDokumen1 halamans9014 Datasheet PDFEduardoEj-DjOlaecheaBelum ada peringkat
- GMT Marking Codes (Ver2)Dokumen45 halamanGMT Marking Codes (Ver2)David SimonBelum ada peringkat
- RLC Circuits PDFDokumen4 halamanRLC Circuits PDFtuvvacBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 Diode CircuitsDokumen140 halamanChapter 4 Diode Circuitsshubhankar palBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Sheet 1 (DC Networks & Transients)Dokumen2 halamanTutorial Sheet 1 (DC Networks & Transients)Mr NobodyBelum ada peringkat
- Post Lab Report 05 (2019-2-80-011)Dokumen5 halamanPost Lab Report 05 (2019-2-80-011)Mohammad Fahim NurBelum ada peringkat
- Icl7660 PDFDokumen11 halamanIcl7660 PDFfran01334Belum ada peringkat
- Mini 360Dokumen6 halamanMini 360Revandra BeniBelum ada peringkat
- CS302 Collection of Old PapersDokumen48 halamanCS302 Collection of Old Paperscs619finalproject.comBelum ada peringkat
- G6 Series and Parallel CircuitsDokumen11 halamanG6 Series and Parallel CircuitsOtenciano MautganonBelum ada peringkat
- LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904 Low Power Dual Operational AmplifiersDokumen23 halamanLM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904 Low Power Dual Operational AmplifiersMoch Bin H. FauziBelum ada peringkat
- Op Amp DesignDokumen23 halamanOp Amp DesignAsihBelum ada peringkat
- Switching Characteristics of Power Devices: The Save Operating Area (SOA)Dokumen8 halamanSwitching Characteristics of Power Devices: The Save Operating Area (SOA)Shubham SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- Pe-Day 8 Commutation CircuitsDokumen25 halamanPe-Day 8 Commutation CircuitsS.Dhandayuthapani SundaramoorthyBelum ada peringkat
- LED Lamp Dimmer CircuitDokumen3 halamanLED Lamp Dimmer CircuitashishBelum ada peringkat
- Pre-Tutorial Assignment: Department of Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Iit GuwahatiDokumen3 halamanPre-Tutorial Assignment: Department of Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Iit GuwahatiArhita KunduBelum ada peringkat
- CS302 2005 2010 Midterm - Solved - MEGA FILEDokumen91 halamanCS302 2005 2010 Midterm - Solved - MEGA FILEAli QureshiBelum ada peringkat
- Ciruit Theory-Eee-Part A Univ - QuestionsDokumen43 halamanCiruit Theory-Eee-Part A Univ - QuestionsnavaneethangcebBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 2 - Nodal AnalysisDokumen27 halamanLecture 2 - Nodal Analysisfedhatom16Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 9Dokumen27 halamanChapter 9hessa 2001Belum ada peringkat
- A Fully-Differential Operational Amplifier Using A New Chopping Technique and Low-Voltage Input DevicesDokumen4 halamanA Fully-Differential Operational Amplifier Using A New Chopping Technique and Low-Voltage Input DevicesBerk AsBelum ada peringkat
- Get PDF3Dokumen11 halamanGet PDF3api-19755952Belum ada peringkat
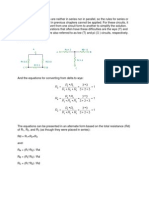
- Wye To Delta and Delta To Wye ConversionDokumen7 halamanWye To Delta and Delta To Wye Conversionrajsathia99Belum ada peringkat
- University of Engineering and Technology Electrical Technology Lab Experiment # 10: Norton's TheoremDokumen3 halamanUniversity of Engineering and Technology Electrical Technology Lab Experiment # 10: Norton's TheoremMuhammad AliBelum ada peringkat