Chapter 9 Exam
Diunggah oleh
raw4rillJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 9 Exam
Diunggah oleh
raw4rillHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 9 testbank SHORT ANSWER.
Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
Figure 9.1 Using Figure 9.1, match the following:
1) Endomysium. 2) Fascicle. 3) The tissue that binds muscles into functional groups. 4) Perimysium. 5) Muscle fiber.
1) 2) 3) 4) 5)
Figure 9.2 Using Figure 9.2, match the following:
6) I band. 7) H zone. 8) A band. 9) Z disc. 10) M line TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 11) Once a motor neuron has fired, all the muscle fibers in a muscle contract.
6) 7) 8) 9) 10)
11) 12)
12) The thin filaments (actin) contain a polypeptide subunit G actin that bear active sites for myosin attachment. 13) The force of muscle contraction is controlled by multiple motor unit summation or recruitment. 14) A motor neuron and all the muscle cells that it stimulates are referred to as a motor end plate. 15) Peristalsis is characteristic of smooth muscle.
13) 14) 15)
16) One of the important functions of skeletal muscle contraction is production of heat. 17) Oxygen debt refers to the oxygen required to make creatine phosphate. 18) Muscle contraction will always promote movement of body parts regardless of how they are attached. 19) Although there are no sarcomeres, smooth muscle still possesses thick and thin filaments. 20) Whereas skeletal muscle cells are electrically coupled, smooth muscle cells appear to be chemically coupled by gap junctions. 21) Single-unit smooth muscle is found in the intestines. 22) A resting potential is caused by a difference in the concentration of certain ions inside and outside the cell. 23) The effect of a neurotransmitter on the muscle cell membrane is to modify its ion permeability properties temporarily. 24) When a muscle fiber contracts, the I bands diminish in size, the H zones disappear, and the A bands move closer together but do not diminish in length. 25) The more slowly a skeletal muscle is stimulated, the greater its exerted force becomes. 26) Contractures are a result of a total lack of ATP. 27) Smooth muscles relax when intracellular Ca2+ levels drop but may not cease contractions. 28) Recruitment is an option in a single-unit smooth muscle cell. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 29) Most muscles contain ________. A) a predominance of slow oxidative fibers C) muscle fibers of the same type B) a mixture of fiber types D) a predominance of fast oxidative fibers
16) 17) 18)
19) 20)
21) 22)
23)
24)
25) 26) 27) 28)
29)
30) Fatigued muscle cells that recover rapidly are the products of ________. A) slow exercise of long duration C) intense exercise of short duration B) intense exercise of long duration D) slow exercise of short duration
30)
31) The strongest muscle contractions are normally achieved by ________. A) recruiting small and medium muscle fibers B) increasing stimulus above the threshold C) increasing the stimulation up to the maximal stimulus D) increasing stimulus above the treppe stimulus 32) Which of the following is not a usual result of resistance exercise? A) increase in the efficiency of the circulatory system B) increase in the number of myofibrils within the muscle cells C) increase in the number of muscle cells D) increase in the efficiency of the respiratory system 33) In skeletal muscle contraction, calcium apparently acts to ________. A) cause ATP to bind to actin B) remove the blocking action of tropomyosin C) increase the action potential transmitted along the sarcolemma D) release the inhibition on Z discs 34) Calcium ions bind to the ________ molecule in skeletal muscle cells. A) tropomyosin 35) Myoglobin ________. A) produces the end plate potential B) is a protein involved in the direct phosphorylation of ADP C) stores oxygen in muscle cells D) breaks down glycogen 36) An elaborate network of membranes in skeletal muscle cells that functions in calcium storage is the ________. A) myofibrillar network C) sarcoplasmic reticulum 37) A sarcomere is ________. A) the area between two intercalated discs B) the nonfunctional unit of skeletal muscle C) the area between two Z discs D) the wavy lines on the cell seen in the microscope B) mitochondria D) intermediate filament network B) troponin C) myosin D) actin
31)
32)
33)
34)
35)
36)
37)
38) Immediately following the arrival of the stimulus at a skeletal muscle cell there is a short period called the ________ period during which the events of excitation-contraction coupling occur. A) contraction B) latent C) relaxation D) refractory
38)
39) Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by ________. A) storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP B) forming a chemical compound with actin C) forming a temporary chemical compound with myosin D) inducing a conformational change in the myofilaments 40) After nervous stimulation of the muscle cell has ceased, the calcium ________. A) is chemically bound to the filaments B) level in the cytoplasm drops C) is destroyed by cholinesterase D) is actively pumped into the extracellular fluid for storage until the next contraction 41) The major function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle contraction is to ________. A) synthesize actin and myosin myofilaments B) regulate intracellular calcium concentration C) provide a source of myosin for the contraction process D) make and store phosphocreatine 42) The striations of a skeletal muscle cell are produced, for the most part, by ________. A) the sarcoplasmic reticulum B) a difference in the thickness of the sarcolemma C) the arrangement of myofilaments D) the T tubules 43) Which of the following are composed of myosin? A) Z discs C) thick filaments B) all myofilaments D) thin filaments
39)
40)
41)
42)
43)
44) During muscle contraction, myosin cross bridges attach to which active sites? A) myosin filaments C) Z discs B) thick filaments D) actin filaments
44)
45) Which of the following surrounds the individual muscle cell? A) epimysium B) fascicle 5 C) endomysium D) perimysium
45)
46) Smooth muscles that act like skeletal muscles but are controlled by autonomic nerves and hormones are ________. A) red muscles C) single-unit muscles 47) Rigor mortis occurs because ________. A) sodium ions leak out of the muscle B) the cells are dead C) proteins are beginning to break down, thus preventing a flow of calcium ions D) no ATP is available to release attached actin and myosin molecules 48) Which of the following does not act as a stimulus to initiate a muscle contraction? A) hormonal activity C) neurotransmitters 49) The term aponeurosis refers to ________. A) the rough endoplasmic reticulum B) the tropomyosin-troponin complex C) a sheetlike indirect attachment to a skeletal element D) the bands of myofibrils 50) The oxygen-binding protein found in muscle cells is ________. A) ATP B) myoglobin C) immunoglobin D) hemoglobin B) a change of temperature D) a change in the pH of a muscle B) white muscles D) multiunit muscles
46)
47)
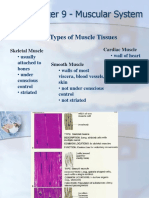
48)
49)
50)
51) The contractile units of skeletal muscles are ________. A) T tubules B) myofibrils C) mitochondria D) microtubules
51)
52) One functional unit of a skeletal muscle is ________. A) a myofilament C) a sarcomere 53) The functional role of the T tubules is to ________. A) synthesize ATP to provide energy for muscle contraction B) hold cross bridges in place in a resting muscle C) stabilize the G and F actin D) enhance cellular communication during muscle contraction B) a myofibril D) the sarcoplasmic reticulum
52)
53)
54) The role of calcium ions in muscle contraction is to ________. A) initiate the conversion of carbon dioxide to oxygen for storage B) act as a third messenger C) bind to regulatory sites on troponin, changing the configuration D) reestablish glycogen stores 55) During vigorous excercise, there may be insufficient oxygen available to completely break down pyruvic acid for energy. As a result, the pyruvic acid is converted to ________. A) lactic acid C) hydrochloric acid B) a strong base D) stearic acid
54)
55)
56) When a muscle is unable to respond to stimuli temporarily, it is in which of the following periods? A) relaxation period C) refractory period 57) The muscle cell membrane is called the ________. A) sarcolemma B) epimysium C) perimysium D) endomysium B) fatigue period D) latent period
56)
57)
58) Smooth muscle is significantly different from striated muscle in several ways. Which of the following is true? A) The fibers of smooth muscle are arranged quadrangularly. B) Smooth muscle is larger and more powerful than striated muscle. C) Smooth muscle contracts in a twisting way. D) Smooth muscle has transverse tubules. 59) The mechanism of contraction in smooth muscle is different from skeletal muscle in that ________. A) the site of calcium regulation differs B) ATP energizes the sliding process C) the trigger for contraction is a rise in intracellular calcium D) actin and myosin interact by the sliding filament mechanism 60) The cells of single-unit visceral muscle ________. A) are chemically coupled to one another by gap junctions B) exhibit spontaneous action potentials C) contract all at once D) consist of muscle fibers that are structurally independent of each other
58)
59)
60)
61) Smooth muscle is characterized by all of the following except ________. A) there are no sarcomeres B) there are more thick filaments than thin filaments C) it appears to lack troponin D) there are noncontractile intermediate filaments that attach to dense bodies within the cell 62) Which of the following statements is true? A) Cardiac muscle cells have many nuclei. B) Smooth muscle cells have T tubules. C) Cardiac muscle cells are found in the heart and large blood vessels. D) Striated muscle cells are long and cylindrical with many nuclei. 63) An anaerobic metabolic pathway that results in the production of two net ATPs per glucose plus two pyruvic acid molecules is ________. A) the citric acid cycle C) glycolysis 64) Muscle tone is ________. A) the condition of athletes after intensive training B) the ability of a muscle to efficiently cause skeletal movements C) a state of sustained partial contraction D) the feeling of well-being following exercise 65) The sliding filament model of contraction involves ________. A) actin and myosin shortening but not sliding past each other B) actin and myosin sliding past each other and partially overlap C) the Z discs sliding over the myofilaments D) the shortening of thick filaments so that thin filaments slide past 66) After nervous stimulation stops, ACh in the synaptic cleft is prevented from continuing stimulation of contraction by ________. A) the tropomyosin blocking the myosin once full contraction is achieved B) the action potential stopped going down the overloaded T tubules C) acetylcholinesterase destroying the ACh D) calcium ions returning to the terminal cisternae B) hydrolysis D) the electron transport chain
61)
62)
63)
64)
65)
66)
67) An individual has just ingested a chemical that binds irreversibly to the ACh receptors in the sarcolemma. By itself it does not alter membrane potential, yet prevents normal neurotransmitter binding. Ignoring the effects on any other system, the consequence to skeletal muscle would be ________. A) irreversible contraction as soon as the first nervous stimulation reached the sarcolemma B) contraction if stimulated by an external electrode C) no contraction at all by nervous mechanisms D) no contraction at all by nervous mechanisms, but contraction if stimulated by an external electrode SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 68) Only ________ muscle cells are alwyas multinucleated. 69) The end of the muscle that typically moves when a muscle contracts is called the ________. 70) In the synaptic cleft of a neuromuscular junction, an enzyme called ________ is always present. 71) The time in which cross bridges are active is called the period of ________. 72) ________ (color) fibers are slow (oxidative) fibers. 73) Only ________ muscle cells commonly branch. 74) A smooth, sustained contraction is called ________. 68) 69) 70)
67)
71) 72) 73) 74)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ch. 9 Student Packet (ANP 1)Dokumen7 halamanCh. 9 Student Packet (ANP 1)Alex Zhang100% (1)
- Muscle QuizDokumen10 halamanMuscle QuizFitzgerald PachecoBelum ada peringkat
- CH 7 Muscle Practice TestDokumen31 halamanCH 7 Muscle Practice TestAia MercBelum ada peringkat
- Part 4 Previous YearsDokumen21 halamanPart 4 Previous Yearsmohamed fakhryBelum ada peringkat
- Sense OrgansDokumen8 halamanSense OrgansKeelah BennBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Quiz On Muscular System: QuestionsDokumen2 halamanLecture Quiz On Muscular System: QuestionsCeline MillerBelum ada peringkat
- PHS MCQ Tutorials 200lDokumen4 halamanPHS MCQ Tutorials 200lcollinsmagBelum ada peringkat
- MCQs On GITDokumen3 halamanMCQs On GITsamuel waiswaBelum ada peringkat
- Histology Final ExamDokumen8 halamanHistology Final Examliz gamezBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ - Test 2Dokumen3 halamanMCQ - Test 2Gaurav SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Skeletal System QuizDokumen3 halamanSkeletal System QuizDANIEL LANCE NEVADOBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of Spinal CordDokumen3 halamanAnatomy of Spinal CordHamed SabryBelum ada peringkat
- Question BankDokumen1 halamanQuestion BankmanasBelum ada peringkat
- Lymphoid System MCQDokumen8 halamanLymphoid System MCQAbduladheemBelum ada peringkat
- Histology 2Dokumen1 halamanHistology 2zaydeeeeBelum ada peringkat
- 01 Anat GoldDokumen44 halaman01 Anat GoldNasser AlbaddaiBelum ada peringkat
- Cerebellum MCQ'S: A) Posterior LobeDokumen2 halamanCerebellum MCQ'S: A) Posterior LobeTahir AzizBelum ada peringkat
- Digestion and Absorption MCQsDokumen3 halamanDigestion and Absorption MCQsSeekerBelum ada peringkat
- Brachial Plexus Self QuizDokumen2 halamanBrachial Plexus Self Quizsan100% (1)
- Upper Limb Exercise - LamuDokumen2 halamanUpper Limb Exercise - LamuLem A SharBelum ada peringkat
- Tissue Exam QnsDokumen4 halamanTissue Exam Qnsvarsha thakurBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ 23 Physio AnswersDokumen8 halamanMCQ 23 Physio AnswersJulyhathul Kuraishi100% (1)
- C. Common Cardinal VeinsDokumen6 halamanC. Common Cardinal VeinsTofik MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Second Year ExamDokumen4 halamanSecond Year ExamSyamil AzharBelum ada peringkat
- Skeletal System ExamDokumen9 halamanSkeletal System ExamBijay Kumar Mahato100% (1)
- Abdomen OSPE Charts Questions OnlyDokumen29 halamanAbdomen OSPE Charts Questions OnlyRathnaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 SEMESTER 18/19: Median Nerve-Carpal Tunnel Weakens Lateral 3 Digits Sensory Loss ParalysisDokumen60 halaman1 SEMESTER 18/19: Median Nerve-Carpal Tunnel Weakens Lateral 3 Digits Sensory Loss ParalysisInsaf AhamedBelum ada peringkat
- Nervemuscle MCQDokumen9 halamanNervemuscle MCQNishanthy PirabakarBelum ada peringkat
- Phsio EXITABLEDokumen12 halamanPhsio EXITABLEmohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 Embryo Q and A ModuleDokumen76 halamanUnit 1 Embryo Q and A ModuleBAYAN NADER YOSRI JABARI 22010404Belum ada peringkat
- Anatomy Final2edDokumen387 halamanAnatomy Final2edIsam SrourBelum ada peringkat
- Chaper 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone StructureDokumen25 halamanChaper 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone StructurelolasparkleBelum ada peringkat
- Thecytoskeleton PPTDokumen11 halamanThecytoskeleton PPTseenu mohapatraBelum ada peringkat
- Section-I Mcqs and SeqsDokumen3 halamanSection-I Mcqs and SeqsSadia NasirBelum ada peringkat
- MCQs & QUs On Fsirst Year First ComDokumen74 halamanMCQs & QUs On Fsirst Year First Commaisara10Belum ada peringkat
- Histology-World! Histology Testbank-Nervous System 1Dokumen3 halamanHistology-World! Histology Testbank-Nervous System 1Kat JornadalBelum ada peringkat
- Ch. 3 Tissues Test: NameDokumen5 halamanCh. 3 Tissues Test: Namestephanieyoung07Belum ada peringkat
- Anatomy 2020 LLDokumen12 halamanAnatomy 2020 LLjhom smith100% (1)
- SMS..exam 1Dokumen8 halamanSMS..exam 1Ozgan SüleymanBelum ada peringkat
- MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (Select The Single Best Answer)Dokumen6 halamanMULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (Select The Single Best Answer)Layo Fatola100% (1)
- Embryo QuestionsDokumen15 halamanEmbryo QuestionsAnon AnonBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy PPR Final 1st Sem-1-2Dokumen5 halamanAnatomy PPR Final 1st Sem-1-2afzal sulemaniBelum ada peringkat
- Feb-2021-Paper IDokumen2 halamanFeb-2021-Paper ITouseefBelum ada peringkat
- Pop Quiz Nervous SystemDokumen5 halamanPop Quiz Nervous Systemapi-242868690100% (1)
- Physiology Essays & Shorts Topic WiseDokumen18 halamanPhysiology Essays & Shorts Topic Wisekoutharapu lasyapriyankaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 12 Muscle Physiology - Important Questions: 6. Mechanism of Muscle ContractionDokumen7 halamanChapter 12 Muscle Physiology - Important Questions: 6. Mechanism of Muscle ContractionIrum RafeeqBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy Notes Week3Dokumen18 halamanAnatomy Notes Week3Zainab Ali100% (1)
- Assessment in CNS and Senses PhysiologyDokumen6 halamanAssessment in CNS and Senses PhysiologyEdgar MandengBelum ada peringkat
- Neuroanatomy 2nd Year Topical Past Papers 2005-22Dokumen4 halamanNeuroanatomy 2nd Year Topical Past Papers 2005-22HussnainBelum ada peringkat
- B 10 Ctsta 831Dokumen6 halamanB 10 Ctsta 831Andhi SoesiloBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Anatomy Questions PDFDokumen63 halamanAdvanced Anatomy Questions PDFJoanne BlancoBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System Grade 6 ReviewerDokumen12 halamanNervous System Grade 6 ReviewerGee ZBelum ada peringkat
- Ch05 Answer Key-TissuesDokumen10 halamanCh05 Answer Key-TissuesGaveen CoatesBelum ada peringkat
- Excitable Tissues: DR Joseph WabwireDokumen38 halamanExcitable Tissues: DR Joseph WabwireJoseph WabwireBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Exams PDFDokumen143 halaman2nd Exams PDFahmed yousefBelum ada peringkat
- Key of SEQs Heart, Nerve and Muscle Revision TestDokumen11 halamanKey of SEQs Heart, Nerve and Muscle Revision TestMudassar Roomi100% (2)
- 47 MCQs On GI and Nutrition PhysiologyDokumen14 halaman47 MCQs On GI and Nutrition Physiologyrazsubedi100% (1)
- Biology, 7e (Campbell) : Chapter 41: Animal NutritionDokumen7 halamanBiology, 7e (Campbell) : Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition123456789123456789hiBelum ada peringkat
- Concepts in Biochemistry2Dokumen38 halamanConcepts in Biochemistry2atefmaboodBelum ada peringkat
- The Muscular System: © 2011 The Mcgraw Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedDokumen67 halamanThe Muscular System: © 2011 The Mcgraw Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedJoanna PoshnjaBelum ada peringkat
- Structure of Skeletal MuscleDokumen12 halamanStructure of Skeletal MuscledilsharakaviBelum ada peringkat
- AIIMS June 2002 PG Entrance Question Paper With Answer KeyDokumen23 halamanAIIMS June 2002 PG Entrance Question Paper With Answer KeywithraviBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetes and Hypertension Physiopathology and Therapeutics: Journal of Human Hypertension May 2000Dokumen7 halamanDiabetes and Hypertension Physiopathology and Therapeutics: Journal of Human Hypertension May 2000chandra9000Belum ada peringkat
- ANP 1105 Blood VesselsDokumen72 halamanANP 1105 Blood VesselsMathios TigerosBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology Notes For Exam 3Dokumen58 halamanAnatomy and Physiology Notes For Exam 3mike921gold100% (2)
- Glenco Health CH 14 l2Dokumen4 halamanGlenco Health CH 14 l2Henry TalackoBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Cardiology For The USMLE and General Medics PDFDokumen287 halamanFundamentals of Cardiology For The USMLE and General Medics PDFCharles Vindo100% (2)
- Vitamin B ComplexDokumen3 halamanVitamin B Complexjoseph_delacruz20Belum ada peringkat
- IVMS Cell Biology and Pathology Flash Facts IDokumen4.999 halamanIVMS Cell Biology and Pathology Flash Facts IMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.0% (2)
- Dotaverine HCLDokumen5 halamanDotaverine HCLalbertsmasudoBelum ada peringkat
- General Principles of GIT PhysiologyDokumen22 halamanGeneral Principles of GIT PhysiologyUsman Ali AkbarBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology of Labor: Ribkhi Amalia Putri Ganot SumulyoDokumen48 halamanPhysiology of Labor: Ribkhi Amalia Putri Ganot SumulyoImelda AtikaBelum ada peringkat
- PlanteDokumen452 halamanPlantePopa FlorinBelum ada peringkat
- Types of ReceptorsDokumen78 halamanTypes of ReceptorsDrPallavi DBelum ada peringkat
- BIOL 2401 Human Anatomy - Phys I - 7.4-7.5 Muscle PhysiologyDokumen20 halamanBIOL 2401 Human Anatomy - Phys I - 7.4-7.5 Muscle PhysiologyKevin WhitesideBelum ada peringkat
- Perinatology Clinics 2008, Vol.35, Issues 4, Neuroprotection in The NewbornDokumen210 halamanPerinatology Clinics 2008, Vol.35, Issues 4, Neuroprotection in The NewbornJhonny MarquezBelum ada peringkat
- Erectile Dysfunction: Management Update: Review SynthèseDokumen9 halamanErectile Dysfunction: Management Update: Review SynthèseAditya Villas-BoasBelum ada peringkat
- Compliance and ResistanceDokumen5 halamanCompliance and ResistanceNissie DegulacionBelum ada peringkat
- Inotropes and VasopressorsDokumen56 halamanInotropes and VasopressorsMuhammad Ali Yousuf100% (6)
- HipertensiuneDokumen9 halamanHipertensiuneCosmin CalanciaBelum ada peringkat
- Smooth and Cardiac MusclesDokumen55 halamanSmooth and Cardiac MusclesIni UsenBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 12 - Muscular SystemDokumen73 halamanBab 12 - Muscular SystemDaeng FarahnazBelum ada peringkat
- ANS Pharmacology-Cholinergic AgentsDokumen55 halamanANS Pharmacology-Cholinergic AgentsMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.Belum ada peringkat
- Anatomy MusclesDokumen76 halamanAnatomy MusclesMathios TigerosBelum ada peringkat
- First Periodical TestDokumen4 halamanFirst Periodical TestLyn Garcia67% (3)
- Lec6 - Circulatory SystemDokumen4 halamanLec6 - Circulatory SystemEloisa Trina GenerosoBelum ada peringkat
- Group VII - Smooth Muscle ContractionDokumen7 halamanGroup VII - Smooth Muscle ContractioniqbalBelum ada peringkat
- EMG Lab Simple Muscle TwitchDokumen8 halamanEMG Lab Simple Muscle TwitchShauki AliBelum ada peringkat