Name of Drug: Gabapentin: Drug Class Therapeutic Actions
Diunggah oleh
Cecile EstebanDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Name of Drug: Gabapentin: Drug Class Therapeutic Actions
Diunggah oleh
Cecile EstebanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
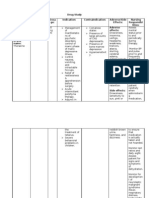
Name of Drug: Gabapentin
Drug class
Nursing considerations
Assessment
Antiepileptic
Therapeutic actions
Mechanism of action not understood; antiepileptic activity may be related to its ability to inhibit polysynaptic responses and block posttetanic potentiation.
Indications
History: Hypersensitivity to gabapentin; lactation, pregnancy Physical: Weight; T; skin color, lesions; orientation, affect, reflexes; P; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, normal output
Interventions
Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures with and without secondary generalization in adults and children 312 yr with epilepsy Orphan drug use: Treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Management of postherpetic neuralgia or pain in the area affected by herpes zoster after the disease has been treated Unlabeled uses: Hot flashes, neuropathic pain
Give drug with food to prevent GI upset. Be aware that patient may be at increased risk for suicidality; monitor accordingly. Arrange for consultation with support groups for people with epilepsy. Warning If overdose occurs, hemodialysis may be an option.
Teaching points
Contraindications and cautions
Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to gabapentin. Use cautiously with pregnancy, lactation.
Adverse effects
CNS: Dizziness, insomnia, nervousness, fatigue, somnolence, ataxia, diplopia, tremor Dermatologic: Pruritus, abrasion GI: Dyspepsia, vomiting, nausea, constipation, dry mouth, diarrhea Respiratory: Rhinitis, pharyngitis Other: Weight gain, facial edema, cancer, impotence, suicidal ideation
Take this drug exactly as prescribed; do not discontinue abruptly or change dosage, except on the advice of your health care provider. Wear a medical alert ID at all times so that any emergency medical personnel will know that you have epilepsy and are taking antiepileptic medication. You may experience these side effects: Dizziness, blurred vision (avoid driving or performing other tasks requiring alertness or visual acuity); GI upset (take drug with food or milk, eat frequent small meals); headache, nervousness, insomnia; fatigue (periodic rest periods may help). Report severe headache, sleepwalking, rash, severe vomiting, chills, fever, difficulty breathing, thoughts of suicide.
Name of Drug: Polynerv
Drug class
Nursing considerations
Assessment
Antiepileptic
Therapeutic actions
Mechanism of action not understood; antiepileptic activity may be related to its ability to inhibit polysynaptic responses and block posttetanic potentiation.
Indications
History: Hypersensitivity to gabapentin; lactation, pregnancy Physical: Weight; T; skin color, lesions; orientation, affect, reflexes; P; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, normal output
Interventions
Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures with and without secondary generalization in adults and children 312 yr with epilepsy Orphan drug use: Treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Management of postherpetic neuralgia or pain in the area affected by herpes zoster after the disease has been treated Unlabeled uses: Hot flashes, neuropathic pain
Give drug with food to prevent GI upset. Be aware that patient may be at increased risk for suicidality; monitor accordingly. Arrange for consultation with support groups for people with epilepsy. Warning If overdose occurs, hemodialysis may be an option.
Teaching points
Contraindications and cautions
Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to gabapentin. Use cautiously with pregnancy, lactation.
Adverse effects
CNS: Dizziness, insomnia, nervousness, fatigue, somnolence, ataxia, diplopia, tremor Dermatologic: Pruritus, abrasion GI: Dyspepsia, vomiting, nausea, constipation, dry mouth, diarrhea Respiratory: Rhinitis, pharyngitis Other: Weight gain, facial edema, cancer, impotence, suicidal ideation
Take this drug exactly as prescribed; do not discontinue abruptly or change dosage, except on the advice of your health care provider. Wear a medical alert ID at all times so that any emergency medical personnel will know that you have epilepsy and are taking antiepileptic medication. You may experience these side effects: Dizziness, blurred vision (avoid driving or performing other tasks requiring alertness or visual acuity); GI upset (take drug with food or milk, eat frequent small meals); headache, nervousness, insomnia; fatigue (periodic rest periods may help). Report severe headache, sleepwalking, rash, severe vomiting, chills, fever, difficulty breathing, thoughts of suicide.
Manufacturer Distributor Contents Indications
S V More S V More Vit B1 250 mg, vit B6 250 mg, vit B12 1,000 mcg Neuritis, polyneuritis, lumbago, cervical & shoulder-arm syndrome, rheumatic pains, herpes zoster, alcoholism, cardiac disorders, diabetic neuropathy, hyperemesis gravidarum, encephalopathies, iatrogenic complications arising from INH, reserpine or phenothiazines. Prophylaxis 1-2 tab daily. Therapeutic 2-4 tab daily. May be taken with or without food. May be taken w/ meals to reduce GI discomfort. Vitamin B-Complex / with C A11DB - Vitamin B1 in combination with vitamin B6 and/or vitamin B12 ; Used as dietary supplements.
Dosage Administration MIMS Class ATC Classification
B-complex consists of eight different vitamins, which include thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5), piroxidine (B6), folic acid (B9), cyanocobalamin (B12), and biotin. All of the above are water soluble, and play a key role in several bodily functions, such as protein, fat, carbohydrate, and mitochondrial energy metabolism; maintenance of the liver, skin, hair, mouth, and eyes; plus so much more, which will be covered thoroughly within the following paragraphs. As mentioned above, vitamin b complex can be further broken down in to 3 general categories; that is, energy releasing, hematopoietic, or other.
Name of Drug: Diphenhydramine HCl
Drug classes
Contraindications and cautions
Antihistamine Antimotion-sickness drug Antiparkinsonian Cough suppressant Sedative-hypnotic
Therapeutic actions
Contraindicated with allergy to antihistamines, third trimester of pregnancy, lactation. Use cautiously with narrow-angle glaucoma, stenosing peptic ulcer, symptomatic prostatic hypertrophy, asthmatic attack, bladder neck obstruction, pyloroduodenal obstruction, pregnancy; elderly patients who may be sensitive to anticholinergic effects.
Competitively blocks the effects of histamine at H1-receptor sites, has atropine-like, antipruritic, and sedative effects.
Indications
Adverse effects
Relief of symptoms associated with perennial and seasonal allergic rhinitis; vasomotor rhinitis; allergic conjunctivitis; mild, uncomplicated urticaria and angioedema; amelioration of allergic reactions to blood or plasma; dermatographism; adjunctive therapy in anaphylactic reactions Active and prophylactic treatment of motion sickness Nighttime sleep aid Parkinsonism (including drug-induced parkinsonism and extrapyramidal reactions), in the elderly intolerant of more potent drugs, for milder forms of the disorder in other age-groups, and in combination with centrally acting anticholinergic antiparkinsonian drugs Syrup formulation: Suppression of cough due to colds or allergy
CNS: Drowsiness, sedation, dizziness, disturbed coordination, fatigue, confusion, restlessness, excitation, nervousness, tremor, headache, blurred vision, diplopia CV: Hypotension, palpitations, bradycardia, tachycardia, extrasystoles
Teaching points
Take as prescribed; avoid excessive dosage. Take with food if GI upset occurs. Avoid alcohol; serious sedation could occur. These side effects may occur: Dizziness, sedation, drowsiness (use caution driving or performing tasks requiring alertness); epigastric distress, diarrhea or constipation (take drug with meals); dry mouth (use frequent mouth care, suck sugarless lozenges); thickening of bronchial secretions, dryness of nasal mucosa (use a humidifier). Report difficulty breathing, hallucinations, tremors, loss of coordination, unusual bleeding or bruising, visual disturbances, irregular heartbeat.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesDari EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- Ncp&drugstudDokumen12 halamanNcp&drugstudSarah Mae Billano BermudezBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcDari EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcBelum ada peringkat
- Name of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolDokumen7 halamanName of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolAnne Monique Moran OngjocoBelum ada peringkat
- Zyprexa: Generic Name: OlanzapineDokumen3 halamanZyprexa: Generic Name: Olanzapinenasir khanBelum ada peringkat
- DiphenhydramineDokumen5 halamanDiphenhydramineShyrra Edades PinderBelum ada peringkat
- Pharma Cards.Dokumen19 halamanPharma Cards.Brent NicholsBelum ada peringkat
- DiazepamDokumen2 halamanDiazepamiesh07Belum ada peringkat
- Clinical Medication ListDokumen181 halamanClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Psych Drug StudyDokumen5 halamanPsych Drug StudyLorina Lynne Apelacio100% (4)
- Zolpidem TartrateDokumen2 halamanZolpidem Tartrateapi-3797941Belum ada peringkat
- NalbuphineDokumen5 halamanNalbuphineGab PagalilauanBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Analysis (RN) - 3Dokumen9 halamanDrug Analysis (RN) - 3Joannalyn Libo-on0% (1)
- CLOZAPINEDokumen5 halamanCLOZAPINEMar OrdanzaBelum ada peringkat
- ANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Dokumen5 halamanANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Rhanne BolanteBelum ada peringkat
- 1.) Generic Name: Gabapentin Brand Name Classification Dosage Route and Frequency Mechanism of ActionDokumen15 halaman1.) Generic Name: Gabapentin Brand Name Classification Dosage Route and Frequency Mechanism of ActionTyron ChuaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen24 halamanDrug StudyMc Joewell HudencialBelum ada peringkat
- PerindoprilDokumen3 halamanPerindoprilWeng Maesa MontemayorBelum ada peringkat
- Pentazine, Phenazine, Phencen,, Phenoject-50, Prometh, Prorex, Prothazine, V-GanDokumen34 halamanPentazine, Phenazine, Phencen,, Phenoject-50, Prometh, Prorex, Prothazine, V-GankotonashiBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen12 halamanDrug StudyMeraflor BahonsuaBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDokumen7 halamanPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen19 halamanDrug StudyCzarinah Ela MesiasBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Cards BarryDokumen6 halamanDrug Cards BarryJessica Lynn DyeBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanDrug StudyKristine Faith AzcuetaBelum ada peringkat
- ClonazepamDokumen3 halamanClonazepamapi-3797941Belum ada peringkat
- NCP DrugDokumen13 halamanNCP DrugMhar CamposanoBelum ada peringkat
- Chlorpheniramine MaleateDokumen3 halamanChlorpheniramine Maleateapi-3797941100% (1)
- C C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentDokumen12 halamanC C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentEarl Tony TrinidadBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study-Grand Case PresDokumen8 halamanDrug Study-Grand Case PresLorina Lynne ApelacioBelum ada peringkat
- Name of Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Ampicillin Sulbactam GI: Diarrhea, NauseaDokumen10 halamanName of Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Ampicillin Sulbactam GI: Diarrhea, NauseaVictor BiñasBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Name Indication Contraindication Drug Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: Route and DosageDokumen6 halamanDrug Name Indication Contraindication Drug Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: Route and Dosageسبوكاي100% (1)
- Therapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicDokumen37 halamanTherapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicApple MaeBelum ada peringkat
- Psychia Drug StudyDokumen11 halamanPsychia Drug StudyJustin 葉志明 Yap Delapaz100% (1)
- Drug Study OrthoDokumen4 halamanDrug Study OrthoJhessa Curie Pitagan100% (1)
- Dizziness Low Blood Pressure Triglycerides Blood Cholesterol EPS Dry MouthDokumen2 halamanDizziness Low Blood Pressure Triglycerides Blood Cholesterol EPS Dry MouthMill Jan CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study HaldolDokumen2 halamanDrug Study HaldolGracia EvangelistaBelum ada peringkat
- Drugstudy and SoapieDokumen17 halamanDrugstudy and SoapieYasi EcheniqueBelum ada peringkat
- LM, KLDokumen5 halamanLM, KLVictor CondeBelum ada peringkat
- Drug-Study-Po (1) EwesdfdsfdsfsddsfdsfdsDokumen14 halamanDrug-Study-Po (1) EwesdfdsfdsfsddsfdsfdsIbrahim RegachoBelum ada peringkat
- 1ST Drug StudyDokumen10 halaman1ST Drug Study황춘히Belum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen6 halamanDrug StudyGracie S. VergaraBelum ada peringkat
- Clorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Dokumen2 halamanClorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888Belum ada peringkat
- Di Query 6Dokumen4 halamanDi Query 6uneesolutionsBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudiesDokumen4 halamanDrug StudiesgyantuazonBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen9 halamanDrug StudyShane Arroyo100% (1)
- NCM106 - Pharmacology: History: Hypersensitivity To Hydantoins, History of SinusDokumen2 halamanNCM106 - Pharmacology: History: Hypersensitivity To Hydantoins, History of SinusBrandy RectoBelum ada peringkat
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDokumen11 halamanName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen7 halamanDrug StudyMariCris CaronanBelum ada peringkat
- Montelukast SodiumDokumen2 halamanMontelukast Sodiumapi-3797941100% (2)
- AntitussiveDokumen7 halamanAntitussiveCucumber WarriorBelum ada peringkat
- Generic Name Captopril Brand NamesDokumen18 halamanGeneric Name Captopril Brand NamesAiko Villacortes100% (1)
- PantoprazoleDokumen3 halamanPantoprazoleapi-3797941Belum ada peringkat
- Drugs For Substances AbuseDokumen4 halamanDrugs For Substances AbuseAriadne MangondatoBelum ada peringkat
- Sertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of ActionDokumen11 halamanSertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of Actionkarl montanoBelum ada peringkat
- Week 13 Drug CardsDokumen5 halamanWeek 13 Drug CardsPRECIOUS wardBelum ada peringkat
- prepworkCynthiaPerkins HaleyVestDokumen5 halamanprepworkCynthiaPerkins HaleyVestHaley Vest MustaficBelum ada peringkat
- RisperidoneDokumen3 halamanRisperidoneapi-3797941Belum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanDrug Studyanon_11638632Belum ada peringkat
- Sandomigran PiDokumen6 halamanSandomigran PiNexi anessaBelum ada peringkat
- CVA Drug StudyDokumen51 halamanCVA Drug StudyKarel LuBelum ada peringkat
- Disaster Action Plan of Sitio Labey and Hilltop, Ambuklao, Bokod, BenguetDokumen3 halamanDisaster Action Plan of Sitio Labey and Hilltop, Ambuklao, Bokod, BenguetCecile EstebanBelum ada peringkat
- Zombie AlligatorDokumen4 halamanZombie AlligatorCecile Esteban100% (2)
- References To Tables or Figures Are From The TextDokumen18 halamanReferences To Tables or Figures Are From The TextCecile EstebanBelum ada peringkat
- Matthias Rath Cancer Book - Vitamin C and Lysine For Cancer TreatmentDokumen40 halamanMatthias Rath Cancer Book - Vitamin C and Lysine For Cancer TreatmentEbook PDF100% (3)
- ArticleDokumen9 halamanArticleCecile EstebanBelum ada peringkat
- Binary StarsDokumen20 halamanBinary StarsCecile EstebanBelum ada peringkat
- Dental AuxillaryDokumen125 halamanDental AuxillaryAME DENTAL COLLEGE RAICHUR, KARNATAKABelum ada peringkat
- Acute Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDokumen58 halamanAcute Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisALI MUMTAZBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage/ Route Indication/ Contraindication Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokumen1 halamanDrug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage/ Route Indication/ Contraindication Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesLowell AgustinBelum ada peringkat
- HPWJ Medical Alert Card SampleDokumen2 halamanHPWJ Medical Alert Card SampleSameer Kumar JubailBelum ada peringkat
- Multi-Speciality HospitalDokumen30 halamanMulti-Speciality Hospitaltushar rautray100% (1)
- XII - Zool Ch4 REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH Hsslive PDFDokumen4 halamanXII - Zool Ch4 REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH Hsslive PDFPrituBelum ada peringkat
- YALE BROWN-TOC en Niños - Confiabilidad y ValidezDokumen7 halamanYALE BROWN-TOC en Niños - Confiabilidad y ValidezLaura Brondo100% (1)
- 2011Dokumen45 halaman2011jimmyBelum ada peringkat
- MOH-National Antimicrobial GuidelinesDokumen65 halamanMOH-National Antimicrobial GuidelinesHamada Hassan AlloqBelum ada peringkat
- Malnutrition in Older AdultsDokumen44 halamanMalnutrition in Older Adultsjohnjoe subaynoBelum ada peringkat
- Adult Dehydration Guideline Final 2015Dokumen3 halamanAdult Dehydration Guideline Final 2015Brillyant S RaintamaBelum ada peringkat
- Verrucous CarcinomaDokumen12 halamanVerrucous Carcinomaanatomimanusia100% (1)
- Big IdeaDokumen11 halamanBig IdeaSuyash MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Asiri Health Intermediate Care Centre: For Covid 19 Patients Siddhalepa Anarva Hotel A 4 Star, 100 Room FacilityDokumen3 halamanAsiri Health Intermediate Care Centre: For Covid 19 Patients Siddhalepa Anarva Hotel A 4 Star, 100 Room FacilityThilanka NiroshanaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Two: 2. Literuture ReviewDokumen14 halamanChapter Two: 2. Literuture ReviewAhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Life Insurance Corporation of India Novel Coronavirus (Covid-19) Questionnaire (Revised Version - 5)Dokumen1 halamanLife Insurance Corporation of India Novel Coronavirus (Covid-19) Questionnaire (Revised Version - 5)பிரேம் முருகன்Belum ada peringkat
- 1238-Article Text-5203-1-10-20220916Dokumen3 halaman1238-Article Text-5203-1-10-20220916srirampharmBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Cap MRDokumen2 halamanNCP Cap MREngely Mercader100% (1)
- Dentistry: Bachelor of Dental Surgery BSC Oral Health SciencesDokumen5 halamanDentistry: Bachelor of Dental Surgery BSC Oral Health SciencesMaria AugustineBelum ada peringkat
- Hipertensi PBLDokumen56 halamanHipertensi PBLVandra PrinosaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan Breast CancerDokumen1 halamanNursing Care Plan Breast CancerAhmed SalahBelum ada peringkat
- DR Veronica Adetunji CVDokumen6 halamanDR Veronica Adetunji CVTobi OlanipekunBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 2 - Birth Spacing Policy in OmanDokumen39 halamanLab 2 - Birth Spacing Policy in OmanMeme 1234Belum ada peringkat
- Telepharmacy ResearchDokumen8 halamanTelepharmacy Researchugwuja marcyBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study Orientation SlidesDokumen88 halamanCase Study Orientation SlidesJoseph Emmanuel CandaBelum ada peringkat
- Minnesota Fall School Planning Guide - Minnesota Department of HealthDokumen16 halamanMinnesota Fall School Planning Guide - Minnesota Department of HealthPatch Minnesota100% (1)
- Oral SURGERY REVALIDA1Dokumen27 halamanOral SURGERY REVALIDA1Bea Y. Bas-ongBelum ada peringkat
- Curcumae: Dosen Pengampu: Rohima Robby, S.PD., M.PDDokumen14 halamanCurcumae: Dosen Pengampu: Rohima Robby, S.PD., M.PDRezkya HenantoBelum ada peringkat
- BMJOpen 2013 LerouxDokumen12 halamanBMJOpen 2013 LerouxadityaBelum ada peringkat
- Eating Disorders: by Pius KigamwaDokumen20 halamanEating Disorders: by Pius KigamwaRahul Kumar DiwakarBelum ada peringkat