Chapter 6 - A Tour of The Cell
Diunggah oleh
hannahkellumDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 6 - A Tour of The Cell
Diunggah oleh
hannahkellumHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
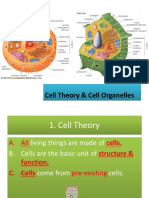
A tour of the Cell Chapter 6 I. Cells Fundamental units of life a. Shows all the properties of life i.
. They use DNA as hereditary material and for protein synthesis ii. Most cells reproduce iii. Transform matter to energy (metabolism) iv. Respond to their environment b. Major events in Cell Biology i. 1st microscope ii. Robert Hooke iii. Leewenhoek iv. Schleiden & Schwann v. 1st Transmission electron microsope Cell Theory (Schleiden & Schwann) a. All organissm are made of cells b. All life forms are made of one or more cells c. The cell is structural & functional uint of all living things d. All cells contain hereditary information e. All cells are basically the same in chemical compostion f. All energy flow of life occurs within cells Cell Size a. Cells are small (1-100 m3) with a few exceptions
II.
III.
IV. Observing cells a. Stereoscopic (dissection) b. Compound Light Microscope (LM) c. Electron Microscope i. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) ii. Transmission electron microscope (TEM) d. Cell Fractionation i. Technique used to study cell structure and function V. Cells can be unicellular a. Having or consisting of one single cell b. Examples i. Bacteria, amoeba
VI. Cells can be multicellular a. Having more than one cell, and having differentiated cells that perform specialized functions b. Examples
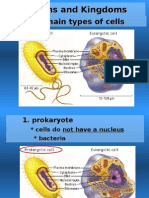
i. Humans, seals, Algae, etc.. VII. Cells Must exchange material with their environment a. Require a large surface area relative to volume VIII. Prokaryotes a. Represented by two Domains i. Bacteria ii. Archaea b. Characteristics i. Great diversity in forms of metabolism ii. Inhabit environmental extremes iii. Most Unicellular that forms chains, filaments or colonies iv. NO true nucleus 1. Nucleoid v. NO membrane bound organelles vi. Cytoplasm/cytosol vii. Plasma membrane viii. Most have a cell wall 1. Peptidoglycan ix. Characteristics present in MOST, but not all 1. Capsule 2. Flagella 3. Pili 4. Photosynthetic membranes IX. Eukaryotes a. Represented by one Domain (Eukarya) with four Kingdoms (Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia). b. Characterisitics i. True Nucleus ii. Membrane Bound organelles iii. Usually larger than prokaryotes iv. Cytoskeleton v. Cytoplasm/cytosol vi. Plasma membrane vii. Organelles structures that have specific shapes and functions 1. Nucleus 2. Ribosomes 3. Endomembrane System a. Endoplasmic reticulum i. Rough ER ii. Smooth ER b. Golgi Apparatus c. Lysosomes
4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
9.
d. Vacuoles i. Food vacuoles ii. Contractiles vacuoles iii. Central Vacuole Mitochondria Chloroplasts Peroxisomes Glyoxysomes Cytoskeleton a. Microfilaments b. Intermediate filaments c. Microtubules Extracellular Structures a. Cell wall of plants b. Extracellular matrix c. Intercellular junctions i. Plasmodesmata (plants) ii. Tight, desomsomes, & gap junctions (animals)
X.
Plant vs. Animal Cells a. What are the differences between the two? b. What are the similarities?
XI. Prokaryotes vs. Eukarytoes a. What are the differences between the two? b. What are the similarities?
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Angelyn M. Morales Beed A-1Dokumen7 halamanAngelyn M. Morales Beed A-1Angelyn MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction, Cell - HandoutDokumen1 halamanIntroduction, Cell - HandoutBillQueBelum ada peringkat
- SY20703 Molecular Cell Biology: (Prof. Madya Dr. Lee Ping Chin, Professor Room 69)Dokumen16 halamanSY20703 Molecular Cell Biology: (Prof. Madya Dr. Lee Ping Chin, Professor Room 69)Charles RajBelum ada peringkat
- Elizondo Cell Theory and Cell Organelles-UpdatedDokumen14 halamanElizondo Cell Theory and Cell Organelles-UpdatedRahanie Gadungan PajijiBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Biology Lecture 1 & 2 Sem I 2011-2012 Introduction To Cell Biology, Cell As The Basic Unit of Life SPINDokumen121 halamanCell Biology Lecture 1 & 2 Sem I 2011-2012 Introduction To Cell Biology, Cell As The Basic Unit of Life SPINPrimo Arc100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Intro To CellDokumen6 halamanChapter 1 Intro To CellrexartoozBelum ada peringkat
- CytologyDokumen59 halamanCytologyCla Nuval100% (1)
- Cell Parts and FunctionDokumen29 halamanCell Parts and Functionplayandhavefun23Belum ada peringkat
- Karp CH 1Dokumen17 halamanKarp CH 1mikadeguzman100% (1)
- ch01 EdDokumen12 halamanch01 EdJinette SurotBelum ada peringkat
- Science Gen EdDokumen17 halamanScience Gen EdDESSA EMBER ESPARESBelum ada peringkat
- Science General EducDokumen24 halamanScience General EducDESSA EMBER ESPARESBelum ada peringkat
- ch01 Ed PDFDokumen18 halamanch01 Ed PDFRachel CajilesBelum ada peringkat
- Cell 1Dokumen23 halamanCell 1Fatima Katrize GoudinBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry (Powerpoint PresentationDokumen39 halamanBiochemistry (Powerpoint PresentationAnonymous Person100% (1)
- Topic 1 Living Cells On-LineDokumen46 halamanTopic 1 Living Cells On-Lineadkin142119Belum ada peringkat
- Life and Cell-2014Dokumen65 halamanLife and Cell-2014Yosep Gita ErdinataBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 4 CellsDokumen9 halamanCHAPTER 4 CellsNadeem IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Summative Test Genbio 1 Q1Dokumen26 halamanSummative Test Genbio 1 Q1Duane0% (1)
- General Biology ReviewerDokumen4 halamanGeneral Biology ReviewerJm Gutierrez50% (6)
- Parasitology ReviewDokumen2 halamanParasitology ReviewKalana maduwanthaBelum ada peringkat
- CellsDokumen9 halamanCellsMg BhoneBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Cell BiologyDokumen7 halamanEssential Cell BiologyKyle Broflovski0% (2)
- 2 4 CellsDokumen159 halaman2 4 Cellsapi-198270301100% (8)
- GenBio1 Midterm Notes 1Dokumen30 halamanGenBio1 Midterm Notes 1Just JasperBelum ada peringkat
- LESSONS-AND-ACTIVITIES-IN-SCIENCE-second-quarter-sy21-22 (f1)Dokumen5 halamanLESSONS-AND-ACTIVITIES-IN-SCIENCE-second-quarter-sy21-22 (f1)kentxy ddfsBelum ada peringkat
- 8 3+Patterns+in+NatureDokumen24 halaman8 3+Patterns+in+NatureSonny Hothi100% (1)
- Bio Lo Gym 2 Cell Structure FunctionDokumen24 halamanBio Lo Gym 2 Cell Structure FunctionMarmorn ArborshateBelum ada peringkat
- Structure and Function of The CellDokumen17 halamanStructure and Function of The CellIrene QuimsonBelum ada peringkat
- A. Two Main Types of CellsDokumen33 halamanA. Two Main Types of Cellsapi-239353579Belum ada peringkat
- Miller & Levine Biology Chapter 7 SummaryDokumen6 halamanMiller & Levine Biology Chapter 7 Summarybob0% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Human BodyDokumen51 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of The Human BodyEight AlykBelum ada peringkat
- ANSWERS Worksheets Cell Structure FunctionsDokumen24 halamanANSWERS Worksheets Cell Structure FunctionsAnghel LopezBelum ada peringkat
- Sciencia Du Gaia - Introduccion Du Sciencia BioDokumen56 halamanSciencia Du Gaia - Introduccion Du Sciencia BioRETLAWBelum ada peringkat
- IB HL Biology Chapter 2 Notes CellsDokumen5 halamanIB HL Biology Chapter 2 Notes CellsTiffani Choy100% (1)
- General Biology Modules 1 3Dokumen36 halamanGeneral Biology Modules 1 3Glen MillarBelum ada peringkat
- Beed1 - Rejano, Mary Grace M.Dokumen6 halamanBeed1 - Rejano, Mary Grace M.GraceBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Organelle NotesDokumen36 halamanCell Organelle NotesChoebe Khaye Shoebe100% (1)
- Cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDokumen1 halamanCell Theory and Cell OrganellesB09 Hernandez, Sean Matthew F.Belum ada peringkat
- Science 8 DLLDokumen9 halamanScience 8 DLLKristin MejaritoBelum ada peringkat
- Module 2 - Cell Structure & Function (Student Guide)Dokumen24 halamanModule 2 - Cell Structure & Function (Student Guide)greggcllam619076100% (7)
- Unit 1 - 3Dokumen32 halamanUnit 1 - 3Sunita SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- The Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeDokumen8 halamanThe Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeCarlo Joseph MoskitoBelum ada peringkat
- Notes On Introduction To CellsDokumen7 halamanNotes On Introduction To Cellsapi-241062194Belum ada peringkat
- Cell StructureDokumen39 halamanCell StructureMarita YaghiBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 1: Benchmark Test I. Multiple ChoiceDokumen14 halamanActivity 1: Benchmark Test I. Multiple ChoiceDan Luigi TipactipacBelum ada peringkat
- Bio-Chemical Engineering: CHE-422 Date: 09/02/2018Dokumen20 halamanBio-Chemical Engineering: CHE-422 Date: 09/02/2018Atif MehfoozBelum ada peringkat
- Biology BookDokumen51 halamanBiology BookRam NepaliBelum ada peringkat
- Biology NotesDokumen154 halamanBiology NotesMarwan YasserBelum ada peringkat
- Arsenii Vasylcehnko BG - Unit 3 - Project - Cellular Structure and FunctionDokumen3 halamanArsenii Vasylcehnko BG - Unit 3 - Project - Cellular Structure and FunctionАрсений ВасильченкоBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Biology Lecture NotesDokumen108 halamanCell Biology Lecture NotesMert PolatBelum ada peringkat
- What Is BiochemistryDokumen11 halamanWhat Is BiochemistryBalangat Regine L.Belum ada peringkat
- Biology Notes 1st QuarterDokumen25 halamanBiology Notes 1st QuarterJascha Isaac PangandianBelum ada peringkat
- Features of Life and The Cell: Chapter #2Dokumen13 halamanFeatures of Life and The Cell: Chapter #2Blaire Gallaza Aungon50% (2)
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksDari EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- 15.09.14. Pro. Nerve Fiber TypesDokumen33 halaman15.09.14. Pro. Nerve Fiber Typesashok_solanki_23Belum ada peringkat
- ReptileDokumen31 halamanReptileWira SentanuBelum ada peringkat
- Soal B. Inggris Xi - 10Dokumen6 halamanSoal B. Inggris Xi - 10Fegi NugrahaBelum ada peringkat
- Taxonomy - Importance, History and Development and Binomial Nomenclature - Definitions of Biotype, Sub-Species, Species, Genus, Family and OrderDokumen4 halamanTaxonomy - Importance, History and Development and Binomial Nomenclature - Definitions of Biotype, Sub-Species, Species, Genus, Family and OrderRakesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Kingdom Fungi RENGIEDokumen5 halamanKingdom Fungi RENGIEFranca AzoresBelum ada peringkat
- THE RULES OF JUDGING RanchuDokumen7 halamanTHE RULES OF JUDGING RanchuMarlofel ParaderoBelum ada peringkat
- Cell MCQDokumen3 halamanCell MCQkaran79Belum ada peringkat
- Clave Coleoptera BorrorDokumen34 halamanClave Coleoptera BorrorFernandaBelum ada peringkat
- Histology of The Eye: Chambers & Refractile MediaDokumen25 halamanHistology of The Eye: Chambers & Refractile MediaCaryl Joy C. ObañaBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet Pembelajaran Berdiferensiasi Konten & Proses Descriptive TextDokumen3 halamanWorksheet Pembelajaran Berdiferensiasi Konten & Proses Descriptive Textxx6002xxBelum ada peringkat
- The Anatomy of The Aging Face - Cotofana Et Al.Dokumen9 halamanThe Anatomy of The Aging Face - Cotofana Et Al.Nelson Calderon100% (1)
- Eugene MunroeDokumen3 halamanEugene MunroeAndrew ZaikinBelum ada peringkat
- Goethean ScienceDokumen161 halamanGoethean Scienceurbano37Belum ada peringkat
- Black-Footed CatDokumen6 halamanBlack-Footed CatSharmistha Talukder KhastagirBelum ada peringkat
- CK 12 BiologyDokumen869 halamanCK 12 Biologychristopher suarez100% (5)
- Morphology of Ovarian Changes During The Reproductive Cycle of Threatened Murrel Channa GachuaDokumen20 halamanMorphology of Ovarian Changes During The Reproductive Cycle of Threatened Murrel Channa GachuajosekinBelum ada peringkat
- The MoneraDokumen19 halamanThe MoneraNaufal Taufiq AmmarBelum ada peringkat
- Read online textbook Storm Mc Unfiltered Nina Levine ebook all chapter pdfDokumen22 halamanRead online textbook Storm Mc Unfiltered Nina Levine ebook all chapter pdfbrad.ferrier611100% (6)
- Birds / The Mysterious Egg Worksheet 1: This Bird Has Got Brown and White Feathers. It Lives - It Eats - This BirdDokumen3 halamanBirds / The Mysterious Egg Worksheet 1: This Bird Has Got Brown and White Feathers. It Lives - It Eats - This BirdTeuku Heriza0% (1)
- Prova Enem 2020Dokumen2 halamanProva Enem 2020Shaine de LimaBelum ada peringkat
- 7th Grade Ostriches Text QuestionsDokumen3 halaman7th Grade Ostriches Text QuestionsSubhash_iimaBelum ada peringkat
- How It Works Book of Dinosaurs 2015Dokumen132 halamanHow It Works Book of Dinosaurs 2015mihaelamihai91% (11)
- Jurnal KloningDokumen6 halamanJurnal KloningYunizardi YoenkBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Reviews in Oral Biology & Medicine: Cementum and Periodontal Wound Healing and RegenerationDokumen12 halamanCritical Reviews in Oral Biology & Medicine: Cementum and Periodontal Wound Healing and RegenerationsevattapillaiBelum ada peringkat
- 7 Linkage MappingDokumen86 halaman7 Linkage MappingEmi JiHyeon KimBelum ada peringkat
- Animalia Foglia 1Dokumen15 halamanAnimalia Foglia 1dirafqBelum ada peringkat
- Ab Production TheoriesDokumen15 halamanAb Production TheoriesDr.Santosh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Acoelomates 2015Dokumen5 halamanAcoelomates 2015premeaunBelum ada peringkat
- Elementary: Pack #3Dokumen6 halamanElementary: Pack #3lin xuBelum ada peringkat