Pythagorean Theorem
Diunggah oleh
ales8806Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Pythagorean Theorem
Diunggah oleh
ales8806Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem 5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Warm Up
Lesson Presentation
Lesson Quiz
Holt Geometry Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Warm Up Classify each triangle by its angle measures. 1. acute 3. Simplify 2. right
12
4. If a = 6, b = 7, and c = 12, find a2 + b2 and find c2. Which value is greater? 85; 144; c2
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Objectives
Use the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse to solve problems.
Use Pythagorean inequalities to classify triangles.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Vocabulary
Pythagorean triple
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean Theorem is probably the most famous mathematical relationship. As you learned in Lesson 1-6, it states that in a right triangle, the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs equals the square of the length of the hypotenuse.
a2 + b2 = c2
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Example 1A: Using the Pythagorean Theorem Find the value of x. Give your answer in simplest radical form. a2 + b2 = c2 22 + 62 = x2 40 = x2 Pythagorean Theorem Substitute 2 for a, 6 for b, and x for c. Simplify.
Find the positive square root.
Simplify the radical.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Example 1B: Using the Pythagorean Theorem Find the value of x. Give your answer in simplest radical form. a2 + b2 = c2 Pythagorean Theorem
(x 2)2 + 42 = x2 Substitute x 2 for a, 4 for b, and x for c.
x2 4x + 4 + 16 = x2 Multiply. 4x + 20 = 0 Combine like terms.
20 = 4x Add 4x to both sides.
5=x
Holt Geometry
Divide both sides by 4.
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Check It Out! Example 1a Find the value of x. Give your answer in simplest radical form. a2 + b2 = c2 Pythagorean Theorem
42 + 82 = x2
80 = x2
Substitute 4 for a, 8 for b, and x for c.
Simplify. Find the positive square root. Simplify the radical.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Check It Out! Example 1b Find the value of x. Give your answer in simplest radical form. a2 + b2 = c2 x2 + 122 = (x + 4)2 Pythagorean Theorem
Substitute x for a, 12 for b, and x + 4 for c.
x2 + 144 = x2 + 8x + 16 Multiply.
128 = 8x
16 = x
Combine like terms.
Divide both sides by 8.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Example 2: Crafts Application
Randy is building a rectangular picture frame. He wants the ratio of the length to the width to be 3:1 and the diagonal to be 12 centimeters. How wide should the frame be? Round to the nearest tenth of a centimeter.
Let l and w be the length and width in centimeters of the picture. Then l:w = 3:1, so l = 3w.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Example 2 Continued
a2 + b2 = c2
(3w)2 + w2 = 122
Pythagorean Theorem
Substitute 3w for a, w for b, and 12 for c.
10w2 = 144
Multiply and combine like terms.
Divide both sides by 10. Find the positive square root and round.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Check It Out! Example 2 What if...? According to the recommended safety ratio of 4:1, how high will a 30-foot ladder reach when placed against a wall? Round to the nearest inch. Let x be the distance in feet from the foot of the ladder to the base of the wall. Then 4x is the distance in feet from the top of the ladder to the base of the wall.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Check It Out! Example 2 Continued a2 + b2 = c2 (4x)2 + x2 = 302 Pythagorean Theorem Substitute 4x for a, x for b, and 30 for c. Multiply and combine like terms.
17x2 = 900
Since 4x is the distance in feet from the top of the ladder to the base of the wall, 4(7.28) 29 ft 1 in.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
A set of three nonzero whole numbers a, b, and c such that a2 + b2 = c2 is called a Pythagorean triple.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Example 3A: Identifying Pythagorean Triples Find the missing side length. Tell if the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple. Explain. a2 + b2 = c2 Pythagorean Theorem
142 + 482 = c2 Substitute 14 for a and 48 for b.
2500 = c2 Multiply and add. 50 = c Find the positive square root.
The side lengths are nonzero whole numbers that satisfy the equation a2 + b2 = c2, so they form a Pythagorean triple.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Example 3B: Identifying Pythagorean Triples Find the missing side length. Tell if the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple. Explain. a2 + b2 = c2 42 + b2 = 122 b2 = 128 Pythagorean Theorem Substitute 4 for a and 12 for c. Multiply and subtract 16 from both sides. Find the positive square root. The side lengths do not form a Pythagorean triple because is not a whole number.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Check It Out! Example 3a Find the missing side length. Tell if the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple. Explain. a2 + b2 = c2 82 + 102 = c2 164 = c2 Pythagorean Theorem Substitute 8 for a and 10 for b. Multiply and add. Find the positive square root. The side lengths do not form a Pythagorean triple because is not a whole number.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Check It Out! Example 3b Find the missing side length. Tell if the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple. Explain. a2 + b2 = c2 Pythagorean Theorem
242 + b2 = 262 Substitute 24 for a and 26 for c.
b2 = 100 Multiply and subtract. b = 10 Find the positive square root. The side lengths are nonzero whole numbers that satisfy the equation a2 + b2 = c2, so they form a Pythagorean triple.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Check It Out! Example 3c Find the missing side length. Tell if the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple. Explain.
No. The side length 2.4 is not a whole number.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Check It Out! Example 3d Find the missing side length. Tell if the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple. Explain.
a2 + b2 = c2
302 + 162 = c2
Pythagorean Theorem
Substitute 30 for a and 16 for b.
c2 = 1156 Multiply.
c = 34
Find the positive square root.
Yes. The three side lengths are nonzero whole numbers that satisfy Pythagorean's Theorem.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
The converse of the Pythagorean Theorem gives you a way to tell if a triangle is a right triangle when you know the side lengths.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
You can also use side lengths to classify a triangle as acute or obtuse.
B
c a b C
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
To understand why the Pythagorean inequalities are true, consider ABC.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Remember! By the Triangle Inequality Theorem, the sum of any two side lengths of a triangle is greater than the third side length.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Example 4A: Classifying Triangles Tell if the measures can be the side lengths of a triangle. If so, classify the triangle as acute, obtuse, or right. 5, 7, 10
Step 1 Determine if the measures form a triangle.
By the Triangle Inequality Theorem, 5, 7, and 10 can be the side lengths of a triangle.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Example 4A Continued Step 2 Classify the triangle. c2 102 = a2 + b2 = 52 + 72
? ? ?
Compare c2 to a2 + b2. Substitute the longest side for c. Multiply. Add and compare.
100 = 25 + 49 100 > 74
Since c2 > a2 + b2, the triangle is obtuse.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Example 4B: Classifying Triangles Tell if the measures can be the side lengths of a triangle. If so, classify the triangle as acute, obtuse, or right. 5, 8, 17
Step 1 Determine if the measures form a triangle.
Since 5 + 8 = 13 and 13 > 17, these cannot be the side lengths of a triangle.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Check It Out! Example 4a Tell if the measures can be the side lengths of a triangle. If so, classify the triangle as acute, obtuse, or right. 7, 12, 16 Step 1 Determine if the measures form a triangle. By the Triangle Inequality Theorem, 7, 12, and 16 can be the side lengths of a triangle.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Check It Out! Example 4a Continued Step 2 Classify the triangle. c2 162 = a2 + b2 = 122 + 72
? ? ?
Compare c2 to a2 + b2. Substitute the longest side for c. Multiply. Add and compare.
256 = 144 + 49 256 > 193
Since c2 > a2 + b2, the triangle is obtuse.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Check It Out! Example 4b Tell if the measures can be the side lengths of a triangle. If so, classify the triangle as acute, obtuse, or right. 11, 18, 34
Step 1 Determine if the measures form a triangle.
Since 11 + 18 = 29 and 29 > 34, these cannot be the sides of a triangle.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Check It Out! Example 4c Tell if the measures can be the side lengths of a triangle. If so, classify the triangle as acute, obtuse, or right. 3.8, 4.1, 5.2 Step 1 Determine if the measures form a triangle. By the Triangle Inequality Theorem, 3.8, 4.1, and 5.2 can be the side lengths of a triangle.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Check It Out! Example 4c Continued Step 2 Classify the triangle. c2 5.22 = a2 + b2 = 3.82 + 4.12
? ? ?
Compare c2 to a2 + b2. Substitute the longest side for c.
27.04 = 14.44 + 16.81 Multiply. 27.04 < 31.25 Add and compare.
Since c2 < a2 + b2, the triangle is acute.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Lesson Quiz: Part I 1. Find the value of x.
12
2. An entertainment center is 52 in. wide and 40 in. high. Will a TV with a 60 in. diagonal fit in it? Explain.
Holt Geometry
5-7 The Pythagorean Theorem
Lesson Quiz: Part II 3. Find the missing side length. Tell if the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple. Explain. 13; yes; the side lengths are nonzero whole numbers that satisfy Pythagoreans Theorem. 4. Tell if the measures 7, 11, and 15 can be the side lengths of a triangle. If so, classify the triangle as acute, obtuse, or right. yes; obtuse
Holt Geometry
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Exponential FormsDokumen4 halamanExponential FormsWella Wella WellaBelum ada peringkat
- Grade5 Geometry PDFDokumen4 halamanGrade5 Geometry PDFEduGainBelum ada peringkat
- Pythagorean TreasuryDokumen42 halamanPythagorean TreasuryVena AgustinaBelum ada peringkat
- Algebra IDokumen5 halamanAlgebra IMatthew SteinBelum ada peringkat
- If God Had Maths Notes, They Would Be These NotesDokumen9 halamanIf God Had Maths Notes, They Would Be These NotescallumkhangBelum ada peringkat
- Gases and Atmospheric ChemistryDokumen10 halamanGases and Atmospheric ChemistryKatheeja MusatheekBelum ada peringkat
- Logarithmic and Exponential FunctionsDokumen22 halamanLogarithmic and Exponential FunctionsAshley MorganBelum ada peringkat
- D - Solving A Triangle With The Law of CosinesDokumen3 halamanD - Solving A Triangle With The Law of Cosinescitisolo0% (1)
- First Quarter DLL June 26 29Dokumen3 halamanFirst Quarter DLL June 26 29BabyrrechBalilu100% (1)
- Math Foundations Session 1 ArithmeticDokumen42 halamanMath Foundations Session 1 ArithmeticBen HollowayBelum ada peringkat
- Pre CalcDokumen2 halamanPre Calcapi-213604106Belum ada peringkat
- Empedoclean Influences On The TimaeusDokumen23 halamanEmpedoclean Influences On The TimaeusFelipe GalhardiBelum ada peringkat
- Sub Folder Contents2012-13Dokumen7 halamanSub Folder Contents2012-13Lee Ann SpillaneBelum ada peringkat
- Scientific MethodDokumen1 halamanScientific MethodJason ShumwayBelum ada peringkat
- CPM Precalculus Chapter 01 SolutionsDokumen34 halamanCPM Precalculus Chapter 01 SolutionsBTS ARMY BTS100% (1)
- Day 38 Right Triangle TrigDokumen32 halamanDay 38 Right Triangle TrigArchessBelum ada peringkat
- Pythagorean Theorem Worksheet 2Dokumen1 halamanPythagorean Theorem Worksheet 2Yeni IrizarryBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11 - Thermal Properties of MatterDokumen6 halamanChapter 11 - Thermal Properties of MatterFirBelum ada peringkat
- Chapin S., Young T. The MATLAB Workbook - A Supplement For Calculus, Differential Equations and Linear Algebra (2003) (En) (73s)Dokumen73 halamanChapin S., Young T. The MATLAB Workbook - A Supplement For Calculus, Differential Equations and Linear Algebra (2003) (En) (73s)Miguel SaavedraBelum ada peringkat
- Refresher Algebra CalculusDokumen2 halamanRefresher Algebra Calculusishaaneja1100% (1)
- Pacing Guide hs3 Spring2017Dokumen3 halamanPacing Guide hs3 Spring2017api-319728952Belum ada peringkat
- Cell Processes Cheat SheetDokumen3 halamanCell Processes Cheat SheetsarasBelum ada peringkat
- What Is AlgebraDokumen14 halamanWhat Is AlgebraEyda RamliBelum ada peringkat
- Timeaus and The Problem of EvilDokumen5 halamanTimeaus and The Problem of EvilRay CoilBelum ada peringkat
- Math BooksDokumen5 halamanMath BooksroylepayneBelum ada peringkat
- Fifty Ways To Find The Volume of A Torus PDFDokumen8 halamanFifty Ways To Find The Volume of A Torus PDFmartim_martinsBelum ada peringkat
- Algebra Reteachings Lessons 1-10Dokumen20 halamanAlgebra Reteachings Lessons 1-10Nathan WongBelum ada peringkat
- Geom CH 08 Polygon Angle Sum PacketDokumen22 halamanGeom CH 08 Polygon Angle Sum PacketAnela100% (1)
- Diagnostic Exam: Algebra 1Dokumen12 halamanDiagnostic Exam: Algebra 1Sujatha VimalBelum ada peringkat
- Appy HourDokumen5 halamanAppy Hourapi-523981161Belum ada peringkat
- DALTON'S LAW OF PARTIAL PRESSURES (Answers)Dokumen1 halamanDALTON'S LAW OF PARTIAL PRESSURES (Answers)Brianna WilsonBelum ada peringkat
- Society - Culture, Race and Ethnicity 2015-16Dokumen32 halamanSociety - Culture, Race and Ethnicity 2015-16Nalini RooplalBelum ada peringkat
- The Relational of The Timaeus To Plato's Later Dialogues (H. Cherniss)Dokumen43 halamanThe Relational of The Timaeus To Plato's Later Dialogues (H. Cherniss)Karol KourotrophaBelum ada peringkat
- Egyptian Fractions, Sylvester's Sequence, and The Erdős-Straus ConjectureDokumen7 halamanEgyptian Fractions, Sylvester's Sequence, and The Erdős-Straus ConjecturekrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Piecewise FunctionDokumen3 halamanPiecewise FunctionPauline Jann SalangaBelum ada peringkat
- Kepler S LawsDokumen15 halamanKepler S LawsArsalan RiazBelum ada peringkat
- Algebra ReviewDokumen29 halamanAlgebra ReviewKim SmithBelum ada peringkat
- Ratio and Proportion Intro Lesson For GeometryDokumen5 halamanRatio and Proportion Intro Lesson For Geometryezmoreldo100% (2)
- Advanced Calculus LecturesDokumen216 halamanAdvanced Calculus LecturesGabriel Vasconcelos100% (1)
- Chapter 4Dokumen6 halamanChapter 4api-239235443Belum ada peringkat
- Algebra I Mid-Year Review (Grade 9)Dokumen6 halamanAlgebra I Mid-Year Review (Grade 9)Ciern TanBelum ada peringkat
- Number Patterns: Formula and TablesDokumen8 halamanNumber Patterns: Formula and TablescinnamororollBelum ada peringkat
- Derivatives and Integrals FormulaDokumen1 halamanDerivatives and Integrals FormulaPaul Daryl CutamoraBelum ada peringkat
- Mother Goose Special Science High SchoolDokumen7 halamanMother Goose Special Science High Schoolmarie-joseph paul yvech roches marquis de lafayetteBelum ada peringkat
- History of Prime Numbers & Riemann ZerosDokumen29 halamanHistory of Prime Numbers & Riemann ZerosΧάρης ΦραντζικινάκηςBelum ada peringkat
- 1.2:rates of Change & Limits Learning GoalsDokumen58 halaman1.2:rates of Change & Limits Learning GoalsMiy ChanBelum ada peringkat
- ss1 Furthermathsnote What Is logic.-WPS OfficeDokumen4 halamanss1 Furthermathsnote What Is logic.-WPS OfficecauchyfjBelum ada peringkat
- Pythagoras Theorem LessonDokumen5 halamanPythagoras Theorem Lessononek1edBelum ada peringkat
- Networking Essentials Exam NotesDokumen6 halamanNetworking Essentials Exam NotesHelen Shi100% (1)
- Real NumbersDokumen6 halamanReal NumberspjojibabuBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Let Basic Algebra - pdf12Dokumen22 halaman5 Let Basic Algebra - pdf12novey_casioBelum ada peringkat
- Softball Stealing Bases Lesson PlanDokumen7 halamanSoftball Stealing Bases Lesson PlankatykohliBelum ada peringkat
- (Answer) Assignment For Physics 1 PDFDokumen8 halaman(Answer) Assignment For Physics 1 PDFTake IchiruBelum ada peringkat
- Scientific Notation NotesDokumen3 halamanScientific Notation Notescaleb castillo100% (1)
- Divisibility Math Tricks To Learn The Facts - CompleteDokumen1 halamanDivisibility Math Tricks To Learn The Facts - CompletePriyank BhargavaBelum ada peringkat
- Math PPT 2Dokumen34 halamanMath PPT 2Zehan SiddiquiBelum ada peringkat
- GR09 Q3W08D00 H Mat 00 SLM GRDokumen10 halamanGR09 Q3W08D00 H Mat 00 SLM GRAddy LoveBelum ada peringkat
- DLC 1229 Pythagorean TheoremDokumen13 halamanDLC 1229 Pythagorean TheoremJDBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Proof: Explanation, Examples and Solutions of Mathematical ProofDari EverandUnderstanding Proof: Explanation, Examples and Solutions of Mathematical ProofBelum ada peringkat
- Section 5.3: Medians and AltitudesDokumen17 halamanSection 5.3: Medians and Altitudesales8806Belum ada peringkat
- Special Interior Lines of Triangles (Sketchpad)Dokumen2 halamanSpecial Interior Lines of Triangles (Sketchpad)ales8806Belum ada peringkat
- Perimeter and AreaDokumen7 halamanPerimeter and Areaales8806Belum ada peringkat
- Directions and Inspiration Example Exported To WordDokumen2 halamanDirections and Inspiration Example Exported To Wordales8806Belum ada peringkat
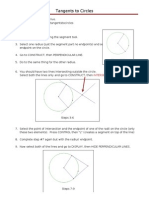
- Tangents To CirclesDokumen3 halamanTangents To Circlesales8806Belum ada peringkat
- Sirs Issues ResearcherDokumen3 halamanSirs Issues Researcherales8806Belum ada peringkat
- Triangle and Parallel Line TheoremsDokumen4 halamanTriangle and Parallel Line Theoremsales8806Belum ada peringkat
- Directions and Inspiration Example Exported To WordDokumen2 halamanDirections and Inspiration Example Exported To Wordales8806Belum ada peringkat
- Triangle Inequality TheoremDokumen1 halamanTriangle Inequality Theoremales8806Belum ada peringkat
- How Iteachch 4Dokumen2 halamanHow Iteachch 4ales8806Belum ada peringkat
- Special Interior Lines of Triangles (Sketchpad)Dokumen2 halamanSpecial Interior Lines of Triangles (Sketchpad)ales8806Belum ada peringkat
- Special Interior Lines of Triangles (Sketchpad)Dokumen2 halamanSpecial Interior Lines of Triangles (Sketchpad)ales8806Belum ada peringkat
- The Circus Is Coming To Town Project B Day Due DatesDokumen1 halamanThe Circus Is Coming To Town Project B Day Due Datesales8806Belum ada peringkat
- Triangle Inequality TheoremDokumen1 halamanTriangle Inequality Theoremales8806Belum ada peringkat
- Triangle Inequality TheoremDokumen1 halamanTriangle Inequality Theoremales8806Belum ada peringkat
- Haunted Locations of North TexasDokumen4 halamanHaunted Locations of North Texasales8806100% (2)
- Haunted Locations of North TexasDokumen4 halamanHaunted Locations of North Texasales8806100% (2)
- Moral AmDokumen1 halamanMoral Amales8806Belum ada peringkat
- How Iteachch 4Dokumen2 halamanHow Iteachch 4ales8806Belum ada peringkat
- How Iteachch 4Dokumen2 halamanHow Iteachch 4ales8806Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 ReviewDokumen10 halamanChapter 7 Reviewales8806Belum ada peringkat
- The Circus Is Coming To Town Project B Day Due DatesDokumen1 halamanThe Circus Is Coming To Town Project B Day Due Datesales8806Belum ada peringkat
- Triangle Inequality TheoremDokumen1 halamanTriangle Inequality Theoremales8806Belum ada peringkat
- Haunted Locations of North TexasDokumen4 halamanHaunted Locations of North Texasales8806100% (2)
- Unit I Mathematical Tools 1.1 Basic Mathematics For Physics: I. Quadratic Equation and Its SolutionDokumen16 halamanUnit I Mathematical Tools 1.1 Basic Mathematics For Physics: I. Quadratic Equation and Its Solutioninsap_dineshBelum ada peringkat
- Very Valuable For Calculus For SurfaceDokumen14 halamanVery Valuable For Calculus For Surface吳庭昕Belum ada peringkat
- Bmat La 1Dokumen11 halamanBmat La 1Ruth AbrogarBelum ada peringkat
- April Math RampUpDokumen15 halamanApril Math RampUpAbhinav PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - Iii Linear Algebraic Equations: X X X XDokumen13 halamanChapter - Iii Linear Algebraic Equations: X X X XTesfayeBelum ada peringkat
- General Interval SystemDokumen14 halamanGeneral Interval Systemmarco antonio Encinas100% (1)
- Simpsons 1-3rd & 3-8th RuleDokumen12 halamanSimpsons 1-3rd & 3-8th RuleVikas RathodBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Riemannian ManifoldsDokumen447 halamanIntroduction To Riemannian ManifoldsJohn Lei100% (4)
- Sohcahtoa: Right TriangleDokumen3 halamanSohcahtoa: Right TriangleKillder Hans Gomez MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- 1603855990SAT Math Level 2Dokumen14 halaman1603855990SAT Math Level 2Ojas SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3 - Time-Domain Analysis (Zero-Input Response)Dokumen5 halamanLecture 3 - Time-Domain Analysis (Zero-Input Response)MnshBelum ada peringkat
- KTLTDokumen44 halamanKTLTflamkagamineBelum ada peringkat
- 1st Periodic Test - Math 9Dokumen3 halaman1st Periodic Test - Math 9RichardRaquenoBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd Periodic Test in MathDokumen6 halaman3rd Periodic Test in MathRowena BalabagnoBelum ada peringkat
- Calculus Mathematics For BusinessDokumen112 halamanCalculus Mathematics For BusinessR. Mega MahmudiaBelum ada peringkat
- Response To Harmonic ExcitationDokumen51 halamanResponse To Harmonic ExcitationAjitsingh JagtapBelum ada peringkat
- Algebra of Matrices & Determinants: Complete Study Guide & Notes OnDokumen8 halamanAlgebra of Matrices & Determinants: Complete Study Guide & Notes OnMay LaddhaBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Motion in A Plane 1Dokumen2 halamanCBSE Class 11 Physics Motion in A Plane 1Punyo SarmingBelum ada peringkat
- 11 Mathematics Mixed Test 02Dokumen4 halaman11 Mathematics Mixed Test 02Nitin KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Algebraic FractionsDokumen35 halamanAlgebraic FractionsZinnat OobayeBelum ada peringkat
- SPE 77949 Determination of Fracture Orientation by Multi-Well Interference TestingDokumen11 halamanSPE 77949 Determination of Fracture Orientation by Multi-Well Interference Testingleonelz6aBelum ada peringkat
- Print CHAPTER 1.docx Logic and Set TheoryDokumen14 halamanPrint CHAPTER 1.docx Logic and Set TheoryShela RamosBelum ada peringkat
- JEE Main 2016 Last 3 Months Stud Planner MathematicsDokumen1 halamanJEE Main 2016 Last 3 Months Stud Planner MathematicsNinderBelum ada peringkat
- Suction Pipeline DesignDokumen64 halamanSuction Pipeline DesignMichael J. BaneBelum ada peringkat
- Computational Line Geometry I PDFDokumen422 halamanComputational Line Geometry I PDFm_t_tsai100% (2)
- LP SolutionsDokumen22 halamanLP Solutionsnitrosc16703Belum ada peringkat
- Final Examination in Enggmath 1Dokumen44 halamanFinal Examination in Enggmath 1Trisha A DVBelum ada peringkat
- Metric On Measure SpaceDokumen2 halamanMetric On Measure SpaceSR CreationBelum ada peringkat
- Plane - 10 Math BrochureDokumen2 halamanPlane - 10 Math BrochureTheSAmeNonsenseBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Mathematics - III0Dokumen4 halamanApplied Mathematics - III0GayatriBelum ada peringkat