Scolio, Heart Failure
Diunggah oleh
Arjay AvesJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Scolio, Heart Failure
Diunggah oleh
Arjay AvesHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ryan Oneil A.
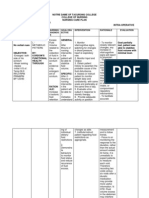
Lomeda BSN 4A2 Assessment Subjective Data: Masakit yung likod ko nagsimula eto dalawang araw ng nakakalipas nung natulog ako sa sofa, as stated Objective Data: 14 y/o 5/10 pain scale on lower back Left shoulder is higher than right Obvious Sshaped spine X-ray revealed a lateral curvature of lumbar spine
SCOLIOSIS Nursing Diagnosis Acute Pain related to structural changes secondary to scoliosis aeb 5/10 pain scale on lower back, left shoulder is higher than right , obvious S-shaped spine, x-ray revealed a lateral curvature of lumbar spine Sci. Explanation Predisposing Factors: Genetics Sex: Female Age: 14 y/o Carrying books on her right side Prolonged improper positioning Spine progressively bends to one side to compensate for the deficit Ligaments surrounding the vertebral joints get stretched and tighten according to position usually maintained (Right) S/sx: Left shoulder is higher than right Spine rotated slightly on its axis S/Sx: Obvious Sshaped spine X-ray revealed a lateral curvature of lumbar spine Ribs rotates as well Planning Discharge Outcome: Upon discharge, the client will be able to report pain is relieved aeb: a. Pain scale 0/10 b. Use of corrective device to alleviate pain Short Term Goal: After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the client will: a. Participate in treatment regimen to alleviate pain b. Demonstrate use of relaxation skills and diversional activities c. Verbalize nonpharmacological methods to provide relief d. Pain scale of 3/10 from 5/10 Nursing Intervention Independent: Re-assess vital signs especially pain and determine the causative / contributing factors of the presenting problem Accept clients description of pain. Acknowledge the pain experience and convey acceptance of clients response to pain Rationale Pain is the fifth vital sign and usually alters the vital signs. Reassessing determines the need to modify interventions set Pain is a subjective experience and cannot be felt by others and to establish appropriate treatment plan specific to individual situation Promotes nonpharmacological pain management
1/19/12 Evaluation Short Term Goal: After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the client: a. Participated in treatment regimen to alleviate pain aeb: -Proper positioning -Adequate rest period between activities -Correct usage of Milwaukee Brace -Intake of Tramadol 50 mg b. Demonstrated use of relaxation skills and diversional activities aeb: -Deep breathing exercise -Watching TV -Guided Imagery c. Verbalized nonpharmacological methods to provide relief aeb: -Usage of Milwaukee Brace -Proper positioning -Adequate rest period between activities d. Verbalized pain scale of 3/10 from 5/10 aeb: -Intake of Tramadol 50 mg -Proper positioning -Adequate rest period between activities Goal Fully Achieved >Terminate Nursing Care
Provide comfort measures ( touch, repositioning, use of warm/cold compress) Encourage use of relaxation techniques and diversional activities (focused breathing, watching TV, imaging) Encourage adequate rest periods
Distracts the attention from pain felt and reduce tension. Promotes nonpharmacological pain management Prevents fatigue and over exhaustion
Acute Pain S/sx: 5/10 pain scale on lower back Reference: Pathophysiology for the Health Professions 3rd ed. by Gould, p. 1245
Prepare the child for immobilization procedure by showing materials to be used and procedure in ageappropriate terms Provide opportunity for the child to express fears and ask questions about deformity and brace wear
Plan Bracing is used to halt the progression of the curve. Discharge Outcome: Upon discharge, the client reported pain is relieved aeb: a. Pain scale 0/10 -Intake of Tramadol 50 mg -Proper positioning -Adequate rest period between activities b. Used of corrective device to correct deformity -Correct usage of Milwaukee Brace 23 hour/day -Demonstrated how to apply Milwaukee Brace Goal Fully Achieved >Terminate Nursing Care Plan
Bracing is used to halt the progression of the curve. Airing out the concern of the child and providing answers will increase the compliance to the regimen Braces touching the skin surfaces can causing skin excoriation and discomfort Brace should be fit and exert adequate compression and traction to correct curvature Braces should be worn over a T-shirt to prevent the plastic pads from touching the skin surfaces and causing skin excoriation
Instruct the child to assess the skin under and around the brace frequently for signs of skin breakdown Instruct the patient to examine brace daily for signs of loosening or breakage Instruct patient to wear cotton shirt under brace to avoid rubbing
Instruct about which previous activities can be continued in the brace
The Milwaukee brace should be worn for 23 hours a day and can be removed for participation in school activities and to promote the correction of curvation and prevent further progress The brace can be taken off when taking a bath but no more than 1 hour to promote the correction of curvation and prevent further progress Brace should be fit and exert adequate compression and traction to correct curvature To maintain acceptable level of pain. To maintain acceptable level of pain.
Inform patient that Milwaukee brace is worn 23 hours a day
Teach mother and patient how to apply the braces
Collaborative: Administer medications as ordered: Tramadol 50 mg q 8 Notify Physician if regimens are inadequate to meet pain control and correction Refer patient to an
Frequent follow-up
Orthopedic Doctor
are necessary to check the fit of the device Reference: Maternal and Child by Pillitteri vol. 2 p. 1627
Ryan Oneil A. Lomeda BSN 4A2 Assessment Subjective Data: Nahihirapan akong huminga at masakit ang dibdib ko, madali akong mapagod at nagigising ako tuwing medaling araw, as stated Objective Data: 66 year old female Vital Signs: HR = 90 RR = 22 T = 37.5 BP = 130-140/90 Dyspnea on exertion with ordinary physical activity mild to moderate chest pains easy fatigability Parosysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (+) Orthopnea Cardiac Asthma with Cheyne-Strokes Respiration S3 gallop on heart sounds cough runny nose (+) DM 2 (+) CAD ST-Elevated Anterior
LEFT-SIDED HEART FAILURE PULMONARY EDEMA & CAP Nursing Diagnosis Fluid volume excess related to impaired cardiac contractility secondary to myocardial infarction aeb dyspnea, chest pain, easy fatigability, orthopnea, cheyne stroke respiration, S3 gallop, cough Sci. Explanation Planning Discharge Outcome: Upon discharge, the client will be able to maintain fluid volume at a normal level aeb: a. individually adequate urine output b. stable vital signs c. absence of cough d. absence of adventitious breath sounds e. absence of extra heart sound Short Term Goal: After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the client will: a. Verbalize understanding of causative factors and purpose of treatment regimen b. Demonstrate at least 3 behaviors to monitor and correct fluid excess c. Demonstrate lifestyle changes to promote cardiac health Nursing Intervention Independent: Re-assess vital signs and determine the causative / contributing factors of the presenting problem Auscultate breath sounds and note for presence of adventitious breath sounds Auscultate heart tones for extra heart sounds and murmur Rationale Establishes a baseline data to determine the need to modify interventions set To note if there is presence of adventitious breath sounds indicating fluids in the lungs To note if there is presence of extra heart sounds or murmur indicating of myocardial injury Increase blood in the lungs impairs the tissue perfusion and causes respiratory acidosis causing changes in sensorium To decrease the amount of circulating blood volume water Measures adequate fluid intake and retention in the body
1/13/12 Evaluation Short Term Goal: After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the client: a. Verbalized understanding of causative factors and purpose of treatment regimen aeb: > Knowing the complications > Knowing the preventions > Knowing the treatments b. Demonstrated 4 interventions to monitor and correct fluid excess -Monitor input and output -Fluid intake restriction to 22.5L/day -Sodium diet restriction -Proper positioning semifowlers position c. Demonstrated lifestyle changes to promote cardiac health aeb: -increased bed rest, rest periods in between activities -decreased stress or stimuli -Fluid intake restriction to 22.5L/day -Sodium diet restriction Goal Fully Achieved >Terminate Nursing Care Plan
Evaluate level of consciousness
Restrict fluid intake to 2-2.5L/day and sodium intake
Monitor I/O accurately, calculate 24 hour fluid balance
Wall Myocardial Infarction Heart Failure stage C ECG= Cardiomegaly Left Ventricular Hypertrophy Old Anterior-Septal Wall MI V1-V3. CHEST PA= Cardiomegaly Atherosclerotic Aorta with significant pulmonary congestion (+) Interstitial Edema with loss of pulmonary markings (+) Kerley A & B Lines with subpleural fluid ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC FINDING= Dilated Cardiomyopathy, with Coronary Artery Disease, Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction (Segmental), with moderate Right Ventricular Dysfunction and Depressed Ejection Fraction L side
Place patient in a semi-fowlers position Weigh patient daily on a regular schedule Provide a quite and peaceful environment and decrease stimulus
Facilitates venous return Evaluates the effectiveness of diuretic therapy To decrease cardiac load, oxygen consumption and risk for decomposition Maintains regular physical activities and prevent contractures Educate the client to be known of pharmacologic regimens
Discharge Outcome: Upon discharge, the client was able to maintain fluid volume at a normal level aeb: a. individually adequate urine output: -30cc/hour b. stable vital signs HR = 80 RR = 20 T = 36.5 BP = 130/90 c. absence of cough d. absence of adventitious breath sounds e. absence of extra heart sound Goal Fully Achieved >Terminate Nursing Care Plan
Encourage 30 mins. Of light physical exercise, as tolerated Inform patient regarding medications to be taken: effect, dosage, frequency, route, adverse effects, routine laboratory monitoring Reinforce to patient the need for heart transplant Inform patient regarding surgery
Educate the client to be known of the need for surgery Educate the client to be known of outcomes regarding condition To support steady rehydration overtime
Collaborative: Establish an IV
line of 0.9 NaCl, as ordered by the physician.
Administer O2 therapy via O2 cannula @ 2-4LPM Administer prescribed medications: ACE inhibitors (captopril) Vasodilator (Nitroglycerin) Beta blockers (metropolol)
O2 therapy is given to supply an adequate amount of O2 in the body
Decreases after load and preload Decreases BP and preload by dilating the coronary artery Blocks adrenergic site receptor causing decrease HR and contractility Inhibits sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule and collecting ducts Improves cardiac contractility
Spironolactone (aldosterone)
Digitalis (digoxin) Calsium Channel Blocker
Prevents calcium ion to enter the smooth muscle causing relaxation and dilation of muscle Reduces cholesterol level
Lipid-Reductase (simvastatin)
Collaborates intervention to
Refer to other healthcare professionals: dietitian, surgeon, cardiologist
improve health and clients well-being Reference: Medical Surgical Nursing 12th ed by Brunner and Suddarth pp. 829-837
Ryan Oneil A. Lomeda BSN 4A2 Assessment Subjective Data: Mabilis akong mapagod ngayon, tsaka nadagdagan ang aking timbang at may manas pa ako, as stated Objective Data: 50 year old male Vital Signs: HR = 98 RR = 22 T = 37 BP = 140/100 Hypertensive Non-compliant Eddematous lower extremities easy fatigability weight gain from 86 lbs to 100 lbs (+) DM 2 Easy satiety Hepato-splenomegaly Elevated jugular venous pressure Ascites ECG= Cardiomegaly and Right Ventricular Hypertrophy CHEST PA= Cardiomegaly Atherosclerotic Aorta with no pulmonary congestion
RIGHT-SIDED HEART FAILURE HYPERTESION Nursing Diagnosis Fluid volume excess related to ineffective right ventricular pump secondary to hypertension aeb dyspnea, chest pain, easy fatigability, orthopnea, cheyne stroke respiration, S3 gallop, cough Sci. Explanation Planning Discharge Outcome: Upon discharge, the client will be able to: a. eliminate or reduce any etiologic b. maintain fluid volume at a normal level aeb: -individually adequate urine output -stable vital signs -absence of peripheral edema Short Term Goal: After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the client will: a. Verbalize understanding of causative factors and purpose of treatment regimen b. Demonstrate at least 3 behaviors to monitor and correct fluid excess c. Demonstrate lifestyle changes to promote cardiac health Nursing Intervention Independent: Re-assess vital signs and determine the causative / contributing factors of the presenting problem Auscultate heart tones for extra heart sounds and murmur Rationale Establishes a baseline data to determine the need to modify interventions set
1/14/12 Evaluation Short Term Goal: After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the client: a. Verbalized understanding of causative factors and purpose of treatment regimen aeb: > Knowing the complications > Knowing the preventions > Knowing the treatments b. Demonstrated 5 interventions to monitor and correct fluid excess -Daily weight -Monitor input and output -Fluid intake restriction to 22.5L/day -Sodium diet restriction -Proper positioning semifowlers position c. Demonstrated lifestyle changes to promote cardiac health aeb: -compliance with medications prescribed -increased bed rest, rest periods in between activities -decreased stress or stimuli -Fluid intake restriction to 22.5L/day -Sodium diet restriction
To note if there is presence of extra heart sounds or murmur indicating of myocardial injury Decreased circulation in edematous areas are at risk for pressure ulcer and skin breakdown Measures adequate fluid intake and retention in the body Evaluates the effectiveness of diuretic therapy To prevent fluid accumulation since sodium attracts water Helps prevent pressure ulcer and increases venous return
Assess for skin breakdown
Monitor I/O accurately, calculate 24 hour fluid balance
Weigh patient daily on a regular schedule
Encourage 30 mins. of light physical
ECHOCARDIOGRAHIC FINDING= Dilated Cardiomyopathy Coronary Artery Disease Right Ventricular Dysfunction moderate Left Ventricular Dysfunction Depressed Ejection Fraction R side
exercise especially the legs or edematous areas, as tolerated Restrict fluid intake to 2-2.5L/day and sodium intake Measure jugular vein distention
To decrease the amount of circulating blood volume Stagnation of blood leads to venous system engorgement and increase CVP Facilitates venous return Venous return is reduced, and pressure on diaphragm is relieved Positioning avoids pressure ulcer and skin breakdown To decrease cardiac load, oxygen consumption and risk for decomposition Educate the client to be known of pharmacologic regimens
Goal Fully Achieved >Terminate Nursing Care Plan Discharge Outcome: Upon discharge, the client was able to a. eliminate or reduce any etiologic b. maintain fluid volume at a normal level aeb: -individually adequate urine output > 30cc/hour -stable vital signs > HR = 80 > RR = 20 > T = 36.5 > BP = 130/90 -absence of peripheral edema > Regained normal weight= 86 lbs > non-tender RUQ > non-edematous lower extremities Goal Fully Achieved >Terminate Nursing Care Plan
Place patient in a semi-fowlers position Elevate edematous areas (legs) or support with pillow
Frequently change the position of the patient Provide a quite and peaceful environment and decrease stimulus
Inform patient regarding medications to be taken: effect, dosage, frequency, route, adverse effects,
To support steady
routine laboratory monitoring Collaborative: Establish an IV line of 0.9 NaCl, as ordered by the physician. Administer O2 therapy via O2 cannula @ 2-4LPM Administer prescribed medications: ACE inhibitors (captopril) Vasodilator (Nitroglycerin) Beta blockers (metropolol)
rehydration overtime O2 therapy is given to supply an adequate amount of O2 in the body
Decreases after load and preload Decreases BP and preload by dilating the coronary artery Blocks adrenergic site receptor causing decrease HR and contractility Inhibits sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule and collecting ducts Improves cardiac contractility Prevents calcium ion to enter the smooth muscle causing relaxation and dilation of muscle Reduces cholesterol level
Spironolactone (aldosterone)
Digitalis (digoxin) Calsium Channel Blocker
Lipid-Reductase (simvastatin) Refer to other healthcare professionals: dietitian, cardiologist
Collaborates intervention to improve health and clients well-being Reference: Medical Surgical Nursing 12th ed by Brunner and Suddarth pp. 829-837
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Varicocele Secrets: The Underground Solution for Getting Rid of Varicocele for The Rest of Your Life [EN]Dari EverandVaricocele Secrets: The Underground Solution for Getting Rid of Varicocele for The Rest of Your Life [EN]Belum ada peringkat
- 5 Benign Febrile Convulsions Nursing Care PlansDokumen19 halaman5 Benign Febrile Convulsions Nursing Care PlansRoanna Alyssa Sy Jimenez75% (4)
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular ImpairmentDokumen17 halamanImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular ImpairmentAileen Lopez83% (6)
- Siegelman Online Advantage 1.1 PDFDokumen39 halamanSiegelman Online Advantage 1.1 PDFDana Ysabelle Ibarra100% (1)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosis and ManagementDokumen53 halamanRheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosis and ManagementamereBelum ada peringkat
- Oiling The NavelDokumen4 halamanOiling The NavelHazel100% (3)
- Assessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen10 halamanAssessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationApol Pen67% (3)
- Cap NCPDokumen6 halamanCap NCPMarlo Parayno100% (2)
- Drug StudyDokumen17 halamanDrug Studyjlg513Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plans for Neurological PatientDokumen9 halamanNursing Care Plans for Neurological PatientJam AbantaoBelum ada peringkat
- Ugib NCPDokumen5 halamanUgib NCPJhuRise Ann Mangana100% (1)
- Step 3 Board-Ready USMLE Junkies 2nd Edition: The Must-Have USMLE Step 3 Review CompanionDari EverandStep 3 Board-Ready USMLE Junkies 2nd Edition: The Must-Have USMLE Step 3 Review CompanionBelum ada peringkat
- Haemodynamic Monitoring & Manipulation: an easy learning guideDari EverandHaemodynamic Monitoring & Manipulation: an easy learning guideBelum ada peringkat
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingDari EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingBelum ada peringkat
- Step 3 Board-Ready USMLE Junkies: The Must-Have USMLE Step 3 Review CompanionDari EverandStep 3 Board-Ready USMLE Junkies: The Must-Have USMLE Step 3 Review CompanionBelum ada peringkat
- 2Dokumen4 halaman2Emmyr JohnBelum ada peringkat
- NCP 28Dokumen9 halamanNCP 28Leanne Joie Lozano100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans for Stroke PtDokumen13 halamanNursing Care Plans for Stroke PtJuls Flares SycaycoBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen8 halamanNCPJose Benit DelacruzBelum ada peringkat
- NCP MiDokumen8 halamanNCP MiPitaca Madiam Annabehl PaulBelum ada peringkat
- GastroenteritisDokumen8 halamanGastroenteritistanlimdania100% (3)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen6 halamanCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- NCPDokumen7 halamanNCPKevin PierroBelum ada peringkat
- NCP FinalDokumen18 halamanNCP FinalJessica Medina100% (1)
- LCPDDokumen7 halamanLCPDakoismeBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Biology MicroDokumen7 halamanCell Biology MicroKim Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Preparation Worksheets For NUR 345 Heart Failure SimDokumen14 halamanPreparation Worksheets For NUR 345 Heart Failure SimclarimerBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis / Inference Planning Intervention / Rationale EvaluationDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis / Inference Planning Intervention / Rationale EvaluationMon ManguilinBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Management of CVA and NIDDMDokumen12 halamanNursing Management of CVA and NIDDMKaloy KamaoBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Acute Pain NCSDokumen3 halamanNCP Acute Pain NCSPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen23 halamanNursing Care PlanLorielle HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlansDokumen5 halamanNursing Care PlansMargaret SibugBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen10 halamanNursing Care PlanGinel Laquiores100% (1)
- Preoperative Nursing Care and Education for Surgical PatientsDokumen122 halamanPreoperative Nursing Care and Education for Surgical PatientshkellyrnBelum ada peringkat
- Ochondra Ca 411Dokumen66 halamanOchondra Ca 411joyrena ochondraBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Prep 2Dokumen9 halamanClinical Prep 2Colin FraleyBelum ada peringkat
- '07 Sullivan CDokumen32 halaman'07 Sullivan CGeo NavarroBelum ada peringkat
- NCP GrandcaseDokumen5 halamanNCP GrandcaseSaima BataloBelum ada peringkat
- Age NCPDokumen2 halamanAge NCPCharmaine Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen11 halamanNCPzharienabBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen10 halamanNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen10 halamanNCPannamargie07Belum ada peringkat
- Health Teaching Plan - Lateral Neck Mass Probably MalignantDokumen5 halamanHealth Teaching Plan - Lateral Neck Mass Probably MalignantRene John FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- NurseLabs QnA#3Dokumen43 halamanNurseLabs QnA#3Jill NoelleBelum ada peringkat
- MI Chest Pain AssessmentDokumen5 halamanMI Chest Pain AssessmentDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For FractureDokumen4 halamanNCP For FracturePeejay Padigdig Feliciano100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen9 halamanNursing Care PlanjmichaelaBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 104 Midterm Exams - 1Dokumen21 halamanNCM 104 Midterm Exams - 1Bing58Belum ada peringkat
- Scorebuilders 6Dokumen58 halamanScorebuilders 6pokharelriwaj82Belum ada peringkat
- Case PresentationDokumen63 halamanCase PresentationIbrahim RegachoBelum ada peringkat
- Ceasarean Section LectureDokumen40 halamanCeasarean Section LectureamvyellicamaricorcoBelum ada peringkat
- Intro To MED-SurgDokumen47 halamanIntro To MED-SurgMarites Santos AquinoBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For ChildrenDokumen17 halamanNCP For ChildrenRachel Niu IIBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Scenario AssessmentsDokumen4 halamanClinical Scenario AssessmentsarchanaBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Nursing ReviewDokumen52 halamanFundamentals of Nursing Reviewclobregas100% (3)
- Client Safety, Security & Privacy: Requirements in Medical-Surgical Nursing PracticeDokumen189 halamanClient Safety, Security & Privacy: Requirements in Medical-Surgical Nursing PracticeJo CarlsBelum ada peringkat
- CHRONIC HEART FAILURE CASE STUDYDokumen12 halamanCHRONIC HEART FAILURE CASE STUDYMary Cris CanonBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlansDokumen6 halamanNursing Care PlansTwobee Kriz LeghidBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen12 halamanNCPJonathan Liscano100% (3)
- NCPDokumen17 halamanNCPShayne Jessemae AlmarioBelum ada peringkat
- Conceptmaptext For EpDokumen9 halamanConceptmaptext For Epapi-272402391Belum ada peringkat
- Esophagectomy Post Surgical Guide: Questions and AnswersDari EverandEsophagectomy Post Surgical Guide: Questions and AnswersBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Students' Perception of and Experience with Research ColloquiumDokumen2 halamanNursing Students' Perception of and Experience with Research ColloquiumArjay AvesBelum ada peringkat
- Attendance Group9ADokumen2 halamanAttendance Group9AArjay AvesBelum ada peringkat
- PolSci PPT - AvesDokumen6 halamanPolSci PPT - AvesArjay AvesBelum ada peringkat
- PharmaDokumen28 halamanPharmaArjay AvesBelum ada peringkat
- Factors Affecting Inter Individual Variations in Drug ResponseDokumen10 halamanFactors Affecting Inter Individual Variations in Drug Responsehumera50% (4)
- Powerful Natural Remedies for COVID-19 and Variant StrainsDokumen24 halamanPowerful Natural Remedies for COVID-19 and Variant StrainsTracyBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical and Social Factors Associated With Violent Behavior in Persons With Schizophrenia Spectrum DisordersDokumen6 halamanClinical and Social Factors Associated With Violent Behavior in Persons With Schizophrenia Spectrum DisordersIJAR JOURNALBelum ada peringkat
- PBL 2 Scarred Glands - Draft 1Dokumen5 halamanPBL 2 Scarred Glands - Draft 1Shellz2428Belum ada peringkat
- Tugas Baca Jurnal BT ShuntDokumen53 halamanTugas Baca Jurnal BT ShuntVashBelum ada peringkat
- Prelim Exam - PEC 1 Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen2 halamanPrelim Exam - PEC 1 Human Anatomy and PhysiologyColeen BentoyBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 113 Prelim ReviewerDokumen5 halamanNCM 113 Prelim ReviewerNathaniel BudayBelum ada peringkat
- Circulatory and Respiratory System Crossword PuzzleDokumen4 halamanCirculatory and Respiratory System Crossword Puzzlejoel jacobBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 Rationality of DrugsDokumen56 halamanChapter 3 Rationality of DrugsS.Srinivasan ('Chinu'); Renu KhannaBelum ada peringkat
- Pex 09 03Dokumen4 halamanPex 09 03Illich Ramirez TantaBelum ada peringkat
- Crohn's Disease Case Study: Matt SimsDokumen14 halamanCrohn's Disease Case Study: Matt SimsKipchirchir AbednegoBelum ada peringkat
- Antibiotic Sensitivity TestDokumen10 halamanAntibiotic Sensitivity TestJ.A. LauronBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Exam For Nursing NLE BLENDokumen14 halamanPractice Exam For Nursing NLE BLENLeizel ApolonioBelum ada peringkat
- Administering Large Volume EnemasDokumen4 halamanAdministering Large Volume EnemasChelleyOllitro100% (1)
- Critical Care Nurse Skills ChecklistDokumen4 halamanCritical Care Nurse Skills Checklistspartacuslives100% (1)
- Uterine Rupture and Cervical TearDokumen16 halamanUterine Rupture and Cervical Tearsangita patil0% (1)
- Trazissin® VASOPRESSIN INJECTION USP 20IU Per 1ml Solution For Injection Package Leaflet - Taj PharmaDokumen1 halamanTrazissin® VASOPRESSIN INJECTION USP 20IU Per 1ml Solution For Injection Package Leaflet - Taj PharmaTAJ PHARMA — A Health Care ProviderBelum ada peringkat
- Mendelson's SyndromeDokumen17 halamanMendelson's SyndromeYuvetha IndranBelum ada peringkat
- AL Amyloidosis Advances in Diagnosis and ManagemenDokumen4 halamanAL Amyloidosis Advances in Diagnosis and Managemenfitra khoBelum ada peringkat
- Acog PromDokumen14 halamanAcog PromjjlazarteBelum ada peringkat
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDokumen10 halamanGestational Trophoblastic Disease Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentAnggie Pradetya MaharaniBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureAina HaravataBelum ada peringkat
- CHICKENPOX: SIGNS, SYMPTOMS, TREATMENT AND NURSING CAREDokumen16 halamanCHICKENPOX: SIGNS, SYMPTOMS, TREATMENT AND NURSING CAREAlbert TerbioBelum ada peringkat
- Torrent Downloaded From ExtraTorrent - CCDokumen26 halamanTorrent Downloaded From ExtraTorrent - CCZorofan Roronoa AzBelum ada peringkat
- MedVantage - Fellowship Program in Diabetes MillitusDokumen2 halamanMedVantage - Fellowship Program in Diabetes MillitusmedvantageBelum ada peringkat
- Endovac BrochureDokumen8 halamanEndovac BrochureGeorge MK100% (1)
- Indranila 2021Dokumen22 halamanIndranila 2021reski utamiBelum ada peringkat
![Varicocele Secrets: The Underground Solution for Getting Rid of Varicocele for The Rest of Your Life [EN]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/544312715/149x198/dc87e19c66/1645158464?v=1)