Baangaloru 2crm
Diunggah oleh
Dr.K.BaranidharanDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Baangaloru 2crm
Diunggah oleh
Dr.K.BaranidharanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGMENT
Introduction
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is the customer-focused business strategy which is not a new concept. Although CRM is more about the customer, it cannot be successful by this definition alone. CRM should be performed in organizations as the combination of three main concepts: people, processes, and technology. Customer relationship management (CRM) is a combination of people, processes, and technology that seeks to provide understanding of customer needs, to support a business strategy, and to build long-term relationships with customers. To increase relationships with all customers the integration of these three is essential. Applying CRMs system in one organization means a change in different areas of the business and seeks a proper balance of people, processes, and technology. One of the main reasons of CRM failures is considering technology as the main part of the system. CRM project success will happen if the CRM users investigate people, process, and technologyeither one by one or together. The goals of CRM are: Building long-term and profitable relationships with chosen customers, Getting closer to those customers at every point of contact with them
Top management
Top management commitment is more essential than CEO attention to the CRM project. This view was reinforced in a recent META Group Report (1998) that singled out top management support and involvement as a key success factor for CRM implementations. Customer-centric management requires top management support and commitment to CRM throughout the entire CRM implementation. Moreover, top management should provide the stage in CRM initiatives for leadership, strategic direction, and alignment of vision and business goals. Also warns against starting a CRM project if senior management does not fundamentally believe in re-engineering a customer-centric business model. Top management must show its commitment to development of company education and training programs, and also enhancing employee skills and knowledge. Furthermore, it should be noted that education increases motivation and commitment of employee and reduces employee disagreements. In addition to these, different reward programs such as compensation programs and reward systems for
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGMENT
employees should be considered by management. CRM projects require absolute attention of all members of the organizational departments such as sales, marketing, manufacturing, customer services, information technology, etc. Top management and marketing and sales management are generally the initiators of a corporate CRM project. In addition, project teams require not only sponsorship by top management but also a project champion that can persuade top management for continuous efforts to change.
People
The people component is the most difficult one in order to adjust employees/staffs to the changes. Those users, who do not have an understanding of the reasons for the changes, usually oppose that change. CRM initiatives require vision and each and every employee must understand the purpose and changes that CRM will bring. CRM success will be in danger by negative feedback. Implementation of enterprise technology, such as CRM and ERP, requires changes to organizational culture. While both technology and business processes are crucial to successful CRM initiatives, the attention is back on individual employees who are the basis of the customer relationship. Along several important elements regarding to management and employee team that successful CRM system requires, top management commitment plays the main role
Process
The process component of CRM is the most delicate one because inappropriate process is the same as continuing your work aimlessly. When the company aims to create an effective process change, first of all it seeks to know the function of existing customer-facing business processes. Then the company needs to redesign or replace the process with ones that have been created and/or agreed upon internally. As an example, the replacement or updating of the business processes happens for most companies that have the process of direct contact with the customers during the purchase, payment, and usage of the company's products and services. CRM as a combination of business processes and technology that seeks to understand a companys customer from the perspective of who they are, what they do, and what they are like. It should be considered that companies have been repeatedly warned that failure is eminent if they believe that CRM is only a technology solution.
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGMENT
The shortage of customer- facing process will not compensate by purchasing CRM software, the solution is agreeing internally on how users would like a process to be done. In fact, CRM as an integrated approach to managing customer relationships with re-engineering of customer value through better service recovery and competitive positioning of the offer. The goals of a customer-centric model are to increase revenue, promote customer loyalty, reduce the cost of sales and service, and improve operations. E mphasized that optimizing customer relationships requires a complete understanding of all customers; profitable as well as non-profitable, and then to organize business processes to treat customers individually based on their needs and their values, Identify, customize, interact, differenciate.
Technology
The technology component is the toughest one, because there are a lot of technology offerings and alternatives. There are two issues related to technology: dealing with CRM software vendors and staying on top of CRM technology trends. CRM is a strategy that puts together a combination of Information Technology (IT) with business processes and services such as Data Warehouse Technology and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Technology Information Technology Whereas CRM collect and analyze data on customer patterns and also deliver customer data by accumulating, storing, maintaining, and distributing customer knowledge throughout the organization, CRM takes so much advantage of different dimensions of technology. Technology innovations have the ability of interpreting customer behavior, developing predictive models, responding with timely and effective customized communications, and delivering product and service value to individual customers. Using technology to optimize interactions with customers, companies can create a 360 degree view of customers to learn from past interactions to optimize future ones . Information Technology (IT) has long been recognized as an enabler to radically redesign business processes in order to achieve dramatic improvements in organizational performance. IT assists with the re-design of a business process by facilitating changes to work practices and establishing innovative methods to link a company with customers, suppliers and internal stakeholders. Innovations in network infrastructure, client/server computing, and
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGMENT
business intelligence applications are the main elements in CRM development. In CRM, an effective management of information has an efficient role. Information is critical for product tailoring, service innovation, consolidated views of customers, and calculating customer lifetime value. Among others, data warehouses, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems are main infrastructures to CRM implementations
Data Warehouse Technology
Data warehouse is the most popular and most needed of systems for providing CRM operating systems such as HR, sales and transaction processing, financial, inventory, purchasing and marketing. Specifically, data warehouses extract, clean, transform, and manage large volumes of data from multiple, heterogeneous systems, creating a historical record of all customer interactions. Constantly extracting knowledge about customers reduces the need for traditional marketing research tools such as customer surveys and focus groups. Thus, it is possible to identify and report by product or service, geographic region, distribution channel, customer group, and individual customer. Data warehouse causes instant access to information throughout the organization and also makes CRM possible because it consolidates, correlates, and transforms customer data into customer intelligence that can used to form a better understanding of customer behavior. Customer data includes all sales, promotions, and customer service activities. In addition to transaction details, information related to billing and account status, customer service interactions, back orders, product shipment, product returns, claims history, and internal operating costs can improve understanding of customers and their purchasing patterns too. A brief outline of organizational benefits with a data warehouse is
Accurate and faster access to information to facilitate responses to customer questions;
Data quality and filtering to eliminate bad and duplicate data; Extract, manipulate and drill-down data quickly for profitability analysis, customer profiling, and retention modelling;
Advanced data consolidation and data analysis tools for higher level summary as well as
detailed reports; and
Calculate total present value and estimate future value of each andevery customer
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGMENT
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Technology
The implementation of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) produces an improvement in the quality and efficiency of business processes. However, when the majority of companies in a sector have optimised their internal processes, this improvement becomes a condition that is necessary to remain in the market, but ceases to be a competitive advantage. Successful ERP links all areas of a company. The management, manufacturing, human resources, financial systems and distribution will connect to external suppliers and customers into a tightly integrated system with shared data and visibility. Organizations with successful ERP marketing, are preparing themselves for creating a good relationship with CRM or taking over other software companies that have been operating in the CRM market. ERP technology and CRM applications have significant differences. CRM applications are web-enabled and designed to extend the data mining capabilities of ERP throughout the supply chain to customers, distributors, and manufacturers. Organizations can use CRM analytical capabilities to predict and answer key business questions on customer intelligence and share the results across channels. Although ERP is not required for CRM, providing customers, suppliers, and employees with web-based access to systems through CRM will only be beneficial if the underlying infrastructure, such as data warehouses and/or ERP, exists. Companies with an ERP system, however, need to understand where they are in the implementation process, as well as assess where other technologies, such as data warehouses, fit in before plunging into CRM applications.
Conclusion
CRM requires a customer-centric business environment to support effective marketing, sales, and service processes. Many firms have switched from a product-centric to a customercentric culture, which emphasizes the whole customer experience. Investigating CRM elements (people, process, and technology) one by one and together shows their high value in managing a proper customer relationship. The main business drives of CRM are increasing customer lifetimes, reducing costs, and improving efficiency. The main obstacles to becoming customercentric are poor performances in some areas. In addition to these, the method used here is personal opinion; the article believes that re-engineering a customer-focus business model in organizations needs the integrating of the main parts of each element, mixing of the related
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGMENT
activities, and eliminating of those which do not add any value to organization and customers. Moreover, successful implementation of CRM means significant changes in some jobs, so it seeks the instant adjustment of employees with those cultural changes which create by CRM implementation. References: 1.Customer Relationship Management. A Strategic Perspective by G. Shainesh & Jagdish n Sheth, Macmillan India ltd.,2006. 2..Knowledge Management, Bharathidasan University, centre for distance education materials. 3.Revitalising Global Business, Conference, Annamalai University, Chidambaram 4..Customer Relationship Management, Jill dyche Pearson Education, New Delhi Prepared by: G. AROCKIA RAJ. Research shcoloar P.G. Assistant in Commerce Little Flower Higher Secondary School Kumbakonam
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Customer Relationship Management: Shikha Sehgal Rajesh Punia Tej Inder Singh Yogesh DbeyDokumen44 halamanCustomer Relationship Management: Shikha Sehgal Rajesh Punia Tej Inder Singh Yogesh DbeyyddubeyBelum ada peringkat
- CRM 1Dokumen26 halamanCRM 1Biju C Menon100% (1)
- Customer Relationship Management - TejDokumen44 halamanCustomer Relationship Management - Tejtej inderBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Success and Failure in Customer Relationship ManagementDokumen18 halamanUnderstanding Success and Failure in Customer Relationship ManagementPranavKathuriaBelum ada peringkat
- CRM BrochureDokumen9 halamanCRM BrochureMehdi AbdelBelum ada peringkat
- Shifting Paradigms On Strategic Customer Relationship ManagementDokumen8 halamanShifting Paradigms On Strategic Customer Relationship ManagementRajeev ChinnappaBelum ada peringkat
- Implementing A CRM System in It Company: Synopsis For Project WorkDokumen14 halamanImplementing A CRM System in It Company: Synopsis For Project Works_coolbugBelum ada peringkat
- CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC CCCCCCCCCCCCC C C: C CCC C C CC C CC C CCDokumen12 halamanCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC CCCCCCCCCCCCC C C: C CCC C C CC C CC C CCBhavika WadhwaniBelum ada peringkat
- A Study On The Customer Relationship Man PDFDokumen13 halamanA Study On The Customer Relationship Man PDFsrikanta dashBelum ada peringkat
- Customer Relationship ManagementDokumen6 halamanCustomer Relationship ManagementGurkaran singhBelum ada peringkat
- Challenges & Opportunities in CRMDokumen37 halamanChallenges & Opportunities in CRMHetal bariaBelum ada peringkat
- Cost Benefit CRMDokumen23 halamanCost Benefit CRMNihal LamgeBelum ada peringkat
- Customer Relationship Management As A Business StrategyDokumen6 halamanCustomer Relationship Management As A Business StrategyRajeev ChinnappaBelum ada peringkat
- Customer Relationship ManagementDokumen5 halamanCustomer Relationship ManagementAbhinandan JenaBelum ada peringkat
- CRM - InfoDokumen9 halamanCRM - Infojadeaa54345Belum ada peringkat
- Customer Relationship Management and ITDokumen42 halamanCustomer Relationship Management and ITamr-zahran5937Belum ada peringkat
- CRM NotesDokumen36 halamanCRM NotesJai JohnBelum ada peringkat
- Unlocking The Value of Your CRM Initiative: The Strategy Plus Technology DynamicDokumen13 halamanUnlocking The Value of Your CRM Initiative: The Strategy Plus Technology DynamicMaxBer73Belum ada peringkat
- CRM at PIZZA HUT M6-17Dokumen26 halamanCRM at PIZZA HUT M6-17altamas_mba6443Belum ada peringkat
- CUSTOMER Relation ManagmentDokumen22 halamanCUSTOMER Relation Managmentapi-3798769Belum ada peringkat
- Report 21501Dokumen8 halamanReport 21501anujiBelum ada peringkat
- Consultancy Project - CRMDokumen3 halamanConsultancy Project - CRMDesh Bhagat University Ms. Khusboo BansalBelum ada peringkat
- Group 5 Mohammed Faisal Priyanka Likhar Sourav Roy Sundar R J Surabhi AgrawalDokumen18 halamanGroup 5 Mohammed Faisal Priyanka Likhar Sourav Roy Sundar R J Surabhi Agrawalpril1489Belum ada peringkat
- CRM NotesDokumen44 halamanCRM Notesash47Belum ada peringkat
- Siebel CRM IntroductionDokumen28 halamanSiebel CRM IntroductionBradGourdoBelum ada peringkat
- CRMDokumen17 halamanCRMNaoman ChBelum ada peringkat
- Preeminent Analysis of Customer Relationship Management (CRM)Dokumen7 halamanPreeminent Analysis of Customer Relationship Management (CRM)jamarnath05Belum ada peringkat
- CRM - Notes by SudarshanDokumen45 halamanCRM - Notes by Sudarshanapi-26355935100% (4)
- Assignment: Name Muhammad Ahmad. Class MBA-1. Course Marketing. Submitted To Sir Shahid Yaqub. Date 5-11-2008Dokumen5 halamanAssignment: Name Muhammad Ahmad. Class MBA-1. Course Marketing. Submitted To Sir Shahid Yaqub. Date 5-11-2008Ali JameelBelum ada peringkat
- The Impact of Customer Relationship Management On BusinessDokumen9 halamanThe Impact of Customer Relationship Management On BusinessDeepak SinghBelum ada peringkat
- CRM NotesDokumen28 halamanCRM NotesmanasidhekaneBelum ada peringkat
- CRM Measurement FrameworkDokumen37 halamanCRM Measurement FrameworkYoussef El MeknessiBelum ada peringkat
- CRM 2Dokumen2 halamanCRM 2Arun MozheBelum ada peringkat
- CRM Project Pramila Final 1Dokumen81 halamanCRM Project Pramila Final 1Anonymous r9cNvGymBelum ada peringkat
- CRM in Banking IndustryDokumen45 halamanCRM in Banking IndustryRaunak Motwani100% (1)
- 27-Customer Relationship ManagementDokumen9 halaman27-Customer Relationship ManagementAnnonymous963258Belum ada peringkat
- Build Strong Customer Relationships with Effective CRM StrategiesDokumen4 halamanBuild Strong Customer Relationships with Effective CRM StrategiesHarshith KBelum ada peringkat
- Project On CRM in BanksDokumen91 halamanProject On CRM in BanksAamir KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Customer relationship management at Galaxy Toyota Pvt. LtdDokumen16 halamanCustomer relationship management at Galaxy Toyota Pvt. LtdWalterBelum ada peringkat
- PrefaceDokumen13 halamanPrefaceDuravesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- The Customer Is KingDokumen33 halamanThe Customer Is KingTajinder SinghBelum ada peringkat
- CRM Strategy for Managing Customer RelationshipsDokumen15 halamanCRM Strategy for Managing Customer RelationshipsMian Usman PervaizBelum ada peringkat
- CRM in Banks Builds Customer RelationshipsDokumen30 halamanCRM in Banks Builds Customer RelationshipsjyotiangelBelum ada peringkat
- MAR 4860 - Quiz and Final ReviewsDokumen51 halamanMAR 4860 - Quiz and Final ReviewsMark FiorentinoBelum ada peringkat
- Customer Relationship ManagementDokumen10 halamanCustomer Relationship ManagementakashBelum ada peringkat
- Customer Relationship ManagementDokumen4 halamanCustomer Relationship Managementg peddaiahBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Marketing SummaryDokumen6 halamanStrategic Marketing SummaryAhmad AliBelum ada peringkat
- MMRB SEM 4 - RBM Unit 4 - CRM and Its Types PDFDokumen4 halamanMMRB SEM 4 - RBM Unit 4 - CRM and Its Types PDFShem W LyngdohBelum ada peringkat
- Customer Relationship Management: By-Mr Saurabh BajpaiDokumen20 halamanCustomer Relationship Management: By-Mr Saurabh BajpaiSoul AkshatBelum ada peringkat
- Customer Relationship Management: Sales Marketing Customer Service Technical SupportDokumen26 halamanCustomer Relationship Management: Sales Marketing Customer Service Technical Supportnaseer337Belum ada peringkat
- CRM ReportDokumen6 halamanCRM ReportPrinceravin GohilBelum ada peringkat
- Customer Relatioship ManagementDokumen6 halamanCustomer Relatioship ManagementsundivanaBelum ada peringkat
- CRM Overview and Evolution in Hospitality IndustryDokumen26 halamanCRM Overview and Evolution in Hospitality IndustryFussy AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Customer Relationship Management in Retail Sector: DECEMBER 5, 2018Dokumen4 halamanCustomer Relationship Management in Retail Sector: DECEMBER 5, 2018Rana FaisalBelum ada peringkat
- CRM ProjectDokumen17 halamanCRM ProjectFaraz KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Executive Summary: Effectiveness of E-Commerce ApplicationDokumen48 halamanExecutive Summary: Effectiveness of E-Commerce ApplicationVivek kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Sameekshya Nanda: Roll no.15KD3UCH050154Dokumen1 halamanSameekshya Nanda: Roll no.15KD3UCH050154Muhurta EventsBelum ada peringkat
- Cash Flow Statement: Dr.K.Baranidharan, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAI 44Dokumen17 halamanCash Flow Statement: Dr.K.Baranidharan, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAI 44Dr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- Temple Ticket PALANI, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDokumen2 halamanTemple Ticket PALANI, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- Types of B o - DR - Baranidharan Kulothungan, Prof Mba, Sri Sairam Institute of Technology, ChennaiDokumen38 halamanTypes of B o - DR - Baranidharan Kulothungan, Prof Mba, Sri Sairam Institute of Technology, ChennaiDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- RESUME How To Prepared, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDokumen2 halamanRESUME How To Prepared, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ - Decision Making - DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDokumen1 halamanMCQ - Decision Making - DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- BioDokumen2 halamanBioDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- Planning Process, DR - Baranidharan Kulothungan, Prof Mba, Sri Sairam Institute of Technology, ChennaiDokumen11 halamanPlanning Process, DR - Baranidharan Kulothungan, Prof Mba, Sri Sairam Institute of Technology, ChennaiDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- BioDokumen2 halamanBioDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- BioDokumen2 halamanBioDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- C V:RES:BIO DATA, How To Prepare, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDokumen4 halamanC V:RES:BIO DATA, How To Prepare, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- Decision Making Skills - DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDokumen10 halamanDecision Making Skills - DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- Goal Setting - DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDokumen23 halamanGoal Setting - DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- BioDokumen2 halamanBioDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- CV How To Prepareds, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDokumen1 halamanCV How To Prepareds, DR - BARANIDHARAN KULOTHUNGAN, PROF MBA, SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, CHENNAIDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- B.E. / B. Tech. Degree ExaminationDokumen2 halamanB.E. / B. Tech. Degree ExaminationDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- National Day On Writing:, Oct 2o, 2020Dokumen14 halamanNational Day On Writing:, Oct 2o, 2020Dr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- How Big Data Analytics Can Transform Businesses in Various IndustriesDokumen3 halamanHow Big Data Analytics Can Transform Businesses in Various IndustriesDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- Join Zoom Meetinghttps://Sairaminstitutions - Zoom.Us/J/8754501114? PWD Vk5Xwgr6Ntbenkczemzhanv6Nwxmdz09 Meeting Id: 875 450 1114 Passcode: SairamnssDokumen1 halamanJoin Zoom Meetinghttps://Sairaminstitutions - Zoom.Us/J/8754501114? PWD Vk5Xwgr6Ntbenkczemzhanv6Nwxmdz09 Meeting Id: 875 450 1114 Passcode: SairamnssDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
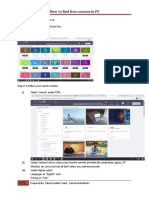
- How To Find The Free Courses in FSDokumen2 halamanHow To Find The Free Courses in FSDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Skills PhotoDokumen2 halaman3 Skills PhotoDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Participative Management StyleDokumen2 halamanWhat Is Participative Management StyleDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- Example: Total Quality ManagementDokumen2 halamanExample: Total Quality ManagementDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- De LigationDokumen1 halamanDe LigationDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- Nss Camp 2020 - SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYDokumen21 halamanNss Camp 2020 - SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- What Are The Four Stages of The Deming CycleDokumen2 halamanWhat Are The Four Stages of The Deming CycleDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Delegation. Dr.K.BaranidharanDokumen1 halamanPrinciples of Delegation. Dr.K.BaranidharanDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- Nss Camp 2020 - SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYDokumen21 halamanNss Camp 2020 - SRI SAIRAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- 1st Sem 2018 MBA RESULTDokumen1 halaman1st Sem 2018 MBA RESULTDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- Decentralisation. Dr.K.BaranidharanDokumen1 halamanDecentralisation. Dr.K.BaranidharanDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- Merits of Decentralisation. Dr. K.BaranidharanDokumen1 halamanMerits of Decentralisation. Dr. K.BaranidharanDr.K.BaranidharanBelum ada peringkat
- The Millionaire Fastlane, 10th Anniversary Edition: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeDari EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane, 10th Anniversary Edition: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (85)
- 12 Months to $1 Million: How to Pick a Winning Product, Build a Real Business, and Become a Seven-Figure EntrepreneurDari Everand12 Months to $1 Million: How to Pick a Winning Product, Build a Real Business, and Become a Seven-Figure EntrepreneurPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- Creating Competitive Advantage: How to be Strategically Ahead in Changing MarketsDari EverandCreating Competitive Advantage: How to be Strategically Ahead in Changing MarketsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- 24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldDari Everand24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (19)
- Summary of The Subtle Art of Not Giving A F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good Life by Mark Manson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDari EverandSummary of The Subtle Art of Not Giving A F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good Life by Mark Manson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (38)
- Invention: A Life of Learning Through FailureDari EverandInvention: A Life of Learning Through FailurePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (28)
- The Science of Positive Focus: Live Seminar: Master Keys for Reaching Your Next LevelDari EverandThe Science of Positive Focus: Live Seminar: Master Keys for Reaching Your Next LevelPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (51)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveDari EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveBelum ada peringkat
- To Pixar and Beyond: My Unlikely Journey with Steve Jobs to Make Entertainment HistoryDari EverandTo Pixar and Beyond: My Unlikely Journey with Steve Jobs to Make Entertainment HistoryPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (26)
- Summary of Zero to One: Notes on Startups, or How to Build the FutureDari EverandSummary of Zero to One: Notes on Startups, or How to Build the FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (100)
- Summary: Who Not How: The Formula to Achieve Bigger Goals Through Accelerating Teamwork by Dan Sullivan & Dr. Benjamin Hardy:Dari EverandSummary: Who Not How: The Formula to Achieve Bigger Goals Through Accelerating Teamwork by Dan Sullivan & Dr. Benjamin Hardy:Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Don't Start a Side Hustle!: Work Less, Earn More, and Live FreeDari EverandDon't Start a Side Hustle!: Work Less, Earn More, and Live FreePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (30)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelDari EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Without a Doubt: How to Go from Underrated to UnbeatableDari EverandWithout a Doubt: How to Go from Underrated to UnbeatablePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (23)
- The Corporate Startup: How established companies can develop successful innovation ecosystemsDari EverandThe Corporate Startup: How established companies can develop successful innovation ecosystemsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- How to Prospect, Sell and Build Your Network Marketing Business with StoriesDari EverandHow to Prospect, Sell and Build Your Network Marketing Business with StoriesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (21)
- Your Next Five Moves: Master the Art of Business StrategyDari EverandYour Next Five Moves: Master the Art of Business StrategyPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (794)
- Anything You Want: 40 lessons for a new kind of entrepreneurDari EverandAnything You Want: 40 lessons for a new kind of entrepreneurPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (46)
- SYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsDari EverandSYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (48)
- Get Scalable: The Operating System Your Business Needs To Run and Scale Without YouDari EverandGet Scalable: The Operating System Your Business Needs To Run and Scale Without YouPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Enough: The Simple Path to Everything You Want -- A Field Guide for Perpetually Exhausted EntrepreneursDari EverandEnough: The Simple Path to Everything You Want -- A Field Guide for Perpetually Exhausted EntrepreneursPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (23)
- Summary of The Lean Startup: How Today's Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses by Eric RiesDari EverandSummary of The Lean Startup: How Today's Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses by Eric RiesPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (99)
- Expert Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Creating a Mass Movement of People Who Will Pay for Your AdviceDari EverandExpert Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Creating a Mass Movement of People Who Will Pay for Your AdvicePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (363)
- Summary of The Four Agreements: A Practical Guide to Personal Freedom (A Toltec Wisdom Book) by Don Miguel RuizDari EverandSummary of The Four Agreements: A Practical Guide to Personal Freedom (A Toltec Wisdom Book) by Don Miguel RuizPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (112)
- What Self-Made Millionaires Do That Most People Don't: 52 Ways to Create Your Own SuccessDari EverandWhat Self-Made Millionaires Do That Most People Don't: 52 Ways to Create Your Own SuccessPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (24)
- The E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andDari EverandThe E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (708)
- Summary of The 33 Strategies of War by Robert GreeneDari EverandSummary of The 33 Strategies of War by Robert GreenePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (20)
- Level Up: How to Get Focused, Stop Procrastinating, and Upgrade Your LifeDari EverandLevel Up: How to Get Focused, Stop Procrastinating, and Upgrade Your LifePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (22)
- AI Money Machine: Unlock the Secrets to Making Money Online with AIDari EverandAI Money Machine: Unlock the Secrets to Making Money Online with AIBelum ada peringkat