Spheres - Na)
Diunggah oleh
amarnath_b5986Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Spheres - Na)
Diunggah oleh
amarnath_b5986Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Homework Q2
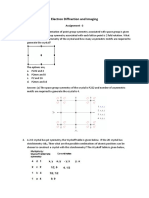
1. Identify the Bravais lattice and describe the basis or motif of each of the following crystal models showed in the pictures: a) NaCl (rock salt) b) CsCl, c) diamond, d) ZnS (blende), e) CaF2 (flurite) f) SrTiO3 (perovskite)
a) NaCl (Red spheres Cl-;
Pink spheres Na)
b) CaF2
c) Diamond
d) ZnS Blende (Red spheres S2-; Green spheres Zn2)
e) SrTiO3 a) NaCl Cubic (F): Na and Cl b) CaF2 Cubic (F): 1 Ca and 2 F c) Diamond Cubic (F): C and C d) ZnS (blende) Cubic (F): Zn and S
f) CsCl
e) SrTiO3 Cubic (P): 1Ca, 1Ti and 3O f) CsCl Cubic (P): Cs and Cl
2. For the crystal structures a), b) and f) at 1, describe the atomic positions and draw a projection of the atom planes. a) /picture (a) NaCl Cl: 0,0,0 Na: e) /picture (b) CaF2 Ca: 0 0 0 F:
b) / picture (f) CsCl Cs: 0 0 0 Cl:
f) /picture (e) SrTiO3 Ti: 0,0,0 Sr: , , O: ,0, 0 (0, ,0; 0, 0, )
3. The drawings in the figures below show patterns of points distributed in orthorhombic shaped unit cells. Identify to which, if any, of the orthorhombic structure Bravais lattice, P, C, I or F each pattern of points corresponds. (Hint: it is helpful to sketch plans of several unit cells, which will show more clearly the patterns of points, and then to outline (if possible) a P, C, I, or F unit cell)
a) Is orthorhombic C b) It is not a Bravais lattice because the points do not all have an identical environment c) Is orthorhombic P (two primitive cells are drawn together)
4. The unit cell of several orthorhombic structures is described below. Draw planes of each and identify the Bravaice lattice, P, C, I or F a) One atom per unit cell located at (x, y, z) b) Two atoms per unit cell of the same type located at (0, , 0) and (1/2, 0, ) c) Two atoms per unit cell, one type located at (0, 0, z) and ( , , z) and the other type at (00(1/2+z)) and (1/2 (1/2+z)) (hint: draw planes of several unit cells and relocate the origin of the axes, x, y, z should be taken as small (non-integral) fractions of the cell edge length)
a) Is orthorhombic P (relocate the origin at xyz) b) Is orthorhombic I (relocate the origin at 0, , 0
c) Is orthorhombic C(relocate the origin at 00z; the motif is two atoms, one of each type)
5. A metal is found to have BCC structure, a lattice constant of 3.31 and a density of 16.6 g/cm . Determine the atomic weight of this element.
3
For BCC structure Z=2 V = a3=36.26 3. FW Z 1.66 ( g / cm 3 ) V D V Fw = = 181.3 ( g / mol ) 1.66 2 D=
6. Determine the first and second nearest neighbor distance for Ni (FCC structure) at 100C if its density at that temperature is 8.83 g/cm .
3
For a FCC structure Z = 4. The first neighbor is on the face diagonal at a distance a2/2 while the second nearest distance is on the cube corner at distance a (cube edge) FwNi=58.7g FW Z 1.66 ( g / cm 3 ) V 4 1.66 58.7 V = = 44.14 A a = 3.53 A 8.83 D=
The first nearest neighbors of Ni is at 2.5 while the second nearest neighbor is at 3.53 .
7. Calculate the volume change (in %) that will occur if (for some reason) a material transforms from BCC to FCC. (Assume hard sphere behavior.)
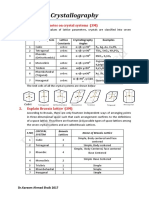
For BCC: Z=2 and the atoms are touching on the cube diagonal a3/2 = 2r a = 4r/3 VBCC= (4r/3)3/2 = 6.16r3 For FCC: Z=4 and the atoms are touching on the face diagonal a2/2 = 2r a = 4r/2 VFCC= (4r/2)3/4 = 5.65r3 The volume change: (VBCC VFCC)/VBCC x100 = 9% 8. a) In how many ways can (mathematical) points be arranged in two (2) dimensions so that every point has identical surroundings? (One possible arrangement is the square distribution of points; if you imagine that this distribution continues to infinity, them every point has neighbors at the same angle) (b) Sketch the possible arrangements (no more than 20 points each).
a = b, = 90
a b, = 90
a b, 90
a = b, 90
a = b, = 60
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- HW 2a KEYDokumen6 halamanHW 2a KEYNaveenDarwinBelum ada peringkat
- McsDokumen13 halamanMcsRodneyBelum ada peringkat
- Engg MaterialsEMP - L3Dokumen39 halamanEngg MaterialsEMP - L3Engr ZainBelum ada peringkat
- Ch-27.2 Crystalline Materials - Detects in Crystalline MaterialsDokumen92 halamanCh-27.2 Crystalline Materials - Detects in Crystalline MaterialsManojBelum ada peringkat
- ESO205A: Nature & Properties of Materials Assignment #1 SolutionDokumen4 halamanESO205A: Nature & Properties of Materials Assignment #1 SolutionLalit DevpalBelum ada peringkat
- Unit IV CrystallographyDokumen17 halamanUnit IV Crystallographyswapniljawadwar1Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - Energy Bands andDokumen134 halamanChapter 1 - Energy Bands andYew Keong NgBelum ada peringkat
- HW1Dokumen8 halamanHW1Kevin Johnmar Urcia VidarteBelum ada peringkat
- 2-Excellent Chemistry Assignment The Solid StatesDokumen5 halaman2-Excellent Chemistry Assignment The Solid StatesSachin B SBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen2 halamanUntitledSwarnava SanyalBelum ada peringkat
- Ch-27.2 Crystalline Materials & Detects in Crystalline MaterialsDokumen93 halamanCh-27.2 Crystalline Materials & Detects in Crystalline MaterialsSmruti Ranjan PattanayakBelum ada peringkat
- HW 4Dokumen2 halamanHW 4meanyackBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 - Chapter 3 AnswerDokumen9 halamanAssignment 1 - Chapter 3 AnswerHarryzam MartelBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Structure (21!10!2011)Dokumen71 halamanCrystal Structure (21!10!2011)Swetha PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Cation Vs AnionDokumen16 halamanCation Vs AnionnobleskyBelum ada peringkat
- Learnivio Class 12th, Chemistry Solid State Analysis of Cubic CrystalDokumen3 halamanLearnivio Class 12th, Chemistry Solid State Analysis of Cubic CrystalDaniyalBelum ada peringkat
- CH 3 ReviewDokumen30 halamanCH 3 ReviewAdamBelum ada peringkat
- Gold Questions: Solid State ChemistryDokumen7 halamanGold Questions: Solid State Chemistryabhishek pathakBelum ada peringkat
- Symmetry & Crystal StructuresDokumen37 halamanSymmetry & Crystal StructuresNurnajihah Sukimi JiehaBelum ada peringkat
- Chem Academy: Exercise - IDokumen11 halamanChem Academy: Exercise - IHamit RanaBelum ada peringkat
- Graded Problems Indicated in BoldDokumen7 halamanGraded Problems Indicated in BoldJigoku KuroakaBelum ada peringkat
- Ch-27.2 Crystalline Materials - Detects in Crystalline MaterialsDokumen102 halamanCh-27.2 Crystalline Materials - Detects in Crystalline MaterialsasjfgauojfgfBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 3Dokumen4 halamanAssignment 3KuthuraikaranBelum ada peringkat
- Solid State Theory - EDokumen27 halamanSolid State Theory - Ethinkiit100% (3)
- Crystallography and Structure: ME 2105 R. R. LindekeDokumen66 halamanCrystallography and Structure: ME 2105 R. R. LindekeMohammad RameezBelum ada peringkat
- Common unit cells and crystal structuresDokumen99 halamanCommon unit cells and crystal structuresasjfgauojfgfBelum ada peringkat
- Solid StateDokumen16 halamanSolid StatePrahasBelum ada peringkat
- Chem 150 PS1 2014Dokumen5 halamanChem 150 PS1 2014Jay CaoBelum ada peringkat
- Subject: Chemistry Solid State: Section-I (Only One Correct)Dokumen16 halamanSubject: Chemistry Solid State: Section-I (Only One Correct)QwertyBelum ada peringkat
- Atomic Structure: Examples of Multiple Choice QuestionsDokumen4 halamanAtomic Structure: Examples of Multiple Choice Questionsngah lidwineBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction and Bravais LatticesDokumen17 halamanIntroduction and Bravais LatticesBilal BarutBelum ada peringkat
- Crystalline Solids: Structure and PropertiesDokumen77 halamanCrystalline Solids: Structure and Propertiesvijayabanu2013Belum ada peringkat
- Chapt 03 Sect 1 To 6Dokumen18 halamanChapt 03 Sect 1 To 6Jesse McClureBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal StructureDokumen16 halamanCrystal StructureᎽᎪsh ᏒᎪj sᎥᏁᎶhBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 / MaterialDokumen39 halamanChapter 3 / MaterialmuslemBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 2Dokumen2 halamanProblem Set 2engineerBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 6. Atomic Structure: Upon Successful Completion of This Unit, The Students Should Be Able ToDokumen7 halamanUnit 6. Atomic Structure: Upon Successful Completion of This Unit, The Students Should Be Able TobillingsleyBelum ada peringkat
- Solid StateDokumen2 halamanSolid StateKamal KishoreBelum ada peringkat
- Review Problems For Chapter3Dokumen11 halamanReview Problems For Chapter3johandreher100% (1)
- Chapter 1. Introduction: 1. Generation of X-RayDokumen127 halamanChapter 1. Introduction: 1. Generation of X-Raynirmal_phyBelum ada peringkat
- Material Science (Unit 1)Dokumen18 halamanMaterial Science (Unit 1)Gaurav AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Solid State Physics MCQsDokumen7 halamanSolid State Physics MCQsAhsan MoinBelum ada peringkat
- 04_1_Solid_State_15_4_2023_pdf_Margdarshan_2_0_Solid_St_JindalJi247Dokumen5 halaman04_1_Solid_State_15_4_2023_pdf_Margdarshan_2_0_Solid_St_JindalJi24735 Pranay KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set IDokumen2 halamanProblem Set ImagnaBelum ada peringkat
- DPP 01 Solid StateDokumen14 halamanDPP 01 Solid Stateanupamgupta112Belum ada peringkat
- EditedDokumen70 halamanEditedVimal PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Condensed Matter and Crystalline Physics 1st Edition Sidebottom Solutions ManualDokumen6 halamanFundamentals of Condensed Matter and Crystalline Physics 1st Edition Sidebottom Solutions ManualElizabethSteelenjzpk100% (15)
- Crystalline StructureDokumen23 halamanCrystalline StructureJuvita Hamizah SouminBelum ada peringkat
- Solid State MCQDokumen7 halamanSolid State MCQshikha nathBelum ada peringkat
- Solid State Structure PropertiesDokumen6 halamanSolid State Structure PropertiesAditi MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Solid StatesDokumen4 halamanSolid StatesAbhi RamBelum ada peringkat
- Crystallography: Classification of Crystal Systems and DefectsDokumen54 halamanCrystallography: Classification of Crystal Systems and DefectsSaad MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Materials Science HW ProblemsDokumen8 halamanMaterials Science HW Problemsamitav_chak9523Belum ada peringkat
- Solid State (Exercise)Dokumen35 halamanSolid State (Exercise)Vishu PatryBelum ada peringkat
- Answer Tutorial 3Dokumen29 halamanAnswer Tutorial 3Sofea IzyanBelum ada peringkat
- Infrared Spectroscopy of Triatomics for Space ObservationDari EverandInfrared Spectroscopy of Triatomics for Space ObservationBelum ada peringkat
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyDari EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyBelum ada peringkat
- Welding robot aviation plug terminal definitionDokumen4 halamanWelding robot aviation plug terminal definitionPhươngNguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Periodic TableDokumen1 halamanPeriodic TableChemist MookaBelum ada peringkat
- Class XII Computer Project - Hotel ManagementDokumen29 halamanClass XII Computer Project - Hotel ManagementLakshmi Puthiyedath71% (7)
- PAPER I MATHEMATICS PRACTICE SETDokumen6 halamanPAPER I MATHEMATICS PRACTICE SETRitesh Raj PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Tendenze Attuali Nei Metodi Di Calcolo Per Progettare GearboxDokumen40 halamanTendenze Attuali Nei Metodi Di Calcolo Per Progettare GearboxLuis TestaBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamic Analysis of Motor Floor: Structure DataDokumen6 halamanDynamic Analysis of Motor Floor: Structure Datap_ignatiusBelum ada peringkat
- Modern Scoring BRASS Manual1Dokumen25 halamanModern Scoring BRASS Manual1Pepe ChorrasBelum ada peringkat
- Oscillation MCQDokumen7 halamanOscillation MCQUmer KhalidBelum ada peringkat
- Drive Fundamentals and DC Motor CharacteristicsDokumen6 halamanDrive Fundamentals and DC Motor CharacteristicsKawooya CharlesBelum ada peringkat
- Measure Runoff and Soil Loss at Erosion Plots in TanzaniaDokumen19 halamanMeasure Runoff and Soil Loss at Erosion Plots in TanzaniaMohd Sofiyan Bin SulaimanBelum ada peringkat
- Discoverer Installation and Integration With EBSDokumen25 halamanDiscoverer Installation and Integration With EBSRajendra PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Perez, Alonso - Unknown - The Ultimate Approach For General Arrangement Definition-AnnotatedDokumen6 halamanPerez, Alonso - Unknown - The Ultimate Approach For General Arrangement Definition-AnnotatedPANJI BRAMMASTABelum ada peringkat
- 5367227Dokumen2 halaman5367227aliha100% (1)
- Roll Handling Data Form: Company DetailsDokumen1 halamanRoll Handling Data Form: Company DetailsAlfredo MinchezBelum ada peringkat
- LIFTING PERFORMANCE OF THE SY215C EXCAVATORDokumen4 halamanLIFTING PERFORMANCE OF THE SY215C EXCAVATORAkhmad SebehBelum ada peringkat
- Smart AntennasDokumen40 halamanSmart AntennasMeeraBelum ada peringkat
- How To Solve AssignmentsDokumen4 halamanHow To Solve AssignmentsHarisBelum ada peringkat
- Understand The Standardization Protocol For Iot Understand The Concepts of Web of Things. Understand The Concepts of Cloud of Things With Understand The Basic Concepts of Aspect OrientedDokumen2 halamanUnderstand The Standardization Protocol For Iot Understand The Concepts of Web of Things. Understand The Concepts of Cloud of Things With Understand The Basic Concepts of Aspect OrientedShanthi GanesanBelum ada peringkat
- ST RDDokumen2 halamanST RDBalteshwar SinghBelum ada peringkat
- OpenGL Basic FunctionsDokumen21 halamanOpenGL Basic FunctionsAishwaryaNawkarBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Introduction - Derivatives GreeksDokumen50 halaman1 - Introduction - Derivatives GreeksThomas GallantBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Class VIII: Chapter As Per NCERT LessonsDokumen1 halamanMaths Class VIII: Chapter As Per NCERT Lessonsabhijeet_sangwanBelum ada peringkat
- openPDC DM-Tools Usage Examples GuideDokumen5 halamanopenPDC DM-Tools Usage Examples GuidealantmurrayBelum ada peringkat
- M6L32Dokumen6 halamanM6L32abimanaBelum ada peringkat
- DT022BTFT v10Dokumen12 halamanDT022BTFT v10Johny JongBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring Propeller Drop With The Help of Poker GaugeDokumen2 halamanMeasuring Propeller Drop With The Help of Poker Gaugeas100% (1)
- Q1 - Answer KeyDokumen2 halamanQ1 - Answer KeyJustine AligangaBelum ada peringkat
- 9th-Implementing Lockout Function With IEC61850 PDFDokumen11 halaman9th-Implementing Lockout Function With IEC61850 PDFBharath SaiBelum ada peringkat
- QST HamClockDokumen3 halamanQST HamClockCPC PHCBelum ada peringkat
- Basic use of datum planes in Creo ParametricDokumen8 halamanBasic use of datum planes in Creo ParametricKartik BhararaBelum ada peringkat