O&M Manual For Vms Pump
Diunggah oleh
Kaushik ChakrabortyJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
O&M Manual For Vms Pump
Diunggah oleh
Kaushik ChakrabortyHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
MANUAL FOR VMS PUMP
Instructions on Installations, Operation and Maintenance of Multi Stage Self Priming Centrifugal Pump
Manufactured By :
Varat Pump & Machinery Pvt. Ltd.
20, Netaji Subhas Road, Kolkata 700001 West Bengal, INDIA Ph. No.: 033-2230 1903, 2243 4500 FAX No.: 033-2230 1535/6274 E-Mail : Varat@cal2.vsnl.net.in
Page 2 of 11
1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3
GENERAL This booklet covers instructions for all Models of VARAT Ring Casing Self-Priming Pump When the pumps are received sometime before the use of the pump it should be located in dry place. The coupling should be rotated once in a month to prevent pilling of bearing surfaces. To avoid jamming of the rotating components, do not keep the pump idle for long period. If so required, put some quantity of preservative washable with water and rotate the shaft several times so that it gives a thin film on the internal faces. To avoid damage to the components, select proper size of tools to open plugs, bolts, nuts etc. INSTALLATION LOCATION The pump should be located as near the liquid source as possible. This will minimise the suction lift and pump will give better performance. Ample space should be provided on all the sides so that the pump can be inspected while in operation and can be serviced conveniently whenever required.
1.4 2.0 2.1
2.2
FOUNDATION The foundation should be sufficiently substantial to absorb any vibration and to form a permanent rigid support for the base plate. This is important in maintaining the alignment of a direct connected unit. A concrete foundation on a solid base is advisable. Foundation bolts of the proper size should be embedded in the concrete located by a drawing or template. A pipe sleeve about two and one-half diameter larger than the bolt should be used to allow movement for the final position of the foundation bolts.
2.3
ALIGNMENT Pumps and drivers that are supplied by the manufacturers, mounted on a common base plate are accurately aligned before despatch. All base plates are flexible to some extent and alignments are likely to be disturbed during transit to some extent and therefore must not be relied upon to maintain the factory alignment. Re-alignment is necessary after the complete unit has been leveled on the foundation and again after the grout has set and foundation bolts have been tightened. The alignment must be checked after the unit is piped up and re-checked periodically.
2.4
LEVELLING When the unit is received with the pump and driver mounted on the base plate, it should be placed on the foundation and the coupling halves disconnected. The coupling should not be reconnected until all alignment operations have been completed. The base plate must be supported evenly and placed closed to the foundation bolt. In each case, the supports should directly under the part base plate carrying the greatest weight and spaced closely enough to give uniform support. A gap of about 25 to 50 mm should be allowed between the base plate and foundation of grouting. Supporting will be such that it will not be distorted or sprung by the uneven distribution of the weight. Adjust the wedges until the shafts of the pump and driver are in level. Check the coupling faces, suction and discharge flanges for the horizontal or vertical position by means of spirit level.
2.5
FLEXIBLE COUPLING A flexible coupling will not compensate for misalignment of the pump and driver shafts. The purpose of the flexible coupling is to compensate for temperature changes and to permit the movement of the shafts without interference with each other while transmitting power from the driver to the pump.
Page 3 of 11
2.6
MISALIGNMENT There are two types of misalignment between the Pump shaft and the driver shaft: (a) Angular misalignment: Shafts with axis concentric but not parallel. (b) Parallel misalignment: Shafts with axis Parallel but not concentric. The unit can then be granted by working soft concrete under the edges.
The faces of the coupling hardens should be spaced for enough apart so that they cannot strike each other when the drive rotor is moved hard over towards the pump. Due allowance should be made for wear of the thrust Bearings. A minimum gap of 3 to 4 mm should be maintained. The necessary tools for approximately checking the alignment of the flexible coupling are a straight edge and a taper gauge or a set of feeler gauge. For pin bush coupling disconnect coupling halves before proceeding with alignment. A check for angular alignment is made by inserting the taper gauge or feelers at four points between the coupling faces and comparing the distance between the faces at four points spaced at 90 degree intervals around the coupling, the unit will be in angular alignment when the measurement show that the coupling faces are the same distance apart at all point (FIG 1). A check for parallel alignment is made by placing a straight edge across both coupling ring at the top bottom and at both sides. The unit will be in parallel alignment when the straight edge rests evenly on the coupling ring at all positions. Care must be taken to have the straight edge parallel to the axis of the shaft (FIG-2). Angular and parallel misalignments are corrected by means of shims under the motor mounting feet. After each change it is necessary to re-check the alignment of the coupling halves. It should not be necessary to adjust the shims, if used, under the pump. 2.7 GROUTING When the alignment is correct, the foundation bolts should be tightened evenly but not too firmly. Working soft concrete under the edges can then grout the unit. Foundation bolts should not be fully tightened until the grout is hardened, usually 48 hours after pouring.
Page 4 of 11
2.8
PIPING Both suction and delivery pipes and accessories should be independently supported near the pump so that when the flange bolts are tightened no strain will be transmitted to the pump casing. It is usually advisable to increase the size of both suction and delivery pipes at the pump nozzles in order to decrease the loss of head from friction and for the same reason piping should be arranged with as minimum bends as possible, as these should be made with a long radius wherever possible. The pipe lines should be free from scales, welding residuals etc., and have to be mounted in such way that they can be connected to suction and delivery flanges without any stress on the pump. Adequate supports should be given to pipe lines so that the weight of the pipelines does not fall on the pump. The use of minimum number of the bends and other fittings will minimise the friction losses.
2.9
SUCTION LINE a) The suction pipe should be as short and direct as possible. Long radius bends may be used if necessary. The line should slope upwards to the suction port of the pump. b) There should be a gate valve in the suction line. A foot valve & strainer should be provided in the suction pipe line. However, for self priming pumps foot valve may not be necessary.
2.10
DELIVERY LINE (a) A gate valve and a non-return valve must be installed in the delivery pipe. (b) Use the elbow and short bend should be avoided, if possible.
2.11
FOOT VALVE It is advisable to install a foot valve to facilitate priming of pump. Foot valve should have sufficient clear passage for water. Care must be taken to prevent foreign matter from being drawn into the pump or choking the foot valve and for this purpose an efficient strainer should be provided.
Page 5 of 11
2.12
BALL BEARING Correct maintenance of ball bearings is essential. The bearing manufacturers give the following as guide to relubrication periods under normal conditions. After three month where on continuous duties. Six monthly when on eight-hour per day duty. The bearings and housings should be completely cleaned and recharged with fresh grease after 2500 hours or the nearest pump overhaul time.
2.13
PRIMING These pumps are usually self priming but no pumping action occurs unless the pump casing is filled with liquid. Pump casing and suction pipe must therefore be completely filled with the liquid first time and thus all air removed before the pump is started. Several different priming methods can be used depending on the kind of installation and service involved. (1) Liquid level above pump level. Pump is set below liquid level of source of supply so that liquid always flows to pump under positive head. Priming with Foot Valve. (a) When pump is installed on suction lift with foot valve at the end of suction line, fill pump with water from some outside source till all air is expelled and water flows through air vent. (b) When there is liquid under some pressure in the discharge pipe, priming can be effected by bypassing the pressure liquid around the check and gate valve. Of course, the initial priming must be affected from some outside source. NOTE: In this case, the foot valve must be capable of withstanding pump pressure and possible surge. Priming by ejector: An ejector operated by steam, compressed air or water under pressure and connected to air vent on top of casing can be used to remove air from and prime the pump on suction lift installations. Priming by dry vacuum pump: A hand or power pump sucks in all the air from the casing and the suction pipe, and thus primes the system PREPARATION OF PUMP STARTING: All pumps are supplied with preservative which should be washed off with water before use. After the pump and the drive are mounted, the plant should be prepared for starting. The following rules should be observed before starting the pump:
(2)
(3)
(4) 3.0
3.1
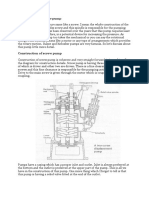
The pins are pad should be inserted into the coupling not before making sure of the correct rotation of drive. In case of the drive rotating in the wrong direction, the connection of two cable conductors supplying the current to the motor should be interchange in case of DOL starting. Check presence of grease / oil in bearings and correct location of water deflector on shafts ensure flashing, quenching and lubrication in case of mechanical seal as well as if required as per design. Gland packing should be tightly stuffed, but not over tightened. The sealing packing should be tightened to such an amount as to allow the pumping liquid to seek to the outside. Over tightening of sealing packing causes quickly wear out of shaft sleeves, increases its friction and lower the efficiency factor of the whole plant. Check the free rotation of pump rotor, turning it by hand to verify any major obstruction or friction with wearing parts.
3.2 3.3
3.4
Page 6 of 11
3.5 3.6 3.7
Check the proper order of suction and pressure pipelines, tightening of flanges, fittings of inlet valve and presence of drain plug. Check the correct direction of rotation of pump and drive. The pump rotor should rotate according to direction of rotation marked on pump. Making reasonably sure of the proper order of the whole plan and its readiness for operation, the suction pipe should be primed with water / liquid. Arrangement for priming funnel and three ways connection of pressure gauge with air-cock after delivery flange but before delivery sluice valve is required. The pump is being filled up (Primed) until the air-cock produces water jet without air bubbles. Then the priming funnel and air-cock is required to be closed and thereafter ensure the sluice valve in full open condition. After all these operation and checking the pump is ready for starting.
3.8
4.0 4.1
STARTING AND STOPPING OF THE PUMP: Before first starting, the pump must be filled with the liquid to be handled, keeping the gate valve open. The pump should be loaded gradually, when the drive is engaged. When the prime mover attains full speed, the regulating sluice valve should be smoothly closed. This will avoid overloading of the drive. On the other hand it should be kept in mind that a lengthy operation with completely close sliding valve is likewise to be avoided. Since this causes unnecessary heating of the liquid in the pump. By controlling the sliding valve the required flow and head may be obtained. After setting of pressure gauge at required point, check ampere consumption, if found exceed required value, pump should be stopped BEARINGS: The shaft is supplied with anti-friction ball bearings or thrust bearing according to size of pump. Generally SKF/NBC/RHP equivalent bearings are used.
4.2
4.3
5.0
6.0
LUBRICATION: Bearings are normally greased lubricated. Refilling period is after 1000 hours of running. Bearing temperature is permissible to rise 40 degree Centigrade above ambient temperature. Grades of recommended grease are INDIAN OIL- SERVOGEM-3 or CALTEX-STARFAX-3, H.P.C.L. NATRA-3 or equivalent. In case of oil lubrication bearing oil should be maintained in the oil indicator. Servo 30/40 may be used for this purpose.
7.0
STUFFING BOX There should be constant slow drip of liquid from the stuffing box gland when the pump runs. Stuffing Boxes are extra deep to reduce the leakage and champion style-3116 G asbestos grease and graphite packing is normally used. However, stuffing Box packing or seal suitable for corrosive liquid is supplied against specific requirements. Generally the stuffing Box packing is sent duly packed in the pump. Mechanical seal must be overoiled before starting the pump after long time storage. GASKET Compressed asbestos/paper packing gasket for joining of ring casing is used. However, packing gasket suitable to handle corrosive liquid and high temperature fluid is supplied against specific requirements.
8.0
Page 7 of 11
9.0
COUPLING Normally pin-pad flexible type or star type spider coupling with or without spacer is used. Other type of coupling may be supplied against specific requirements. SPARE PARTS One set Anti-friction bearing, Shaft, Coupling pad, Gland Packing, Gasket, and Impeller must always be kept as spare.
10.0
11.0 1. DEFECTS Pump does not deliver liquid.
TROUBLE SHOOTING CAUSES (1)Insufficient quantity of water/water not filled in pump casing (2) Incorrect direction of rotation. (3) Pump is clogged. (4) Pump speed too low. (5) Suc. Lift too high. (6) Leakage in Suc. Pipe. (7) Incorrect layout of Suc. Line. (8)Valve in Suc. Line not open properly. (9) Shaft Sleeve & Gland packing worn and air leaks. (10) Delivery liquid too viscous. (11) Incorrect selection of pump for operating condition. (1) Speed too low. (2) Leakage in Suction side fitting and piping (3) Discharge Head too high. (4) Pump Casing empty. (5) Rubber Flap Valve clogged. (6) Shaft Sleeve/Gland packing worn and air leaks. (7) More clearance between Impeller and Wearing Plate. (8) Suction lift too high or suction pipe too long.
2.
Not enough water delivered.
REMEDY (1) Fill up pump casing with clear water or liquid to be pumped. (2) Change the direction of rotation of prime mover. (3) Check up Impeller may clog. Clean Suction pipe and Strainer. (4) Check up speed of prime mover and adjust. (5) Reduce Suc. Lift. (6) Prevent leakage in suc. Pipe. (7) Correctly install the Suc. Line. (8) Check up the opening of line valve. (9) Replace Shaft-Sleeve & Gland Packings. (10) Liquid viscosity to be checked & corrected. (11) Replace the pump with a suitable designed capacity. (1) Check up speed of prime mover and adjust. (2) Prevent leakage in suction pipe and fittings. (3) Check up vertical head and frictional losses. (4) Fill up the pump casing. (5) Check up rubber Flap assembly & leakage from pump casing. (6) Replace the shaft Sleeve/Gland Packing. (7) Measure the clearance between Impeller and Wearing Plate and adjust by using proper Packing. (8) Avoid High Suction lift and Suction piping.
Page 8 of 11
SL. NO. 3.
DEFECTS Pump takes More Power.
CAUSES 1) Speed too high. (2) Head less than rating. (3) Shaft Bent
REMEDY (1) Check and correct the speed. (2) Provide minimum head. (3) Check and replace the Shaft. (4) Correct the alignment. (1) Check the speed of Prime mover and correct it. (2) Replace Gland Packing. (3) Measure the clearance between Impeller and Wearing plate and adjust by using proper packings. (1) Fill up the pump casing.
4.
Not enough pressure.
(4) Mis-alignment of the set. (1) Prime mover not running at rated speed. (2) Leakage through Gland Packing. (3) Too much clearance between Impeller and Wearing plate. (1) Pump casing not filled with Water/Liquid (it is only possible only during priming time). (2) Suction lift too high. (3) Mis- alignment (4) Foundation not rigid (5) Shaft bent (6) Bearing Worn out (7) Lack of Lubrication (8) Pump operating at very low capacity. (1) Mis- alignment (2) Shaft bent (3) Excessive Grease or lack of grease. (4) Dirty water getting into Bearings.
5.
Pump vibrates and makes more noise.
(2) Reduce the suction lift or install the Foot valve. (3) Correct the alignment. (4) Check up the foundation bolt. (5) Replace the shaft (6) Check & replace Bearing. (7) Lubricate the Bearings. (8) Reduce total head. (1) Correct the alignment. (2) Check the shaft condition. (3) Check up lubrication. (4) Protect bearing neatly.
6.
Bearings have short life.
12.0
MAINTENANCE Preventative maintenance schedule is the periodical checks and precautions by which possibilities of failures and breakdowns are made very remote.
12.1
Daily Checks 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Pressure gauge reading Bearing temperature Leakage through stuffing box Noise and vibration Voltage and current
Page 9 of 11
1.6 12.2
Constant flow of cooling water.
Periodical Maintenance 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Replenish the grease Change the stuffing box packing Check the alignment of the pump set Calibrate the measuring instruments Check the sealing and cooling connections for leakage etc.
13.0
OVERHAULING Normally the pump will be due for overhauling after about 3000 working hours. Pump dismantling and assembling should be done by skilled personal. Special attention should be given to continuous running pumps & advice to keep stand by pump for emergency services.
Page 10 of 11
Page 11 of 11
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- VWS Pump Manual (Varat Pump & Machinery Pvt. LTD.)Dokumen20 halamanVWS Pump Manual (Varat Pump & Machinery Pvt. LTD.)Kaushik ChakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- Omega 600S ManualDokumen36 halamanOmega 600S ManualLeandroBelum ada peringkat
- Berkeley Ownwes ManualDokumen28 halamanBerkeley Ownwes ManualMoses Alvarado100% (1)
- Sykes Pump BookletDokumen105 halamanSykes Pump BooklethipsterzBelum ada peringkat
- HPS3000 Pump & GearboxDokumen2 halamanHPS3000 Pump & GearboxFrederik CañabiBelum ada peringkat
- General Pump VHDokumen18 halamanGeneral Pump VHnabit pedrozoBelum ada peringkat
- TX-450SB - Pump - 2009Dokumen2 halamanTX-450SB - Pump - 2009mawannnBelum ada peringkat
- Varat Pump and Machinery Pvt. Ltd.Dokumen59 halamanVarat Pump and Machinery Pvt. Ltd.Kaushik ChakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- HPS2200 Pump & GearboxDokumen2 halamanHPS2200 Pump & GearboxFrederik CañabiBelum ada peringkat
- Side Channel Pump SeroDokumen5 halamanSide Channel Pump SeroAdanaBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Cat Pump Model 45Dokumen4 halamanManual Cat Pump Model 45Jhon Jairo Maestre UribeBelum ada peringkat
- Engine Alignment DetailsDokumen13 halamanEngine Alignment DetailsNaufal HilmiBelum ada peringkat
- Split Case PDFDokumen8 halamanSplit Case PDFnitin lageju100% (1)
- Catalogo Cameron 1Dokumen32 halamanCatalogo Cameron 1RoyBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of Oil ExpellerDokumen2 halamanParts of Oil Expellerrahul rkBelum ada peringkat
- Centrifugal Pump 2Dokumen4 halamanCentrifugal Pump 2Juan UlinBelum ada peringkat
- EBSRAY V30 V35 InstallMaintenanceManual Type 23-24-27Dokumen13 halamanEBSRAY V30 V35 InstallMaintenanceManual Type 23-24-27bambang ismailBelum ada peringkat
- Plumbing For Non Mechanical EngineersDokumen61 halamanPlumbing For Non Mechanical Engineersmohd farhan ariff zaitonBelum ada peringkat
- DB 40-20 PDFDokumen22 halamanDB 40-20 PDFMahendra AsawaleBelum ada peringkat
- Bombas Gorman RuppDokumen12 halamanBombas Gorman RuppRafael Hernández RcrewBelum ada peringkat
- Jensen Mixer Series 600 IOM 2010Dokumen24 halamanJensen Mixer Series 600 IOM 2010SergioBelum ada peringkat
- BB1Dokumen8 halamanBB1Roozbeh PBelum ada peringkat
- Flygt Vertical Column FAS VersionDokumen8 halamanFlygt Vertical Column FAS VersioncomedyboBelum ada peringkat
- Lowara Multi-Stage Pumps CatalogueDokumen64 halamanLowara Multi-Stage Pumps Cataloguepinkypacho0% (1)
- Horizontal Split-Case Centrifugal PumpsDokumen2 halamanHorizontal Split-Case Centrifugal PumpsabbasithBelum ada peringkat
- KSB CPKNDokumen70 halamanKSB CPKNAbdul Hafeez100% (1)
- Suction and Discharge Stabilizers: TriplexDokumen2 halamanSuction and Discharge Stabilizers: Triplexnardo_ingBelum ada peringkat
- Air Starters - Series 150bmpDokumen16 halamanAir Starters - Series 150bmpAntonio SerranoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter I General Information of Pump UnitDokumen42 halamanChapter I General Information of Pump UnitRahmat Budi HartantoBelum ada peringkat
- Lip Seal InstallationDokumen11 halamanLip Seal InstallationMachineryengBelum ada peringkat
- Shaft AlignmentDokumen7 halamanShaft AlignmentAmitanshu SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Two Stage Water Ring Vacuum Pump PDFDokumen24 halamanTwo Stage Water Ring Vacuum Pump PDFvallamreddyBelum ada peringkat
- Pump Motor TripDokumen4 halamanPump Motor TripKamal UddinBelum ada peringkat
- Belarus OP 2022 User Manual EngDokumen265 halamanBelarus OP 2022 User Manual EngaritmeticsBelum ada peringkat
- Pump STDRDokumen7 halamanPump STDRsopian320Belum ada peringkat
- Specifications KTA38 G DRIVEDokumen2 halamanSpecifications KTA38 G DRIVEMehdi ChakrouneBelum ada peringkat
- Series 270 & 270h RegulatorDokumen12 halamanSeries 270 & 270h RegulatorSergio Gaete CovarrubiasBelum ada peringkat
- Manual 38731 PDFDokumen79 halamanManual 38731 PDFMartín AlonsoBelum ada peringkat
- Bomba Pratissoli MSDokumen20 halamanBomba Pratissoli MSAlliin Urbina100% (1)
- BPCL Training ReportDokumen34 halamanBPCL Training ReportVishalVaishBelum ada peringkat
- Type DSM (Thru Bore) : Instructions On Installation Operation and Maintenance For Kirloskar PumpDokumen43 halamanType DSM (Thru Bore) : Instructions On Installation Operation and Maintenance For Kirloskar Pumpkprasad_56900Belum ada peringkat
- Warman SHW BrochureDokumen4 halamanWarman SHW BrochureRoberto RuizBelum ada peringkat
- Assembling Procedure For Framo Pump Sd200Dokumen4 halamanAssembling Procedure For Framo Pump Sd200Gonçalo CruzeiroBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance On Unit 5Dokumen10 halamanMaintenance On Unit 5Mazhar UddeenBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Manual en KYP TDDokumen25 halamanTechnical Manual en KYP TDbeqsBelum ada peringkat
- Stanadyne DB2 and DB4 Pump Removal and InstallationDokumen3 halamanStanadyne DB2 and DB4 Pump Removal and InstallationJoseph100% (1)
- Triplex Pump ManualDokumen11 halamanTriplex Pump ManualDustin WhiteBelum ada peringkat
- ViFlow Funke GB PDFDokumen8 halamanViFlow Funke GB PDFukalBelum ada peringkat
- Centrifugal Pump OverloadingDokumen2 halamanCentrifugal Pump OverloadingAbdul AlimBelum ada peringkat
- Oiling System 101: To Restrict or Not To Restrict?: - From Dart Cylinder HeadsDokumen7 halamanOiling System 101: To Restrict or Not To Restrict?: - From Dart Cylinder Headsm_najmanBelum ada peringkat
- Screw Oil Press/ Oil Expeller: Dr. Hammad KhanDokumen15 halamanScrew Oil Press/ Oil Expeller: Dr. Hammad KhanAhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Lowara Cat GeralDokumen288 halamanLowara Cat GeralVitor Padrão100% (1)
- Bolts and Bolt TorqueDokumen1 halamanBolts and Bolt TorqueRichard ChuaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction of Screw PumpDokumen3 halamanIntroduction of Screw PumpPanji Kresno Wijanarko100% (1)
- Steam TurbineDokumen25 halamanSteam TurbineIshan JunejaBelum ada peringkat
- Mud Pump Expendables Gardner DenverDokumen8 halamanMud Pump Expendables Gardner Denverleo0% (1)
- Metal Valves & Pipe Fittings World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryDari EverandMetal Valves & Pipe Fittings World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryBelum ada peringkat
- Sewage Plant Operator: Passbooks Study GuideDari EverandSewage Plant Operator: Passbooks Study GuideBelum ada peringkat
- Manual VSCDokumen15 halamanManual VSCKaushik ChakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance Manual VCP Upto 80mmDokumen16 halamanMaintenance Manual VCP Upto 80mmKaushik Chakraborty0% (1)
- Goods and Services Tax: Group 3Dokumen16 halamanGoods and Services Tax: Group 3Kaushik ChakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- Mobile Wallet Usage in IndiaDokumen20 halamanMobile Wallet Usage in IndiaKaushik ChakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- Case Analysis of Thomas GreenDokumen6 halamanCase Analysis of Thomas GreenKaushik ChakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- Manual: STD: Is-5120: Series: VCPDokumen21 halamanManual: STD: Is-5120: Series: VCPKaushik ChakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- Varat Pump and Machinery Pvt. Ltd.Dokumen59 halamanVarat Pump and Machinery Pvt. Ltd.Kaushik ChakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance Manual VCP Upto 80mmDokumen16 halamanMaintenance Manual VCP Upto 80mmKaushik Chakraborty0% (1)
- Manual VSCDokumen15 halamanManual VSCKaushik ChakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- Solutions Manual To Introduction To Continuum Mechanics: Second EditionDokumen247 halamanSolutions Manual To Introduction To Continuum Mechanics: Second EditionRaj Pratyush80% (5)
- The Core-Periphery Model With Three Regions and MoreDokumen25 halamanThe Core-Periphery Model With Three Regions and MoreJomit C PBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 6 (Calibration of Temperature Measuring Devices - A4)Dokumen16 halamanExperiment 6 (Calibration of Temperature Measuring Devices - A4)Jamiel CatapangBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 24 - Prestressed ConcreteDokumen12 halamanLecture 24 - Prestressed ConcretejeovanBelum ada peringkat
- Class 7 - 9 State Space Representation To Transfer Function and Vice VersaDokumen13 halamanClass 7 - 9 State Space Representation To Transfer Function and Vice Versaapi-26676616Belum ada peringkat
- JUMP Math CC AP Book 7-2 Sample RP7-31 To 35-0-0Dokumen12 halamanJUMP Math CC AP Book 7-2 Sample RP7-31 To 35-0-0Sónia RodriguesBelum ada peringkat
- C 14Dokumen26 halamanC 14pfylBelum ada peringkat
- KrishnaDokumen9 halamanKrishnaKrishna KashyapBelum ada peringkat
- Apex CCTV - Catalog Q2-2013Dokumen78 halamanApex CCTV - Catalog Q2-2013avtechpanamaBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank EC802CDokumen7 halamanQuestion Bank EC802CSatyaki PalBelum ada peringkat
- Regulation 391ADokumen6 halamanRegulation 391Adnageshm4n244100% (1)
- LPO / Low Power ObjectiveDokumen2 halamanLPO / Low Power ObjectiveFor AstroBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Signal Processing: Instructor: Jen-Hui Chuang Instructor: Jen-Hui ChuangDokumen31 halamanDigital Signal Processing: Instructor: Jen-Hui Chuang Instructor: Jen-Hui ChuangRakesh InaniBelum ada peringkat
- CSL361 Programming Assignment 2:: March 9, 2014Dokumen2 halamanCSL361 Programming Assignment 2:: March 9, 2014Jam SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Zdorovye - The Means To PrepareDokumen4 halamanZdorovye - The Means To PrepareBrett DrinkwaterBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To GeologyDokumen76 halamanChapter 1 - Introduction To GeologyZulaikha KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Science 8 ExamDokumen5 halamanScience 8 Examangge21100% (1)
- Pressure Rating For SSII Float EquipmentDokumen2 halamanPressure Rating For SSII Float EquipmentMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikBelum ada peringkat
- 2 & 3 Wheeler Lab ManualDokumen36 halaman2 & 3 Wheeler Lab ManualKarthi100% (1)
- IB Lab - 07 Loaded Metre Rule (DCP)Dokumen3 halamanIB Lab - 07 Loaded Metre Rule (DCP)ringo_tigerBelum ada peringkat
- Module Listing - AY1617 - Updated PDFDokumen4 halamanModule Listing - AY1617 - Updated PDFcmBelum ada peringkat
- Korea Herald 20090512Dokumen1 halamanKorea Herald 20090512raiseyBelum ada peringkat
- CALC SHEET ZOLA - CompressedDokumen33 halamanCALC SHEET ZOLA - CompressedSami Abdelgadir MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- (Darryl D. Hol,) Geometric Mechanics Rotating, TR (B-Ok - CC) PDFDokumen304 halaman(Darryl D. Hol,) Geometric Mechanics Rotating, TR (B-Ok - CC) PDFOceanBelum ada peringkat
- Marine CompositesDokumen390 halamanMarine Compositesbblagonic93% (14)
- A Kinetic Model of The Peirce-Smith Converter: Part I. Model Formulation and ValidationDokumen11 halamanA Kinetic Model of The Peirce-Smith Converter: Part I. Model Formulation and ValidationJaime MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- Spesifikasi Teknis Girder A20 b5Dokumen16 halamanSpesifikasi Teknis Girder A20 b5IkhsanRizaldiBelum ada peringkat
- QTMS Brochure Rev2Dokumen8 halamanQTMS Brochure Rev2ManibalanBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm Exam Fall 2012Dokumen5 halamanMidterm Exam Fall 2012Asanka RodrigoBelum ada peringkat
- STAD Balancing ValvesDokumen10 halamanSTAD Balancing ValvesNestramiBelum ada peringkat