Quantitative Management
Diunggah oleh
Jade Clarisse GarciaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Quantitative Management
Diunggah oleh
Jade Clarisse GarciaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
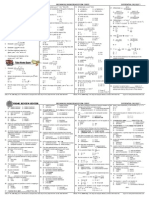
Quantitative approach to MNGT-translating business to a mathematical model ELIMINATION, SUBSTITUTION, MATRIX, GAUSS-JORDAN ELIMINATION Equation of a line a.
point slope form y-y1 = m(x-x1) b. slope intercept form y=mx + b (where m = y2-y1/x2-x1) c. general equation of a line ax+by+c=0 GAUSS-JORDAN ELIMINATION Example: 4x+2y=60 2x+4y=48 4x+2y=60 2x+4y=48 0.5 4 0.5 3 0.5 1 0 1
R1/4 15 48 15 18 15 6 12 6 -2 (R1+R2) R2/3 -0.5 (R2+R1) x=12 y=6
1 2 1 0 1 0 1 0
DECISION THEORY -the choice of model depends upon the characteristics of the decision (ex. Significance, time and cost, complexity) -decisions that are more complex when a data describing the variables are incomplete/uncertain, the degree of certainty is classified into: a. certainty b. risk c. uncertainty ELEMENTS OF DECISION MAKING 1. Doing all feasible alternatives that must be considered in the decision 2. Listing the future events affecting demands that may occur
3. Construct a table which indicates the relationships between pairs of decision elements. This table may also shows the payoffs expressed in profits/any other measures of benefits which would result from each possible combination of decision alternatives and state of nature Ex. State of Nature (demand) increasing stable decreasing Investment Medium 250000 500000 -100000
Large 600000 400000 -260000
Small 200000 150000 120000
NON-PROBABILITY CRITERIA a. Maximax- carries the highest possible payoffs (all under increasing) b. Maximin- choosing the best of the worst ( 120000) c. Minimax regret criterion- considers the result of wrong alternatives (large value in each nature minus each value in the row/nature, ex. 600-600,600-250,600-200) increasing 0 stable 100 decreasing 380 350 kasi pinakamababa sa pinakamatataas 350 0 220 400 350 0
d. Probability criteria- to determine unexpected value, we must consider the probabilities for each possible outcomes EV = XiPi Xi specific alternative measure in peso Pi probability EV is the payoffs (0.3x600000=180000, 180000 is the payoff) Expected Value with Perfect Information- Summation of highest probabilities minus summation of payoffs of each nature 180+300+12=492K Ex. 492-394(394 is summation of payoffs in increasing)=98 492-365= 127 492-162=330 98+127+330=555k opportunity profit DECISION TREE ANALYSIS -a technique to aid the decision makers in identifying the outcome for each decision alternative assessing probability associated with each outcome assigning cashflow in the form of payoffs and cost and keeping the sequence of outcomes and decision in the proper chronological order
BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS- algebraic and/or graphic model for describing relationship between cost and revenue for different volumes of production FC fixed cost VC variable cost Q quantity output/units TR total revenue TC total cost PR profit PS selling price PR = TR-TC TC= FC +TVC TVC = VC x Q PR = TR [FC + (VC)(Q)]
Assumptions 1. All cost and volume are known 2. Cost-volume relationship are equal 3. All output can be sold Advantage 1. Simple and easy to visualize 2. Focuses upon profitability 3. Uses algebraic and/or graphical display
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Calculating pump head and specific speed using Euler's equationDokumen9 halamanCalculating pump head and specific speed using Euler's equationspdhimanBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Application Programming GuideDokumen210 halamanApplication Programming GuideZaki La ColombeBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Automatic Parallel Parking System ReportDokumen23 halamanAutomatic Parallel Parking System ReportFrances Ekenedilichukwu Awachie50% (2)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- Chapter 11 TestDokumen7 halamanChapter 11 Testkaderrto1986Belum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Demand System Estimation NewDokumen13 halamanDemand System Estimation NewGaurav JakhuBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Spring - 2008 - MSIS 301 - STUDY GUIDE FINAL EXAM - StudentsDokumen11 halamanSpring - 2008 - MSIS 301 - STUDY GUIDE FINAL EXAM - StudentsAkame KuromeBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- SSPC PA2 Measurement of Dry Coating Thickness With Magnetic GagesDokumen11 halamanSSPC PA2 Measurement of Dry Coating Thickness With Magnetic Gageslonglong3003Belum ada peringkat
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- IV B.Tech CAD/CAM Lab ManualDokumen127 halamanIV B.Tech CAD/CAM Lab ManualSantosh SantuBelum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- 1 Nature of MathematicsDokumen15 halaman1 Nature of MathematicsAngelica GeronBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- Maths AnxietyDokumen14 halamanMaths AnxietyZahida ParveenBelum ada peringkat
- 6.045 Class 7: Computability Theory FundamentalsDokumen53 halaman6.045 Class 7: Computability Theory FundamentalsMuhammad Al KahfiBelum ada peringkat
- Representing Sequences Recursively and ExplicitlyDokumen4 halamanRepresenting Sequences Recursively and Explicitlytwitch tv caibingweiBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Physics 1C Midterm With SolutionDokumen9 halamanPhysics 1C Midterm With SolutionSarita DokaniaBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Mathematics for Business Students Worksheet No. 7 SolutionDokumen6 halamanMathematics for Business Students Worksheet No. 7 Solutionahmed wahshaBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Development of Turning Fixture For Flywheel"Dokumen48 halamanDevelopment of Turning Fixture For Flywheel"KIRAN YADAVBelum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Computer Applications (ICSE) Sample Paper 8Dokumen4 halamanComputer Applications (ICSE) Sample Paper 8Guide For School77% (13)
- Answers pt1 PDFDokumen33 halamanAnswers pt1 PDFJason SchellerBelum ada peringkat
- ცდომილებათა თეორიის ელემენტები - 1, თსუ, 2003Dokumen3 halamanცდომილებათა თეორიის ელემენტები - 1, თსუ, 2003Marina MenteshashviliBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Pizza Hut Pakistan Customer SurveyDokumen4 halamanPizza Hut Pakistan Customer SurveyMaham MasaudBelum ada peringkat
- 1st Periodical TestDokumen1 halaman1st Periodical TestbjnatsBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Philosophy of Mind - Mental States and Brain States (Leibniz and Kripke)Dokumen6 halamanPhilosophy of Mind - Mental States and Brain States (Leibniz and Kripke)Victoria RoncoBelum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Research Chapter 3Dokumen9 halamanResearch Chapter 3Ashly MacandiliBelum ada peringkat
- 2.8 Index of Refraction LabDokumen4 halaman2.8 Index of Refraction LabsashaBelum ada peringkat
- Differential Calculus ME 2010Dokumen2 halamanDifferential Calculus ME 2010Maralyssa Dela Rosa BicoBelum ada peringkat
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- LECTURE (NOTE) - Module 01 - MeasurementDokumen86 halamanLECTURE (NOTE) - Module 01 - Measurement821A 45RajBelum ada peringkat
- Gaining Confidence With GD T - Part 3Dokumen20 halamanGaining Confidence With GD T - Part 3Abraham ThomasBelum ada peringkat
- Accelerated Bridge ConstructionDokumen260 halamanAccelerated Bridge Constructionkhx2100% (1)
- Kangaroo GraphDokumen2 halamanKangaroo Graphapi-302577842Belum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- James Mcivor: A B C BDokumen4 halamanJames Mcivor: A B C BMatthew StevenBelum ada peringkat
- Distance Rate and Time Problems WorksheetDokumen15 halamanDistance Rate and Time Problems Worksheetmahisa agniBelum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)