DVT Prophylaxis Safety Contraindicat
Diunggah oleh
a1b140 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
67 tayangan1 halamanThis document provides recommendations for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prophylaxis regimens based on a patient's total risk factor score. For a score of 0-1 (low risk), options include out of bed activity and compression sleeves. For a score of 2 (moderate risk), options include daily low molecular weight heparin injections or unfractionated heparin twice daily. For a score of 3 or higher (high risk), options include daily low molecular weight heparin injections. Contraindications to anticoagulation therapy include active bleeding, high bleeding risk, and low platelet count. Mechanical methods like compression sleeves are recommended for high bleeding risk patients.
Deskripsi Asli:
DVT Prophylaxis Safety Contraindicat
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis document provides recommendations for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prophylaxis regimens based on a patient's total risk factor score. For a score of 0-1 (low risk), options include out of bed activity and compression sleeves. For a score of 2 (moderate risk), options include daily low molecular weight heparin injections or unfractionated heparin twice daily. For a score of 3 or higher (high risk), options include daily low molecular weight heparin injections. Contraindications to anticoagulation therapy include active bleeding, high bleeding risk, and low platelet count. Mechanical methods like compression sleeves are recommended for high bleeding risk patients.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
67 tayangan1 halamanDVT Prophylaxis Safety Contraindicat
Diunggah oleh
a1b14This document provides recommendations for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prophylaxis regimens based on a patient's total risk factor score. For a score of 0-1 (low risk), options include out of bed activity and compression sleeves. For a score of 2 (moderate risk), options include daily low molecular weight heparin injections or unfractionated heparin twice daily. For a score of 3 or higher (high risk), options include daily low molecular weight heparin injections. Contraindications to anticoagulation therapy include active bleeding, high bleeding risk, and low platelet count. Mechanical methods like compression sleeves are recommended for high bleeding risk patients.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
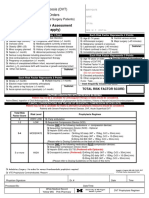
NYPH Recommended DVT Prophylaxis Regimen
Total Risk Factor Score 0-1 2 Incidence of DVT 10% 10-20% Risk Level Low Risk Moderate Risk Prophylaxis Regimen Options Out of Bed Ad Lib & Venodyne Segmental Compression Sleeves Enoxaparin injection 40 mg subcutaneous daily Dalteparin injection 2500 units subcutaneous daily UH 5000 units subcutaneous q12hr Fondaparinux (RESTRICTED) 2.5 mg subcutaneous daily, Consider Venodyne Segmental Compression Sleeves Enoxaparin injection 30 mg subcutaneous q 12h Dalteparin injection 5000 units subcutaneous daily Unfractionated Heparin 5000 units subcutaneous q 8h Fondaparinux (RESTRICTED) 2. 5mg subcutaneous daily and consider Venodyne Segmental Compression Sleeves
3 or Above
20-80%
High Risk
Enoxaparin 40 mg subcutaneous daily (PREVAIL Trial recommendations)
For Orthopedic patients only: Warfarin po, dose accordingly for INR 2-3
For Acute Ischemic Stroke only:
Prophylaxis Safety Considerations
Potential Medical Contraindications Patient is experiencing active bleeding or bleeding within past 72 hours Patient is at significant risk for major bleed Patients platelet count 50,000/mm3 Recent major procedure with significant concern for ongoing bleeding NOTE: If any of the above boxes are checked, the patient may not be a candidate for anticoagulant therapy and should be considered for alternative prophylactic measures (such as ambulation and Venodyne Segmental Compression Sleeves). Potential Mechanical Contraindications: Venodyne Segmental Compression Sleeves Patient has severe peripheral arterial disease Patient has acute DVT Patient has severe ulcers NOTE: It is recommended that mechanical methods of thromboprophylaxis be used primarily in patients at high risk of bleeding or as an adjunct to anticoagulant-based thromboprophylaxis. Specific Detail for Medical Contraindications: 1. Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a contraindication to heparin therapy, but patients may receive Fondaparinux. 2. Renal insufficiency (GFR <30) is a contraindication to LMWH, however Unfractionated Heparin can be safely used. 3. Dissecting or cerebral aneurysm 4. Bacterial endocarditits or pericarditis 5. Active peptic ulcer disease, ulcerative GI lesions 6. Hypertension: severe, uncontrolled, malignant, hypertensive crisis 7. Severe head trauma 8. INR or a PTT Ratio >1.5 (unless antiphospholipid antibodies) 9. Recent TURP 10. Eye, brain or spinal cord injury within past 48 hours 11. For Heparin or Enoxaparin: History of HIT 12. For Enoxaparin: Epidural catheter removal or spinal tap <2 hours prior to dose, weight <45kg; hemodialysis
Source: *Hirsch, J., et al, (2008) */Executive Summary*: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). /133(6) (Supplement):71S-109S, June 200.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Deep Vein ThrombosisDokumen22 halamanDeep Vein ThrombosisEznal MahidinBelum ada peringkat
- Anticoagulatio N Asra Guidelines: Sravya VemuriDokumen62 halamanAnticoagulatio N Asra Guidelines: Sravya VemuriSiva Prasad AspBelum ada peringkat
- Haematology DrugsDokumen17 halamanHaematology DrugsParyBelum ada peringkat
- UFH LMWH Fonda - 06september2020Dokumen7 halamanUFH LMWH Fonda - 06september2020gabrimarteBelum ada peringkat
- Deep Vein Thrombosis - 2003Dokumen34 halamanDeep Vein Thrombosis - 2003farmasi_hm100% (1)
- Venous ThromboembolismDokumen12 halamanVenous ThromboembolismAhmad ElgazzarBelum ada peringkat
- Volume 10, No. 5 January 2020Dokumen4 halamanVolume 10, No. 5 January 2020zoran cukovicBelum ada peringkat
- ACCP Anticoagulation Guidelines SummaryDokumen11 halamanACCP Anticoagulation Guidelines Summaryd40sithui100% (3)
- Medications Sheet PreopDokumen37 halamanMedications Sheet Preopapi-503879428Belum ada peringkat
- MILgfgsd V1Dokumen4 halamanMILgfgsd V1garywall.ukBelum ada peringkat
- Anticoagulation Protocol For PostDokumen8 halamanAnticoagulation Protocol For PostMohammed IbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Thromboprophylaxis & RADokumen38 halamanThromboprophylaxis & RASiva SankarBelum ada peringkat
- Now What-How Do I Protect Them From HarmDokumen1 halamanNow What-How Do I Protect Them From HarmMohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Deep Vein Thrombosis Pharmacology: Paulo Arwin G. Baduria, RNDokumen34 halamanDeep Vein Thrombosis Pharmacology: Paulo Arwin G. Baduria, RNPaulo Arwin BaduriaBelum ada peringkat
- UHS Anticoagulation Therapy Guideline Y12 04Dokumen7 halamanUHS Anticoagulation Therapy Guideline Y12 04staylor235Belum ada peringkat
- Farmakologi Kel 3Dokumen33 halamanFarmakologi Kel 3SalsabilaRiyadiniBelum ada peringkat
- AnticogulantDokumen3 halamanAnticogulantWan TokBelum ada peringkat
- DrugsDokumen27 halamanDrugspeterjongBelum ada peringkat
- Icu Drug StudyDokumen23 halamanIcu Drug StudyApril LebrilloBelum ada peringkat
- Vit KguidelinesDokumen2 halamanVit KguidelinesMayer Rosenberg100% (1)
- Peri-Operative Management of Patients Receiving AnticoagulantsDokumen22 halamanPeri-Operative Management of Patients Receiving AnticoagulantsCheuk Hei LauBelum ada peringkat
- Pre and Post Operative CareDokumen9 halamanPre and Post Operative CareSara Abdi OsmanBelum ada peringkat
- Anticoagulants: Julene FunkDokumen25 halamanAnticoagulants: Julene FunkJulieBelum ada peringkat
- Anticoagulation in Presence of Neuraxial Anesthesia (Guidelines Do Not Apply To Peripheral NerveDokumen3 halamanAnticoagulation in Presence of Neuraxial Anesthesia (Guidelines Do Not Apply To Peripheral NerveShoyeb KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac AnesthesiologyDokumen48 halamanCardiac AnesthesiologyNiaBelum ada peringkat
- WarfarinDokumen4 halamanWarfarinekramBelum ada peringkat
- Anx 135796 enDokumen108 halamanAnx 135796 enMohamed RawyBelum ada peringkat
- 2022-OXFORD-HANDBOOK-OF-ANAESTHESIA-Oxford-Press-5th-Edition ExportDokumen4 halaman2022-OXFORD-HANDBOOK-OF-ANAESTHESIA-Oxford-Press-5th-Edition ExportHany ElbarougyBelum ada peringkat
- Procoagulantes Guias PDFDokumen30 halamanProcoagulantes Guias PDFtsntbBelum ada peringkat
- Perioperative Management of AnticoagulationDokumen33 halamanPerioperative Management of Anticoagulationmonge20Belum ada peringkat
- Warfarin Therapy Management: ScopeDokumen9 halamanWarfarin Therapy Management: ScopesastiraBelum ada peringkat
- Warfarin Perioperative ManagementDokumen8 halamanWarfarin Perioperative Managementzoran cukovicBelum ada peringkat
- ASRA Guidelines For CNBDokumen66 halamanASRA Guidelines For CNBAshiyan IrfanBelum ada peringkat
- Neuraxial Blockade and AnticoagulantsDokumen69 halamanNeuraxial Blockade and Anticoagulantskamel6Belum ada peringkat
- Liverpool Ni Modi PineDokumen5 halamanLiverpool Ni Modi Pinerachmat fajar noor kBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3: Perioperative ManagementDokumen14 halamanChapter 3: Perioperative ManagementpoddataBelum ada peringkat
- Receiving Concurrent Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Erythromycin, Saquinavir, Verapamil, Fluconazole) - 25 MG Once Daily InitiallyDokumen272 halamanReceiving Concurrent Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Erythromycin, Saquinavir, Verapamil, Fluconazole) - 25 MG Once Daily InitiallyFatima Doran PandaogBelum ada peringkat
- Anaesthetic Management of PheochromocytomaDokumen22 halamanAnaesthetic Management of PheochromocytomaZoelBelum ada peringkat
- Heparin Guideline: Intended AudienceDokumen16 halamanHeparin Guideline: Intended AudienceKingsley AmamchukwuBelum ada peringkat
- 1b. Ambulatory AnesthesiaDokumen47 halaman1b. Ambulatory AnesthesiaBakingpancakes100% (4)
- VTEDokumen45 halamanVTEABREHAM BUKULOBelum ada peringkat
- HeparinDokumen4 halamanHeparinTri Purma SariBelum ada peringkat
- Guideline On The Management of Bleeding in Patients On Antithrombotic Agents.Dokumen10 halamanGuideline On The Management of Bleeding in Patients On Antithrombotic Agents.Madalina TalpauBelum ada peringkat
- 443e Technique of Lumbar PunctureDokumen4 halaman443e Technique of Lumbar PunctureEXB GensanBelum ada peringkat
- Mini Warfarin GuidelinesDokumen2 halamanMini Warfarin GuidelinesPeunn NattaphatBelum ada peringkat
- An Update Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: SurotoDokumen36 halamanAn Update Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: SurotoShinta DianBelum ada peringkat
- Bivalirudine Drug Presentation From Nicvd DhakaDokumen28 halamanBivalirudine Drug Presentation From Nicvd DhakaNavojit ChowdhuryBelum ada peringkat
- LMWH QML 06Dokumen7 halamanLMWH QML 06pd7qmlBelum ada peringkat
- Antiretroviral Therapy (ART)Dokumen41 halamanAntiretroviral Therapy (ART)Ashik Jithu JohnBelum ada peringkat
- Anticoagulantele Si Explorarile Invazive 2021Dokumen33 halamanAnticoagulantele Si Explorarile Invazive 2021GabrielaOaneBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology CardiovascularDokumen86 halamanPharmacology Cardiovascularamasoud96 amasoud96Belum ada peringkat
- Thrombosis Risk Factor Assessment (Choose All That Apply) : Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Prophylaxis OrdersDokumen2 halamanThrombosis Risk Factor Assessment (Choose All That Apply) : Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Prophylaxis OrdersPutu Gizha Satrya GautamaBelum ada peringkat
- Ecart For PrintingDokumen10 halamanEcart For PrintingbluennaBelum ada peringkat
- A NTICOAGULANTDokumen48 halamanA NTICOAGULANTSharliza S100% (1)
- Covid 19 Medications ConferenceDokumen68 halamanCovid 19 Medications ConferenceSaraBelum ada peringkat
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE)Dokumen40 halamanDeep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE)Shahab AlamBelum ada peringkat
- 07 - 10 - 21 Treatment of Covid 19 InfectionDokumen26 halaman07 - 10 - 21 Treatment of Covid 19 InfectionStonefalconBelum ada peringkat
- Anticoagulants Preoperative InstructionsDokumen3 halamanAnticoagulants Preoperative InstructionsDevaki VisvalingamBelum ada peringkat
- Top Trials in Gastroenterology & HepatologyDari EverandTop Trials in Gastroenterology & HepatologyPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (7)
- Margaret Sanger Thesis StatementDokumen7 halamanMargaret Sanger Thesis StatementJim Webb100% (2)
- Person Gordon'S Approach: Before Hospitalization During Hospitalization PsychologicalDokumen2 halamanPerson Gordon'S Approach: Before Hospitalization During Hospitalization Psychologicalpearlannesanford1995Belum ada peringkat
- State of Florida Vs Varsha Bevin, Case Number 20-TR-063015Dokumen8 halamanState of Florida Vs Varsha Bevin, Case Number 20-TR-06301520-TR-063015100% (4)
- Ethics - Nursing Test QuestionsDokumen31 halamanEthics - Nursing Test QuestionsRNStudent1100% (5)
- Eye Infection and Blepharitis by MHSNDokumen18 halamanEye Infection and Blepharitis by MHSNMhsn0% (1)
- Font Office TopicDokumen27 halamanFont Office TopicJon LexemeneBelum ada peringkat
- Answer Script-Wound and Pain Management Formative Test-Quiz 2 (July 13)Dokumen6 halamanAnswer Script-Wound and Pain Management Formative Test-Quiz 2 (July 13)Ariputhiran NarayananBelum ada peringkat
- Collado 2010Dokumen20 halamanCollado 2010JoãoBelum ada peringkat
- Wellness Tourism Sector Strategy - National Export Strategy (2018-2022)Dokumen55 halamanWellness Tourism Sector Strategy - National Export Strategy (2018-2022)Ministry of Development Strategies and International TradeBelum ada peringkat
- Kendall Marino Final Research ArticleDokumen4 halamanKendall Marino Final Research Articleapi-311434856Belum ada peringkat
- Jurnal Crossbite Anterior PDFDokumen4 halamanJurnal Crossbite Anterior PDFThania Olivia FahrieBelum ada peringkat
- Chemosensitivity Vol 2Dokumen461 halamanChemosensitivity Vol 2pmendez00Belum ada peringkat
- A Short Review of Wintergreen - Methyl Salicylate Toxicity - IJPHA - Winter-2015 - Digitalworking - p43-49Dokumen7 halamanA Short Review of Wintergreen - Methyl Salicylate Toxicity - IJPHA - Winter-2015 - Digitalworking - p43-49Alain RatataBelum ada peringkat
- The Psychobiotic Revolution Mood, Food, and The New Science of The Gut-Brain ConnectionDokumen160 halamanThe Psychobiotic Revolution Mood, Food, and The New Science of The Gut-Brain ConnectionjinooBelum ada peringkat
- ENPC and TNCC in Portugal - RBennetDokumen5 halamanENPC and TNCC in Portugal - RBennetFernando Almeida SantosBelum ada peringkat
- SOP Stroke RehabilitationDokumen43 halamanSOP Stroke RehabilitationThanty Putrantii WijayantiBelum ada peringkat
- Addiction Severity Index Baseline Followup 4Dokumen15 halamanAddiction Severity Index Baseline Followup 4Ashok Kumar KrishnamoorthyBelum ada peringkat
- Module 9, Decentralization and Local GovernanceDokumen36 halamanModule 9, Decentralization and Local GovernanceJulius BrillantesBelum ada peringkat
- NoDust BookletDokumen16 halamanNoDust BookletDen OpialaBelum ada peringkat
- Cadbury Grp5Dokumen8 halamanCadbury Grp5Debashree MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Calisthenics For Beginners Beginner Calisthenics Workout at HomeDokumen43 halamanCalisthenics For Beginners Beginner Calisthenics Workout at HomePaolo PolveriniBelum ada peringkat
- GRADE 5 - SOCIAL STUDIES - NotesDokumen34 halamanGRADE 5 - SOCIAL STUDIES - NotesJaveria FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Child Protection Safeguarding Policy FirstPoint SchoolDokumen43 halamanChild Protection Safeguarding Policy FirstPoint SchoolRoss MintonBelum ada peringkat
- Business Case ProposalDokumen14 halamanBusiness Case ProposalAnooshayBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Clients With Disturbances in OxygenationDokumen13 halamanManagement of Clients With Disturbances in OxygenationClyde CapadnganBelum ada peringkat
- Books by Robie H. HarrisDokumen2 halamanBooks by Robie H. HarrisCandlewick PressBelum ada peringkat
- Hotel ClassificationDokumen9 halamanHotel ClassificationEricka Rose AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- Lier Upper Secondary SchoolDokumen8 halamanLier Upper Secondary SchoolIES Río CabeBelum ada peringkat
- 1 PDFDokumen359 halaman1 PDFHira PujariBelum ada peringkat
- Cantas Company Profile 01oct2019Dokumen10 halamanCantas Company Profile 01oct2019Fatih CahyoBelum ada peringkat