Clot Expands: Deformity/injury To The Endocardium
Diunggah oleh
Jynrose Kaye GulpanyJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Clot Expands: Deformity/injury To The Endocardium
Diunggah oleh
Jynrose Kaye GulpanyHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Gulpany, Jynrose Kaye L.
BSN 4A
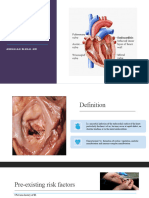
Infective Endocarditis - microbial infection of the endolethial surface of the heart -usually develops in people with prosthetic heart valves or structural cardiac defects - more common in older people, who are more likely to have degenerative or calcific valve lesions, reduced immunologic response to infection, and metabolic alterations associated with aging PATHOPHYSIOLOGY deformity/injury to the endocardium
clot expands
vegetations may embolize to other tissues throughout the body
body's normal defenses does not recognize new clots
clot formation
infection erode through the endocardium and underlying structures
infectious organisms invade the clot and endocardial lesion
platelets, fibrin, and microorganisms cluster as vegetations on the endocardium
tears/deformities to other valvular leaflets, dehiscence of prosthetic valves, deformity of chordae tendonae, mural abscesses
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS fever heart murmur clusters of petechiae small, painful nodules in the pads of fingers or toes (Osler nodes) irregular, red or purple, painless, flat macules may be present on the palms, fingers, hands, soles, and toes (Janeway lesions) hemorrhages with pale centers caused by emboli may be observed in the fundi of the eyes (Roth spots) reddish brown lines and streaks (Splinter hemorrhages) cardiomegaly, heart failure, tachycardia, or splenomegaly may occur headache temporary or transient cerebral ischemia strokes
ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSTIC FINDINGS definitive diagnosis is made when a microorganism is found in two separate blood culture, in a vegetation or in an abscess 3 sets of blood cultures drawn over a 24hour period should be obtained Elevated WBC Anemic Positive rheumatoid factor
Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) or C-reactive protein Microscopic hematuria Echocardiogram to view a mass
PREVENTION: Antibiotic prophylaxis for high risk patients Good oral hygiene Avoid nail biting Minimize outbreaks of acne and psoriasis Female patients must not use intrauterine devices Avoid body piercing Aseptic technique in caring for patients with IV catheters and also during invasive procedures
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT: - Antibiotic therapy for 2-6weeks - Monitor serum levels of antibiotic - Blood cultures are taken periodically - Temperature is regularly monitored SURGICAL MANAGEMENT - Valve debridement or excision - Debridement of vegetations - Debridement and closure of abscess - Closure of fistula NURSING MANAGEMENT Monitor pts temp Assess heart sounds WOF s/sx of systemic embolization, pulmonary infarction and infiltrates WOF s/sx of organ damage Management of infection Invasive lines must be assessed regularly Activity restriction Supervise and monitor antibiotic treatment
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 2 - RH Fev, Inf EndoDokumen37 halaman2 - RH Fev, Inf EndoLobna ElkilanyBelum ada peringkat
- Infective Endocarditis.... MshembaDokumen39 halamanInfective Endocarditis.... MshembaTimothy Casmiry MshembaBelum ada peringkat
- Ug Infective Endocarditis SubmitDokumen49 halamanUg Infective Endocarditis SubmitAhmed FaizalBelum ada peringkat
- Infectious EndocarditisDokumen19 halamanInfectious Endocarditisinyanji.barasaBelum ada peringkat
- Infective EndocarditisDokumen67 halamanInfective EndocarditisDr. Rajesh PadhiBelum ada peringkat
- Infective EndocarditisDokumen45 halamanInfective Endocarditissathish LakshmananBelum ada peringkat
- PEDIA - Acquired Heart DiseaseDokumen5 halamanPEDIA - Acquired Heart DiseaseStephen Pilar PortilloBelum ada peringkat
- 9) Infective Endocarditis (IE)Dokumen3 halaman9) Infective Endocarditis (IE)Aris PaparisBelum ada peringkat
- Infective EndocarditisDokumen49 halamanInfective EndocarditismajdBelum ada peringkat
- S Infective EndocarditisDokumen24 halamanS Infective EndocarditisMpanso Ahmad AlhijjBelum ada peringkat
- Infections of The Cardiovascular System 2024Dokumen46 halamanInfections of The Cardiovascular System 2024aguilarjanicaBelum ada peringkat
- Recog Manag Diff Type Carditis Endo Myo PericardiditDokumen7 halamanRecog Manag Diff Type Carditis Endo Myo PericardiditArdi WidiatmikaBelum ada peringkat
- Infective EndocarditisDokumen57 halamanInfective EndocarditisRika FitriaBelum ada peringkat
- Cardio InfectionDokumen6 halamanCardio InfectionCindy Mae de la TorreBelum ada peringkat
- Bacterial EndocarditisDokumen5 halamanBacterial EndocarditisAMOS MELIBelum ada peringkat
- Infective Endocarditis IeDokumen26 halamanInfective Endocarditis IeAnthie FitriBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Infective EndocarditisDokumen37 halamanLecture Infective EndocarditisJohnson OlawaleBelum ada peringkat
- CASE STUDY - Infective EndocarditisDokumen6 halamanCASE STUDY - Infective EndocarditisDudil GoatBelum ada peringkat
- Infective EndocarditisDokumen66 halamanInfective Endocarditistummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (4)
- Infective EndocarditisDokumen12 halamanInfective EndocarditisYoulin KohBelum ada peringkat
- ValvularHeartDisease Notes S5w4Dokumen6 halamanValvularHeartDisease Notes S5w4razzletothedazzleBelum ada peringkat
- PathologyDokumen28 halamanPathologyakkashamrishBelum ada peringkat
- Vasculitis in ChildrenDokumen22 halamanVasculitis in ChildrenRashed ShatnawiBelum ada peringkat
- Infective Endocardits: Dr. Abhay Kumar MODERATOR-Dr. Rajesh KumarDokumen42 halamanInfective Endocardits: Dr. Abhay Kumar MODERATOR-Dr. Rajesh KumarAbhay BarnwalBelum ada peringkat
- EndocarditisDokumen53 halamanEndocarditisمحمد ربيعيBelum ada peringkat
- EndocarditisDokumen38 halamanEndocarditiseviherdiantiBelum ada peringkat
- Infective EndocarditisDokumen68 halamanInfective EndocarditisDr. Rajesh PadhiBelum ada peringkat
- CVS 5 PDFDokumen24 halamanCVS 5 PDFafaq alismailiBelum ada peringkat
- Endocarditis: by - Mr. Rahul P KshirsagarDokumen50 halamanEndocarditis: by - Mr. Rahul P KshirsagarIndomedikgramBelum ada peringkat
- 9 - Invefctive EndocarditiesDokumen71 halaman9 - Invefctive EndocarditiesMahmoud OmarBelum ada peringkat
- Infective EndocarditisDokumen37 halamanInfective EndocarditisBiruk WorkuBelum ada peringkat
- Micro - CVS InfectionsDokumen55 halamanMicro - CVS InfectionsMahmoud hilmyBelum ada peringkat
- Infective Endocarditis WORDDokumen24 halamanInfective Endocarditis WORDHashmithaBelum ada peringkat
- VASCULITIS by Dr. AJ. 1Dokumen34 halamanVASCULITIS by Dr. AJ. 1Abira KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Meningitis Bacterial: EtiologyDokumen22 halamanMeningitis Bacterial: EtiologyRhima KemalaBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study Worksheet EndocarditisDokumen6 halamanCase Study Worksheet EndocarditisSharlee StoneBelum ada peringkat
- Infective Endocarditis: Uaepong Limpapanasit July 5, 2010Dokumen45 halamanInfective Endocarditis: Uaepong Limpapanasit July 5, 2010Rapid MedicineBelum ada peringkat
- Rheumatic HeartDokumen5 halamanRheumatic HeartMariahnaSadjaluddinBelum ada peringkat
- Case Presentation of Infective Endocarditis-1Dokumen23 halamanCase Presentation of Infective Endocarditis-1pritidinda3070Belum ada peringkat
- Die (20 Versus 12 Percent) Experience An Embolic Event (60 Versus 31 Percent) Have A CNS Event (20 Versus 13 Percent) Not Undergo Surgery (26 Versus 39 PercentDokumen37 halamanDie (20 Versus 12 Percent) Experience An Embolic Event (60 Versus 31 Percent) Have A CNS Event (20 Versus 13 Percent) Not Undergo Surgery (26 Versus 39 Percentnathan asfahaBelum ada peringkat
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDokumen41 halamanValvular Heart DiseaseVirendra Shekhawat100% (1)
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokumen14 halamanRheumatic Heart Diseaseudaybujji100% (1)
- Anak 3.1 Infective Endocarditis DRTLTDokumen21 halamanAnak 3.1 Infective Endocarditis DRTLTAnastasia PinkyBelum ada peringkat
- Sbe in ChildrenDokumen42 halamanSbe in Childrengrim reaperBelum ada peringkat
- 8 EndocarditisDokumen19 halaman8 EndocarditisdaisyBelum ada peringkat
- Infective EndocarditisDokumen45 halamanInfective EndocarditisReem 10Belum ada peringkat
- Infective Endocarditis: Ainal Fadly Adigama PF Enny SuryantiDokumen50 halamanInfective Endocarditis: Ainal Fadly Adigama PF Enny SuryantiFaisal Reza AdiebBelum ada peringkat
- Infective EndocarditisDokumen18 halamanInfective EndocarditisSam100% (1)
- Rheuamatic Heart DiseaseDokumen28 halamanRheuamatic Heart DiseaseNITHA KBelum ada peringkat
- Infective Endocarditis FinalDokumen32 halamanInfective Endocarditis FinalAbdallahBelum ada peringkat
- Infective EndocarditisDokumen66 halamanInfective Endocarditissanjivdas100% (4)
- Endocarditis Lecture FinalDokumen63 halamanEndocarditis Lecture FinalFlorencio D. Santos IVBelum ada peringkat
- Aureus or Escherichia Coli. Less Typically, Polymicrobial Abscesses Have Been NotedDokumen7 halamanAureus or Escherichia Coli. Less Typically, Polymicrobial Abscesses Have Been NotedDiana MinzatBelum ada peringkat
- Infective Endocarditis: Hariprasad KDokumen28 halamanInfective Endocarditis: Hariprasad KHari Prasad K100% (1)
- Vascular DiseasesDokumen9 halamanVascular DiseasesJose SirittBelum ada peringkat
- VasculitisDokumen184 halamanVasculitisRada NemirovskiBelum ada peringkat
- EndocarditisDokumen13 halamanEndocarditisSumathi GopinathBelum ada peringkat
- Cardio - InfectiveDokumen13 halamanCardio - InfectiveHgiel100% (1)
- Special Medical Conditions 1 1Dokumen87 halamanSpecial Medical Conditions 1 1Kurt JanssenBelum ada peringkat
- Pericardial EffusionDokumen1 halamanPericardial EffusionJynrose Kaye GulpanyBelum ada peringkat
- Open Heart Surgery-Post Op CareDokumen6 halamanOpen Heart Surgery-Post Op CareJynrose Kaye Gulpany100% (4)
- University of Perpetual Help System DALTA: College of Radiologic TechnologyDokumen2 halamanUniversity of Perpetual Help System DALTA: College of Radiologic TechnologyJynrose Kaye GulpanyBelum ada peringkat
- University of Perpetual Help System DALTA: College of Radiologic TechnologyDokumen3 halamanUniversity of Perpetual Help System DALTA: College of Radiologic TechnologyJynrose Kaye GulpanyBelum ada peringkat
- MalariaDokumen18 halamanMalariaJynrose Kaye GulpanyBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study of Psycho Therapeutic AgentDokumen6 halamanDrug Study of Psycho Therapeutic AgentJynrose Kaye GulpanyBelum ada peringkat
- Discharge PlanningDokumen1 halamanDischarge PlanningJynrose Kaye GulpanyBelum ada peringkat
- 6: Diagnostic Microbiology and Laboratory Methods - Pocket DentistryDokumen9 halaman6: Diagnostic Microbiology and Laboratory Methods - Pocket Dentistrykam LinBelum ada peringkat
- The Diabetic FootDokumen553 halamanThe Diabetic Footjustme_adry100% (1)
- Sindromul - De.epuizare (Bourn-Out) La Medici. F Matache. Full PDFDokumen10 halamanSindromul - De.epuizare (Bourn-Out) La Medici. F Matache. Full PDFCosmin BurleanuBelum ada peringkat
- Smoking Is Injurious To HealthDokumen11 halamanSmoking Is Injurious To HealthÏmŗäņPŗïņċë100% (1)
- Healthy Foods and The Body Parts They ResembleDokumen4 halamanHealthy Foods and The Body Parts They ResembleRobert AndujarBelum ada peringkat
- Drug-Food Interactions in Anti-Cancer TherapyDokumen16 halamanDrug-Food Interactions in Anti-Cancer Therapyさゆう FayaBelum ada peringkat
- Molecular Genetics ConservationDokumen498 halamanMolecular Genetics ConservationDiaconu Sofia0% (1)
- Freud and AnesthesiaDokumen5 halamanFreud and AnesthesiaRaluca LBelum ada peringkat
- Time Delays in The Human Baroreceptor ReflexDokumen11 halamanTime Delays in The Human Baroreceptor ReflexaontreochBelum ada peringkat
- Zoonoses-In A NutshellDokumen1 halamanZoonoses-In A NutshellGeetika PremanBelum ada peringkat
- Balleine and Doherty 2010 - NeuropsychopharmacologyDokumen22 halamanBalleine and Doherty 2010 - NeuropsychopharmacologySirathpulBelum ada peringkat
- Hornsby Girls High School: Trial HSC Examination 2019 HSC BiologyDokumen29 halamanHornsby Girls High School: Trial HSC Examination 2019 HSC BiologyDrewBelum ada peringkat
- EDV022302Dokumen31 halamanEDV022302Smith Quanco AlexsanderBelum ada peringkat
- Page From Thompson Thompson Genetics in Medicine 8Dokumen2 halamanPage From Thompson Thompson Genetics in Medicine 8jorgegrodlBelum ada peringkat
- Saprolegnia Diclina IIIA and S. Parasitica Employ Different Infection Strategies When Colonizing Eggs of Atlantic Salmon, Salmo Salar LDokumen10 halamanSaprolegnia Diclina IIIA and S. Parasitica Employ Different Infection Strategies When Colonizing Eggs of Atlantic Salmon, Salmo Salar LcamilaBelum ada peringkat
- Covid 19 Infographic enDokumen1 halamanCovid 19 Infographic enTrilok AshpalBelum ada peringkat
- MCQs VTEDokumen7 halamanMCQs VTEMUHAMMADBelum ada peringkat
- Access 25 (OH) Vitamin D Assay Total IFUDokumen16 halamanAccess 25 (OH) Vitamin D Assay Total IFUcarineBelum ada peringkat
- M-E 4th YearDokumen57 halamanM-E 4th YearDavid LyeluBelum ada peringkat
- Germ Theory of Diseases Von PlencizDokumen2 halamanGerm Theory of Diseases Von PlencizAamni SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Case Taking Proforma - Respiratory SystemDokumen7 halamanCase Taking Proforma - Respiratory SystemK Haynes Raja100% (11)
- 2015 Peperiksaan Percubaan Bahasa Inggeris SPM Pulau Pinang Kertas 2Dokumen18 halaman2015 Peperiksaan Percubaan Bahasa Inggeris SPM Pulau Pinang Kertas 2Pete Wang83% (6)
- Eng PDFDokumen98 halamanEng PDFMark Anthony MadridanoBelum ada peringkat
- Rabbies Health Talk NewDokumen10 halamanRabbies Health Talk NewAmit Ranjan100% (1)
- December 2018 Ophthalmic PearlsDokumen2 halamanDecember 2018 Ophthalmic PearlsFathirBelum ada peringkat
- RESEARCH (Edited)Dokumen6 halamanRESEARCH (Edited)Navarrete, AliceBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Illness BrochureDokumen2 halamanCritical Illness BrochureBrijesh RaiBelum ada peringkat
- II. Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersDokumen98 halamanII. Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersarielleortuosteBelum ada peringkat
- Test 1 Part 1 TapecsriptDokumen19 halamanTest 1 Part 1 TapecsriptMerryBelum ada peringkat
- Scabies NotesDokumen9 halamanScabies NotesAvi eBelum ada peringkat