24 AP FR Quiz 24 Review Key
Diunggah oleh
Tien NguyenDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
24 AP FR Quiz 24 Review Key
Diunggah oleh
Tien NguyenHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
WEEKEND AP REVIEW HW #24 KEY Magnetism
Sorry you get 4 questions this weekend.
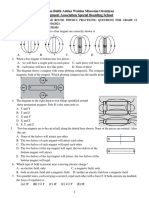
1998B8 (10 points) The long, straight wire shown in Figure 1 above is in the plane of the page and carries a current I. Point A is also in the plane of the page and is a perpendicular distance d from the wire. Gravitational effects are negligible. a. With reference to the coordinate system in Figure 1, what is the direction of the magnetic field at point A due to the current in the wire? A particle of mass m and positive charge a is initially moving parallel to the wire with a speed do when it is at point P. as shown in Figure 2 below.
b. c. d.
With reference to the coordinate system above, what is the direction of the magnetic force acting on the particle at point A ? Determine the magnitude of the magnetic force acting on the particle at point A in terms of the given quantities and fundamental constants. An electric field is applied that causes the net force on the particle to be zero at point P. i. With reference to the coordinate system in Figure 2, what is the direction of the electric field at point A that could accomplish this? ii. Determine the magnitude of the electric field in terms of the given quantities and fundamental constants.
1994B6. A force F is applied to a conducting rod so that the rod slides with constant speed v over a frictionless pair of parallel conducting rails that are separated by a distance l. The rod and rails have negligible resistance, but the rails are connected by a resistance R, as shown above. There is a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to and directed out of the plane of the paper. a. On the following diagram, indicate the direction of the induced current in the resistor.
Determine expressions for the following in terms of v, B, l, and R. b. The induced emf in the rod c. The electric field in the rod d. The magnitude of the induced current in the resistor R e. The power dissipated in the resistor as the rod moves in the magnetic field f. The magnitude of the external force F applied to the rod to keep it moving with constant speed v
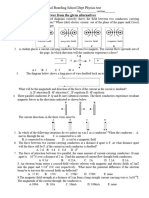
1994B4. In a linear accelerator, protons are accelerated from rest through a potential difference to a speed of approximately 3.1 x 106 meters per second. The resulting proton beam produces a current of 2 x 10-6ampere. a. Determine the potential difference through which the protons were accelerated. b. If the beam is stopped in a target, determine the amount of thermal energy that is produced in the target in one minute. The proton beam enters a region of uniform magnetic field B, as shown above, that causes the beam to follow a semicircular path. c. Determine the magnitude of the field that is required to cause an arc of radius 0.10 meter. d. What is the direction of the magnetic field relative to the axes shown above on the right?
An electric field is later established in the same region as the magnetic field such that the electron now passes through the magnetic and electric fields without deflection. d. Determine the magnitude of the electric field.
1992B5. The figure above shows a cross section of a cathode ray tube. An electron in the tube initially moves horizontally in the plane of the cross section at a speed of 2.0 x 107 meters per second. The electron is deflected upward by a magnetic field that has a field strength of 6.0 x 10-4 tesla. a. What is the direction of the magnetic field?
e. b. Determine the magnitude of the magnetic force acting on the electron.
What is the direction of the electric field?
c.
Determine the radius of curvature of the path followed by the electron while it is in the magnetic field.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Principles and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsDari EverandPrinciples and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsBelum ada peringkat
- AP Physics C Magnetism FRQ PDFDokumen28 halamanAP Physics C Magnetism FRQ PDFShameem AkhterBelum ada peringkat
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsDari EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Magnetic Effect of CurrentDokumen2 halamanMagnetic Effect of CurrentHarsh JuyalBelum ada peringkat
- AP B Webrev 19 and 20 MagnetismDokumen7 halamanAP B Webrev 19 and 20 MagnetismMelanie ValleBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet Xii (2) Magnetic Effect 22Dokumen6 halamanWorksheet Xii (2) Magnetic Effect 22Yug GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- PHY2049 Fall2015 Test3Dokumen6 halamanPHY2049 Fall2015 Test3kevin fernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Name - AP Physics Unit 13: MagnetismDokumen5 halamanName - AP Physics Unit 13: MagnetismNadiaBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 1st Sem Second Round PQ For G 12 in 2024 (2016 EC)Dokumen14 halamanPhysics 1st Sem Second Round PQ For G 12 in 2024 (2016 EC)sample nameBelum ada peringkat
- Screenshot 2022-08-16 at 10.04.10 PMDokumen5 halamanScreenshot 2022-08-16 at 10.04.10 PMKanak TaldaBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Q BankDokumen15 halamanMagnetic Q BankAnand Classes50% (2)
- Moving Charges and MagnetismDokumen6 halamanMoving Charges and MagnetismKoyal GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 04 (Magnetic Effects of Currents)Dokumen3 halamanChapter - 04 (Magnetic Effects of Currents)ghuBelum ada peringkat
- MovingChargesMagnetismDokumen4 halamanMovingChargesMagnetismSheena RizviBelum ada peringkat
- PS I AP Physics 2 Electromagnetic Induction Multiple Choice QuestionsDokumen15 halamanPS I AP Physics 2 Electromagnetic Induction Multiple Choice QuestionsIvanah Mae Guaro AcloBelum ada peringkat
- Test 9 CH 4Dokumen3 halamanTest 9 CH 4kumarvishwaa1Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic FieldDokumen37 halamanChapter 28 Sources of Magnetic FieldheyyyaleBelum ada peringkat
- Electrostatics Practice Questions AP PhysicsDokumen7 halamanElectrostatics Practice Questions AP PhysicsJeremy LeungBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetism TestDokumen2 halamanElectromagnetism Testdaalee1997Belum ada peringkat
- Summative Test 1Dokumen2 halamanSummative Test 1andrejosefpunsalanBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet II ElectromagnetismDokumen7 halamanWorksheet II Electromagnetismboomshakalakab13Belum ada peringkat
- Multiple Choice Questions I: Exemplar Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 4-Moving Charges and MagnetismDokumen14 halamanMultiple Choice Questions I: Exemplar Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 4-Moving Charges and MagnetismSri MeenakshiBelum ada peringkat
- Ib Magnetism - AllDokumen14 halamanIb Magnetism - AllAarav VermaBelum ada peringkat
- AP Physics Test: Electricity and Magnetism-Solutions: Multiple Choice QuestionsDokumen6 halamanAP Physics Test: Electricity and Magnetism-Solutions: Multiple Choice QuestionsChen JohnBelum ada peringkat
- 2021 - SemTest02 - PHYS 1624 (AutoRecovered)Dokumen4 halaman2021 - SemTest02 - PHYS 1624 (AutoRecovered)Siyabonga MdluliBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Currents: Novita Triwidianingsih, S.PDDokumen25 halamanMagnetic Effects of Electric Currents: Novita Triwidianingsih, S.PDAulia Pengdaviera JuntamiBelum ada peringkat
- RHR Questions Tep 3312Dokumen15 halamanRHR Questions Tep 3312Speedstar RoomiBelum ada peringkat
- 21 Magnetic Forces and FieldsDokumen11 halaman21 Magnetic Forces and Fieldssoe0303Belum ada peringkat
- LAQs - Current Electricity & Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDokumen6 halamanLAQs - Current Electricity & Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentLanaBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Effect Full ChapterDokumen17 halamanMagnetic Effect Full ChaptervasanthiBelum ada peringkat
- AP Physc em Electromagnetic Problem Solving Techniques 2020-03-20Dokumen64 halamanAP Physc em Electromagnetic Problem Solving Techniques 2020-03-20Armored SumanBelum ada peringkat
- SodapdfDokumen8 halamanSodapdfsdfbvshbdfBelum ada peringkat
- Question 961019Dokumen11 halamanQuestion 961019rajaBelum ada peringkat
- QP - Physics - Xii - SPDokumen7 halamanQP - Physics - Xii - SPriteshsamrath440Belum ada peringkat
- G-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2Dokumen12 halamanG-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2annahiazBelum ada peringkat
- Wa0004.Dokumen11 halamanWa0004.ffffffgBelum ada peringkat
- (101 Marks) : (1 Mark)Dokumen31 halaman(101 Marks) : (1 Mark)trishaBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Important Questions 2022-23Dokumen34 halamanCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Important Questions 2022-23Rohan SenapathiBelum ada peringkat
- QuestionDokumen5 halamanQuestionlingkamkitBelum ada peringkat
- STPM U6 21 1Dokumen2 halamanSTPM U6 21 1Tutor_KLBelum ada peringkat
- SG REVISION18324 65f84fed822447.65f84ff0083ad0.57491304Dokumen15 halamanSG REVISION18324 65f84fed822447.65f84ff0083ad0.57491304Neil MotianiBelum ada peringkat
- 1661934883physics SAT Practice Test 33Dokumen4 halaman1661934883physics SAT Practice Test 33modkdamaBelum ada peringkat
- 12th PhysicsDokumen5 halaman12th PhysicsUnwantedBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Magnetic EffectsDokumen3 halamanAssignment Magnetic EffectsabcdefgBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism: Previous Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016)Dokumen36 halamanMagnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism: Previous Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016)Rishabh AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Electricity 12 07Dokumen20 halamanElectricity 12 07nguyentrongtinBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetism - BDokumen7 halamanElectromagnetism - BUsama hameedBelum ada peringkat
- Moving Charges and MagnDokumen7 halamanMoving Charges and Magnatharvbaghel4444Belum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Ch21 SolutionDokumen7 halamanTutorial Ch21 SolutiontonyformedBelum ada peringkat
- AP Physics C E&M Unit 3 1. Magnetic Field and Force HandoutDokumen28 halamanAP Physics C E&M Unit 3 1. Magnetic Field and Force HandoutmoonidiveBelum ada peringkat
- Answered Thread3-1 (Muhammad Hamsyah) - 20230716101921Dokumen6 halamanAnswered Thread3-1 (Muhammad Hamsyah) - 20230716101921Hamzah Muhammad SayfuddinBelum ada peringkat
- 09.electromagntic and Faraday Law - InductionDokumen53 halaman09.electromagntic and Faraday Law - InductionAudrey Patrick KallaBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetism STUDokumen19 halamanElectromagnetism STUFirdaus BhathenaBelum ada peringkat
- Mid Test Physics 11 IPADokumen5 halamanMid Test Physics 11 IPAYosca YolantaBelum ada peringkat
- Mid TermDokumen11 halamanMid TermMaha TharwatBelum ada peringkat
- G12 Phy Pa2 Q.PDokumen8 halamanG12 Phy Pa2 Q.PnjragavendaraBelum ada peringkat
- 200512-Application of Motion of Charged Particles-SS SolutionDokumen25 halaman200512-Application of Motion of Charged Particles-SS SolutionZeyad EssamBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetism Sub BCDokumen6 halamanMagnetism Sub BCshivanshBelum ada peringkat
- Physics-2-Exam 221108 194245Dokumen4 halamanPhysics-2-Exam 221108 194245Huy Phan Duc NhatBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 7 ExercisesDokumen6 halamanUnit 7 ExercisesBao Hoang LeBelum ada peringkat
- Alfred LessingDokumen3 halamanAlfred LessingKarinaAikoBelum ada peringkat
- IUK Routemap - GovernanceDokumen27 halamanIUK Routemap - GovernanceTom RedwayBelum ada peringkat
- Kelley DavisDokumen3 halamanKelley Davisapi-626701108Belum ada peringkat
- ZEOS-AS ManualDokumen2 halamanZEOS-AS Manualrss1311Belum ada peringkat
- BUCA IMSEF 2021 Jury Evaluation ScheduleDokumen7 halamanBUCA IMSEF 2021 Jury Evaluation SchedulePaulina Arti WilujengBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Unit 3 MCQDokumen11 halaman1 - Unit 3 MCQRAMESH KUMAR MAURYABelum ada peringkat
- Civil & Structural Designer'S Data Pack: Section 7: MasonryDokumen5 halamanCivil & Structural Designer'S Data Pack: Section 7: MasonryMirea Florentin0% (1)
- Conventional and Box-Shaped Piled RaftsDokumen6 halamanConventional and Box-Shaped Piled RaftsAdrian VechiuBelum ada peringkat
- Definition, Scope and Nature of EconomicsDokumen29 halamanDefinition, Scope and Nature of EconomicsShyam Sunder BudhwarBelum ada peringkat
- SRM OverviewDokumen37 halamanSRM Overviewbravichandra24Belum ada peringkat
- Getting Started in Steady StateDokumen24 halamanGetting Started in Steady StateamitBelum ada peringkat
- ECON 304 Course ContentDokumen2 halamanECON 304 Course ContentAanand JhaBelum ada peringkat
- 19 - 22187 - Pritchard RD (1969)Dokumen36 halaman19 - 22187 - Pritchard RD (1969)Isaias MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- Q3 - Summative Test2 - Statprob 2022 2023Dokumen2 halamanQ3 - Summative Test2 - Statprob 2022 2023Christian Lloyd ReandinoBelum ada peringkat
- SkepticismDokumen5 halamanSkepticismstevenspillkumarBelum ada peringkat
- Almugea or Proper FaceDokumen5 halamanAlmugea or Proper FaceValentin BadeaBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 8 For Demo Cigarette SmokingDokumen3 halamanGrade 8 For Demo Cigarette SmokingSteven TaperoBelum ada peringkat
- CAT 438 3kk Esquema ElectricoDokumen2 halamanCAT 438 3kk Esquema ElectricocasigreBelum ada peringkat
- DESBLOQUEADO Synesis Erik Hollnagel 2022Dokumen81 halamanDESBLOQUEADO Synesis Erik Hollnagel 2022Tribu de SSOBelum ada peringkat
- Ficha Tecnica Castrol Hyspin AWS RangeDokumen2 halamanFicha Tecnica Castrol Hyspin AWS Rangeel pro jajaja GonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- Oracle Pac 2nd KeyDokumen48 halamanOracle Pac 2nd KeyKrishna Kumar GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Transient Thermal Conduction ExampleDokumen14 halamanTransient Thermal Conduction ExampleDevendra BangarBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Project Paper ChromatographyDokumen20 halamanChemistry Project Paper ChromatographyAmrita SBelum ada peringkat
- Brochure Exterior LightingDokumen49 halamanBrochure Exterior Lightingmurali_227Belum ada peringkat
- Gravitational Fields 1Dokumen18 halamanGravitational Fields 1Smart linkBelum ada peringkat
- Student Material CN Version - 2017.11.10Dokumen25 halamanStudent Material CN Version - 2017.11.10Jagaddeesha BRBelum ada peringkat
- Interior Plains Unit PlanDokumen6 halamanInterior Plains Unit Planapi-256482747Belum ada peringkat
- Job No. 25800: Quebrada Blanca Fase 2Dokumen1 halamanJob No. 25800: Quebrada Blanca Fase 2Benjamín Muñoz MuñozBelum ada peringkat
- FINAL Shivani Confined Space PermitDokumen1 halamanFINAL Shivani Confined Space PermitVimal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Nteq Lesson PlanDokumen4 halamanNteq Lesson Planeva.bensonBelum ada peringkat
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDari EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDari EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2193)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyDari EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyBelum ada peringkat
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDari EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniversePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (69)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldDari EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (64)
- Higgs Discovery: The Power of Empty SpaceDari EverandHiggs Discovery: The Power of Empty SpacePenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (30)
- How Cosmic Forces Shape Our DestiniesDari EverandHow Cosmic Forces Shape Our DestiniesPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (45)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDari EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and SciencePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (51)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayDari EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (125)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDari EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Dari EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (157)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDari EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (410)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceDari EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in SciencePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Vibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeDari EverandVibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (13)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldDari EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (54)
- The 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishDari EverandThe 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (4)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDari EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (49)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldDari EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (60)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDari EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeBelum ada peringkat
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityDari EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (78)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessDari EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (57)
- The Illustrated Theory of Everything: The Origin and Fate of the UniverseDari EverandThe Illustrated Theory of Everything: The Origin and Fate of the UniversePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDari EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1396)
- AP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeDari EverandAP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeBelum ada peringkat