Urine Analysis
Diunggah oleh
Raad SaadounDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Urine Analysis
Diunggah oleh
Raad SaadounHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
URINE ANALYSIS Urine analysis is performed to detect abnormal constituents that indicate a pathological state.
General characteristics of urine: 1. Volume: normally 1.5 2 L / Day. 2. Color: urochrome (amber yellow). 3. Transparency: Clear transparent. 4. Odor: faint aromatic odor due to the presence of volatile organic acid. 5. PH : slightly acidic 5.5 6.5. Physiological and normal constituents of urine: Normally the urine is composed of 99% water and 1% solids. Solids are: a. organic substances: urea, uric acid, creatine, creatinine, amino acids, lactic acid , vitamins, pigments, enzymes inorganic substances: NH4, SO4, Ca+2, Cl-, PO4, Co3, Na+, K+, Mg+2, NO3, Fe, F, silicate.
b.
SOME PATHOLOGICAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE The following parameters are normally not present in urine: Glucose: if serum glucose level exceeds the renal glucose threshold (180 mg/dl), it appears in urine (GLUCOSUREA), as in diabetes mellitus.
1.
Protein: the presence of protein in urine (PROTEINUREA OR ALBUMINUREA) can be seen in patients with glomerulonephritis.
2.
Blood: blood in urine (HEMATUREA OR HEMOGLOBINUREA) could be seen in patients with bilharziasis or hemolytic anemia.
3. 4.
Bile salts: can be seen in patients with Jaundice.
Ketone bodies or Acetone: could appear in urine in late stages of diabetes mellitus.
5.
-2-
TESTS FOR ABNORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE
TEST FOR GLUCOSE: 2 Fehling test: 1 ml urine 1 ml fehling B 1 ml fehling A
Mix green, orange Boil 2 min or red ppt + ve test
2 Benedict test:
1 ml urine 5 ml benedict reagent
Mix
Boil 2 min
green, orange
or red ppt
+ ve test
TEST FOR PROTEINS:
2
Heat coagulation test:
5 ml urine
BOIL
White ppt formed
White ppt + ve test
add 1 ml acetic acid 2% Mix
2 Sulfo-salicylic acid test:
2 ml sulfo-salicylic acid 2 ml urine -1White ppt formed + ve test
TEST FOR BLOOD: Benzidine test:
1 ml H2O2 3 ml urine (Mix well)then add 3 ml Benzidine reagent Blue ink color + ve test
TEST FOR BILE SALTS: In a small beaker take 10 ml urine then sprinkle some sulfur powder over it. If sulfur powder floats - ve test (no bile salts) If sulfur powder sinks to the bottom of the beaker + ve test
TEST FOR ACETONE: a. Nitroprusside test:
2 ml conc. Ammonia 0.5 ml sod. Nitroprusside ( mix well) 5 ml urine
Permanganate colour +ve test
b. Iodo-form test:
excess iodine(2 ml) 1 ml NaoH (10%) (mix well) 5 ml urine -3yellow ppt odor of iodo-form +ve test
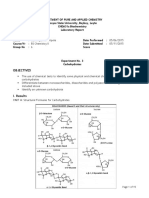
URINE ANALYSIS EXPERIMENT GLUCOSE 1) FEHLING TEST 1ml urine + 1ml Fehling A +1ml Fehling B. Mix Boil well 2) BENEDICT TEST 1ml urine + 5ml Benedict reagent.Mix. Boil well. PROTEINS 1) HEAT COAGULATION TEST: 5ml urine.Boil well. Add 1ml acetic acid. 2)SULFO SALICYLIC ACID TEST 2ml urine+ 2ml sulfosalicylic acid. Mix. BLOOD BENZIDINE TEST: Mix 3ml Benzidine reagent + 3ml urine. Add 1ml H2O2. BILE SALTS 5ml urine in a small beaker sprinkle sulphur powder. KETONE BODIES 1)NIRTOPRUSSIDE TEST 5ml urine + 0.5ml Na Nitroprusside. Mix well. +2ml conc. Ammonia. Mix. 2)IODOFORM TEST 5ml urine + 1ml NaOH(1%). Mix.Add excess iodine soln. (about 2 ml) OBSERVATION COMMENT
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Biochemical Examination of UrineDokumen40 halamanBiochemical Examination of UrineAshley Nicole Delizo100% (1)
- Analysis OF: UrineDokumen30 halamanAnalysis OF: UrineAebee AlcarazBelum ada peringkat
- Urine and Blood PPT (Handout Print Form) Chua, RDokumen10 halamanUrine and Blood PPT (Handout Print Form) Chua, RKirsten Hazel Mejia100% (1)
- Biochemistry Postlab FinalsDokumen42 halamanBiochemistry Postlab FinalsMelissa España100% (2)
- Pathological Urine ConstituentsDokumen22 halamanPathological Urine Constituentsmanni1001100% (3)
- Analysis of LipidsDokumen2 halamanAnalysis of LipidsHoney Joy Cruz CapiralBelum ada peringkat
- Color Reactions of ProteinsDokumen1 halamanColor Reactions of ProteinsZarah Pauline JimenezBelum ada peringkat
- Extraction of Total Lipids From Chicken Egg Yolk, Column Chromatography and Qualitative Tests For LipidsDokumen10 halamanExtraction of Total Lipids From Chicken Egg Yolk, Column Chromatography and Qualitative Tests For Lipidsmarilujane75% (8)
- Isolation and Characterization of Nucleic AcidDokumen4 halamanIsolation and Characterization of Nucleic AcidLinggonilus MasturandaBelum ada peringkat
- Qualitative Tests For ProteinsDokumen8 halamanQualitative Tests For ProteinsFaye Cortez100% (1)
- Isolation and Characterization of ProteinsDokumen3 halamanIsolation and Characterization of ProteinsVern NuquiBelum ada peringkat
- Isolation of Casein From Skimmed Milk and Seperation and Identification of Amino Acids by Paper ChromatographyDokumen8 halamanIsolation of Casein From Skimmed Milk and Seperation and Identification of Amino Acids by Paper ChromatographyKc CalderonBelum ada peringkat
- NinhydrinDokumen8 halamanNinhydrinpherrera_gazaBelum ada peringkat
- Isolation and Characterization of Saponifiable and NonDokumen18 halamanIsolation and Characterization of Saponifiable and NonJhoanna Rein Duzon100% (2)
- Extraction of Total Lipids From Chicken Egg Yolk and Qualitative Test For LipidsDokumen4 halamanExtraction of Total Lipids From Chicken Egg Yolk and Qualitative Test For LipidsKizer Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- 245ejuecgtnuhikj6 Unfinished Analysis of Lipids in Egg Yolk Formal ReportDokumen8 halaman245ejuecgtnuhikj6 Unfinished Analysis of Lipids in Egg Yolk Formal ReportChristine DelmendoBelum ada peringkat
- CHEM 40.1 Expt. 11Dokumen3 halamanCHEM 40.1 Expt. 11May Lacdao0% (1)
- Biochemistry LaboratoryDokumen7 halamanBiochemistry LaboratoryAIra OrtegaBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrolysis of Nucleic AcidsDokumen25 halamanHydrolysis of Nucleic AcidsVictor Emmanuel AzucenaBelum ada peringkat
- Biochem LabMidtermDokumen6 halamanBiochem LabMidtermRafael PangilinanBelum ada peringkat
- Standardization of HCL SolutionDokumen12 halamanStandardization of HCL SolutionPranav KulkarniBelum ada peringkat
- Classification Tests For Hydrocarbons-Formal ReportDokumen3 halamanClassification Tests For Hydrocarbons-Formal ReportJaneBelum ada peringkat
- Formal ReportDokumen3 halamanFormal ReportRiczen Mae F. Vila33% (3)
- Isolation and Characterization of Starch by Abarca - 2017 USTDokumen5 halamanIsolation and Characterization of Starch by Abarca - 2017 USTWynlor AbarcaBelum ada peringkat
- Qualitative TestsDokumen36 halamanQualitative Testscruztriccia100% (1)
- Experiment 9 Total Serum CholesterolDokumen8 halamanExperiment 9 Total Serum CholesterolGneiss Louie Gem AlmazanBelum ada peringkat
- Chem 40.1 - Midterms Reviewer Discussion: Buffers: - (Aq) 2 4 - (Aq) 4 2 - (Aq) 2Dokumen5 halamanChem 40.1 - Midterms Reviewer Discussion: Buffers: - (Aq) 2 4 - (Aq) 4 2 - (Aq) 2Steffi GatdulaBelum ada peringkat
- Methods of Protein PrecipitationDokumen3 halamanMethods of Protein PrecipitationKathleenMayJoyEnriquezCabral100% (1)
- Lab 3 FullDokumen17 halamanLab 3 FullAmni MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Isolation and Qualitative Analysis of Nucleic Acids (DNA From Onion)Dokumen3 halamanIsolation and Qualitative Analysis of Nucleic Acids (DNA From Onion)Elina Lantion100% (1)
- 1 Bio ChemDokumen23 halaman1 Bio ChemRuwi Loren Villocino100% (2)
- Chemical Test To Determine The Presence of A Protein in A Sample Biuret MethodDokumen4 halamanChemical Test To Determine The Presence of A Protein in A Sample Biuret MethodAnupam AdhikaryBelum ada peringkat
- Isolation and Characterization of Onion's DNADokumen5 halamanIsolation and Characterization of Onion's DNAGab Fondevilla100% (9)
- Acid Hydrolysis of DNA Isolated From Allium Cepa and Analysis of DNA Components Using Qualitative Color Reaction TestDokumen6 halamanAcid Hydrolysis of DNA Isolated From Allium Cepa and Analysis of DNA Components Using Qualitative Color Reaction Testmissy_macy11100% (1)
- Introduction For PH Measurement and Buffer PreparationDokumen2 halamanIntroduction For PH Measurement and Buffer PreparationJennifer HerediaBelum ada peringkat
- Biotech FR Exp 2Dokumen14 halamanBiotech FR Exp 2Nico YowBelum ada peringkat
- Buffers CompleteDokumen46 halamanBuffers CompleteSunshine_Bacla_4275100% (2)
- Lowry AssayDokumen7 halamanLowry AssayGrace AquinoBelum ada peringkat
- Qualitative Test For CarbohydratesDokumen2 halamanQualitative Test For CarbohydratesMomerBelum ada peringkat
- Properties and Composition of Most OrganDokumen7 halamanProperties and Composition of Most OrganChris TurffBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 11 Nucleic Acid PDFDokumen10 halamanLab 11 Nucleic Acid PDFprincessfarah hussinBelum ada peringkat
- Qualitative Color Reactions of AlbuminDokumen6 halamanQualitative Color Reactions of AlbuminJennifer HerediaBelum ada peringkat
- Buffer Preparation and PH Measurement Using The Electrometric Method and Colorimetric MethodDokumen2 halamanBuffer Preparation and PH Measurement Using The Electrometric Method and Colorimetric MethodArndrei CunananBelum ada peringkat
- Qualitative Analysis of Lipids Through The Extraction of Total Lipids From Chicken Egg YolkDokumen5 halamanQualitative Analysis of Lipids Through The Extraction of Total Lipids From Chicken Egg YolkJessa Mateum VallangcaBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 1 PH Measurement and Buffer PreparationDokumen5 halamanExperiment 1 PH Measurement and Buffer PreparationAnonymouscatBelum ada peringkat
- NurBio Activity 12 Analysis of SalivaDokumen4 halamanNurBio Activity 12 Analysis of SalivaAlliyah Jhane0% (1)
- Gravimetric Analysis and Precipitation EquilibriaDokumen55 halamanGravimetric Analysis and Precipitation EquilibriaasdfBelum ada peringkat
- Carbohydrates: Introductory ArticleDokumen12 halamanCarbohydrates: Introductory ArticleMauricio VidalBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 4bDokumen9 halamanExperiment 4banon_853164953Belum ada peringkat
- Isolation and Characterization of RNADokumen3 halamanIsolation and Characterization of RNAEvans DionBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory Test For MacromoleculesDokumen4 halamanLaboratory Test For MacromoleculesOdessa KwonBelum ada peringkat
- Precepitation of ProteinsDokumen25 halamanPrecepitation of ProteinsNaufal QaweimBelum ada peringkat
- Qualitative Color Reactions For CarbohydratesDokumen5 halamanQualitative Color Reactions For CarbohydratesAhiarenzBelum ada peringkat
- Biochem Pre-Lab 3bDokumen2 halamanBiochem Pre-Lab 3bOla Anna GamutinBelum ada peringkat
- Janir Ty Datukan Department of Physical Sciences College of Science Philippine Normal UniversityDokumen32 halamanJanir Ty Datukan Department of Physical Sciences College of Science Philippine Normal UniversityCharles Dave Mendoza100% (4)
- Experiment 3 - CarbohydratesDokumen15 halamanExperiment 3 - CarbohydratesNur Setsu100% (1)
- Experiment 2Dokumen8 halamanExperiment 2Corina Faye RosarioBelum ada peringkat
- Postlab Report RevisedDokumen90 halamanPostlab Report RevisedKai ChenBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 19 - Normal UrineDokumen4 halamanExperiment 19 - Normal UrineBismah SaeedBelum ada peringkat
- The Morality of Human SexualityDokumen2 halamanThe Morality of Human SexualityJec Luceriaga Biraquit100% (2)
- Lesson Plan - Special Right Triangles ReteachDokumen1 halamanLesson Plan - Special Right Triangles Reteachapi-448318028Belum ada peringkat
- Manual Watchdog 1200 PDFDokumen30 halamanManual Watchdog 1200 PDFdanielBelum ada peringkat
- VocabularyDokumen7 halamanVocabularyReynald Satria Dwiky IrawanBelum ada peringkat
- Elements of User Interface DesignDokumen30 halamanElements of User Interface DesignRomer Garcia100% (1)
- Karling Aguilera-Fort ResumeDokumen4 halamanKarling Aguilera-Fort Resumeapi-3198760590% (1)
- Product Manual 85018V2 (Revision F) : 505E Digital Governor For Extraction Steam TurbinesDokumen160 halamanProduct Manual 85018V2 (Revision F) : 505E Digital Governor For Extraction Steam Turbinesrahilshah100Belum ada peringkat
- 00 FA17 ENG 2070 SyllabusDokumen9 halaman00 FA17 ENG 2070 SyllabusLauren SalisburyBelum ada peringkat
- Best Trusts and Estates OutlineDokumen84 halamanBest Trusts and Estates OutlineJavi Luis100% (4)
- Indian Standard: General Technical Delivery Requirements FOR Steel and Steel ProductsDokumen17 halamanIndian Standard: General Technical Delivery Requirements FOR Steel and Steel ProductsPermeshwara Nand Bhatt100% (1)
- Ultimate Power Errata: Ultimate Power Mutants & Masterminds Mutants & Masterminds FAQ Mutants & MastermindsDokumen2 halamanUltimate Power Errata: Ultimate Power Mutants & Masterminds Mutants & Masterminds FAQ Mutants & MastermindsYunus Emre AtalayBelum ada peringkat
- Recount TextDokumen17 halamanRecount TextalunaBelum ada peringkat
- Cargill Web Application Scanning ReportDokumen27 halamanCargill Web Application Scanning ReportHari KingBelum ada peringkat
- IBbusiness Revision NotesDokumen58 halamanIBbusiness Revision NotesMayankJhaBelum ada peringkat
- Lost On Mystery Mountain - The Ghost (PG 3&4)Dokumen52 halamanLost On Mystery Mountain - The Ghost (PG 3&4)Olivia LeeBelum ada peringkat
- E-Fim OTNM2000 Element Management System Operation GuideDokumen614 halamanE-Fim OTNM2000 Element Management System Operation GuidePrabin Mali86% (7)
- Engineering Code of EthicsDokumen4 halamanEngineering Code of EthicsBeth Beth DiancoBelum ada peringkat
- DD McqsDokumen21 halamanDD McqsSyeda MunazzaBelum ada peringkat
- Expansion and Contraction of Demand:: Change in Demand vs. Change in Quantity DemandedDokumen6 halamanExpansion and Contraction of Demand:: Change in Demand vs. Change in Quantity DemandedbadarBelum ada peringkat
- KISS Notes The World CommunicatesDokumen30 halamanKISS Notes The World CommunicatesJenniferBackhus100% (4)
- Ayurveda Secrets of Healing Maya Tiwari.07172 2seasonal CleansingDokumen5 halamanAyurveda Secrets of Healing Maya Tiwari.07172 2seasonal CleansingkidiyoorBelum ada peringkat
- 5 - Data Room Procedure TemplatesDokumen8 halaman5 - Data Room Procedure TemplatesnajahBelum ada peringkat
- ST Learning Task 10Dokumen6 halamanST Learning Task 10Jermaine DoloritoBelum ada peringkat
- Abra State Institute of Sciences and TechnologyDokumen9 halamanAbra State Institute of Sciences and TechnologyTintin Bejarin100% (3)
- EJ1266040Dokumen11 halamanEJ1266040John Lester CalleBelum ada peringkat
- 1st Year Unit 7 Writing A Letter About A CelebrationDokumen2 halaman1st Year Unit 7 Writing A Letter About A CelebrationmlooooolBelum ada peringkat
- May 29Dokumen2 halamanMay 29gerrymattinglyBelum ada peringkat
- DR Jeremiah Revelation Prophecy Chart PDFDokumen2 halamanDR Jeremiah Revelation Prophecy Chart PDFkoinoniabcn93% (14)
- Help Us Clean The Government HospitalsDokumen3 halamanHelp Us Clean The Government HospitalsSelva GanapathyBelum ada peringkat
- (Cambridge Studies in Opera) Victoria Johnson, Jane F. Fulcher, Thomas Ertman-Opera and Society in Italy and France From Monteverdi To Bourdieu-Cambridge University Press (2007) PDFDokumen440 halaman(Cambridge Studies in Opera) Victoria Johnson, Jane F. Fulcher, Thomas Ertman-Opera and Society in Italy and France From Monteverdi To Bourdieu-Cambridge University Press (2007) PDFnbozekidis100% (3)