Chemistry Edexcel As Keywords Unit 1
Diunggah oleh
Ashan BopitiyaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chemistry Edexcel As Keywords Unit 1
Diunggah oleh
Ashan BopitiyaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chemistry Edexcel AS keywords Unit 1
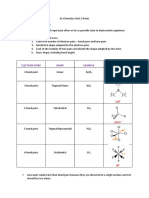
Here is a big list of all the keywords you need for AS chemistry Unit 1 edexcel. I have mixed them all up!!! Enjoy = ] Moles: A mole of a substance is 6.02x10^23 chemical units or the same number of chemical units as 12g of carbon-12. Addition reaction: When you add two substances together without replacing or removing anything. Electrophile: An atom, ion or molecule which is short of electrons, so it is attracted to places where there are lots of electrons. Risk: The probability that a given hazard will cause damage to health or harm you. Structural isomerism: An isomer with the same molecular formula but a different structural formula. First ionisation energy: The energy required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions. Van de waals forces: Weak intermolecular attractions that form between uncharged molecules, temporarily. Mass number: The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom OR the mass of the nucleus of an atom. Geometric isomerism: Isomers with the same molecular and structural formulas but different spatial relationship. Ionic bonding: Bonding where one atom has complete control of the electrons in the bonding pair, forming ions, which are strongly attracted by electrostatic attractions. Enthalpy: The total energy content of reacting materials. Monomer: A single unit of a substance. Elimination reaction: A reaction where something is removed from a substance without it being replaced. Alkane: A saturated hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n+2
Nucleophile: A chemical "species" that donates an electron pair to an electrophile to form a chemical bond in a reaction. Relative atomic mass: The average weighted mass of the isotopes of an element relative to 1/12 of carbon-12. Compound: A substance which contains more than one element chemically bonded together. Bond enthalpy: The energy required to break a bond. hydrogen bonds: Weak intermolecular bonds that form permanently within a substance. Avogadro's constant: 6.02x10^23 particles of a chemical unit. Standard enthalpy change: This refers to a reaction which takes place Polymer: Multiple monomers chemically joined together. Alkene: An unsaturated hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n. Substitution reaction: A reaction where one element/substance is replaced with another. Covalent bonding: When the bonding electrons are shared between the two atoms equally. Enthalpy of vaporisation: This is the enthalpy change when one mole of liquid is evaporated to form one mole of gas. Pi Bond: A weaker, more reactive bond, which forms using the p orbitals to create a double bond with a sigma bond. Molecules: A group of atoms chemically bonded together. Hazard: An activity or substance which can cause damage to health. Enthalpy change: The total exchange of energy that takes place with the surroundings. Dative covalent bonding: A covalent bond where both of the electrons in the bonding pair come from one atom. Atom: The smallest unit of an element that can still be called that element. Element: A substance made up of one type of atom. Hess'Law: The total enthalpy change is independent of the route taken. Polarity: The distortion of the electron cloud of one atom by another.
Lattice dissociation enthalpy: The enthalpy change when one mole of an ionic compound is split into it's constituent ions. Ion: A charged atoms, which has more/less electrons than protons. Empirical formula: A formula which shows the simplest whole number ratio of atoms in a compound. Relative molecular mass: The mass of a substance's molecules relative to 1/12 of carbon-12. Electronegativity: The attraction of the bonding pair of electrons. Metallic bonding: The electrostatic attractions which form between the positive metal ions and their free moving delocalised electrons. Standard enthalpy of formation: The standard enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from it's elements under standard conditions. Molecular formula: A formula which shows the actual type and number of atoms in a compound. Isotopes: An atom which has a different number of neutrons, but the same number of protons and electrons. Standard enthalpy of atomisation: The standard enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms is formed from it's elements under standard conditions. Atomic number: The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Sigma bond: The strong single bond which forms between two atoms. It is less reactive than a pi bond. Relative isotopic mass: The mass of an element's isotopes relative to 1/12 of carbon-12. Isoelectronic: Two or more atoms which have the same electronic configuration. Standard enthalpy of neutralisation: The standard enthalpy change when one mole of water is formed from an acid and an alkali reacting together. Electron affinity: The energy required to add 1 mole of electrons to 1 mole of atoms to form 1 mole of -1 ions. Lattice energy: The enthalpy change when one mole of an ionic compound is formed from it's ions. Free radical: An ion, atom or molecule with a lone electron from a bonding pair.
Hope this helps!
Keep Calm and Learn Keywords!!!
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Moles Equations AtomsDokumen44 halamanMoles Equations AtomsRamesh IyerBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel IAL As Physics Revision Guide Unit 1ADokumen54 halamanEdexcel IAL As Physics Revision Guide Unit 1ATHE PSYCOBelum ada peringkat
- Qdoc - Tips Chemistry Unit 1 Edexcel Notes As LevelDokumen1 halamanQdoc - Tips Chemistry Unit 1 Edexcel Notes As LevelM KBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 NotesDokumen26 halamanUnit 2 NotesRameez Mazhar Siddiqi100% (1)
- Edexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 6Dokumen148 halamanEdexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 6AbdulRahman MustafaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Unit 4 Part 2 ReallyacademicsDokumen45 halamanChemistry Unit 4 Part 2 ReallyacademicsWill AndyBelum ada peringkat
- A2 ChemDokumen81 halamanA2 ChemJana Mohamed100% (1)
- DefinitionsDokumen6 halamanDefinitionsali ahsan khanBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Unit 4 Part 1 ReallyacademicsDokumen41 halamanChemistry Unit 4 Part 1 ReallyacademicsWill AndyBelum ada peringkat
- 2007 Jun Exam PaperDokumen20 halaman2007 Jun Exam PapertheoggmonsterBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 Commonly QuestionsDokumen3 halamanUnit 1 Commonly QuestionsRaiyad RezaBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Tests U5Dokumen15 halamanPractice Tests U5Ihshan Destro IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Thermochemistry (Important Notes)Dokumen2 halamanThermochemistry (Important Notes)HenrySeowBelum ada peringkat
- A2-Chemistry Unit 5 Sample PaperDokumen22 halamanA2-Chemistry Unit 5 Sample PaperDimuthu SandaruwanBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel A-Level Chemistry Redox I NotesDokumen6 halamanEdexcel A-Level Chemistry Redox I NotesttjjjBelum ada peringkat
- Section 3 EnergeticsDokumen47 halamanSection 3 Energeticsapi-3734333Belum ada peringkat
- AS Chemistry Unit 1 Class Test Jan 2015 QuestionsDokumen26 halamanAS Chemistry Unit 1 Class Test Jan 2015 Questionsecs90603Belum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Edexcel Unit 2 AsDokumen18 halamanChemistry Edexcel Unit 2 Asminayoki0% (1)
- Halogenoalkane Reactions and Environmental EffectsDokumen21 halamanHalogenoalkane Reactions and Environmental Effectsallaura1Belum ada peringkat
- Definitions - Chemistry IAL EdexcelDokumen7 halamanDefinitions - Chemistry IAL EdexcelPanagiotis ScordisBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Oxidation Numbers Through Electronegativity and Partial ChargesDokumen14 halamanUnderstanding Oxidation Numbers Through Electronegativity and Partial ChargesEricBelum ada peringkat
- Photochemical ReactionDokumen16 halamanPhotochemical ReactionChandra ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Organic Chemistry Introduction 2Dokumen126 halaman03 Organic Chemistry Introduction 2Hamid Hussain HamidBelum ada peringkat
- Models of The AtomDokumen13 halamanModels of The AtomAbhinav TripathiBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 5Dokumen386 halamanEdexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 5AbdulRahman Mustafa100% (1)
- Summary Notes - Topic 5 Edexcel (A) Biology A-LevelDokumen6 halamanSummary Notes - Topic 5 Edexcel (A) Biology A-LevelAhmad MohdBelum ada peringkat
- 3-2 MSDokumen60 halaman3-2 MSputriBelum ada peringkat
- Y6/AS Physics Final Exam 11 - 12 Unit 1 - AnswersDokumen21 halamanY6/AS Physics Final Exam 11 - 12 Unit 1 - AnswersPaul Burgess100% (2)
- Unit 5 - Physics From Creation To Collapse: Thermal EnergyDokumen12 halamanUnit 5 - Physics From Creation To Collapse: Thermal EnergyShivani MajithiaBelum ada peringkat
- Formulae, equations and calculationsDokumen39 halamanFormulae, equations and calculationsNandi100% (1)
- VSEPR Handout PDFDokumen2 halamanVSEPR Handout PDFAriel ChenBelum ada peringkat
- Benzene (Arene) Notes On Chemical ReactionsDokumen33 halamanBenzene (Arene) Notes On Chemical ReactionsdanielmahsaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry A2 Summary - Nitrogen CompoundsDokumen4 halamanChemistry A2 Summary - Nitrogen CompoundsFrancisca FuchsBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Unit 4 Part 3 ReallyacademicsDokumen35 halamanChemistry Unit 4 Part 3 ReallyacademicsWill AndyBelum ada peringkat
- Semiconductor Physics TutorialDokumen12 halamanSemiconductor Physics TutorialKadis PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Electron Affinity and Ionization EnergiesDokumen251 halamanElectron Affinity and Ionization Energiesgkawsar22Belum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Unit 4 Notes: 4.1 Rates of ReactionsDokumen36 halamanChemistry Unit 4 Notes: 4.1 Rates of ReactionssarawongBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Notes Topic 5 Formulae Equations and Amounts of Substance Edexcel Chemistry A LevelDokumen7 halamanDetailed Notes Topic 5 Formulae Equations and Amounts of Substance Edexcel Chemistry A LevelttjjjBelum ada peringkat
- Shapes of Molecules and Ions PDFDokumen9 halamanShapes of Molecules and Ions PDFMagenta SparklegemBelum ada peringkat
- U3 Oxidation and Reduction PPT WatermarkDokumen45 halamanU3 Oxidation and Reduction PPT Watermarkapi-125934329Belum ada peringkat
- As Physics UncertaintiesDokumen8 halamanAs Physics Uncertaintiesmeesam.razaBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel IAL Chemistry Unit 1Dokumen22 halamanEdexcel IAL Chemistry Unit 1Aliya KBelum ada peringkat
- POGIL Avg Atomic Mass KEYDokumen4 halamanPOGIL Avg Atomic Mass KEYbobBelum ada peringkat
- Ib Screwed Chapter 1Dokumen16 halamanIb Screwed Chapter 1Adnan YousafBelum ada peringkat
- 6B Revision Notes ExtraDokumen15 halaman6B Revision Notes ExtraMoustafa Sohdy100% (7)
- 3 Fajan's RuleDokumen13 halaman3 Fajan's RuleNazmi LatifBelum ada peringkat
- 12th Physics Additional Questions (Vol 1)Dokumen135 halaman12th Physics Additional Questions (Vol 1)Ashok Pradhan50% (2)
- Chemistry SME Notes (Organic Chemmistry)Dokumen14 halamanChemistry SME Notes (Organic Chemmistry)Sayeef MahdiBelum ada peringkat
- Chem-Study - Transition A Level WorkDokumen47 halamanChem-Study - Transition A Level WorkAdeeba AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- What Is The Atomic NumberDokumen31 halamanWhat Is The Atomic NumberMennatallah Mohamed HamedBelum ada peringkat
- EDEXCEL A Level Protein SynthesisDokumen29 halamanEDEXCEL A Level Protein SynthesisKesithan AnandarashBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry Topic 2: Inorganic ChemistryDokumen4 halamanEdexcel IGCSE Chemistry Topic 2: Inorganic ChemistryVenant HakizimanaBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 12 Entropy-Energetics Chemistry Ial EdexcelDokumen26 halamanTopic 12 Entropy-Energetics Chemistry Ial EdexcelZubanaBelum ada peringkat
- Ionic Bonding 4. Bonding: Evidence For The Existence of IonsDokumen9 halamanIonic Bonding 4. Bonding: Evidence For The Existence of IonsAnastasia ErshBelum ada peringkat
- Pixl Knowledge Test Powerpoint - Aqa c1 Core Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017Dokumen27 halamanPixl Knowledge Test Powerpoint - Aqa c1 Core Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017api-342297566Belum ada peringkat
- Rates and EquilibriaDokumen15 halamanRates and EquilibriaThaarvena RetinaBelum ada peringkat
- Structure of AtomDokumen5 halamanStructure of AtomSaurabh DhyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Transition Metal ToxicityDari EverandTransition Metal ToxicityG. W. RichterBelum ada peringkat
- Congenital Heart DIseasesDokumen3 halamanCongenital Heart DIseasesAshan BopitiyaBelum ada peringkat
- AnkiDokumen3 halamanAnkiAshan BopitiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Initial Visit H&PDokumen3 halamanInitial Visit H&Pashythegreat93Belum ada peringkat
- Management of Asthma in ChildrenDokumen30 halamanManagement of Asthma in ChildrenMohamed Rikarz Ahamed RikarzBelum ada peringkat
- A2 Chemistry Unit 4 NotesDokumen27 halamanA2 Chemistry Unit 4 NotesRebecca78% (9)
- 6 - CardiomyopathyDokumen15 halaman6 - CardiomyopathyAshan BopitiyaBelum ada peringkat
- A2 Chemistry Unit 4 NotesDokumen27 halamanA2 Chemistry Unit 4 NotesRebecca78% (9)
- Pathogenesis of AtherosclerosisDokumen2 halamanPathogenesis of AtherosclerosisAshan BopitiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel Biology A2 Core Practical WorkbookDokumen39 halamanEdexcel Biology A2 Core Practical WorkbookTim Filtness80% (20)
- Revision TimeTableDokumen15 halamanRevision TimeTableAshan BopitiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Biomass Combustion ManojDokumen16 halamanBiomass Combustion Manojsugandaraj522Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 - StudentDokumen69 halamanChapter 4 - Studenteja70Belum ada peringkat
- Limiting Reagent ProblemsDokumen7 halamanLimiting Reagent ProblemsKaiRisBelum ada peringkat
- Genchem Reviewer Long Test TypeDokumen2 halamanGenchem Reviewer Long Test TypeGabriel Louis GuañoBelum ada peringkat
- JRAHS Year 11 Chemistry Exam ReviewDokumen17 halamanJRAHS Year 11 Chemistry Exam ReviewYu-Tang LinBelum ada peringkat
- NEET TEST SERIES ALL IN ONEDokumen14 halamanNEET TEST SERIES ALL IN ONEManmeet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- CAPE Chemistry U1 - Breakdown of SyllabusDokumen24 halamanCAPE Chemistry U1 - Breakdown of SyllabusJevon SiddonBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry SPM SyllabusDokumen5 halamanChemistry SPM SyllabusAcyl Chloride HaripremBelum ada peringkat
- Common Name Chemical Name FormulaDokumen6 halamanCommon Name Chemical Name FormulaJanelyn GarinBelum ada peringkat
- Redox, Group 2 and Group 7 Extra Questions MS: State Symbols Not RequiredDokumen4 halamanRedox, Group 2 and Group 7 Extra Questions MS: State Symbols Not RequiredAnshu MovvaBelum ada peringkat
- Jee Advanced 2015 Paper 1 SolutionDokumen62 halamanJee Advanced 2015 Paper 1 SolutionAbhimanyu MundaryBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Interim Assessment 2 Teacher Booklet: Kipp New Orleans SchoolsDokumen20 halamanChemistry Interim Assessment 2 Teacher Booklet: Kipp New Orleans SchoolsTyneishah SpearsBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical BondDokumen223 halamanChemical BondChelleBelum ada peringkat
- Ref PropDokumen66 halamanRef Proppeter panBelum ada peringkat
- Class XI Chemistry Worksheet 2021Dokumen43 halamanClass XI Chemistry Worksheet 2021Muffadal AlaviBelum ada peringkat
- Mass and Energy Balances: Dr. Rakesh KumarDokumen16 halamanMass and Energy Balances: Dr. Rakesh KumarVishal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Chem 80 class exercise on mass relationships and chemical reactionsDokumen3 halamanChem 80 class exercise on mass relationships and chemical reactionsMary Kate BacongaBelum ada peringkat
- Homework 7.1 Stoichiometry in Chemical Reactions 1Dokumen3 halamanHomework 7.1 Stoichiometry in Chemical Reactions 1Mark Emmanuel HidalgoBelum ada peringkat
- ENG2000: Atoms and Bonding BasicsDokumen29 halamanENG2000: Atoms and Bonding BasicsManuel Tutacha ™Belum ada peringkat
- Science Quest Reviewer Gas LawsDokumen5 halamanScience Quest Reviewer Gas LawsEva esperaBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring The Amount of Vitamin C in Fruit Drinks Student Sheet - 731053Dokumen2 halamanMeasuring The Amount of Vitamin C in Fruit Drinks Student Sheet - 731053Hanithra AnanthanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 Objective - Question and AnswerDokumen2 halamanChapter 6 Objective - Question and AnswerChristina T Z-chYnBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Quantities and UnitsDokumen28 halamanChapter 1 Quantities and UnitsAbdirahman Elmi Gurre100% (1)
- General Chemistry 1 Learning Pack (Third Quarter)Dokumen94 halamanGeneral Chemistry 1 Learning Pack (Third Quarter)Kim Kalibay100% (2)
- Solutions: WWW - Crackjee.xyzDokumen6 halamanSolutions: WWW - Crackjee.xyzRashmi Ranjan DasBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Chep 353l1Dokumen4 halamanAssignment Chep 353l1Joshua Arrojo100% (3)
- Simulation Report: Object: MethanoloutDokumen3 halamanSimulation Report: Object: MethanoloutniralBelum ada peringkat
- January 2015 (IAL) MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelDokumen24 halamanJanuary 2015 (IAL) MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelNabindra RuwaliBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 13 Practice Exercises SolutionsDokumen25 halamanChapter 13 Practice Exercises SolutionsBelaFistaBelum ada peringkat
- Analytical Chemistry ActivityDokumen4 halamanAnalytical Chemistry ActivityAgyao Yam FaithBelum ada peringkat